5155(F): The Windows Filtering Platform has blocked an application or service from listening on a port for incoming connections.
By default Windows firewall won't prevent a port from being listened by an application. In the other word, Windows system won't generate Event 5155 by itself.
You can add your own filters using the WFP APIs to block listen to reproduce this event: https://msdn.microsoft.com/library/aa364046(v=vs.85).aspx.
Subcategory: Audit Filtering Platform Connection
Event Description:
This event generates every time the Windows Filtering Platform blocks an application or service from listening on a port for incoming connections.
Event XML:
<Event
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/win/2004/08/events/event">
<System>
<Provider Name="Microsoft-Windows-Security-Auditing" Guid="{54849625-5478-4994-A5BA-3E3B0328C30D}" />
<EventID>5155</EventID>
<Version>0</Version>
<Level>0</Level>
<Task>12810</Task>
<Opcode>0</Opcode>
<Keywords>0x8010000000000000</Keywords>
<TimeCreated SystemTime="2019-04-18T03:49:08.507780900Z" />
<EventRecordID>42196</EventRecordID>
<Correlation />
<Execution ProcessID="4" ThreadID="2788" />
<Channel>Security</Channel>
<Computer>NATHAN-AGENT2</Computer>
<Security />
</System>
<EventData>
<Data Name="ProcessId">2628</Data>
<Data Name="Application">\device\harddiskvolume2\users\test\desktop\netcat\nc.exe</Data>
<Data Name="SourceAddress">0.0.0.0</Data>
<Data Name="SourcePort">5555</Data>
<Data Name="Protocol">6</Data>
<Data Name="FilterRTID">84576</Data>
<Data Name="LayerName">%%14609</Data>
<Data Name="LayerRTID">40</Data>
</EventData>
</Event>
Required Server Roles: None.
Minimum OS Version: Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista.
Event Versions: 0.
Field Descriptions:
Application Information:
Process ID [Type = Pointer]: Hexadecimal Process ID (PID) of the process that was permitted to bind to the local port. The PID is a number used by the operating system to uniquely identify an active process. To see the PID for a specific process you can, for example, use Task Manager (Details tab, PID column):
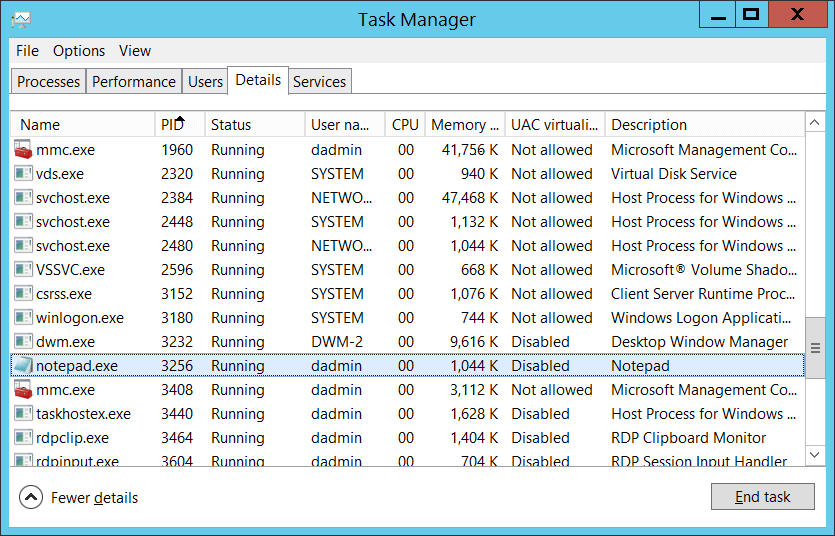
If you convert the hexadecimal value to decimal, you can compare it to the values in Task Manager.
You can also correlate this process ID with a process ID in other events, for example, “4688: A new process has been created” Process Information\New Process ID.
Application Name [Type = UnicodeString]: Full path and the name of the executable for the process.
Logical disk is displayed in the format \device\harddiskvolume#. You can get all local volume numbers by using the diskpart utility. The command to get volume numbers using diskpart is “list volume”:
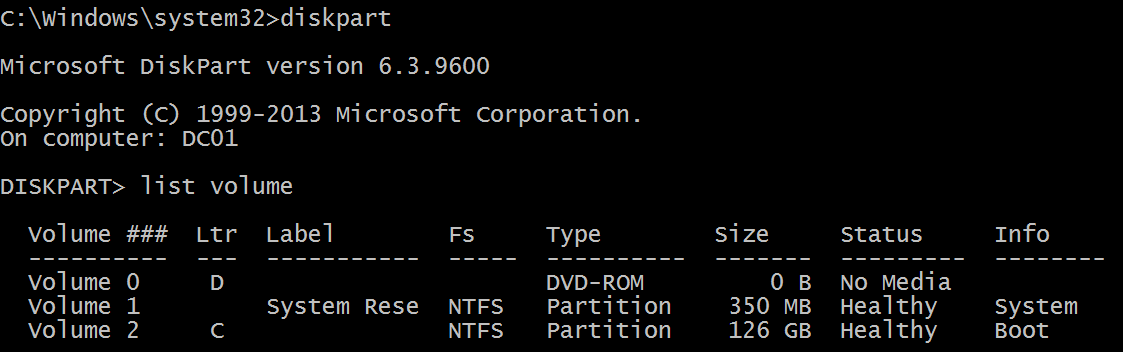
Network Information:
Source Address [Type = UnicodeString]: The local IP address of the computer running the application.
