Nuta
Dostęp do tej strony wymaga autoryzacji. Możesz spróbować się zalogować lub zmienić katalog.
Dostęp do tej strony wymaga autoryzacji. Możesz spróbować zmienić katalogi.
This walkthrough will guide you through how to use custom rewrite providers with URL Rewrite Module 2.0. The walkthrough uses the URL Rewrite 2.0 Extensibility Samples, which can be downloaded from URL Rewrite Extensibility Samples at MSDN Code Gallery.
Install URL Rewrite Extensibility Samples
In order to complete this walkthrough, download and install IIS URL Rewrite 2.1. The URL Rewrite Extensibility Samples for 2.0 are no longer available.
- Storing of the rewrite or redirect mappings in a SQL database;
- Storing of the rewrite or redirect mappings in a text file;
- Storing of the lookup substrings in a text file.
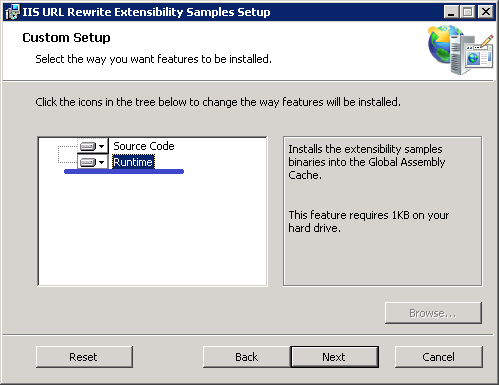
During the installation make sure to select the "Runtime" option in the custom setup. This will register the sample providers in .NET Global Assembly Cache so that they can be used by URL Rewrite Module.
Registering the Providers
There are 3 rewrite providers included in the installation package:
- DbProvider - this provider can be used to retrieve rewrite mappings from a SQL Server database table by executing a stored procedure
- FileMapProvider - this provider can be used to retrieve rewrite mappings stored in a text file
- FileContainsProvider - this provider can be used to check if any string in a text file is a substring of the provider's input string.
In order to use the sample providers in the rewrite rules the providers must be registered with IIS. To register a provider you can use the IIS Manager user interface:
- Open URL Rewrite feature in IIS Manager;
- Select the "View Providers..." action in the "Actions" pane on right hand side;

- Select the "Add Provider..." action in the "Actions" pane;
- In the "Add Provider" dialog, enter the name that you want to use for this provider when referring to it from a rewrite rule.
- After that choose the corresponding .NET type for the provider in the "Managed Type" drop down list. Note that it may take some time for the provider types to appear there.

- Repeat the above steps to register all three providers.
Using DbProvider
To use DbProvider you will need access to Microsoft SQL Server. The provider connects to a SQL Server database and executes a stored procedure that takes a NVARCHAR input parameter containing the input URL string and returns a one row, one column result set containing the output URL string of NVARCHAR type.
Creating a Sample Database
Open a SQL Server Management Studio, open a new query window and execute the following SQL script:
USE [master]
CREATE LOGIN [IIS APPPOOL\DefaultAppPool] FROM WINDOWS WITH DEFAULT_DATABASE=[master]
CREATE DATABASE [RewriteDB]
GO
USE [RewriteDB]
GO
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[RewriteTable](
[OriginalUrl] [nvarchar](256) NOT NULL,
[NewUrl] [nvarchar](256) NOT NULL
) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[GetRewrittenUrl]
@input nvarchar(256)
AS
SELECT rt.NewUrl
FROM dbo.RewriteTable rt
WHERE rt.OriginalUrl = @input
GO
CREATE USER [IIS APPPOOL\DefaultAppPool] FOR LOGIN [IIS APPPOOL\DefaultAppPool]
GRANT EXECUTE ON dbo.GetRewrittenUrl TO [IIS APPPOOL\DefaultAppPool];
GO
INSERT INTO dbo.RewriteTable VALUES ('old/catalog/product.html', 'new/category/product.html');
INSERT INTO dbo.RewriteTable VALUES ('old/contactus/index.html', 'new/contactus.html');
GO
The above script creates a new database called RewriteDB, which has a table RewriteTable and a stored procedure GetRewrittenURL. It also grants permissions to IIS APPPOOL\DefaultAppPool account to execute that stored procedure. Also it fills up the database table with two URL mappings.
Configuring DbProvider settings
Configure the DbProvider instance to call the stored procedure:
- In IIS Manager in the URL Rewrite feature view select "View Providers..." int the action pane.
