Nuta
Dostęp do tej strony wymaga autoryzacji. Możesz spróbować się zalogować lub zmienić katalog.
Dostęp do tej strony wymaga autoryzacji. Możesz spróbować zmienić katalogi.
Column-level security is applied for columns that contain sensitive information. Passwords, bank account numbers, government ID, telephone numbers, or email addresses can be secured at the column level.
This article explains how developers can work with column-level security capabilities using code and the Dataverse SDK for .NET or Web API. You don't need to write code to use this feature. Learn how to configure column-level security to control access. Developers should also understand how to configure column-level security using Power Apps.
Discover which columns are secured
Detect which columns are secured by retrieving the definition of the column and examining the boolean AttributeMetadata.IsSecured property.
There are two ways to discover which columns are secured with code. These ways are described in the following two sections:
- Retrieve column data filtered on IsSecured
- Retrieve FieldSecurityProfile for System Administrator role
Retrieve column data filtered on IsSecured
This method queries the organization's metadata to identify columns marked with the IsSecured property set to true. Everyone has access to view this data. Learn how to Query schema definitions
The resulting CSV file contains two columns: Table and Column, representing the schema names of the tables and their secured columns, respectively.
/// <summary>
/// Generates a CSV file containing the names of secured columns for all tables
/// in the organization.
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>This method queries the organization's metadata to identify columns
/// marked as secured (i.e., columns with the <c>IsSecured</c> property set to
/// <see langword="true"/>). The resulting CSV file contains two columns: "Table"
/// and "Column", representing the schema names of the tables and their secured
/// columns, respectively. <para> Ensure that the provided
/// <paramref name="filepath"/> is writable and that the user has appropriate
/// permissions to access the specified directory. </para></remarks>
/// <param name="service">The <see cref="IOrganizationService"/> instance used to
/// retrieve metadata from the organization.</param>
/// <param name="filepath">The directory path where the CSV file will be saved.
/// Must be a valid and accessible file path.</param>
/// <param name="filename">The name of the CSV file to be created. Defaults to
/// "SecuredColumns.csv" if not specified.</param>
static internal void GetSecuredColumns(IOrganizationService service,
string filepath, string filename = "SecuredColumns.csv")
{
EntityQueryExpression query = new()
{
Properties = new MetadataPropertiesExpression(
"SchemaName",
"Attributes"),
Criteria = new MetadataFilterExpression(),
AttributeQuery = new()
{
Properties = new MetadataPropertiesExpression(
"SchemaName",
"AttributeTypeName"),
Criteria = new MetadataFilterExpression()
{
Conditions = {
{
new MetadataConditionExpression(
"IsSecured",
MetadataConditionOperator.Equals,
true)
}
}
}
}
};
RetrieveMetadataChangesRequest request = new()
{
Query = query
};
var response = (RetrieveMetadataChangesResponse)service.Execute(request);
// Create a StringBuilder to hold the CSV data
StringBuilder csvContent = new();
string[] columns = {
"Table",
"Column" };
// Add headers
csvContent.AppendLine(string.Join(",", columns));
foreach (var table in response.EntityMetadata)
{
foreach (var column in table.Attributes)
{
string[] values = {
table.SchemaName,
column.SchemaName
};
// Add values
csvContent.AppendLine(string.Join(",", values));
}
}
File.WriteAllText(
Path.Combine(filepath, filename),
csvContent.ToString());
}
Retrieve FieldSecurityProfile for System Administrator role
This method queries the Dataverse field permission table to identify columns that the Field Security Profile (FieldSecurityProfile) record with ID 572329c1-a042-4e22-be47-367c6374ea45 secures. This record manages access to secured columns for system administrators. Typically, only system administrators have the prvReadFieldPermission privilege to retrieve this data.
The static GetSecuredColumnList method returns fully qualified column names in the format TableName.ColumnName, sorted alphabetically.
/// <summary>
/// Retrieves a list of secured columns managed by the specified field security
/// profile.
