Nuta
Dostęp do tej strony wymaga autoryzacji. Możesz spróbować się zalogować lub zmienić katalog.
Dostęp do tej strony wymaga autoryzacji. Możesz spróbować zmienić katalogi.
W tym artykule pokazano, jak utworzyć sieć bloków przepływu danych, które wykonują przetwarzanie obrazów w aplikacji Windows Forms.
W tym przykładzie ładuje pliki obrazów z określonego folderu, tworzy obraz złożony i wyświetla wynik. W przykładzie użyto modelu przepływu danych do kierowania obrazów za pośrednictwem sieci. W modelu przepływu danych niezależne składniki programu komunikują się ze sobą, wysyłając komunikaty. Gdy składnik odbiera komunikat, wykonuje jakąś akcję, a następnie przekazuje wynik do innego składnika. Porównaj to z modelem przepływu sterowania, w którym aplikacja używa struktur sterujących, na przykład instrukcji warunkowych, pętli itd., aby kontrolować kolejność operacji w programie.
Wymagania wstępne
Przed rozpoczęciem tego przewodnika przeczytaj przepływ danych .
Uwaga / Notatka
Biblioteka przepływów danych TPL ( System.Threading.Tasks.Dataflow przestrzeń nazw) jest zawarta na platformie .NET 6 i nowszych wersjach. W przypadku projektów .NET Framework i .NET Standard należy zainstalować 📦 pakiet NuGet System.Threading.Tasks.Dataflow.
Sekcje
Ten przewodnik zawiera następujące sekcje:
Tworzenie aplikacji Windows Forms
W tej sekcji opisano sposób tworzenia podstawowej aplikacji Windows Forms i dodawania kontrolek do formularza głównego.
Aby utworzyć aplikację Windows Forms
W programie Visual Studio utwórz projekt aplikacji Visual C# lub Visual Basic Windows Forms . W tym dokumencie projekt nosi nazwę
CompositeImages.W projektancie formularzy formularza głównego Form1.cs (Form1.vb dla języka Visual Basic) dodaj kontrolkę ToolStrip .
Dodaj kontrolkę ToolStripButton do kontrolki ToolStrip . Ustaw właściwość DisplayStyle na Text, a tę właściwość Text na Wybierz folder.
Dodaj drugą ToolStripButton kontrolkę do kontrolki ToolStrip . Ustaw właściwość DisplayStyle na Text, właściwość Text na Anuluj, a właściwość Enabled na
False.PictureBox Dodaj obiekt do formularza głównego. Ustaw właściwość Dock na wartość Fill.
Tworzenie sieci przepływu danych
W tej sekcji opisano sposób tworzenia sieci przepływu danych, która wykonuje przetwarzanie obrazów.
Aby utworzyć sieć przepływu danych
Dodaj odwołanie do System.Threading.Tasks.Dataflow.dll do projektu.
