Nota
O acesso a esta página requer autorização. Pode tentar iniciar sessão ou alterar os diretórios.
O acesso a esta página requer autorização. Pode tentar alterar os diretórios.
A microservices architecture can bring many benefits. Managing the security of microservices, however, is a challenge and different than managing traditional monolithic applications security.
With a monolith, the application is typically running on one or more servers within a network and it's easier to identify the exposed ports and APIs and IP address. There is often one perimeter or boundary and one database to protect. If that system is compromised because of a security breach or attack, it is likely that everything within the system will be available to the attacker. With microservices, the system is more complex. Services are decentralized and distributed across many hosts and migrate from host to host. With proper security, you limit the privileges an attacker can get and the amount of data available in a single attack by breaching one service. Communication is not internal, but happens over a network, and there are many exposed ports and interactions between services. Knowing what these service interactions are and when they happen is crucial to your application security.
This article is not a guide to microservices security, there are many such resources available online, but describes how different aspects of security can be accomplished in Service Fabric.
Autenticação e autorização
It is often necessary for resources and APIs exposed by a service to be limited to certain trusted users or clients. Authentication is the process of reliably ascertaining a user’s identity. Authorization is the process that makes APIs or services available to some authenticated users but not others.
Autenticação
The first step to making API-level trust decisions is authentication. Authentication is the process of reliably ascertaining a user’s identity. Em cenários de microsserviços, a autenticação normalmente é tratada centralmente. If you are using an API Gateway, you can offload authentication to the gateway. If you use this approach, make sure that the individual services cannot be reached directly (without the API Gateway) unless additional security is in place to authenticate messages whether they come from the gateway or not.
Se os serviços puderem ser acessados diretamente, um serviço de autenticação como o Microsoft Entra ID ou um microsserviço de autenticação dedicado atuando como um serviço de token de segurança (STS) poderá ser usado para autenticar usuários. As decisões de confiança são partilhadas entre serviços com tokens de segurança ou cookies.
For ASP.NET Core, the primary mechanism for authenticating users is the ASP.NET Core Identity membership system. ASP.NET Core Identity stores user information (including sign-in information, roles, and claims) in a data store configured by the developer. ASP.NET Core Identity supports two-factor authentication. External authentication providers are also supported, so users can sign in using existing authentication processes from providers like Microsoft, Google, Facebook, or X.
Autorização
After authentication, services need to authorize user access or determine what a user is able to do. This process allows a service to make APIs available to some authenticated users, but not to all. Authorization is orthogonal and independent from authentication, which is the process of ascertaining who a user is. Authentication may create one or more identities for the current user.
ASP.NET Core authorization can be done based on users’ roles or based on custom policy, which might include inspecting claims or other heuristics.
Restrict and secure access using an API gateway
Geralmente, as aplicações da cloud precisam de um gateway de front-end que forneça um único ponto de entrada para utilizadores, dispositivos ou outras aplicações. An API gateway sits between clients and services and is the entry point to all the services that your application is providing. Ele atua como um proxy reverso, roteando solicitações de clientes para serviços. It may also perform various cross-cutting tasks such as authentication and authorization, TLS termination, and rate limiting. If you don't deploy a gateway, clients must send requests directly to front-end services.
In Service Fabric, a gateway can be any stateless service such as an ASP.NET Core application, or another service designed for traffic ingress, such as Traefik, Event Hubs, IoT Hub, or Azure API Management.
API Management integrates directly with Service Fabric, allowing you to publish APIs with a rich set of routing rules to your back-end Service Fabric services. You can secure access to backend services, prevent DOS attacks by using throttling, or verify API keys, JWT tokens, certificates, and other credentials. To learn more, read Service Fabric with Azure API Management overview.
Manage application secrets
Os segredos podem ser qualquer informação confidencial, como cadeias de conexão de armazenamento, senhas ou outros valores que não devem ser manipulados em texto sem formatação. This article uses Azure Key Vault to manage keys and secrets. No entanto, o uso de segredos em um aplicativo é independente da plataforma de nuvem para permitir que os aplicativos sejam implantados em um cluster hospedado em qualquer lugar.
A maneira recomendada de gerir definições de configuração de serviço é através de pacotes de configuração de serviço. Os pacotes de configuração são versionados e atualizáveis por meio de atualizações contínuas gerenciadas com validação de integridade e reversão automática. Isso é preferível à configuração global, pois reduz as chances de uma interrupção global do serviço. Os segredos encriptados não são exceção. O Service Fabric possui recursos internos destinados a criptografar e descriptografar valores em um arquivo de configuração Settings.xml usando criptografia de certificado.
