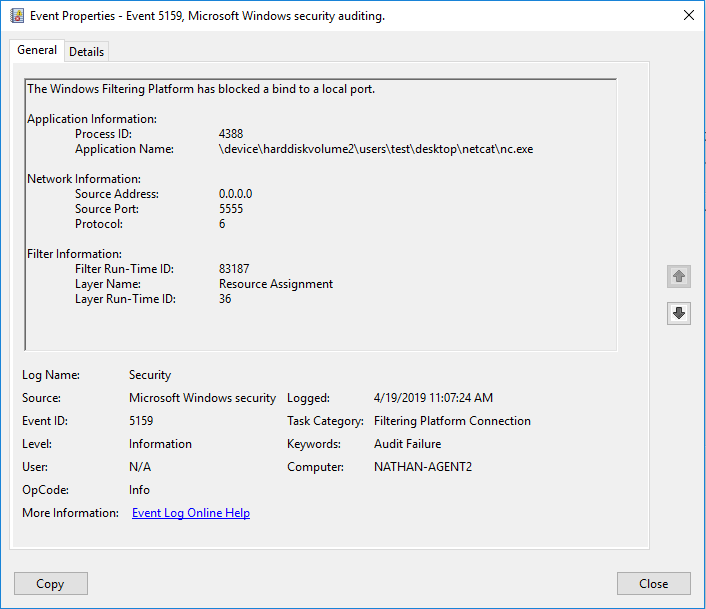
5159(F): The Windows Filtering Platform has blocked a bind to a local port.
Subcategory: Audit Filtering Platform Connection
Event Description:
This event is logged if the Windows Filtering Platform has blocked a bind to a local port.
Event XML:
- <Event xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/win/2004/08/events/event">
- <System>
<Provider Name="Microsoft-Windows-Security-Auditing" Guid="{54849625-5478-4994-A5BA-3E3B0328C30D}" />
<EventID>5159</EventID>
<Version>0</Version>
<Level>0</Level>
<Task>12810</Task>
<Opcode>0</Opcode>
<Keywords>0x8010000000000000</Keywords>
<TimeCreated SystemTime="2019-04-19T07:36:55.955388300Z" />
<EventRecordID>44097</EventRecordID>
<Correlation />
<Execution ProcessID="4" ThreadID="6480" />
<Channel>Security</Channel>
<Computer>DC01.contoso.local</Computer>
<Security />
</System>
- <EventData>
<Data Name="ProcessId">7924</Data>
<Data Name="Application">\device\harddiskvolume2\users\test\desktop\netcat\nc.exe</Data>
<Data Name="SourceAddress">0.0.0.0</Data>
<Data Name="SourcePort">5555</Data>
<Data Name="Protocol">6</Data>
<Data Name="FilterRTID">84614</Data>
<Data Name="LayerName">%%14608</Data>
<Data Name="LayerRTID">36</Data>
</EventData>
</Event>
Required Server Roles: None.
Minimum OS Version: Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista.
Event Versions: 0.
Field Descriptions:
Application Information:
Process ID [Type = Pointer]: hexadecimal Process ID of the process that was permitted to bind to the local port. Process ID (PID) is a number used by the operating system to uniquely identify an active process. To see the PID for a specific process you can, for example, use Task Manager (Details tab, PID column):
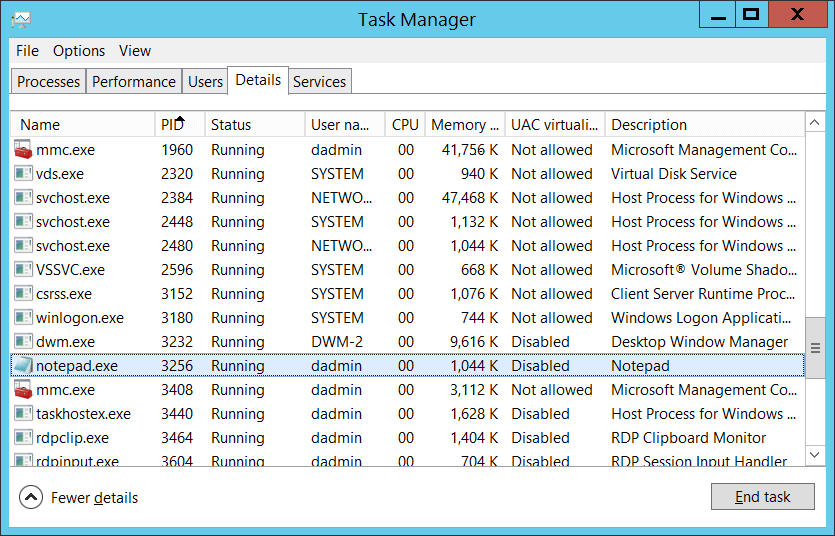
If you convert the hexadecimal value to decimal, you can compare it to the values in Task Manager.