Upewnij się, że Form1.cs (Form1.vb dla języka Visual Basic) zawiera następujące
usinginstrukcje (Usingw Visual Basic):using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Drawing; using System.Drawing.Imaging; using System.IO; using System.Linq; using System.Threading; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Threading.Tasks.Dataflow; using System.Windows.Forms;Dodaj następujące składowe danych do
Form1klasy:// The head of the dataflow network. ITargetBlock<string> headBlock = null; // Enables the user interface to signal cancellation to the network. CancellationTokenSource cancellationTokenSource;Dodaj następującą metodę ,
CreateImageProcessingNetworkdoForm1klasy . Ta metoda tworzy sieć przetwarzania obrazów.// Creates the image processing dataflow network and returns the // head node of the network. ITargetBlock<string> CreateImageProcessingNetwork() { // // Create the dataflow blocks that form the network. // // Create a dataflow block that takes a folder path as input // and returns a collection of Bitmap objects. var loadBitmaps = new TransformBlock<string, IEnumerable<Bitmap>>(path => { try { return LoadBitmaps(path); } catch (OperationCanceledException) { // Handle cancellation by passing the empty collection // to the next stage of the network. return Enumerable.Empty<Bitmap>(); } }); // Create a dataflow block that takes a collection of Bitmap objects // and returns a single composite bitmap. var createCompositeBitmap = new TransformBlock<IEnumerable<Bitmap>, Bitmap>(bitmaps => { try { return CreateCompositeBitmap(bitmaps); } catch (OperationCanceledException) { // Handle cancellation by passing null to the next stage // of the network. return null; } }); // Create a dataflow block that displays the provided bitmap on the form. var displayCompositeBitmap = new ActionBlock<Bitmap>(bitmap => { // Display the bitmap. pictureBox1.SizeMode = PictureBoxSizeMode.StretchImage; pictureBox1.Image = bitmap; // Enable the user to select another folder. toolStripButton1.Enabled = true; toolStripButton2.Enabled = false; Cursor = DefaultCursor; }, // Specify a task scheduler from the current synchronization context // so that the action runs on the UI thread. new ExecutionDataflowBlockOptions { TaskScheduler = TaskScheduler.FromCurrentSynchronizationContext() }); // Create a dataflow block that responds to a cancellation request by // displaying an image to indicate that the operation is cancelled and // enables the user to select another folder. var operationCancelled = new ActionBlock<object>(delegate { // Display the error image to indicate that the operation // was cancelled. pictureBox1.SizeMode = PictureBoxSizeMode.CenterImage; pictureBox1.Image = pictureBox1.ErrorImage; // Enable the user to select another folder. toolStripButton1.Enabled = true; toolStripButton2.Enabled = false; Cursor = DefaultCursor; }, // Specify a task scheduler from the current synchronization context // so that the action runs on the UI thread. new ExecutionDataflowBlockOptions { TaskScheduler = TaskScheduler.FromCurrentSynchronizationContext() }); // // Connect the network. // // Link loadBitmaps to createCompositeBitmap. // The provided predicate ensures that createCompositeBitmap accepts the // collection of bitmaps only if that collection has at least one member. loadBitmaps.LinkTo(createCompositeBitmap, bitmaps => bitmaps.Count() > 0); // Also link loadBitmaps to operationCancelled. // When createCompositeBitmap rejects the message, loadBitmaps // offers the message to operationCancelled. // operationCancelled accepts all messages because we do not provide a // predicate. loadBitmaps.LinkTo(operationCancelled); // Link createCompositeBitmap to displayCompositeBitmap. // The provided predicate ensures that displayCompositeBitmap accepts the // bitmap only if it is non-null. createCompositeBitmap.LinkTo(displayCompositeBitmap, bitmap => bitmap != null); // Also link createCompositeBitmap to operationCancelled. // When displayCompositeBitmap rejects the message, createCompositeBitmap // offers the message to operationCancelled. // operationCancelled accepts all messages because we do not provide a // predicate. createCompositeBitmap.LinkTo(operationCancelled); // Return the head of the network. return loadBitmaps; }Zaimplementuj metodę
