Nota
O acesso a esta página requer autorização. Podes tentar iniciar sessão ou mudar de diretório.
O acesso a esta página requer autorização. Podes tentar mudar de diretório.
Este artigo demonstra como criar uma rede de blocos de fluxo de dados que realizam processamento de imagens numa aplicação Windows Forms.
Este exemplo carrega ficheiros de imagem a partir da pasta especificada, cria uma imagem composta e mostra o resultado. O exemplo utiliza o modelo de fluxo de dados para encaminhar imagens através da rede. No modelo de fluxo de dados, componentes independentes de um programa se comunicam entre si enviando mensagens. Quando um componente recebe uma mensagem, executa alguma ação e depois passa o resultado a outro componente. Compare isto com o modelo de fluxo de controlo, em que uma aplicação utiliza estruturas de controlo, por exemplo, instruções condicionais, ciclos, e assim por diante, para controlar a ordem das operações num programa.
Pré-requisitos
Leia Dataflow antes de começar este tutorial.
Observação
A biblioteca TPL dataflow (o System.Threading.Tasks.Dataflow namespace) está incluída no .NET 6 e versões posteriores. Para projetos .NET Framework e .NET Standard, é necessário instalar o 📦 pacote NuGet System.Threading.Tasks.Dataflow.
Secções
Este passo a passo contém as seguintes seções:
Criação da Aplicação Windows Forms
Esta secção descreve como criar a aplicação básica do Windows Forms e adicionar controlos ao formulário principal.
Para criar a aplicação Windows Forms
No Visual Studio, crie um projeto de aplicação Visual C# ou Visual Basic Windows Forms . Neste documento, o projeto é nomeado
CompositeImages.No designer do formulário principal, Form1.cs (Form1.vb para Visual Basic), adicione um controlo ToolStrip.
Adiciona um ToolStripButton controle ao ToolStrip controle. Defina a DisplayStyle propriedade como Text e a Text propriedade para Escolher Pasta.
Adicionar um segundo ToolStripButton ao controlador ToolStrip. Defina a DisplayStyle propriedade para Text, a Text propriedade para Cancelar, e a Enabled propriedade para
False.Adicione um PictureBox objeto ao formulário principal. Defina a propriedade Dock como Fill.
Criação da Rede de Fluxo de Dados
Esta secção descreve como criar a rede de fluxo de dados que realiza o processamento de imagens.
Para criar a Rede de Fluxo de Dados
Adicione uma referência a System.Threading.Tasks.Dataflow.dll ao seu projeto.
Certifique-se de que Form1.cs (Form1.vb para Visual Basic) contém as seguintes
usinginstruções (Usingem Visual Basic):using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Drawing; using System.Drawing.Imaging; using System.IO; using System.Linq; using System.Threading; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Threading.Tasks.Dataflow; using System.Windows.Forms;Adicione os seguintes membros de dados à
Form1classe:// The head of the dataflow network. ITargetBlock<string> headBlock = null; // Enables the user interface to signal cancellation to the network. CancellationTokenSource cancellationTokenSource;Adicione o seguinte método,
CreateImageProcessingNetwork, àForm1classe. Este método cria a rede de processamento de imagem.// Creates the image processing dataflow network and returns the // head node of the network. ITargetBlock<string> CreateImageProcessingNetwork() { // // Create the dataflow blocks that form the network. // // Create a dataflow block that takes a folder path as input // and returns a collection of Bitmap objects. var loadBitmaps = new TransformBlock<string, IEnumerable<Bitmap>>(path => { try { return LoadBitmaps(path); } catch (OperationCanceledException) { // Handle cancellation by passing the empty collection // to the next stage of the network. return Enumerable.Empty<Bitmap>(); } }); // Create a dataflow block that takes a collection of Bitmap objects // and returns a single composite bitmap. var createCompositeBitmap = new TransformBlock<IEnumerable<Bitmap>, Bitmap>(bitmaps => { try { return CreateCompositeBitmap(bitmaps); } catch (OperationCanceledException) { // Handle cancellation by passing null to the next stage // of the network. return null; } }); // Create a dataflow block that displays the provided bitmap on the form. var displayCompositeBitmap = new ActionBlock<Bitmap>(bitmap => { // Display the bitmap. pictureBox1.SizeMode = PictureBoxSizeMode.StretchImage; pictureBox1.Image = bitmap; // Enable