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>This method queries the Dataverse field permission table to identify
/// columns that are secured by the field security profile with ID
/// <c>572329c1-a042-4e22-be47-367c6374ea45</c>. The returned list contains fully
/// qualified column names in the format <c>TableName.ColumnName</c>, sorted
/// alphabetically.</remarks>
/// <param name="service">The <see cref="IOrganizationService"/> instance used to
/// interact with the Dataverse service.</param>
/// <returns>A sorted list of strings representing the fully qualified names of
/// secured columns.</returns>
/// <exception cref="Exception">Thrown if the calling user does not have read
/// access to the field permission table or if an error occurs while retrieving
/// field permissions.</exception>
static internal List<string> GetSecuredColumnList(IOrganizationService service)
{
QueryExpression query = new("fieldpermission")
{
ColumnSet = new ColumnSet("entityname", "attributelogicalname"),
Criteria = new FilterExpression(LogicalOperator.And)
{
Conditions =
{
// Field security profile with ID '572329c1-a042-4e22-be47-367c6374ea45'
// manages access for system administrators. It always contains
// references to each secured column
new ConditionExpression("fieldsecurityprofileid", ConditionOperator.Equal,
new Guid("572329c1-a042-4e22-be47-367c6374ea45"))
}
}
};
EntityCollection fieldPermissions;
try
{
fieldPermissions = service.RetrieveMultiple(query);
}
catch (FaultException<OrganizationServiceFault> ex)
{
if (ex.Detail.ErrorCode.Equals(-2147220960))
{
string message = "The calling user doesn't have read access to the fieldpermission table";
throw new Exception(message);
}
else
{
throw new Exception($"Dataverse error retrieving field permissions: {ex.Message}");
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw new Exception($"Error retrieving field permissions: {ex.Message}", ex);
}
List<string> values = [];
foreach (var fieldpermission in fieldPermissions.Entities)
{
string tableName = fieldpermission.GetAttributeValue<string>("entityname")!;
string columnName = fieldpermission.GetAttributeValue<string>("attributelogicalname")!;
values.Add($"{tableName}.{columnName}");
}
values.Sort();
return values;
}
Discover which columns can be secured
You can't secure every column. When you enable column security using Power Apps, the Enable column security checkbox is disabled for certain fields. You don't need to manually check each column to find out if you can secure it. Write a query to retrieve which columns you can secure.
Three boolean AttributeMetadata properties control whether you can secure any column:
When all of these properties are false, the column can't be secured. Some columns might only be secured for one or two of the three operations: Create, Read, and Update.
The following queries return this data so you can discover which columns in your environment can be secured:
This static DumpColumnSecurityInfo method retrieves metadata about entity attributes, including security-related properties, and writes the information to a CSV file. The output file contains details such as whether columns are secured, can be secured for create, update, or read operations, and other relevant metadata.
/// <summary>
/// Exports column security information for all entities in the organization to a
/// CSV file.
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>This method retrieves metadata about entity attributes, including
/// security-related properties, and writes the information to a CSV file. The output
/// file contains details such as whether columns are secured, can be secured for
/// create, update, or read operations, and other relevant metadata.</remarks>
/// <param name="service">The <see cref="IOrganizationService"/> instance used to
/// retrieve metadata from the organization.</param>
/// <param name="filepath">The directory path where the CSV file will be saved. This
/// must be a valid, writable directory.</param>
/// <param name="filename">The name of the CSV file to create. Defaults to
/// "ColumnSecurityInfo.csv" if not specified.</param>
static internal void DumpColumnSecurityInfo(IOrganizationService service,
string filepath, string filename = "ColumnSecurityInfo.csv")
{
EntityQueryExpression query = new()
{
Properties = new MetadataPropertiesExpression("SchemaName", "Attributes"),
Criteria = new MetadataFilterExpression
{
FilterOperator = LogicalOperator.And,
Conditions =
{
new MetadataConditionExpression(
"IsPrivate",
MetadataConditionOperator.Equals,
false),
}
},
AttributeQuery = new()
{
Properties = new MetadataPropertiesExpression(
"SchemaName",
"AttributeTypeName",
"IsPrimaryName",
"IsSecured",
"CanBeSecuredForCreate",
"CanBeSecuredForUpdate",
"CanBeSecuredForRead"),
Criteria = new MetadataFilterExpression()
{
Conditions = {
{ // Exclude Virtual columns
new MetadataConditionExpression(
"AttributeTypeName",
MetadataConditionOperator.NotEquals,
AttributeTypeDisplayName.VirtualType)
}
}
}
}
};
RetrieveMetadataChangesRequest request = new()
{