- Select "Add Provider" and choose DbProvider. Name it DB; that will be the name by which you will refer to the provider from a rewrite rule
- Select the DbProvider instance called DB and click "Add Provider Setting..." action.
- Use the "Edit Provider Setting" dialog to configure the provider:

Use the following values for the provider settings:
- SQL Server connection string: provide a SQL Server connection string, for example:
"Data Source=servername\sqlexpress;Initial Catalog=RewriteDB;Integrated Security=True" - Stored procedure name: GetRewrittenUrl
- Cache minutes interval: set to 0 if values in the SQL table do not change, or set to a positive integer so that provider periodically refreshes the module's internal rewrite cache. If not specified the value of 0 is assumed.
Calling DbProvider from a Rewrite Rule
In the root directory of a web site open web.config file. If you use IIS Default Web Site, then the file should be located in C:\inetpub\wwwroot\ folder.
Paste the following redirect rule into the web.config file inside of the /<configuration>/<system.webServer>/<rewrite>/<rules> element:
<rule name="DbProviderTest" stopProcessing="true">
<match url="(.*)" />
<conditions>
<add input="{DB:{R:1}}" pattern="(.+)" />
</conditions>
<action type="Redirect" url="{C:1}" />
</rule>
The complete content of the web.config file should look similar to below:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration>
<system.webServer>
<rewrite>
<providers>
<provider name="DB" type="DbProvider, Microsoft.Web.Iis.Rewrite.Providers, Version=1.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35">
<settings>
<add key="ConnectionString" value="Data Source=ruslany-server\sqlexpress;Initial Catalog=RewriteDB;Integrated Security=True" />
<add key="StoredProcedure" value="GetRewrittenUrl" />
<add key="CacheMinutesInterval" value="0" />
</settings>
</provider>
</providers>
<rules>
<rule name="DbProviderTest" stopProcessing="true">
<match url="(.*)" />
<conditions>
<add input="{DB:{R:1}}" pattern="(.+)" />
</conditions>
<action type="Redirect" url="{C:1}" />
</rule>
</rules>
</rewrite>
This rule performs HTTP redirect to a URL that is obtained from a SQL Server database via DbProvider. The DbProvider instance named "DB" is invoked from the rule's condition and if the result returned from the provider is not empty then the HTTP redirection is performed.
To test the rule open a web browser and make a request to http://localhost/old/catalog/product.html or http://localhost/old/contactus/index.html. Notice that the browser gets redirected to a new URL based on the redirect mappings defined in the RewriteDB database table. The web server will return HTTP 404 error for the redirected URL because there is no such file or directory on the server, but that is not relevant for the purposes of this walkthrough. The important part is that the web server issued a redirect response based on the rule that used the DbProvider.
Using FileMapProvider
FileMapProvider reads the URL mappings from a text file. It can be used instead of the built-in rewrite maps functionality when the amount of rewrite map entries is very large and it is not practical to keep them in a web.config file.
Creating a Sample Mappings File
Create a new directory called App_Data in the root directory of your web site. In that directory create a text file called redirectmappings.txt. Add the following lines to the file:
old/catalog/product.html, new/category/product.html
old/contactus/index.html, new/contactus.html
 WARNING: Always make sure that the text file is not directly accessible from the Web. Use IIS Request Filtering module or place the file inside of App_Data folder to prevent HTTP clients from directly accessing the content of this file.
WARNING: Always make sure that the text file is not directly accessible from the Web. Use IIS Request Filtering module or place the file inside of App_Data folder to prevent HTTP clients from directly accessing the content of this file.
Configuring FileMapProvider
Configure the FileMapProvider by following the same steps as described in Configuring DbProvider. Use these values for the provider settings:
- FilePath: {DOCUMENT_ROOT}\App_Data\redirectmappings.txt (note the usage of {DOCUMENT_ROOT} in the file path. This gets replaced with the actual path during provider initialization. This is useful when you do not want to place an absolute file path in web.config file)
- IgnoreCase: 1
- Separator: "," (if not specified then the TAB symbol will be used as a separator)
Calling FileMapProvider from a Rewrite Rule
In the root directory of a web site open web.config file. If you use IIS Default Web Site, then the file should be located in C:\inetpub\wwwroot\ folder.