the user to select another folder. toolStripButton1.Enabled = true; toolStripButton2.Enabled = false; Cursor = DefaultCursor; }, // Specify a task scheduler from the current synchronization context // so that the action runs on the UI thread. new ExecutionDataflowBlockOptions { TaskScheduler = TaskScheduler.FromCurrentSynchronizationContext() }); // Create a dataflow block that responds to a cancellation request by // displaying an image to indicate that the operation is cancelled and // enables the user to select another folder. var operationCancelled = new ActionBlock<object>(delegate { // Display the error image to indicate that the operation // was cancelled. pictureBox1.SizeMode = PictureBoxSizeMode.CenterImage; pictureBox1.Image = pictureBox1.ErrorImage; // Enable the user to select another folder. toolStripButton1.Enabled = true; toolStripButton2.Enabled = false; Cursor = DefaultCursor; }, // Specify a task scheduler from the current synchronization context // so that the action runs on the UI thread. new ExecutionDataflowBlockOptions { TaskScheduler = TaskScheduler.FromCurrentSynchronizationContext() }); // // Connect the network. // // Link loadBitmaps to createCompositeBitmap. // The provided predicate ensures that createCompositeBitmap accepts the // collection of bitmaps only if that collection has at least one member. loadBitmaps.LinkTo(createCompositeBitmap, bitmaps => bitmaps.Count() > 0); // Also link loadBitmaps to operationCancelled. // When createCompositeBitmap rejects the message, loadBitmaps // offers the message to operationCancelled. // operationCancelled accepts all messages because we do not provide a // predicate. loadBitmaps.LinkTo(operationCancelled); // Link createCompositeBitmap to displayCompositeBitmap. // The provided predicate ensures that displayCompositeBitmap accepts the // bitmap only if it is non-null. createCompositeBitmap.LinkTo(displayCompositeBitmap, bitmap => bitmap != null); // Also link createCompositeBitmap to operationCancelled. // When displayCompositeBitmap rejects the message, createCompositeBitmap // offers the message to operationCancelled. // operationCancelled accepts all messages because we do not provide a // predicate. createCompositeBitmap.LinkTo(operationCancelled); // Return the head of the network. return loadBitmaps; }Implemente o método
LoadBitmaps.// Loads all bitmap files that exist at the provided path. IEnumerable<Bitmap> LoadBitmaps(string path) { List<Bitmap> bitmaps = new List<Bitmap>(); // Load a variety of image types. foreach (string bitmapType in new string[] { "*.bmp", "*.gif", "*.jpg", "*.png", "*.tif" }) { // Load each bitmap for the current extension. foreach (string fileName in Directory.GetFiles(path, bitmapType)) { // Throw OperationCanceledException if cancellation is requested. cancellationTokenSource.Token.ThrowIfCancellationRequested(); try { // Add the Bitmap object to the collection. bitmaps.Add(new Bitmap(fileName)); } catch (Exception) { // TODO: A complete application might handle the error. } } } return bitmaps; }Implemente o método
CreateCompositeBitmap.// Creates a composite bitmap from the provided collection of Bitmap objects. // This method computes the average color of each pixel among all bitmaps // to create the composite image. Bitmap CreateCompositeBitmap(IEnumerable<Bitmap> bitmaps) { Bitmap[] bitmapArray = bitmaps.ToArray(); // Compute the maximum width and height components of all // bitmaps in the collection. Rectangle largest = new Rectangle(); foreach (var bitmap in bitmapArray) { if (bitmap.Width > largest.Width) largest.Width = bitmap.Width; if (bitmap.Height > largest.Height) largest.Height = bitmap.Height; } // Create a 32-bit Bitmap object with the greatest dimensions. Bitmap result = new Bitmap(largest.Width, largest.Height, PixelFormat.Format32bppArgb); // Lock the result Bitmap. var resultBitmapData = result.LockBits( new Rectangle(new Point(), result.Size), ImageLockMode.WriteOnly, result.PixelFormat); // Lock each source bitmap to create a parallel list of BitmapData objects. var bitmapDataList = (from bitmap in bitmapArray select bitmap.LockBits( new Rectangle(new Point(), bitmap.Size), ImageLockMode.ReadOnly, PixelFormat.Format32bppArgb)) .ToList(); // Compute each column in parallel. Parallel.For(0, largest.Width, new ParallelOptions { CancellationToken = cancellationTokenSource.Token }, i => { // Compute each row. for (int j = 0; j < largest.Height; j++) { // Counts the number of bitmaps whose dimensions // contain the current location. int count = 0; // The sum of all alpha, red, green, and blue components. int a = 0, r = 0, g = 0, b = 0; // For each bitmap, compute the sum of all color components. foreach (var bitmapData in bitmapDataList) { // Ensure that we stay within the bounds of the image. if (bitmapData.Width > i && bitmapData.Height > j) { unsafe { byte* row = (byte*)(bitmapData.Scan0 + (j * bitmapData.Stride)); byte* pix = (byte*)(row + (4 * i)); a += *pix; pix++; r += *pix; pix++; g += *pix; pix++; b += *pix; } count++; } } //prevent divide by zero in bottom right pixelless corner if (count == 0) break; unsafe { // Compute the average of each color component. a /= count; r /= count; g /= count; b /= count; // Set the result pixel. byte* row = (byte*)(resultBitmapData.Scan0 + (j * resultBitmapData.Stride)); byte* pix = (byte*)(row + (4 * i)); *pix = (byte)a; pix++; *pix = (byte)r; pix++; *pix = (byte)g; pix++; *pix = (byte)b; } } }); // Unlock the source bitmaps. for (int i = 0; i < bitmapArray.Length; i++) { bitmapArray[i].UnlockBits(bitmapDataList[i]); } // Unlock the result bitmap. result.UnlockBits(resultBitmapData); // Return the result. return result; }Observação
A versão C# do
CreateCompositeBitmapmétodo utiliza ponteiros para permitir um processamento eficiente dos System.Drawing.Bitmap objetos. Por isso, deve ativar a opção Permitir código inseguro no seu projeto para usar a palavra-chave insegura . Para mais informações sobre como ativar código inseguro num projeto Visual C#, consulte Página de Construção, Project Designer (C#).
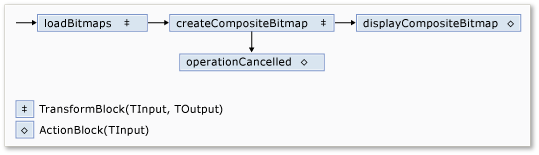
A tabela a seguir descreve os membros da rede.
| Membro | Tipo | Description |
|---|---|---|
loadBitmaps |
TransformBlock<TInput,TOutput> | Toma um caminho de pasta como entrada e produz uma coleção de Bitmap objetos como saída. |
createCompositeBitmap |
TransformBlock<TInput,TOutput> | Recebe uma coleção de Bitmap objetos como entrada e produz um bitmap composto como saída. |
displayCompositeBitmap |
ActionBlock<TInput> | Mostra o bitmap composto no formulário. |
operationCancelled |
ActionBlock<TInput> | Mostra uma imagem para indicar que a operação foi cancelada e permite ao utilizador selecionar outra pasta. |
Para ligar os blocos de fluxo de dados para formar uma rede, este exemplo utiliza o LinkTo método. O LinkTo método contém uma versão sobrecarregada que recebe um Predicate<T> objeto que determina se o bloco alvo aceita ou rejeita uma mensagem. Este mecanismo de filtragem permite que blocos de mensagens recebam apenas certos valores. Neste exemplo, a rede pode ramificar-se de duas formas. O ramo principal carrega as imagens a partir do disco, cria a imagem composta e exibe essa imagem no formulário. O ramal alternativo cancela a operação atual. Os Predicate<T> objetos permitem que os blocos de fluxo de dados ao longo do ramo principal mudem para o ramo alternativo ao rejeitar certas mensagens. Por exemplo, se o utilizador cancelar a operação, o bloco createCompositeBitmap de fluxo de dados produz null (Nothing no Visual Basic ) como sua saída. O bloco de fluxo de dados displayCompositeBitmap rejeita valores de entrada null, e, por isso, a mensagem é oferecida a operationCancelled. O bloco operationCancelled de fluxo de dados aceita todas as mensagens e, por isso, apresenta uma imagem que indica que a operação foi cancelada.
A ilustração a seguir mostra a rede de processamento de imagem:
Como os blocos displayCompositeBitmap e operationCancelled dataflow atuam na interface do utilizador, é importante que estas ações ocorram no thread da interface do utilizador. Para conseguir isto, durante a construção, cada um destes objetos fornece um objeto ExecutionDataflowBlockOptions que tem a propriedade TaskScheduler definida como TaskScheduler.FromCurrentSynchronizationContext. O TaskScheduler.FromCurrentSynchronizationContext método cria um TaskScheduler objeto que realiza trabalho no contexto de sincronização atual. Como o método CreateImageProcessingNetwork é chamado a partir do manipulador do botão Escolher Pasta, que corre na thread da interface de utilizador, as ações dos blocos de fluxo de dados displayCompositeBitmap e operationCancelled também correm na thread da interface de utilizador.