Query = query
};
var response = (RetrieveMetadataChangesResponse)service.Execute(request);
// Create a StringBuilder to hold the CSV data
StringBuilder csvContent = new();
string[] columns = {
"Column",
"Type",
"IsPrimaryName",
"IsSecured",
"CanBeSecuredForCreate",
"CanBeSecuredForUpdate",
"CanBeSecuredForRead" };
// Add headers
csvContent.AppendLine(string.Join(",", columns));
foreach (var table in response.EntityMetadata)
{
foreach (AttributeMetadata column in table.Attributes)
{
string[] values = {
$"{table.SchemaName}.{column.SchemaName}",
column.AttributeTypeName.Value,
column.IsPrimaryName?.ToString() ?? "False",
column.IsSecured?.ToString() ?? "False",
column.CanBeSecuredForCreate?.ToString() ?? "False",
column.CanBeSecuredForUpdate.ToString() ?? "False",
column.CanBeSecuredForRead.ToString() ?? "False"
};
// Add values
csvContent.AppendLine(string.Join(",", values));
}
}
File.WriteAllText(
Path.Combine(filepath, filename),
csvContent.ToString());
}
Secure a column with code
It's easiest to Secure a column using Power Apps. If you need to automate securing a column, use code to update the column definition to set the AttributeMetadata.IsSecured property property as shown in the following examples:
This static SetColumnIsSecured method retrieves the current definition of the specified column and updates its security status only if the provided value differs from the current value. If the column is already set to the specified security status, no update request is sent.
/// <summary>
/// Updates the security status of a column in a Dataverse table.
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>This method retrieves the current definition of the specified column
/// and updates its security status only if the provided value differs from the
/// current value. If the column is already set to the specified security status,
/// no update request is sent.</remarks>
/// <param name="service">The <see cref="IOrganizationService"/> instance used to
/// interact with the Dataverse service.</param>
/// <param name="tableLogicalName">The logical name of the table containing the
/// column to be updated. Cannot be null or empty.</param>
/// <param name="columnLogicalName">The logical name of the column whose security
/// status is to be updated. Cannot be null or empty.</param>
/// <param name="value">A <see langword="true"/> value indicates that the column
/// should be secured; otherwise, <see langword="false"/>.</param>
/// <param name="solutionUniqueName">The unique name of the solution in which the
/// column update should be applied. Cannot be null or empty.</param>
/// <exception cref="Exception">Thrown if an error occurs while retrieving or
/// updating the column definition.</exception>
static internal void SetColumnIsSecured(
IOrganizationService service,
string tableLogicalName,
string columnLogicalName,
bool value,
string solutionUniqueName)
{
// Update request requires the entire column definition,
// So retrieving that first
RetrieveAttributeRequest retrieveRequest = new()
{
EntityLogicalName = tableLogicalName,
LogicalName = columnLogicalName
};
AttributeMetadata columnDefinition;
try
{
var retrieveResponse = (RetrieveAttributeResponse)service.Execute(retrieveRequest);
columnDefinition = retrieveResponse.AttributeMetadata;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw new Exception($"Error retrieving column definition: {ex.Message}", ex);
}
if (!columnDefinition.IsSecured.HasValue || columnDefinition.IsSecured.Value != value)
{
// Set the IsSecured property to value
columnDefinition.IsSecured = value;
UpdateAttributeRequest updateRequest = new()
{
EntityName = tableLogicalName,
Attribute = columnDefinition,
MergeLabels = true,
SolutionUniqueName = solutionUniqueName
};
try
{
service.Execute(updateRequest);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw new Exception($"Error updating column definition: {ex.Message}", ex);
}
}
else
{
//Don't send a request to set the value to what it already is.
}
}
Provide access to secured columns
By default, when a column is secured, only people who have the system administrator security role can read or set the value. A system administrator can provide other users access to secured columns in two ways:
- Manage access using field security profiles: Use field security profiles to give access to column data for all records to groups.
- Share data in secured fields: Use field sharing to give a specific principal or team access to data in a secure column for a specific record.
Manage access using field security profiles
This approach is the most common when you have different groups of users who require different levels of access. See the Column-level security example that describes how to secure fields for different users using the Power Platform admin center.
To do this using code, create Field Security Profile (FieldSecurityProfile) records that associate principals (users and teams) with Field Permission (FieldPermission) records that control which data operations can be performed on that column for any record.