LoadBitmaps.// Loads all bitmap files that exist at the provided path. IEnumerable<Bitmap> LoadBitmaps(string path) { List<Bitmap> bitmaps = new List<Bitmap>(); // Load a variety of image types. foreach (string bitmapType in new string[] { "*.bmp", "*.gif", "*.jpg", "*.png", "*.tif" }) { // Load each bitmap for the current extension. foreach (string fileName in Directory.GetFiles(path, bitmapType)) { // Throw OperationCanceledException if cancellation is requested. cancellationTokenSource.Token.ThrowIfCancellationRequested(); try { // Add the Bitmap object to the collection. bitmaps.Add(new Bitmap(fileName)); } catch (Exception) { // TODO: A complete application might handle the error. } } } return bitmaps; }Zaimplementuj metodę
CreateCompositeBitmap.// Creates a composite bitmap from the provided collection of Bitmap objects. // This method computes the average color of each pixel among all bitmaps // to create the composite image. Bitmap CreateCompositeBitmap(IEnumerable<Bitmap> bitmaps) { Bitmap[] bitmapArray = bitmaps.ToArray(); // Compute the maximum width and height components of all // bitmaps in the collection. Rectangle largest = new Rectangle(); foreach (var bitmap in bitmapArray) { if (bitmap.Width > largest.Width) largest.Width = bitmap.Width; if (bitmap.Height > largest.Height) largest.Height = bitmap.Height; } // Create a 32-bit Bitmap object with the greatest dimensions. Bitmap result = new Bitmap(largest.Width, largest.Height, PixelFormat.Format32bppArgb); // Lock the result Bitmap. var resultBitmapData = result.LockBits( new Rectangle(new Point(), result.Size), ImageLockMode.WriteOnly, result.PixelFormat); // Lock each source bitmap to create a parallel list of BitmapData objects. var bitmapDataList = (from bitmap in bitmapArray select bitmap.LockBits( new Rectangle(new Point(), bitmap.Size), ImageLockMode.ReadOnly, PixelFormat.Format32bppArgb)) .ToList(); // Compute each column in parallel. Parallel.For(0, largest.Width, new ParallelOptions { CancellationToken = cancellationTokenSource.Token }, i => { // Compute each row. for (int j = 0; j < largest.Height; j++) { // Counts the number of bitmaps whose dimensions // contain the current location. int count = 0; // The sum of all alpha, red, green, and blue components. int a = 0, r = 0, g = 0, b = 0; // For each bitmap, compute the sum of all color components. foreach (var bitmapData in bitmapDataList) { // Ensure that we stay within the bounds of the image. if (bitmapData.Width > i && bitmapData.Height > j) { unsafe { byte* row = (byte*)(bitmapData.Scan0 + (j * bitmapData.Stride)); byte* pix = (byte*)(row + (4 * i)); a += *pix; pix++; r += *pix; pix++; g += *pix; pix++; b += *pix; } count++; } } //prevent divide by zero in bottom right pixelless corner if (count == 0) break; unsafe { // Compute the average of each color component. a /= count; r /= count; g /= count; b /= count; // Set the result pixel. byte* row = (byte*)(resultBitmapData.Scan0 + (j * resultBitmapData.Stride)); byte* pix = (byte*)(row + (4 * i)); *pix = (byte)a; pix++; *pix = (byte)r; pix++; *pix = (byte)g; pix++; *pix = (byte)b; } } }); // Unlock the source bitmaps. for (int i = 0; i < bitmapArray.Length; i++) { bitmapArray[i].UnlockBits(bitmapDataList[i]); } // Unlock the result bitmap. result.UnlockBits(resultBitmapData); // Return the result. return result; }Uwaga / Notatka
Wersja języka
CreateCompositeBitmapC# metody używa wskaźników w celu umożliwienia wydajnego przetwarzania System.Drawing.Bitmap obiektów. W związku z tym należy włączyć opcję Zezwalaj na niebezpieczny kod w projekcie, aby użyć niebezpiecznego słowa kluczowego. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat włączania niebezpiecznego kodu w projekcie Visual C#, zobacz Strona kompilacji, Projektant projektu (C#).
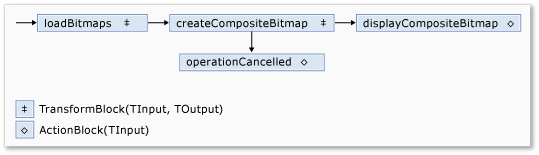
W poniższej tabeli opisano elementy członkowskie sieci.
