Nuta
Dostęp do tej strony wymaga autoryzacji. Możesz spróbować się zalogować lub zmienić katalog.
Dostęp do tej strony wymaga autoryzacji. Możesz spróbować zmienić katalogi.
Rejestrowanie typu pliku jest pierwszym krokiem tworzenia skojarzenia pliku, co sprawia, że ten typ pliku jest "znany" w powłoce. Jednak bez procedur obsługi typów plików powłoka nie może uwidocznić informacji użytkownikowi z pliku i o tym pliku.
Ten temat jest zorganizowany w następujący sposób:
- utwórz typ pliku znany powłoki
- Opisy obsługi typów plików
- Tematy pokrewne
Tworzenie typu pliku znanego w powłoce
Na poniższym zrzucie ekranu Eksploratora Windows plik obrazu Desert.known pojawia się w bibliotece shell Pictures i jest skojarzony tylko z aplikacją Paint.
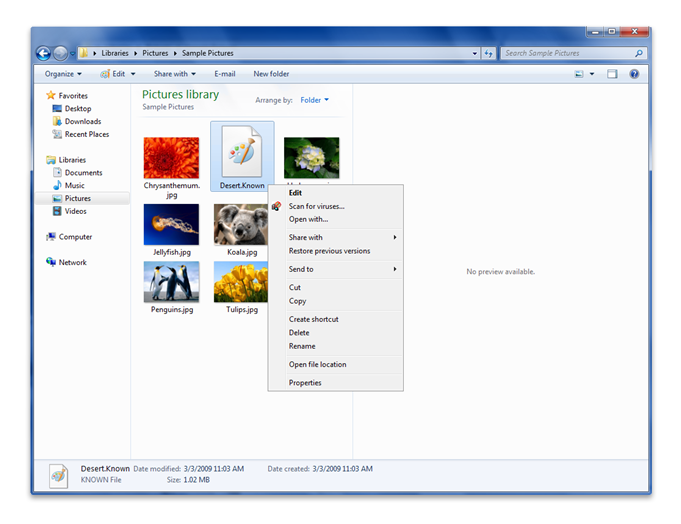
Plik Desert.known w poprzednim zrzucie ekranu nie ma następującej funkcjonalności, która jest włączona przez program obsługi typów plików:
- Miniatura lub podgląd
- Czasowniki specyficzne dla obrazu w menu skrótów, takie jak:
- Obracanie podglądu
- Ustaw jako tło pulpitu
- Drukować
- Właściwości specyficzne dla obrazu w okienku Szczegóły, takie jak:
- Data wykonania
- Tagi
- Ocena
- Indeksowanie tekstu pliku
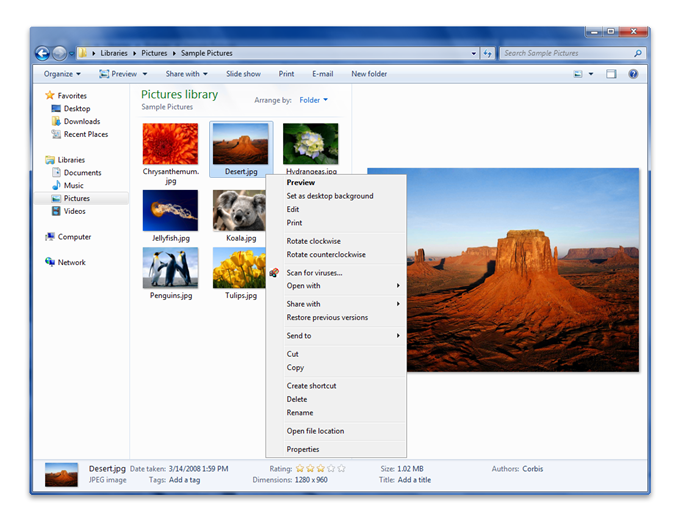
Na poniższym zrzucie ekranu ten sam plik (Desert.known) ma rozszerzenie .jpg, które jest zarejestrowanym typem pliku, który ma skojarzone programy obsługi typów plików, więc jest wyświetlany obraz miniatury i więcej właściwości.
Opisy procedury obsługi typów plików
Funkcjonalność zapewniana przez poszczególne procedury obsługi typów plików znajduje się w poniższej tabeli:
| Obsługi | Opis |
|---|---|
| menu skrótów | Procedura obsługi menu skrótów, czasami nazywana procedurą obsługi menu kontekstowego, jest procedurą obsługi typów plików, która dodaje polecenia do istniejącego menu kontekstowego. Te programy obsługi są skojarzone z określonym typem pliku i są wywoływane za każdym razem, gdy menu kontekstowe jest wyświetlane dla elementu członkowskiego typu pliku. |
| Miniatura | Procedura obsługi udostępniająca obraz reprezentujący element powłoki. |
| właściwości | Procedura obsługi właściwości, która zapewnia dostęp do właściwości elementu dla usługi Windows Search, Eksploratora Windows i innych aplikacji, które muszą uzyskiwać dostęp do właściwości. |
| (wersja zapoznawcza) | Procedura obsługi, która szybko tworzy uproszczony widok elementu tylko do odczytu, który ma być wyświetlany w okienku podglądu Eksploratora Windows. |
| filtry | Filtr, implementacja interfejsu IFilter, który skanuje dokumenty pod kątem tekstu i właściwości (nazywanych również atrybutami). Wyodrębnia fragmenty tekstu z tych dokumentów, filtrując osadzone formatowanie i zachowując informacje o położeniu tekstu. Wyodrębnia również fragmenty wartości, które są właściwościami całego dokumentu lub dobrze zdefiniowanymi częściami dokumentu. IFilter stanowi podstawę do tworzenia aplikacji wyższego poziomu, takich jak indeksatory dokumentów i osoby przeglądające niezależne od aplikacji. |
Tematy pokrewne