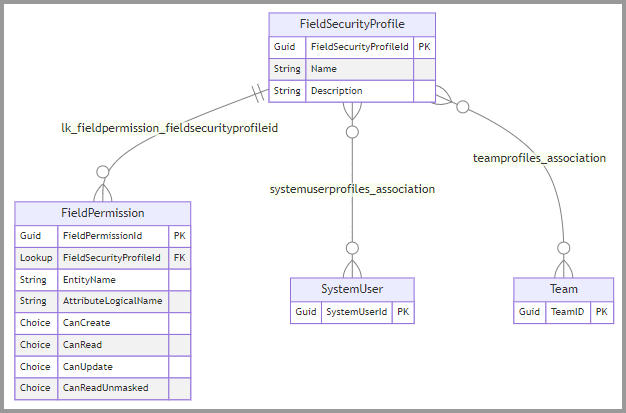
You can associate system users and teams to your field security profile using the systemuserprofiles_association and teamprofiles_association many-to-many relationships respectively.
Associate field permissions to the field security profiles using the lk_fieldpermission_fieldsecurityprofileid one-to-many relationship. The following table describes important field permission table columns:
| Column | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
FieldSecurityProfileId |
Lookup | Refers to the field security profile this field permission applies to. |
EntityName |
String | The logical name of the table that contains the secured column. |
AttributeLogicalName |
String | The logical name of the secured column. |
CanCreate |
Choice | Whether create access is allowed. See Field security permission type options |
CanRead |
Choice | Whether read access is allowed. See Field security permission type options |
CanUpdate |
Choice | Whether update access is allowed. See Field security permission type options |
CanReadUnmasked |
Choice | Whether an unmasked value can be retrieved when CanRead is Allowed. |
Field security permission type options
The CanCreate, CanRead, and CanUpdate choice columns use the values defined by the field_security_permission_type global choice:
0Not Allowed4Allowed
Note
Don't set CanReadUnmasked column unless you're using the display masked data feature and you want to enable an app to return the unmasked value.
Share data in secured fields
Create Field Sharing (PrincipalObjectAttributeAccess) records to share access to a secured field for a specific record with someone else.
Note
Conceptually, this process is similar to the PrincipalObjectAccess table that manages sharing of records. The difference is that with record sharing you use the GrantAccess, ModifyAccess, and RevokeAccess messages to add, modify, and remove records from the PrincipalObjectAccess table. Learn more about sharing records
With field sharing, use the PrincipalObjectAttributeAccess table to grant, modify, and revoke field access using create, update, and delete operations on a table row.
The PrincipalObjectAttributeAccess table has these columns:
| Column | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
AttributeId |
Guid | The AttributeMetadata.MetadataId of the secured column. |
ObjectId |
Lookup | A reference to the record that contains the secured column. |
PrincipalId |
Lookup | A reference to the principal (user or team) you're granting access to. |
ReadAccess |
Bool | Whether to grant read access to the field data |
UpdateAccess |
Bool | Whether to grant update access to the field data |
Getting column AttributeId
The PrincipalObjectAttributeAccess.AttributeId column uses the AttributeMetadata.MetadataId rather than the column logical name. You need to retrieve this value from the metadata. If your application has a metadata cache, you can include this data and access it as needed.
Retrieve column AttributeId example
This example shows how to get the AttributeMetadata.MetadataId value you need to set the PrincipalObjectAttributeAccess.AttributeId column value.
The Grant column access, Modify column access, and Revoke column access SDK for .NET examples use the RetrieveColumnId static method to retrieve the AttributeMetadata.MetadataId value used in the PrincipalObjectAttributeAccess.AttributeId column.
/// <summary>
/// Retrieves the unique identifier (MetadataId) of a column in a specified
/// Dataverse table.
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>
/// This method queries the organization's metadata to locate the specified column
/// within the given table and returns its MetadataId. If the table or column is
/// not found, an exception is thrown.