O diagrama a seguir ilustra o fluxo básico para o gerenciamento de segredos em um aplicativo do Service Fabric:
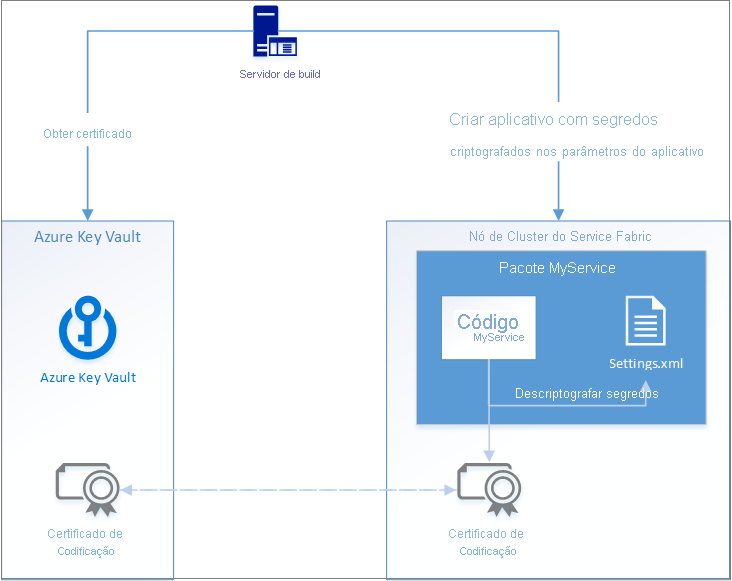
Há quatro etapas principais nesse fluxo:
- Obtenha um certificado de codificação de dados.
- Install the certificate in your cluster.
- Criptografe valores secretos ao implantar um aplicativo com o certificado e injete-os no arquivo de configuração Settings.xml de um serviço.
- Leia valores encriptados a partir de Settings.xml, desencriptando-os com o mesmo certificado de encriptação.
O Azure Key Vault é usado aqui como um local de armazenamento seguro para certificados e como uma maneira de obter certificados instalados em clusters do Service Fabric no Azure. Se você não estiver implantando no Azure, não precisará usar o Cofre da Chave para gerenciar segredos em aplicativos do Service Fabric.
For an example, see Manage application secrets.
Secure the hosting environment
By using Azure Service Fabric, you can secure applications that are running in the cluster under different user accounts. Service Fabric also helps secure the resources that are used by applications at the time of deployment under the user accounts--for example, files, directories, and certificates. This makes running applications, even in a shared hosted environment, more secure from one another.
The application manifest declares the security principals (users and groups) required run the service(s) and secure resources. These security principals are referenced in policies, for example the run-as, endpoint binding, package sharing, or security access policies. Policies are then applied to service resources in the ServiceManifestImport section of the application manifest.
When declaring principals, you can also define and create user groups so that one or more users can be added to each group to be managed together. This is useful when there are multiple users for different service entry points and they need to have certain common privileges that are available at the group level.
By default, Service Fabric applications run under the account that the Fabric.exe process runs under. Service Fabric also provides the capability to run applications under a local user account or local system account, which is specified within the application manifest. For more information, see Run a service as a local user account or local system account. You can also Run a service startup script as a local user or system account.
When you're running Service Fabric on a Windows standalone cluster, you can run a service under Active Directory domain accounts or group managed service accounts.
Contentores seguros
O Service Fabric fornece um mecanismo para que os serviços dentro de um contêiner acessem um certificado instalado nos nós em um cluster Windows ou Linux (versão 5.7 ou superior). Este certificado PFX pode ser usado para autenticar o aplicativo ou serviço ou comunicação segura com outros serviços. For more information, see Import a certificate into a container.
In addition, Service Fabric also supports gMSA (group Managed Service Accounts) for Windows containers. For more information, see Set up gMSA for Windows containers.
Secure service communication
In Service Fabric, a service runs somewhere in a Service Fabric cluster, typically distributed across multiple VMs. Service Fabric provides several options for securing your service communications.
You can enable HTTPS endpoints in your ASP.NET Core or Java web services.
You can establish secure connection between the reverse proxy and services, thus enabling an end to end secure channel. Connecting to secure services is supported only when reverse proxy is configured to listen on HTTPS. For information on configuring the reverse proxy, read Reverse proxy in Azure Service Fabric. Connect to a secure service describes how to establish secure connection between the reverse proxy and services.
The Reliable Services application framework provides a few prebuilt communication stacks and tools that you can use to improve security. Learn how to improve security when you're using service remoting (in C# or Java) or using WCF.
Include endpoint certificate in Service Fabric applications
To configure your application endpoint certificate, include the certificate by adding a EndpointCertificate element along with the User element for the principal account to the application manifest. By default the principal account is NetworkService. This will provide management of the application certificate private key ACL for the provided principal.
<ApplicationManifest … >
...
<Principals>
<Users>
<User Name="Service1" AccountType="NetworkService" />
</Users>
</Principals>
<Certificates>
<EndpointCertificate Name="MyCert" X509FindType="FindByThumbprint" X509FindValue="[YourCertThumbprint]"/>
</Certificates>
</ApplicationManifest>
Encrypt application data at rest
Each node type in a Service Fabric cluster running in Azure is backed by a virtual machine scale set. Using an Azure Resource Manager template, you can attach data disks to the scale set(s) that make up the Service Fabric cluster. If your services save data to an attached data disk, you can encrypt those data disks to protect your application data.