You can also correlate this process ID with a process ID in other events, for example, “4688: A new process has been created” Process Information\New Process ID.
Application Name [Type = UnicodeString]: full path and the name of the executable for the process.
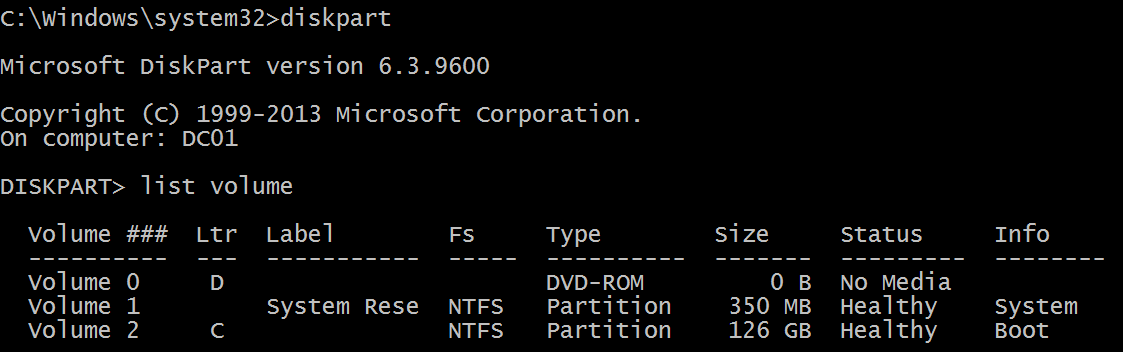
Logical disk is displayed in format \device\harddiskvolume#. You can get all local volume numbers by using diskpart utility. The command to get volume numbers using diskpart is “list volume”:
Network Information:
Source Address [Type = UnicodeString]: the local IP address of the computer running the application.
IPv4 Address
IPv6 Address
:: - all IP addresses in IPv6 format
0.0.0.0 - all IP addresses in IPv4 format
127.0.0.1, ::1 - localhost
Source Port [Type = UnicodeString]: the port number used by the application.
Protocol [Type = UInt32]: the protocol number being used.