| Członek | Typ | Description |
|---|---|---|
loadBitmaps |
TransformBlock<TInput,TOutput> | Pobiera ścieżkę folderu jako dane wejściowe i tworzy kolekcję Bitmap obiektów jako danych wyjściowych. |
createCompositeBitmap |
TransformBlock<TInput,TOutput> | Pobiera kolekcję Bitmap obiektów jako dane wejściowe i tworzy złożoną mapę bitową jako dane wyjściowe. |
displayCompositeBitmap |
ActionBlock<TInput> | Wyświetla złożoną mapę bitową w formularzu. |
operationCancelled |
ActionBlock<TInput> | Wyświetla obraz wskazujący, że operacja została anulowana i umożliwia użytkownikowi wybranie innego folderu. |
Aby połączyć bloki przepływu danych w celu utworzenia sieci, w tym przykładzie użyto LinkTo metody . Metoda LinkTo zawiera przeciążoną wersję, która przyjmuje Predicate<T> obiekt, który określa, czy blok docelowy akceptuje lub odrzuca komunikat. Ten mechanizm filtrowania umożliwia blokom komunikatów odbieranie tylko określonych wartości. W tym przykładzie sieć może rozgałęzić się na jeden z dwóch sposobów. Gałąź główna ładuje obrazy z dysku, tworzy obraz złożony i wyświetla ten obraz na formularzu. Gałąź alternatywna anuluje bieżącą operację. Obiekty Predicate<T> umożliwiają blokom przepływu danych wzdłuż gałęzi głównej przełączenie się do alternatywnej gałęzi przez odrzucenie niektórych komunikatów. Jeśli na przykład użytkownik anuluje operację, blok createCompositeBitmap przepływu danych tworzy null (Nothing w Visual Basic) jako dane wyjściowe. Blok displayCompositeBitmap przepływu danych odrzuca null wartości wejściowe, dlatego komunikat jest oferowany do operationCancelled. Blok operationCancelled przepływu danych akceptuje wszystkie komunikaty, a w związku z tym wyświetla obraz wskazujący, że operacja została anulowana.
Poniższa ilustracja przedstawia sieć przetwarzania obrazów:
displayCompositeBitmap Ponieważ bloki przepływu danych i operationCancelled działają na interfejsie użytkownika, ważne jest, aby te akcje były wykonywane w wątku interfejsu użytkownika. Aby to osiągnąć, podczas budowy każdy z tych obiektów zapewnia obiekt ExecutionDataflowBlockOptions, który ma właściwość TaskScheduler ustawioną na TaskScheduler.FromCurrentSynchronizationContext. Metoda TaskScheduler.FromCurrentSynchronizationContext tworzy TaskScheduler obiekt, który wykonuje pracę w bieżącym kontekście synchronizacji.
CreateImageProcessingNetwork Ponieważ metoda jest wywoływana z procedury obsługi przycisku Wybierz folder, który jest uruchamiany w wątku interfejsu użytkownika, akcje dla displayCompositeBitmap bloków przepływu danych i operationCancelled są również uruchamiane w wątku interfejsu użytkownika.
W tym przykładzie użyto wspólnego tokenu anulowania zamiast ustawienia właściwości CancellationToken, ponieważ właściwość CancellationToken trwale zatrzymuje wykonywanie bloku przepływu danych. Token anulowania umożliwia wielokrotne ponowne użycie tej samej sieci przepływu danych, nawet jeśli użytkownik anuluje co najmniej jedną operację. Aby zapoznać się z przykładem, który używa CancellationToken do trwałego anulowania wykonywania bloku przepływu danych, zobacz Jak: anulowanie bloku przepływu danych.
Łączenie sieci przepływu danych z interfejsem użytkownika
W tej sekcji opisano sposób łączenia sieci przepływu danych z interfejsem użytkownika. Tworzenie obrazu złożonego i anulowanie operacji jest inicjowane za pomocą przycisków Wybierz folder i Anuluj . Gdy użytkownik wybierze jeden z tych przycisków, odpowiednie działanie jest inicjowane w sposób asynchroniczny.
Aby połączyć sieć przepływu danych z interfejsem użytkownika
W projektancie formularzy dla formularza głównego utwórz procedurę obsługi dla zdarzenia Click dotyczącego przycisku Wybierz folder.
Zaimplementuj Click zdarzenie dla przycisku Wybierz folder.