IPv4 Address
IPv6 Address
:: - all IP addresses in IPv6 format
0.0.0.0 - all IP addresses in IPv4 format
127.0.0.1, ::1 - localhost
Source Port [Type = UnicodeString]: The port number used by the application.
Protocol [Type = UInt32]: the protocol number being used.
| Service | Protocol Number |
|---|---|
| Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) | 1 |
| Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) | 6 |
| User Datagram Protocol (UDP) | 17 |
| General Routing Encapsulation (PPTP data over GRE) | 47 |
| Authentication Header (AH) IPSec | 51 |
| Encapsulation Security Payload (ESP) IPSec | 50 |
| Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) | 8 |
| Gateway-Gateway Protocol (GGP) | 3 |
| Host Monitoring Protocol (HMP) | 20 |
| Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) | 88 |
| MIT Remote Virtual Disk (RVD) | 66 |
| OSPF Open Shortest Path First | 89 |
| PARC Universal Packet Protocol (PUP) | 12 |
| Reliable Datagram Protocol (RDP) | 27 |
| Reservation Protocol (RSVP) QoS | 46 |
Filter Information:
Filter Run-Time ID [Type = UInt64]: A unique filter ID that blocks the application from binding to the port. By default, Windows firewall won't prevent a port from binding to an application, and if this application doesn’t match any filters, you'll get a 0 value in this field.
To find a specific Windows Filtering Platform filter by ID, you need to execute the following command: netsh wfp show filters. As a result of this command, a filters.xml file will be generated. You need to open this file and find the specific substring with the required filter ID (<filterId>), for example:
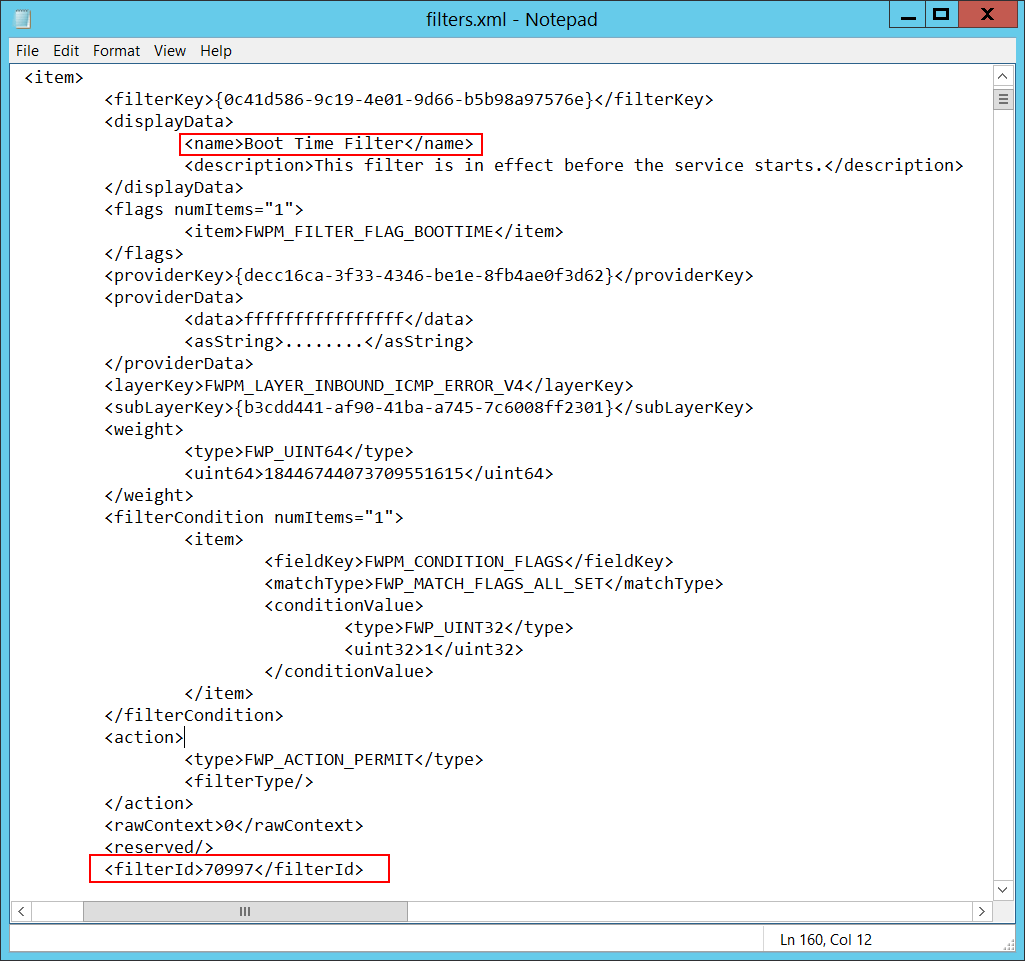
Layer Name [Type = UnicodeString]: Application Layer Enforcement layer name.