/// </remarks>
/// <param name="service">The <see cref="IOrganizationService"/> instance used to
/// retrieve metadata from the organization.</param>
/// <param name="tableLogicalName">The logical name of the table containing the
/// column. Must not be null or empty.</param>
/// <param name="columnLogicalName">The logical name of the column whose MetadataId
/// is to be retrieved. Must not be null or empty.</param>
/// <returns>The <see cref="Guid"/> representing the MetadataId of the specified
/// column.</returns>
/// <exception cref="Exception">Thrown if the table or column is not found in the
/// metadata.</exception>
private static Guid RetrieveColumnId(
IOrganizationService service,
string tableLogicalName,
string columnLogicalName)
{
EntityQueryExpression query = new()
{
Properties = new MetadataPropertiesExpression("Attributes"),
Criteria = new MetadataFilterExpression(filterOperator: LogicalOperator.Or)
{
Conditions = {
{
new MetadataConditionExpression(
propertyName:"LogicalName",
conditionOperator: MetadataConditionOperator.Equals,
value:tableLogicalName)
}
},
},
AttributeQuery = new AttributeQueryExpression
{
Properties = new MetadataPropertiesExpression("MetadataId"),
Criteria = new MetadataFilterExpression(filterOperator: LogicalOperator.And)
{
Conditions = {
{
new MetadataConditionExpression(
propertyName:"LogicalName",
conditionOperator: MetadataConditionOperator.Equals,
value:columnLogicalName)
}
}
}
}
};
RetrieveMetadataChangesRequest request = new()
{
Query = query
};
var response = (RetrieveMetadataChangesResponse)service.Execute(request);
Guid columnId;
if (response.EntityMetadata.Count == 1)
{
if (response.EntityMetadata[0].Attributes.Length == 1)
{
// Nullable property will not be null when retrieved. It is set by the system.
columnId = response.EntityMetadata[0].Attributes[0].MetadataId!.Value;
}
else
{
throw new Exception($"Column {columnLogicalName} not found in {tableLogicalName}.");
}
}
else
{
throw new Exception($"Table {tableLogicalName} not found");
}
return columnId;
}
Grant column access example
These examples create a new Field Sharing (PrincipalObjectAttributeAccess) record to share access to the specified field.
This method allows you to share read and/or update permissions for a secured column in a Dataverse table with a specific principal (user or team). The column must be configured as a secured field in Dataverse.
This example depends on the RetrieveColumnId example function found in Retrieve column AttributeId example.
/// <summary>
/// Grants access to a secured column for a specified principal in Dataverse.
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>This method allows you to share read and/or update permissions for a
/// secured column in a Dataverse table with a specific principal (user or team).
/// The column must be configured as a secured field in Dataverse.</remarks>
/// <param name="service">The <see cref="IOrganizationService"/> instance used to
/// interact with Dataverse.</param>
/// <param name="record">A reference to the record (entity instance) containing the
/// secured column.</param>
/// <param name="columnLogicalName">The logical name of the secured column to grant
/// access to.</param>
/// <param name="principal">A reference to the principal (user or team) to whom
/// access is being granted.</param>
/// <param name="readAccess"><see langword="true"/> to grant read access to the
/// secured column; otherwise, <see langword="false"/>.</param>
/// <param name="updateAccess"><see langword="true"/> to grant update access to the
/// secured column; otherwise, <see langword="false"/>.</param>
/// <exception cref="Exception">Thrown if the column has already been shared or if
/// an error occurs during the operation.</exception>
static internal void GrantColumnAccess(
IOrganizationService service,
EntityReference record,
string columnLogicalName,
EntityReference principal,
bool readAccess,
bool updateAccess)
{
// This information should come from cached metadata,
// but for this sample it is retrieved each time.
Guid columnId = RetrieveColumnId(
service: service,
tableLogicalName: record.LogicalName,
columnLogicalName: columnLogicalName);
// https://learn.microsoft.com/power-apps/developer/data-platform/reference/entities/principalobjectattributeaccess
Entity poaa = new("principalobjectattributeaccess")
{
//Unique identifier of the shared secured field
["attributeid"] = columnId,
//Unique identifier of the entity instance with shared secured field
["objectid"] = record,
//Unique identifier of the principal to which secured field is shared
["principalid"] = principal,
// Read permission for secured field instance
["readaccess"] = readAccess,
//Update permission for secured field instance
["updateaccess"] = updateAccess
};
try
{
service.Create(poaa);
}
catch (FaultException<OrganizationServiceFault> ex)
{
if (ex.Detail.ErrorCode.Equals(-2147158773))
{
throw new Exception("The column has already been shared");
}
throw new Exception($"Dataverse error in GrantColumnAccess: {ex.Message}");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw new Exception($"Error in GrantColumnAccess: {ex.Message}");
}
}
Modify column access example
These examples retrieve and update an existing Field Sharing (PrincipalObjectAttributeAccess) record to modify access to the specified field.