// Event handler for the Choose Folder button. private void toolStripButton1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { // Create a FolderBrowserDialog object to enable the user to // select a folder. FolderBrowserDialog dlg = new FolderBrowserDialog { ShowNewFolderButton = false }; // Set the selected path to the common Sample Pictures folder // if it exists. string initialDirectory = Path.Combine( Environment.GetFolderPath(Environment.SpecialFolder.CommonPictures), "Sample Pictures"); if (Directory.Exists(initialDirectory)) { dlg.SelectedPath = initialDirectory; } // Show the dialog and process the dataflow network. if (dlg.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK) { // Create a new CancellationTokenSource object to enable // cancellation. cancellationTokenSource = new CancellationTokenSource(); // Create the image processing network if needed. headBlock ??= CreateImageProcessingNetwork(); // Post the selected path to the network. headBlock.Post(dlg.SelectedPath); // Enable the Cancel button and disable the Choose Folder button. toolStripButton1.Enabled = false; toolStripButton2.Enabled = true; // Show a wait cursor. Cursor = Cursors.WaitCursor; } }W projektancie formularzy dla formularza głównego utwórz procedurę obsługi zdarzenia Click dla przycisku Anuluj.
Zaimplementuj Click zdarzenie dla przycisku Anuluj .
// Event handler for the Cancel button. private void toolStripButton2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { // Signal the request for cancellation. The current component of // the dataflow network will respond to the cancellation request. cancellationTokenSource.Cancel(); }
Kompletny przykład
W poniższym przykładzie przedstawiono kompletny kod dla tego przewodnika.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Drawing.Imaging;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading.Tasks.Dataflow;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace CompositeImages
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
// The head of the dataflow network.
ITargetBlock<string> headBlock = null;
// Enables the user interface to signal cancellation to the network.
CancellationTokenSource cancellationTokenSource;
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
// Creates the image processing dataflow network and returns the
// head node of the network.
ITargetBlock<string> CreateImageProcessingNetwork()
{
//
// Create the dataflow blocks that form the network.
//
// Create a dataflow block that takes a folder path as input
// and returns a collection of Bitmap objects.
var loadBitmaps = new TransformBlock<string, IEnumerable<Bitmap>>(path =>
{
try
{
return LoadBitmaps(path);
}
catch (OperationCanceledException)
{
// Handle cancellation by passing the empty collection
// to the next stage of the network.
return Enumerable.Empty<Bitmap>();
}
});
// Create a dataflow block that takes a collection of Bitmap objects
// and returns a single composite bitmap.
var createCompositeBitmap = new TransformBlock<IEnumerable<Bitmap>, Bitmap>(bitmaps =>
{
try
{
return CreateCompositeBitmap(bitmaps);
}
catch (OperationCanceledException)
{
// Handle cancellation by passing null to the next stage
// of the network.
return null;
}
});
// Create a dataflow block that displays the provided bitmap on the form.
var displayCompositeBitmap = new ActionBlock<Bitmap>(bitmap =>
{
// Display the bitmap.
pictureBox1.SizeMode = PictureBoxSizeMode.StretchImage;
pictureBox1.Image = bitmap;
// Enable the user to select another folder.
toolStripButton1.Enabled = true;
toolStripButton2.Enabled = false;
Cursor = DefaultCursor;
},
// Specify a task scheduler from the current synchronization context
// so that the action runs on the UI thread.
new ExecutionDataflowBlockOptions
{
TaskScheduler = TaskScheduler.FromCurrentSynchronizationContext()
});
// Create a dataflow block that responds to a cancellation request by
// displaying an image to indicate that the operation is cancelled and
// enables the user to select another folder.
var operationCancelled = new ActionBlock<object>(delegate
{
// Display the error image to indicate that the operation
// was cancelled.
pictureBox1.SizeMode = PictureBoxSizeMode.CenterImage;
pictureBox1.Image = pictureBox1.ErrorImage;
// Enable the user to select another folder.
toolStripButton1.Enabled = true;
toolStripButton2.Enabled = false;
Cursor = DefaultCursor;
},
// Specify a task scheduler from the current synchronization context
// so that the action runs on the UI thread.
new ExecutionDataflowBlockOptions
{
TaskScheduler = TaskScheduler.FromCurrentSynchronizationContext()
});
//
// Connect the network.
