Tutorial: Deploy SQL Server Big Data Clusters in AD mode on Azure Kubernetes Services (AKS)
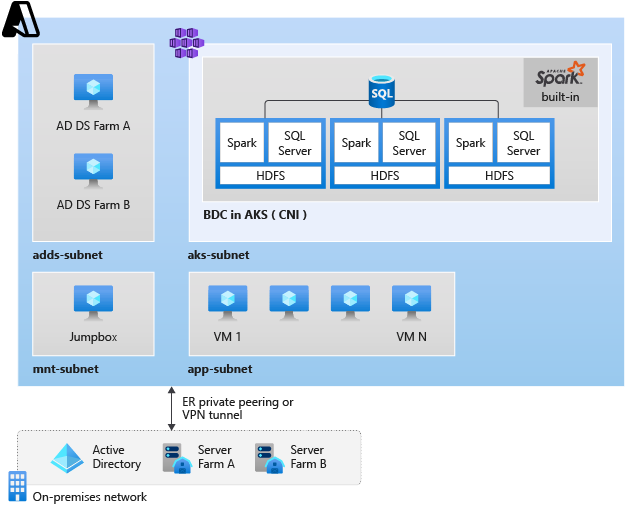
This article explains how to deploy a SQL Server big data cluster in the Active Directory authentication mode with a reference architecture. The reference architecture extends your on-premises Active Directory domain Service (AD DS) to Azure. You can deploy it from Azure Architecture Center with Azure building blocks.
Important
The Microsoft SQL Server 2019 Big Data Clusters add-on will be retired. Support for SQL Server 2019 Big Data Clusters will end on February 28, 2025. All existing users of SQL Server 2019 with Software Assurance will be fully supported on the platform and the software will continue to be maintained through SQL Server cumulative updates until that time. For more information, see the announcement blog post and Big data options on the Microsoft SQL Server platform.
Prerequisites
Before deploying a SQL Server big data cluster, you need to:
- Access an Azure VM for management. This VM requires access to the Azure Virtual Network (VNet) where you will deploy the big data cluster. It must either reside on the same VNet, or on peered VNet.
- Install the big data tools on the management VM.
- Prepare to deploy the cluster in the Active Directory authentication mode in your on-premises AD controller.
Create AKS subnet
Set environment variables
export REGION_NAME=< your Azure Region > export RESOURCE_GROUP=<your resource group > export SUBNET_NAME=aks-subnet export VNet_NAME= adds-vnet export AKS_NAME= <your aks cluster name>Create the AKS subnet
SUBNET_ID=$(az network vnet subnet show \ --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP \ --vnet-name $VNet_NAME \ --name $SUBNET_NAME \ --query id -o tsv)
The following screenshot shows how we plan the subnets resides in the VNet in the architecture.
Create an AKS private cluster
You can use the following command to deploy AKS private cluster. If you do not require a private cluster, remove --enable-private-cluster parameter in the command. For information about any other requirements, see how to deploy an Azure Kubernetes Cluster (AKS).
az aks create \
--resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP \
--name $AKS_NAME \
--load-balancer-sku standard \
--enable-private-cluster \
--network-plugin azure \
--vnet-subnet-id $SUBNET_ID \
--docker-bridge-address 172.17.0.1/16 \
--dns-service-ip 10.3.0.10 \
--service-cidr 10.3.0.0/24 \
--node-vm-size Standard_D13_v2 \
--node-count 2 \
--generate-ssh-keys
After deploying an AKS cluster, connect to the AKS cluster.
Verify reverse DNS entry for domain controller
Before starting the SQL Server Big Data Clusters deployment in AD mode in AKS cluster, verify that the domain controller itself has both A record and PTR record (reverse DNS entry), registered in the DNS server.
To verify this setting, run nslookup command or run the PowerShell script to confirm if you have reverse DNS entry (PTR record) configured.
Create big data cluster deployment profile
The following command creates a deployment profile:
azdata bdc config init --source kubeadm-prod --target bdc-ad-aks
The following commands are utilized to set parameters for a deployment profile.
control.json
azdata bdc config replace -p bdc-ad-aks/control.json -j "$.spec.storage.data.className=default"
azdata bdc config replace -p bdc-ad-aks/control.json -j "$.spec.storage.logs.className=default"
azdata bdc config replace -p bdc-ad-aks/control.json -j "$.spec.endpoints[0].serviceType=NodePort"
azdata bdc config replace -p bdc-ad-aks/control.json -j "$.spec.endpoints[1].serviceType=NodePort"
azdata bdc config replace -p bdc-ad-aks/control.json -j "$.spec.endpoints[0].dnsName=controller.contoso.com"
azdata bdc config replace -p bdc-ad-aks/control.json -j "$.spec.endpoints[1].dnsName=proxys.contoso.com"
# security settings
azdata bdc config replace -p bdc-ad-aks/control.json -j "$.security.activeDirectory.ouDistinguishedName=OU\=bdc\,DC\=contoso\,DC\=com"
azdata bdc config replace -p bdc-ad-aks/control.json -j "$.security.activeDirectory.dnsIpAddresses=[\"192.168.0.4\"]"
azdata bdc config replace -p bdc-ad-aks/control.json -j "$.security.activeDirectory.domainControllerFullyQualifiedDns=[\"ad1.contoso.com\"]"
azdata bdc config replace -p bdc-ad-aks/control.json -j "$.security.activeDirectory.domainDnsName=contoso.com"
azdata bdc config replace -p bdc-ad-aks/control.json -j "$.security.activeDirectory.clusterAdmins=[\"bdcadminsgroup\"]"
azdata bdc config replace -p bdc-ad-aks/control.json -j "$.security.activeDirectory.clusterUsers=[\"bdcusersgroup\"]"
bdc.json
azdata bdc config replace -p bdc-ad-aks/bdc.json -j "$.spec.resources.master.spec.endpoints[0].dnsName=master.contoso.com"
azdata bdc config replace -p bdc-ad-aks/bdc.json -j "$.spec.resources.master.spec.endpoints[0].serviceType=NodePort"
azdata bdc config replace -p bdc-ad-aks/bdc.json -j "$.spec.resources.master.spec.endpoints[1].dnsName=mastersec.contoso.com"
azdata bdc config replace -p bdc-ad-aks/bdc.json -j "$.spec.resources.master.spec.endpoints[1].serviceType=NodePort"
azdata bdc config replace -p bdc-ad-aks/bdc.json -j "$.spec.resources.gateway.spec.endpoints[0].dnsName=gateway.contoso.com"
azdata bdc config replace -p bdc-ad-aks/bdc.json -j "$.spec.resources.gateway.spec.endpoints[0].serviceType=NodePort"
azdata bdc config replace -p bdc-ad-aks/bdc.json -j "$.spec.resources.appproxy.spec.endpoints[0].dnsName=approxy.contoso.com"
azdata bdc config replace -p bdc-ad-aks/bdc.json -j "$.spec.resources.appproxy.spec.endpoints[0].serviceType=NodePort"
Initiate deployment
The following command initiates a big data cluster deployment:
azdata bdc create --config-profile bdc-ad-aks --accept-eula yes