Este exemplo utiliza um token de cancelamento partilhado em vez de definir a CancellationToken propriedade porque a CancellationToken propriedade cancela permanentemente a execução do bloco dataflow. Um token de cancelamento permite que este exemplo reutilize a mesma rede de fluxo de dados várias vezes, mesmo quando o utilizador cancela uma ou mais operações. Para um exemplo que é usado CancellationToken para cancelar permanentemente a execução de um bloco de fluxo de dados, veja Como: Cancelar um Bloco de Fluxo de Dados.
Ligação da Rede de Fluxo de Dados à Interface do Utilizador
Esta secção descreve como ligar a rede de fluxo de dados à interface do utilizador. A criação da imagem composta e o cancelamento da operação são iniciados a partir dos botões Escolher Pasta e Cancelar . Quando o utilizador escolhe qualquer um destes botões, a ação apropriada é iniciada de forma assíncrona.
Para ligar a rede de fluxo de dados à interface do utilizador
No designer do formulário principal, crie um gestor de eventos para o evento Click do botão Escolher Pasta.
Implemente o evento Click para o botão Escolher Pasta.
// Event handler for the Choose Folder button. private void toolStripButton1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { // Create a FolderBrowserDialog object to enable the user to // select a folder. FolderBrowserDialog dlg = new FolderBrowserDialog { ShowNewFolderButton = false }; // Set the selected path to the common Sample Pictures folder // if it exists. string initialDirectory = Path.Combine( Environment.GetFolderPath(Environment.SpecialFolder.CommonPictures), "Sample Pictures"); if (Directory.Exists(initialDirectory)) { dlg.SelectedPath = initialDirectory; } // Show the dialog and process the dataflow network. if (dlg.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK) { // Create a new CancellationTokenSource object to enable // cancellation. cancellationTokenSource = new CancellationTokenSource(); // Create the image processing network if needed. headBlock ??= CreateImageProcessingNetwork(); // Post the selected path to the network. headBlock.Post(dlg.SelectedPath); // Enable the Cancel button and disable the Choose Folder button. toolStripButton1.Enabled = false; toolStripButton2.Enabled = true; // Show a wait cursor. Cursor = Cursors.WaitCursor; } }No designer do formulário principal, crie um gestor de eventos para o Click evento com o botão Cancelar .
Implementa o Click evento para o botão Cancelar .
// Event handler for the Cancel button. private void toolStripButton2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { // Signal the request for cancellation. The current component of // the dataflow network will respond to the cancellation request. cancellationTokenSource.Cancel(); }
O exemplo completo
O exemplo seguinte mostra o código completo deste procedimento.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Drawing.Imaging;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading.Tasks.Dataflow;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace CompositeImages
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
// The head of the dataflow network.
ITargetBlock<string> headBlock = null;
// Enables the user interface to signal cancellation to the network.
CancellationTokenSource cancellationTokenSource;
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
// Creates the image processing dataflow network and returns the
// head node of the network.
ITargetBlock<string> CreateImageProcessingNetwork()
{
//
// Create the dataflow blocks that form the network.
//
// Create a dataflow block that takes a folder path as input
// and returns a collection of Bitmap objects.
var loadBitmaps = new TransformBlock<string, IEnumerable<Bitmap>>(path =>
{
try
{
return LoadBitmaps(path);
}
catch (OperationCanceledException)
{
// Handle cancellation by passing the empty collection
// to the next stage of the network.
return Enumerable.Empty<Bitmap>();
}
});
// Create a dataflow block that takes a collection of Bitmap objects
// and returns a single composite bitmap.
var createCompositeBitmap = new TransformBlock<IEnumerable<Bitmap>, Bitmap>(bitmaps =>
{
try
{
return CreateCompositeBitmap(bitmaps);
}
catch (OperationCanceledException)
{
// Handle cancellation by passing null to the next stage
// of the network.
return null;
}
});
// Create a dataflow block that displays the provided bitmap on the form.
var displayCompositeBitmap = new ActionBlock<Bitmap>(bitmap =>
{
// Display the bitmap.