//
// Link loadBitmaps to createCompositeBitmap.
// The provided predicate ensures that createCompositeBitmap accepts the
// collection of bitmaps only if that collection has at least one member.
loadBitmaps.LinkTo(createCompositeBitmap, bitmaps => bitmaps.Count() > 0);
// Also link loadBitmaps to operationCancelled.
// When createCompositeBitmap rejects the message, loadBitmaps
// offers the message to operationCancelled.
// operationCancelled accepts all messages because we do not provide a
// predicate.
loadBitmaps.LinkTo(operationCancelled);
// Link createCompositeBitmap to displayCompositeBitmap.
// The provided predicate ensures that displayCompositeBitmap accepts the
// bitmap only if it is non-null.
createCompositeBitmap.LinkTo(displayCompositeBitmap, bitmap => bitmap != null);
// Also link createCompositeBitmap to operationCancelled.
// When displayCompositeBitmap rejects the message, createCompositeBitmap
// offers the message to operationCancelled.
// operationCancelled accepts all messages because we do not provide a
// predicate.
createCompositeBitmap.LinkTo(operationCancelled);
// Return the head of the network.
return loadBitmaps;
}
// Loads all bitmap files that exist at the provided path.
IEnumerable<Bitmap> LoadBitmaps(string path)
{
List<Bitmap> bitmaps = new List<Bitmap>();
// Load a variety of image types.
foreach (string bitmapType in
new string[] { "*.bmp", "*.gif", "*.jpg", "*.png", "*.tif" })
{
// Load each bitmap for the current extension.
foreach (string fileName in Directory.GetFiles(path, bitmapType))
{
// Throw OperationCanceledException if cancellation is requested.
cancellationTokenSource.Token.ThrowIfCancellationRequested();
try
{
// Add the Bitmap object to the collection.
bitmaps.Add(new Bitmap(fileName));
}
catch (Exception)
{
// TODO: A complete application might handle the error.
}
}
}
return bitmaps;
}
// Creates a composite bitmap from the provided collection of Bitmap objects.
// This method computes the average color of each pixel among all bitmaps
// to create the composite image.
Bitmap CreateCompositeBitmap(IEnumerable<Bitmap> bitmaps)
{
Bitmap[] bitmapArray = bitmaps.ToArray();
// Compute the maximum width and height components of all
// bitmaps in the collection.
Rectangle largest = new Rectangle();
foreach (var bitmap in bitmapArray)
{
if (bitmap.Width > largest.Width)
largest.Width = bitmap.Width;
if (bitmap.Height > largest.Height)
largest.Height = bitmap.Height;
}
// Create a 32-bit Bitmap object with the greatest dimensions.
Bitmap result = new Bitmap(largest.Width, largest.Height,
PixelFormat.Format32bppArgb);
// Lock the result Bitmap.
var resultBitmapData = result.LockBits(
new Rectangle(new Point(), result.Size), ImageLockMode.WriteOnly,
result.PixelFormat);
// Lock each source bitmap to create a parallel list of BitmapData objects.
var bitmapDataList = (from bitmap in bitmapArray
select bitmap.LockBits(
new Rectangle(new Point(), bitmap.Size),
ImageLockMode.ReadOnly, PixelFormat.Format32bppArgb))
.ToList();
// Compute each column in parallel.