This example depends on the RetrieveColumnId example function found in Retrieve column AttributeId example.
/// <summary>
/// Modifies access permissions for a secure column in a table for a specified
/// principal.
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>This method updates or creates a record in the
/// PrincipalObjectAttributeAccess table to reflect the specified access
/// permissions. If no matching record is found, an exception is thrown.</remarks>
/// <param name="service">The <see cref="IOrganizationService"/> instance used to
/// interact with the organization service.</param>
/// <param name="record">An <see cref="EntityReference"/> representing the record
/// containing the secure column.</param>
/// <param name="columnLogicalName">The logical name of the secure column whose
/// access permissions are being modified.</param>
/// <param name="principal">An <see cref="EntityReference"/> representing the
/// principal (user or team) for whom access permissions are being
/// modified.</param>
/// <param name="readAccess">A <see langword="bool"/> indicating whether read
/// access to the secure column should be granted (<see langword="true"/>) or
/// revoked (<see langword="false"/>).</param>
/// <param name="updateAccess">A <see langword="bool"/> indicating whether update
/// access to the secure column should be granted (<see langword="true"/>) or
/// revoked (<see langword="false"/>).</param>
/// <exception cref="Exception">Thrown if no matching
/// PrincipalObjectAttributeAccess record is found for the specified column,
/// record, and principal.</exception>
static internal void ModifyColumnAccess(
IOrganizationService service,
EntityReference record,
string columnLogicalName,
EntityReference principal,
bool readAccess,
bool updateAccess)
{
// This information should come from cached metadata,
// but for this sample it is retrieved each time.
Guid columnId = RetrieveColumnId(
service: service,
tableLogicalName: record.LogicalName,
columnLogicalName: columnLogicalName);
// Retrieve the record
QueryExpression query = new("principalobjectattributeaccess")
{
ColumnSet = new ColumnSet(
"principalobjectattributeaccessid",
"readaccess",
"updateaccess"),
Criteria = new FilterExpression(LogicalOperator.And)
{
// There can only be one record or zero records matching these criteria.
Conditions = {
{
new ConditionExpression(
attributeName:"attributeid",
conditionOperator: ConditionOperator.Equal,
value:columnId)
},
{
new ConditionExpression(
attributeName:"objectid",
conditionOperator: ConditionOperator.Equal,
value:record.Id)
},
{
new ConditionExpression(
attributeName:"principalid",
conditionOperator: ConditionOperator.Equal,
value:principal.Id)
},
{
new ConditionExpression(
attributeName:"principalidtype",
conditionOperator: ConditionOperator.Equal,
value:principal.LogicalName)
}
}
}
};
EntityCollection queryResults = service.RetrieveMultiple(query);
if (queryResults.Entities.Count == 1)
{
// Update the record that granted access to the secure column
Entity retrievedPOAARecord = queryResults.Entities[0];
// Get the current values and only update if different
bool currentRead = retrievedPOAARecord.GetAttributeValue<bool>("readaccess");
bool currentUpdate = retrievedPOAARecord.GetAttributeValue<bool>("updateaccess");
Entity POAAForUpdate = new("principalobjectattributeaccess", retrievedPOAARecord.Id);
if (currentRead != readAccess)
{
POAAForUpdate.Attributes.Add("readaccess", readAccess);
}
if (currentUpdate != updateAccess)
{
POAAForUpdate.Attributes.Add("updateaccess", updateAccess);
}
// Don't update if nothing there is nothing to change
if (POAAForUpdate.Attributes.Count > 0)
{
// Update the principalobjectattributeaccess record
service.Update(POAAForUpdate);
}
}
else
{
throw new Exception("No matching PrincipalObjectAttributeAccess record found.");
}
}
Revoke column access example
These examples retrieve and delete an existing Field Sharing (PrincipalObjectAttributeAccess) record to revoke access to the specified field.
This example depends on the RetrieveColumnId example function found in Retrieve column AttributeId example.