pictureBox1.SizeMode = PictureBoxSizeMode.StretchImage;
pictureBox1.Image = bitmap;
// Enable the user to select another folder.
toolStripButton1.Enabled = true;
toolStripButton2.Enabled = false;
Cursor = DefaultCursor;
},
// Specify a task scheduler from the current synchronization context
// so that the action runs on the UI thread.
new ExecutionDataflowBlockOptions
{
TaskScheduler = TaskScheduler.FromCurrentSynchronizationContext()
});
// Create a dataflow block that responds to a cancellation request by
// displaying an image to indicate that the operation is cancelled and
// enables the user to select another folder.
var operationCancelled = new ActionBlock<object>(delegate
{
// Display the error image to indicate that the operation
// was cancelled.
pictureBox1.SizeMode = PictureBoxSizeMode.CenterImage;
pictureBox1.Image = pictureBox1.ErrorImage;
// Enable the user to select another folder.
toolStripButton1.Enabled = true;
toolStripButton2.Enabled = false;
Cursor = DefaultCursor;
},
// Specify a task scheduler from the current synchronization context
// so that the action runs on the UI thread.
new ExecutionDataflowBlockOptions
{
TaskScheduler = TaskScheduler.FromCurrentSynchronizationContext()
});
//
// Connect the network.
//
// Link loadBitmaps to createCompositeBitmap.
// The provided predicate ensures that createCompositeBitmap accepts the
// collection of bitmaps only if that collection has at least one member.
loadBitmaps.LinkTo(createCompositeBitmap, bitmaps => bitmaps.Count() > 0);
// Also link loadBitmaps to operationCancelled.
// When createCompositeBitmap rejects the message, loadBitmaps
// offers the message to operationCancelled.
// operationCancelled accepts all messages because we do not provide a
// predicate.
loadBitmaps.LinkTo(operationCancelled);
// Link createCompositeBitmap to displayCompositeBitmap.
// The provided predicate ensures that displayCompositeBitmap accepts the
// bitmap only if it is non-null.
createCompositeBitmap.LinkTo(displayCompositeBitmap, bitmap => bitmap != null);
// Also link createCompositeBitmap to operationCancelled.
// When displayCompositeBitmap rejects the message, createCompositeBitmap
// offers the message to operationCancelled.
// operationCancelled accepts all messages because we do not provide a
// predicate.
createCompositeBitmap.LinkTo(operationCancelled);
// Return the head of the network.
return loadBitmaps;
}
// Loads all bitmap files that exist at the provided path.
IEnumerable<Bitmap> LoadBitmaps(string path)
{
List<Bitmap> bitmaps = new List<Bitmap>();
// Load a variety of image types.
foreach (string bitmapType in
new string[] { "*.bmp", "*.gif", "*.jpg", "*.png", "*.tif" })
{
// Load each bitmap for the current extension.
foreach (string fileName in Directory.GetFiles(path, bitmapType))
{
// Throw OperationCanceledException if cancellation is requested.
cancellationTokenSource.Token.ThrowIfCancellationRequested();
try
{
// Add the Bitmap object to the collection.
bitmaps.Add(new Bitmap(fileName));
}
catch (Exception)
{
// TODO: A complete application might handle the error.
}
}
}
return bitmaps;
}
// Creates a composite bitmap from the provided collection of Bitmap objects.
// This method computes the average color of each pixel among all bitmaps
// to create the composite image.
Bitmap CreateCompositeBitmap(IEnumerable<Bitmap> bitmaps)
{
Bitmap[] bitmapArray = bitmaps.ToArray();
// Compute the maximum width and height components of all
// bitmaps in the collection.
Rectangle largest = new Rectangle();
foreach (var bitmap in bitmapArray)
{
if (bitmap.Width > largest.Width)
largest.Width = bitmap.Width;
if (bitmap.Height > largest.Height)
largest.Height = bitmap.Height;
}
// Create a 32-bit Bitmap object with the greatest dimensions.
Bitmap result = new Bitmap(largest.Width, largest.Height,
PixelFormat.Format32bppArgb);
// Lock the result Bitmap.
var resultBitmapData = result.LockBits(
new Rectangle(new Point(), result.Size), ImageLockMode.WriteOnly,
result.PixelFormat);
// Lock each source bitmap to create a parallel list of BitmapData objects.
var bitmapDataList = (from bitmap in bitmapArray
select bitmap.LockBits(
new Rectangle(new Point(), bitmap.Size),
ImageLockMode.ReadOnly, PixelFormat.Format32bppArgb))
.ToList();
// Compute each column in parallel.