Paste the following redirect rule into the web.config file inside of the /<configuration>/<system.webServer>/<rewrite>/<rules> element:
<rule name="FileMapProviderTest" stopProcessing="true">
<match url="(.*)" />
<conditions>
<add input="{FileMap:{R:1}}" pattern="(.+)" />
</conditions>
<action type="Redirect" url="{C:1}" />
</rule>
The complete content of the web.config file should look similar to below:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration>
<system.webServer>
<rewrite>
<providers>
<provider name="FileMap" type="FileMapProvider, Microsoft.Web.Iis.Rewrite.Providers, Version=1.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35">
<settings>
<add key="FilePath" value="{DOCUMENT_ROOT}\App_Data\redirectmappings.txt" />
<add key="IgnoreCase" value="1" />
<add key="Separator" value="," />
</settings>
</provider>
</providers>
<rules>
<rule name="FileMapProviderTest" stopProcessing="true">
<match url="(.*)" />
<conditions>
<add input="{FileMap:{R:1}}" pattern="(.+)" />
</conditions>
<action type="Redirect" url="{C:1}" />
</rule>
</rules>
</rewrite>
This rule performs HTTP redirect to a URL that is obtained from a text file via FileMapProvider. The FileMapProvider instance named "FileMap" is invoked from the rule's condition and if the result returned from the provider is not empty then the HTTP redirection is performed.
To test the rule open a web browser and make a request to http://localhost/old/catalog/product.html or http://localhost/old/contactus/index.html. Notice that the browser gets redirected to a new URL based on the redirect mappings defined in the redirectmappings.txt file. The web server will return HTTP 404 error for the redirected URL because there is no such file or directory on the server, but that is not relevant for the purposes of this walkthrough. The important part is that the web server issued a redirect response based on the rule that used the FileMapProviders.
Using FileContainsProvider
FileContainsProvider reads the set of strings from a text file and then checks if the provider's input string contains any of those strings as a substring. The provider can be used for example with rewrite rules that block access based on user-agent header.
Creating a Sample Disallowed User-Agents File
Create a new directory called App_Data in the root directory of your web site. In that directory create a text file called disalloweduseragents.txt. Add the following lines to the file:
badrobot1
badrobot2
 WARNING: Always make sure that the text file is not directly accessible from the Web. Use IIS Request Filtering module or place the file inside of App_Data folder to prevent HTTP clients from directly accessing the content of this file.
WARNING: Always make sure that the text file is not directly accessible from the Web. Use IIS Request Filtering module or place the file inside of App_Data folder to prevent HTTP clients from directly accessing the content of this file.
Configuring FileContainsProvider
Configure the FileMapProvider by following the same steps as described in Configuring DbProvider. Use these values for the provider settings:
- FilePath: {DOCUMENT_ROOT}\App_Data\disalloweduseragents.txt (note the usage of {DOCUMENT_ROOT} in the file path. This gets replaced with the actual path during provider initialization. This is useful when you do not want to place an absolute file path in web.config file)
- IgnoreCase: 1
Calling FileContainsProvider from a Rewrite Rule
In the root directory of a web site open web.config file. If you use IIS Default Web Site, then the file should be located in C:\inetpub\wwwroot\ folder.
Paste the following redirect rule into the web.config file inside of the /<configuration>/<system.webServer>/<rewrite>/<rules> element:
<rule name="FileContainsProviderTest" stopProcessing="true">
<match url=".*" />
<conditions>
<add input="{FileContains:{HTTP_USER_AGENT}}" pattern=".+" />
</conditions>
<action type="AbortRequest" />
</rule>
The complete content of the web.config file should look similar to below:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration>
<system.webServer>
<rewrite>
<providers>
<provider name="FileContains" type="FileContainsProvider, Microsoft.Web.Iis.Rewrite.Providers, Version=1.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35">
<settings>
<add key="FilePath" value="{DOCUMENT_ROOT}\App_Data\disalloweduseragents.txt" />
<add key="IgnoreCase" value="1" />
</settings>
</provider>
</providers>
<rules>
<rule name="FileContainsProviderTest" stopProcessing="true">
<match url=".*" />
<conditions>
<add input="{FileContains:{HTTP_USER_AGENT}}" pattern=".+" />
</conditions>
<action type="AbortRequest" />
</rule>
</rules>
</rewrite>
This rule aborts the HTTP connection if the user agent of the HTTP request matches any of the strings listed in disalloweduseragents.txt file. The FileContainsProvider instance named "FileContains" is invoked from the rule's condition and if the result returned from the provider is not empty then the HTTP connection is aborted.
To test the rule open WFetch and add a user-agent header to the request as below:
user-agent: badrobot1\r\n
From WFetch make a request to http://localhost/test/. You should see that the connection gets aborted because the user agent string has matched one of the strings in disalloweduseragents.txt file.