Parallel.For(0, largest.Width, new ParallelOptions
{
CancellationToken = cancellationTokenSource.Token
},
i =>
{
// Compute each row.
for (int j = 0; j < largest.Height; j++)
{
// Counts the number of bitmaps whose dimensions
// contain the current location.
int count = 0;
// The sum of all alpha, red, green, and blue components.
int a = 0, r = 0, g = 0, b = 0;
// For each bitmap, compute the sum of all color components.
foreach (var bitmapData in bitmapDataList)
{
// Ensure that we stay within the bounds of the image.
if (bitmapData.Width > i && bitmapData.Height > j)
{
unsafe
{
byte* row = (byte*)(bitmapData.Scan0 + (j * bitmapData.Stride));
byte* pix = (byte*)(row + (4 * i));
a += *pix; pix++;
r += *pix; pix++;
g += *pix; pix++;
b += *pix;
}
count++;
}
}
//prevent divide by zero in bottom right pixelless corner
if (count == 0)
break;
unsafe
{
// Compute the average of each color component.
a /= count;
r /= count;
g /= count;
b /= count;
// Set the result pixel.
byte* row = (byte*)(resultBitmapData.Scan0 + (j * resultBitmapData.Stride));
byte* pix = (byte*)(row + (4 * i));
*pix = (byte)a; pix++;
*pix = (byte)r; pix++;
*pix = (byte)g; pix++;
*pix = (byte)b;
}
}
});
// Unlock the source bitmaps.
for (int i = 0; i < bitmapArray.Length; i++)
{
bitmapArray[i].UnlockBits(bitmapDataList[i]);
}
// Unlock the result bitmap.
result.UnlockBits(resultBitmapData);
// Return the result.
return result;
}
// Event handler for the Choose Folder button.
private void toolStripButton1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Create a FolderBrowserDialog object to enable the user to
// select a folder.
FolderBrowserDialog dlg = new FolderBrowserDialog
{
ShowNewFolderButton = false
};
// Set the selected path to the common Sample Pictures folder
// if it exists.
string initialDirectory = Path.Combine(
Environment.GetFolderPath(Environment.SpecialFolder.CommonPictures),
"Sample Pictures");
if (Directory.Exists(initialDirectory))
{
dlg.SelectedPath = initialDirectory;
}
// Show the dialog and process the dataflow network.
if (dlg.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
// Create a new CancellationTokenSource object to enable
// cancellation.
cancellationTokenSource = new CancellationTokenSource();
// Create the image processing network if needed.
headBlock ??= CreateImageProcessingNetwork();
// Post the selected path to the network.
headBlock.Post(dlg.SelectedPath);
// Enable the Cancel button and disable the Choose Folder button.
toolStripButton1.Enabled = false;
toolStripButton2.Enabled = true;
// Show a wait cursor.
Cursor = Cursors.WaitCursor;
}
}
// Event handler for the Cancel button.
private void toolStripButton2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Signal the request for cancellation. The current component of
// the dataflow network will respond to the cancellation request.
cancellationTokenSource.Cancel();
}
~Form1()
{
cancellationTokenSource.Dispose();
}
}
}
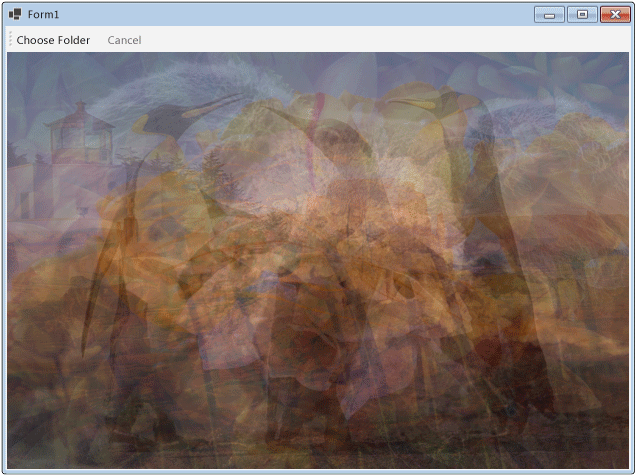
Poniższa ilustracja przedstawia typowe dane wyjściowe dla wspólnego folderu \Sample Pictures\.