/// <summary>
/// Revokes access to a secure column for a specified principal in a given record.
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>This method removes the access granted to a secure column for the
/// specified principal. If no matching access record is found, an exception is
/// thrown.</remarks>
/// <param name="service">The <see cref="IOrganizationService"/> instance used to
/// interact with the Dataverse service.</param>
/// <param name="record">An <see cref="EntityReference"/> representing the record
/// containing the secure column.</param>
/// <param name="columnLogicalName">The logical name of the secure column for which
/// access is being revoked.</param>
/// <param name="principal">An <see cref="EntityReference"/> representing the
/// principal (user or team) whose access to the secure column is being
/// revoked.</param>
/// <exception cref="Exception">Thrown if no matching
/// PrincipalObjectAttributeAccess record is found for the specified column,
/// record, and principal.</exception>
internal static void RevokeColumnAccess(IOrganizationService service,
EntityReference record,
string columnLogicalName,
EntityReference principal)
{
// This information should come from cached metadata,
// but for this sample it is retrieved each time.
Guid columnId = RetrieveColumnId(
service: service,
tableLogicalName: record.LogicalName,
columnLogicalName: columnLogicalName);
QueryExpression query = new("principalobjectattributeaccess")
{
ColumnSet = new ColumnSet("principalobjectattributeaccessid"),
Criteria = new FilterExpression(LogicalOperator.And)
{
// These conditions return one or zero records
Conditions = {
{
new ConditionExpression(
attributeName:"attributeid",
conditionOperator: ConditionOperator.Equal,
value:columnId)
},
{
new ConditionExpression(
attributeName:"objectid",
conditionOperator: ConditionOperator.Equal,
value:record.Id)
},
{
new ConditionExpression(
attributeName:"principalid",
conditionOperator: ConditionOperator.Equal,
value:principal.Id)
},
{
new ConditionExpression(
attributeName:"principalidtype",
conditionOperator: ConditionOperator.Equal,
value:principal.LogicalName)
}
}
}
};
EntityCollection queryResults = service.RetrieveMultiple(query);
if (queryResults.Entities.Count == 1)
{
// Delete the record that granted access to the secure column
service.Delete("principalobjectattributeaccess", queryResults.Entities[0].Id);
}
else
{
throw new Exception("No matching PrincipalObjectAttributeAccess record found.");
}
}
Display Masked data
The default API behavior when returning a value for a secured column is to return no data. The calling application can't distinguish between a value that is secured and a value that is null.
There's now a preview feature you can use to specify that a string value is returned when data exists. This string might totally obfuscate the value or show portions of the data depending on masking rules you define. In this way, the application can better manage sensitive data.
With this feature, you can configure Field Permission (FieldPermission) records to create field security profiles that enable applications to send requests to retrieve records with the masking removed so that the data can be shown under controlled circumstances. Learn more about retrieving unmasked data
Create a secure masking rule
Every column that displays masked data needs to refer to a Secured Masking Rule (MaskingRule) table row. You can create secure masking rules in Power Apps and add them to your solution, or you can use any of the existing rules.
Create Secured Masking Column (AttributeMaskingRule) table records to specify which masking rule a secure column should use.
The following diagram describes these tables:
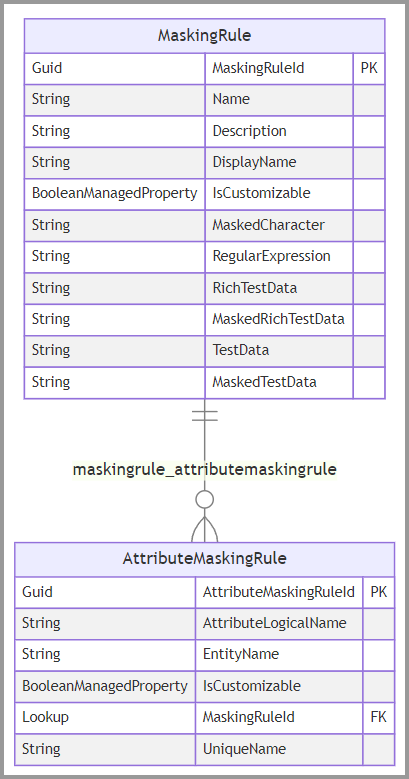
Secured Masking Rule columns
The Secured Masking Rule (MaskingRule) table has these write-able columns:
| Column | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Name |
String | The unique name of the secured masking rule. |
Description |
String | Description of the secured masking rule. |
DisplayName |
String | The display name of the secured masking rule. |
MaskedCharacter |
String | Character used to mask. |
RegularExpression |
String | Regular Expression in C#. |
IsCustomizable |
BooleanManagedProperty | Information that specifies whether this component can be customized. Learn more about managed properties |
RichTestData |
String | Set rich text test data to test this secured masking rule. |
MaskedRichTestData |
String | RichTestData column data evaluated by this secured masking rule. |
TestData |
String | Set test data to test this secured masking rule. |
MaskedTestData |
String | TestData column data evaluated by a secured masking rule. |
Note
The RichTestData, MaskedRichTestData, TestData, and MaskedTestData columns exist to support the experience to test masking rules in Power Apps. Learn more about creating masking rules.
