elements_view class (Standardowa biblioteka C++)
Widok elementów w wybranym indeksie w każdej wartości podobnej do krotki w zakresie. Na przykład, biorąc pod uwagę zakres std::tuple<string, int>, utwórz widok składający się z string elementów z każdej krotki.
Składnia
template<input_range V, size_t N>
class elements_view : public view_interface<elements_view<V, N>>;
Parametry szablonu
N
Indeks elementu do wybrania dla widoku.
V
Typ bazowego zakresu. Ten typ musi spełniać ranges::input_rangewartość .
Właściwości widoku
Opis poniższych wpisów można znaleźć w temacie View class characteristics (Wyświetlanie właściwości klas)
| Characteristic | opis |
|---|---|
| Adapter zakresu | views::elements |
| Zakres bazowy | Musi spełniać input_range lub wyższe |
| Typ elementu | Taki sam jak typ indeksowanego elementu krotki |
| Wyświetl kategorię iteratora | forward_range, bidirectional_range lub random_access_range |
| Wielkości | Tylko wtedy, gdy zakres bazowy spełnia sized_range |
Jest constiterowalne |
Tylko wtedy, gdy zakres bazowy spełnia const-iterable |
| Wspólny zakres | Tylko wtedy, gdy zakres bazowy spełnia common_range |
| Pożyczony zakres | Tylko wtedy, gdy zakres bazowy spełnia borrowed_range |
Członkowie
| Funkcje składowe | Opis |
|---|---|
| KonstruktoryC++20 | Skonstruuj element elements_view. |
baseC++20 |
Pobierz zakres bazowy. |
beginC++20 |
Pobierz iterator do pierwszego elementu. |
endC++20 |
Pobierz element sentinel na końcu widoku. |
sizeC++20 |
Pobierz liczbę elementów w tym widoku. Zakres bazowy musi spełniać sized_rangewartość . |
Dziedziczone z view_interface |
Opis |
backC++20 |
Pobierz ostatni element. |
emptyC++20 |
Sprawdź, czy element elements_view jest pusty. |
frontC++20 |
Pobierz pierwszy element. |
operator[]C++20 |
Pobierz element na określonej pozycji. |
operator boolC++20 |
Sprawdź, czy element elements_view nie jest pusty. |
Wymagania
Nagłówek:<ranges> (od C++20)
Obszaru nazw:std::ranges
Opcja kompilatora:/std:c++20 lub nowsza jest wymagana.
Uwagi
Typy podobne do krotki, których można używać, elements_view to std::tuple, std::pairi std::array.
Konstruktory
Skonstruuj wystąpienie klasy elements_view.
1) constexpr elements_view(V base);
2) elements_view() requires std::default_initializable<V> = default;
Parametry
base
Zakres bazowy.
Aby uzyskać informacje o typie parametru szablonu, zobacz Parametry szablonu.
Wartość zwracana
Wystąpienie elements_view .
Uwagi
Najlepszym sposobem utworzenia elementu elements_view jest użycie adaptera elements zakresu. Adaptery zakresów są zamierzonym sposobem tworzenia klas widoków. Typy widoków są widoczne w przypadku utworzenia własnego niestandardowego typu widoku.
1) Utwórz element elements_view z określonego widoku.
2) Domyślna konstrukcja elementu elements_view.
Przykład: elements_view
// requires /std:c++20 or later
#include <array>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <ranges>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <utility>
int main()
{
// ========== work with a std::map
std::map<std::string, int> cpp_standards
{
{"C++98", 1988},
{"C++03", 2003},
{"C++11", 2011},
{"C++14", 2014},
{"C++17", 2017},
{"C++20", 2020}
};
// create an elements_view of all the string elements (<1>) from each tuple
for (int const year : std::views::elements<1>(cpp_standards))
{
std::cout << year << ' '; // 2003 2011 2014 2017 1988 2020
}
std::cout << '\n';
// Another way to call the range adaptor using pipe (|) syntax
for (auto&& name : cpp_standards | std::views::elements<0>)
{
std::cout << name << ' '; // C++03 C++11 C++14 C++17 C++98 C++20
}
std::cout << '\n';
// ========== working with arrays
std::array<std::array<int, 4>, 3> arr = { {{0,1,2,3}, {4,5,6,7}, {8,9,10,11}} };
for (int& fourth : arr | std::views::elements<3>)
{
std::cout << fourth << ' '; // 3 7 11
}
std::cout << '\n';
// ========== work with a std::pair
std::vector<std::pair<std::string, int>> windows
{
{"Windows 1.0", 1985},
{"Windows 2.0", 1987},
{"Windows 3.0", 1990},
{"Windows 3.1", 1992},
{"Windows NT 3.1", 1993},
{"Windows 95", 1995},
{"Windows NT 4.0", 1996},
{"Windows 98", 1998},
{"Windows 2000", 2000}
};
for (int year : std::views::elements<1>(windows))
{
std::cout << year << ' '; // 1985 1987 1990 1992 1993 1995 1996 1998 2000
}
}
2003 2011 2014 2017 1988 2020
C++03 C++11 C++14 C++17 C++98 c++20
3 7 11
1985 1987 1990 1992 1993 1995 1996 1998 2000
base
Pobiera kopię bazowego zakresu.
// Uses a copy constructor to return the underlying range
constexpr V base() const& requires std::copy_constructible<V>;
// Uses a move constructor to return the underlying range
constexpr V base() &&;
Parametry
Brak.
Wartość zwracana
Zakres bazowy.
begin
Pobierz iterator do pierwszego elementu w pliku elements_view.
1) constexpr auto begin() requires (!Simple_view<V>);
2) constexpr auto begin() const requires range<const V>;
Parametry
Brak.
Wartość zwracana
Iterator wskazujący pierwszy element w elemecie elements_view.
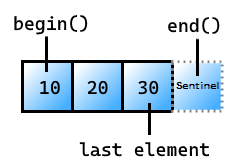
end
Pobierz sentinel na końcu elements_view
1) constexpr auto end() requires (!Simple_view<V> && !ranges::common_range<V>);
2) constexpr auto end() requires (!Simple_view<V> && ranges::common_range<V>);
3) constexpr auto end() const requires ranges::range<const V>;
4) constexpr auto end() const requires ranges::common_range<const V>;
Parametry
Brak.
Wartość zwracana
Sentinel, który jest zgodny z ostatnim elementem w pliku elements_view:

size
Pobierz liczbę elementów w widoku.
constexpr auto size() requires sized_range<V>;
constexpr auto size() const requires sized_range<const V>;
Parametry
Brak.
Wartość zwracana
Liczba elementów w elem.elements_view
Uwagi
Rozmiar widoku jest dostępny tylko wtedy, gdy zakres bazowy to sized_range, lub innymi słowy, ograniczony.
Zobacz też
Opinia
Dostępne już wkrótce: W 2024 r. będziemy stopniowo wycofywać zgłoszenia z serwisu GitHub jako mechanizm przesyłania opinii na temat zawartości i zastępować go nowym systemem opinii. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji, sprawdź: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Prześlij i wyświetl opinię dla