Layer Run-Time ID [Type = UInt64]: Windows Filtering Platform layer identifier. To find a specific Windows Filtering Platform layer ID, you need to execute the following command: netsh wfp show state. As a result of this command, a wfpstate.xml file will be generated. You need to open this file and find the specific substring with the required layer ID (<layerId>), for example:
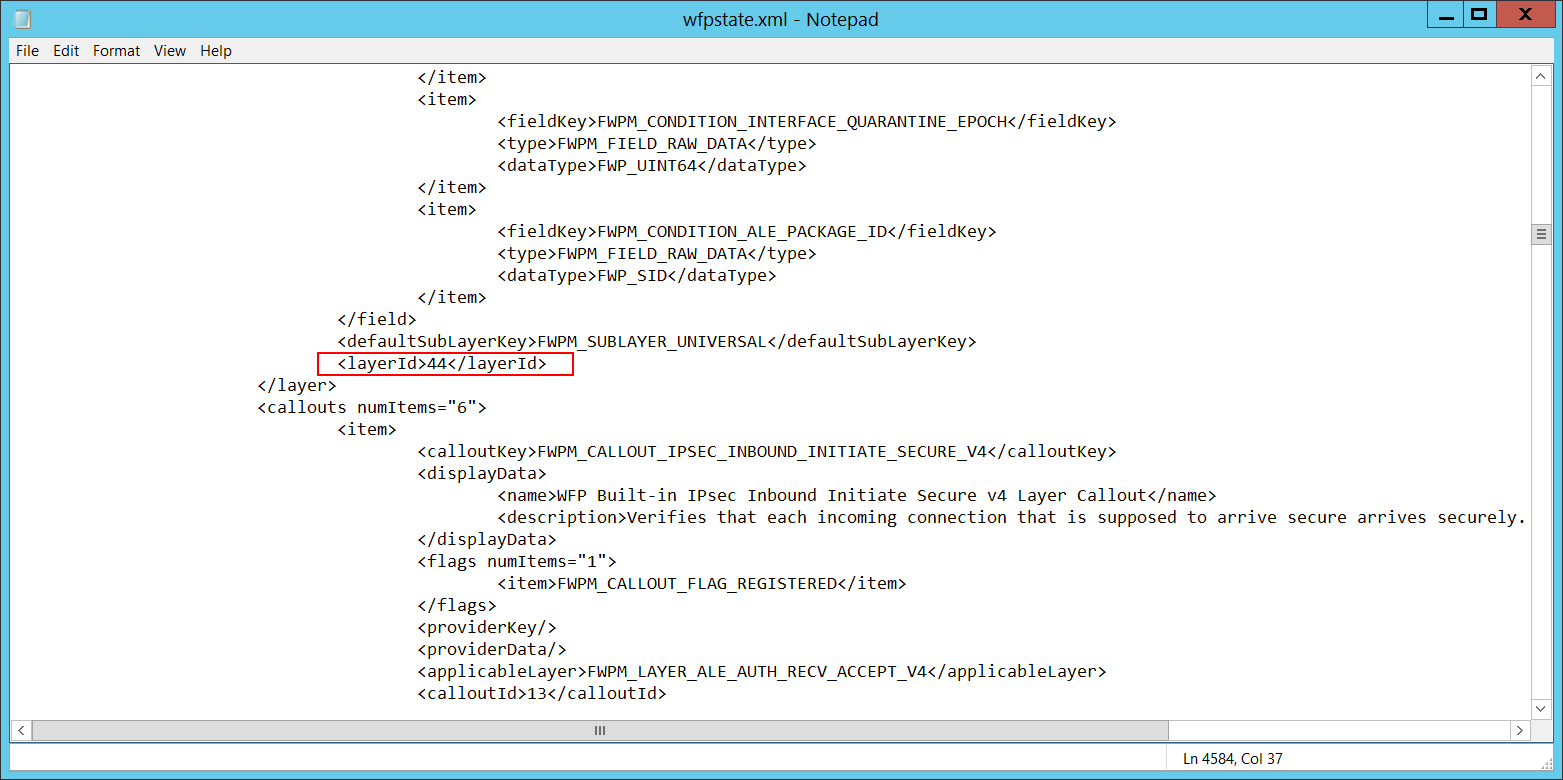
Security Monitoring Recommendations
- If you use Windows Filtering Platform APIs to block application or services from listening on a port, then you can use this event for troubleshooting and monitoring.