| Service | Protocol Number |
|---|---|
| Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) | 1 |
| Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) | 6 |
| User Datagram Protocol (UDP) | 17 |
| General Routing Encapsulation (PPTP data over GRE) | 47 |
| Authentication Header (AH) IPSec | 51 |
| Encapsulation Security Payload (ESP) IPSec | 50 |
| Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) | 8 |
| Gateway-Gateway Protocol (GGP) | 3 |
| Host Monitoring Protocol (HMP) | 20 |
| Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) | 88 |
| MIT Remote Virtual Disk (RVD) | 66 |
| OSPF Open Shortest Path First | 89 |
| PARC Universal Packet Protocol (PUP) | 12 |
| Reliable Datagram Protocol (RDP) | 27 |
| Reservation Protocol (RSVP) QoS | 46 |
Filter Information:
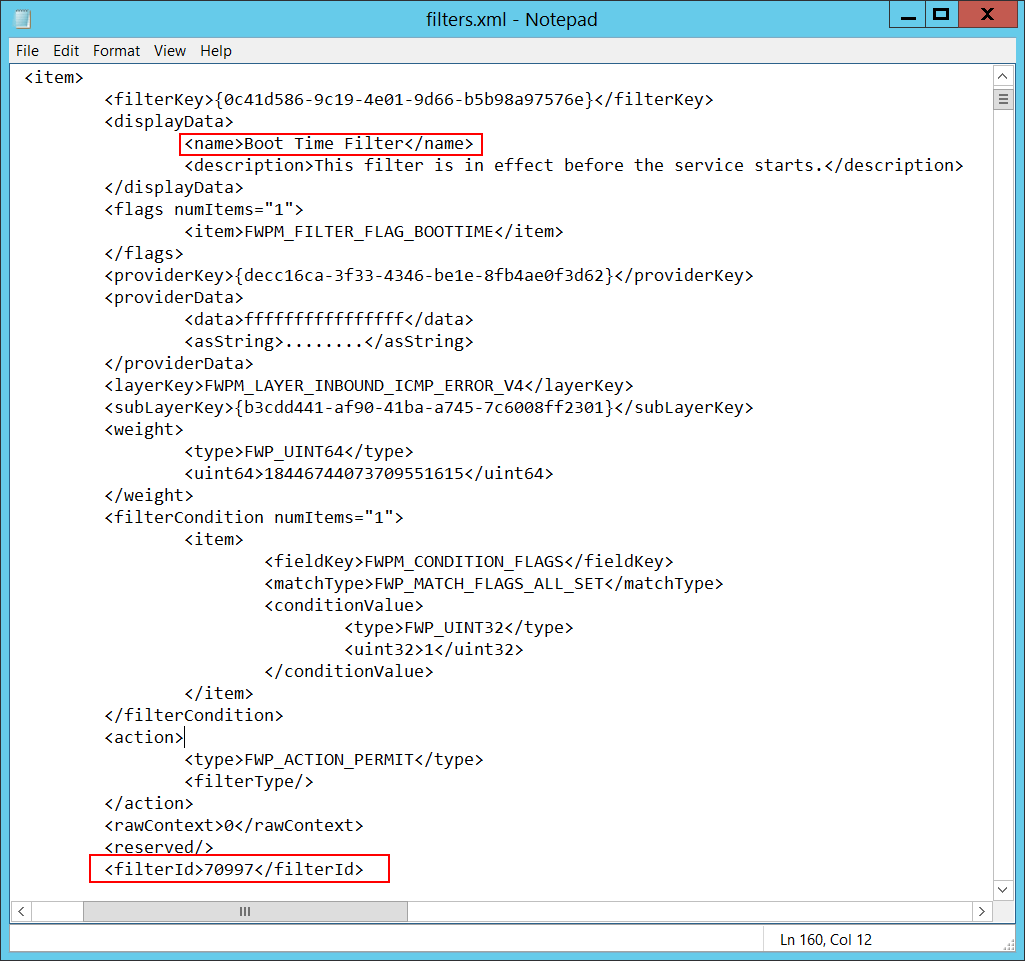
Filter Run-Time ID [Type = UInt64]: unique filter ID that blocks the application from binding to the port. By default, Windows firewall won't prevent a port from binding by an application, and if this application doesn’t match any filters, you'll get value 0 in this field.
To find a specific Windows Filtering Platform filter by ID, run the following command: netsh wfp show filters. As a result of this command, the filters.xml file will be generated. Open this file and find the specific substring with the required filter ID (<filterId>), for example:
Layer Name [Type = UnicodeString]: Application Layer Enforcement layer name.