Secured Masking Column columns
The Secured Masking Column (AttributeMaskingRule) table has these write-able columns:
| Column | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
AttributeLogicalName |
String | Logical name of the column for which the secured masking rule is used. |
EntityName |
String | Logical name of the table that contains the column. |
MaskingRuleId |
Lookup | The masking rule that the column uses |
UniqueName |
String | The unique name of the secured masking column. |
IsCustomizable |
BooleanManagedProperty | Information that specifies whether this component can be customized. Learn more about managed properties |
Retrieve unmasked data
When a Field Permission (FieldPermission) record CanRead column is Allowed, you can set the CanReadUnmasked choice column when the column has an Secured Masking Column (AttributeMaskingRule) record associated with it.
The CanReadUnmasked column supports the following options defined by the field_security_permission_readunmasked global choice.
| Value | Label | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Not Allowed | The default value. If there isn't an AttributeMaskingRule for the column, you can't set any other value. |
| 1 | One Record | Unmasked data can be returned using the a Retrieve operation only. |
| 3 | All Records | Unmasked data can be returned using the a Retrieve and RetrieveMultiple operations. |
Retrieve unmasked data example
The following examples show how to use the UnMaskedData optional parameter to request that the unmasked value is returned when the configuration of the field permission allows it.
The GetUnmaskedExampleRows example returns unmasked values for any of the requested columns where the field permission CanReadUnmasked column value is set to All Records because the optional UnMaskedData parameter is added to the RetrieveMultiple request.
This method queries the sample_example table and retrieves specific columns, including sensitive data such as government ID and date of birth. The query results are ordered by the sample_name column in descending order.
/// <summary>
/// Retrieves a collection of example entities with unmasked data.
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>This method queries the "sample_example" entity and retrieves specific
/// columns, including sensitive data such as government ID and date of birth. The
/// query results are ordered by the "sample_name" column in descending order. The
/// method uses the "UnMaskedData" optional parameter to ensure that sensitive data
/// is returned unmasked. For more information on optional parameters, see <see
/// href="https://learn.microsoft.com/power-apps/developer/data-platform/optional-parameters">Optional
/// Parameters in Dataverse</see>.</remarks>
/// <param name="service">The <see cref="IOrganizationService"/> instance used to
/// execute the query.</param>
/// <returns>An <see cref="EntityCollection"/> containing the retrieved entities.
/// The collection includes unmasked data for the specified columns.</returns>
internal static EntityCollection GetUnmaskedExampleRows(IOrganizationService service)
{
QueryExpression query = new("sample_example")
{
ColumnSet = new ColumnSet(
"sample_name",
"sample_email",
"sample_governmentid",
"sample_telephonenumber",
"sample_dateofbirth"),
Criteria = new FilterExpression(),
Orders = {
{
new OrderExpression(
"sample_name",
OrderType.Descending)
}
}
};
RetrieveMultipleRequest request = new()
{
Query = query,
// This example uses 'UnMaskedData' as an optional parameter
// https://learn.microsoft.com/power-apps/developer/data-platform/optional-parameters
["UnMaskedData"] = true
};
var response = (RetrieveMultipleResponse)service.Execute(request);
return response.EntityCollection;
}
Related articles
Security and data access
Sharing and assigning
Sample: Column-level security using Dataverse SDK for .NET
Sample: Column-level security using Dataverse Web API (PowerShell)