Parallel.For(0, largest.Width, new ParallelOptions
{
CancellationToken = cancellationTokenSource.Token
},
i =>
{
// Compute each row.
for (int j = 0; j < largest.Height; j++)
{
// Counts the number of bitmaps whose dimensions
// contain the current location.
int count = 0;
// The sum of all alpha, red, green, and blue components.
int a = 0, r = 0, g = 0, b = 0;
// For each bitmap, compute the sum of all color components.
foreach (var bitmapData in bitmapDataList)
{
// Ensure that we stay within the bounds of the image.
if (bitmapData.Width > i && bitmapData.Height > j)
{
unsafe
{
byte* row = (byte*)(bitmapData.Scan0 + (j * bitmapData.Stride));
byte* pix = (byte*)(row + (4 * i));
a += *pix; pix++;
r += *pix; pix++;
g += *pix; pix++;
b += *pix;
}
count++;
}
}
//prevent divide by zero in bottom right pixelless corner
if (count == 0)
break;
unsafe
{
// Compute the average of each color component.
a /= count;
r /= count;
g /= count;
b /= count;
// Set the result pixel.
byte* row = (byte*)(resultBitmapData.Scan0 + (j * resultBitmapData.Stride));
byte* pix = (byte*)(row + (4 * i));
*pix = (byte)a; pix++;
*pix = (byte)r; pix++;
*pix = (byte)g; pix++;
*pix = (byte)b;
}
}
});
// Unlock the source bitmaps.
for (int i = 0; i < bitmapArray.Length; i++)
{
bitmapArray[i].UnlockBits(bitmapDataList[i]);
}
// Unlock the result bitmap.
result.UnlockBits(resultBitmapData);
// Return the result.
return result;
}
// Event handler for the Choose Folder button.
private void toolStripButton1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Create a FolderBrowserDialog object to enable the user to
// select a folder.
FolderBrowserDialog dlg = new FolderBrowserDialog
{
ShowNewFolderButton = false
};
// Set the selected path to the common Sample Pictures folder
// if it exists.
string initialDirectory = Path.Combine(
Environment.GetFolderPath(Environment.SpecialFolder.CommonPictures),
"Sample Pictures");
if (Directory.Exists(initialDirectory))
{
dlg.SelectedPath = initialDirectory;
}
// Show the dialog and process the dataflow network.
if (dlg.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
// Create a new CancellationTokenSource object to enable
// cancellation.
cancellationTokenSource = new CancellationTokenSource();
// Create the image processing network if needed.
headBlock ??= CreateImageProcessingNetwork();
// Post the selected path to the network.
headBlock.Post(dlg.SelectedPath);
// Enable the Cancel button and disable the Choose Folder button.
toolStripButton1.Enabled = false;
toolStripButton2.Enabled = true;
// Show a wait cursor.
Cursor = Cursors.WaitCursor;
}
}
// Event handler for the Cancel button.
private void toolStripButton2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Signal the request for cancellation. The current component of
// the dataflow network will respond to the cancellation request.
cancellationTokenSource.Cancel();
}
~Form1()
{
cancellationTokenSource.Dispose();
}
}
}
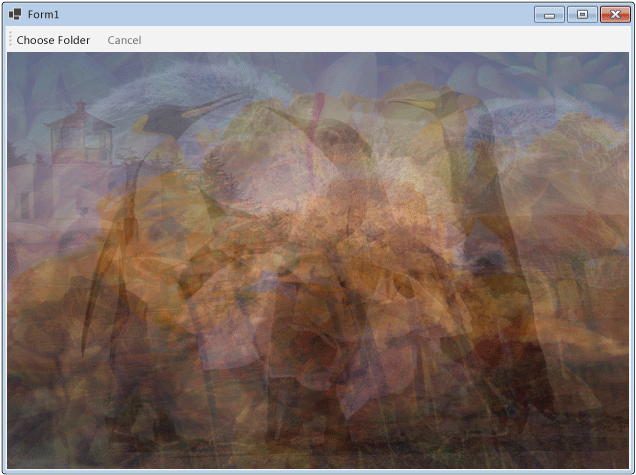
A ilustração seguinte mostra a saída típica da pasta comum \Sample Pictures\.