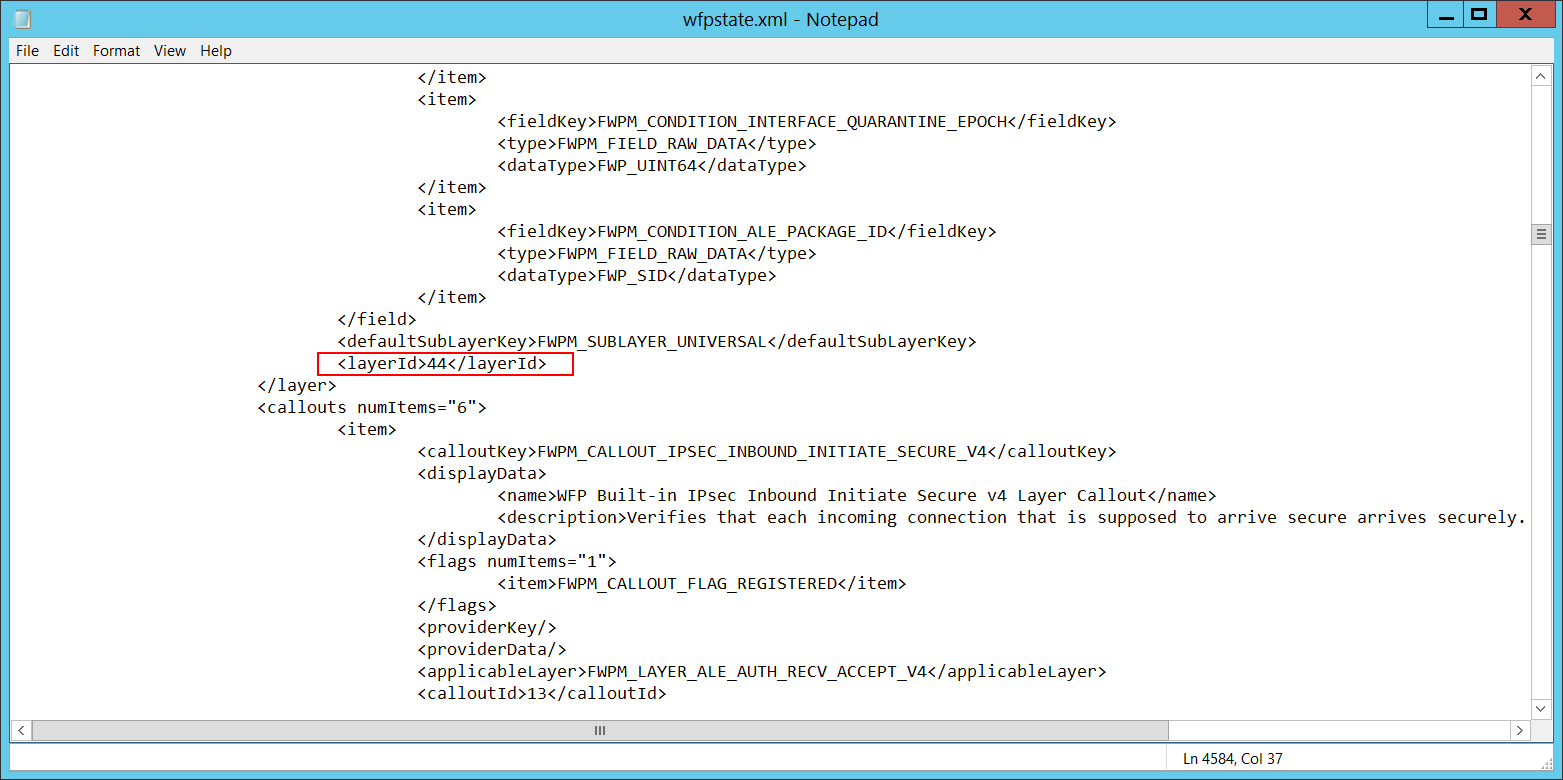
Layer Run-Time ID [Type = UInt64]: Windows Filtering Platform layer identifier. To find a specific Windows Filtering Platform layer ID, run the following command: netsh wfp show state. As a result of this command, the wfpstate.xml file will be generated. Open this file and find the specific substring with the required layer ID (<layerId>), for example:
Security Monitoring Recommendations
- There's no recommendation for this event in this document.