Tutorial: Migrate PostgreSQL to Azure Database for PostgreSQL online using DMS (classic) via the Azure portal
Important
We recommend that you use the new migration service in Azure Database for PostgreSQL for a more streamlined and efficient migration experience. This service simplifies the process by supporting a variety of source environments, ensuring a hassle-free transition to Azure Database for PostgreSQL.
For more information about Azure Database Migration Service, see the article What is Azure Database Migration Service?
You can use Azure Database Migration Service to migrate the databases from an on-premises PostgreSQL instance to Azure Database for PostgreSQL with minimal downtime to the application. In this tutorial, you migrate the listdb sample database from an on-premises instance of PostgreSQL 13.10 to Azure Database for PostgreSQL by using the online migration activity in Azure Database Migration Service.
In this tutorial, you learn how to:
- Migrate the sample schema using the pg_dump utility.
- Create an instance of Azure Database Migration Service.
- Create a migration project in Azure Database Migration Service.
- Run the migration.
- Monitor the migration.
- Perform migration cutover.
Using Azure Database Migration Service to perform an online migration requires creating an instance based on the Premium pricing tier. We encrypt disk to prevent data theft during the process of migration
Important
For an optimal migration experience, Microsoft recommends creating an instance of Azure Database Migration Service in the same Azure region as the target database. Moving data across regions or geographies can slow down the migration process and introduce errors.
Prerequisites
To complete this tutorial, you need to:
Download and install PostgreSQL community edition. The source PostgreSQL Server version must be >= 9.4. For more information, see Supported PostgreSQL versions in Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server.
Also note that the target Azure Database for PostgreSQL version must be equal to or later than the on-premises PostgreSQL version. For example, PostgreSQL 12 can migrate to Azure Database for PostgreSQL >= 12 version but not to Azure Database for PostgreSQL 11.
Create a Microsoft Azure Virtual Network for Azure Database Migration Service by using the Azure Resource Manager deployment model, which provides site-to-site connectivity to your on-premises source servers by using either ExpressRoute or VPN. For more information about creating a virtual network, see the Virtual Network Documentation, and especially the quickstart articles with step-by-step details.
During virtual network setup, if you use ExpressRoute with network peering to Microsoft, add the following service endpoints to the subnet in which the service will be provisioned:
- Target database endpoint (for example, SQL endpoint, Azure Cosmos DB endpoint, and so on)
- Storage endpoint
- Service bus endpoint
This configuration is necessary because Azure Database Migration Service lacks internet connectivity.
Ensure that the Network Security Group (NSG) rules for your virtual network don't block the outbound port 443 of ServiceTag for ServiceBus, Storage and AzureMonitor. For more detail on virtual network NSG traffic filtering, see the article Filter network traffic with network security groups.
Configure your Windows Firewall for database engine access.
Open your Windows firewall to allow Azure Database Migration Service to access the source PostgreSQL Server, which by default is TCP port 5432.
When using a firewall appliance in front of your source database(s), you might need to add firewall rules to allow the Azure Database Migration Service to access the source database(s) for migration.
Create a server-level firewall rule for Azure Database for PostgreSQL to allow Azure Database Migration Service to access to the target databases. Provide the subnet range of the virtual network used for Azure Database Migration Service.
Enable logical replication in the postgresql.config file, and set the following parameters:
- wal_level = logical
- max_replication_slots = [number of slots], recommend setting to five slots
- max_wal_senders =[number of concurrent tasks] - The max_wal_senders parameter sets the number of concurrent tasks that can run, recommend setting to 10 tasks
The user must have the REPLICATION role on the server hosting the source database.
Important
All tables in your existing database need a primary key to ensure that changes can be synced to the target database.
Migrate the sample schema
To complete all the database objects like table schemas, indexes and stored procedures, we need to extract schema from the source database and apply to the database.
Use pg_dump -s command to create a schema dump file for a database.
pg_dump -O -h hostname -U db_username -d db_name -s > your_schema.sqlFor example, to create a schema dump file for the listdb database:
pg_dump -O -h localhost -U postgres -d listdb -s -x > listdbSchema.sqlFor more information about using the pg_dump utility, see the examples in the pg-dump tutorial.
Create an empty database in your target environment, which is Azure Database for PostgreSQL.
For details on how to connect and create a database, see the article Create an Azure Database for PostgreSQL server in the Azure portal.
Import the schema into the target database you created by restoring the schema dump file.
psql -h hostname -U db_username -d db_name < your_schema.sqlFor example:
psql -h mypgserver-20170401.postgres.database.azure.com -U postgres -d migratedb < listdbSchema.sqlNote
The migration service internally handles the enable/disable of foreign keys and triggers to ensure a reliable and robust data migration. As a result, you don't have to worry about making any modifications to the target database schema.
Register the resource provider
Register the Microsoft.DataMigration resource provider before you create your first instance of the Database Migration Service.
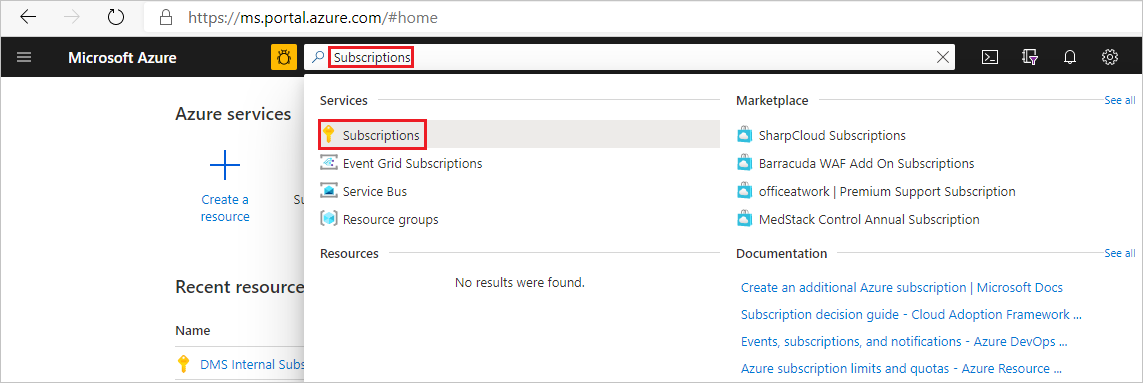
Sign in to the Azure portal. Search for and select Subscriptions.
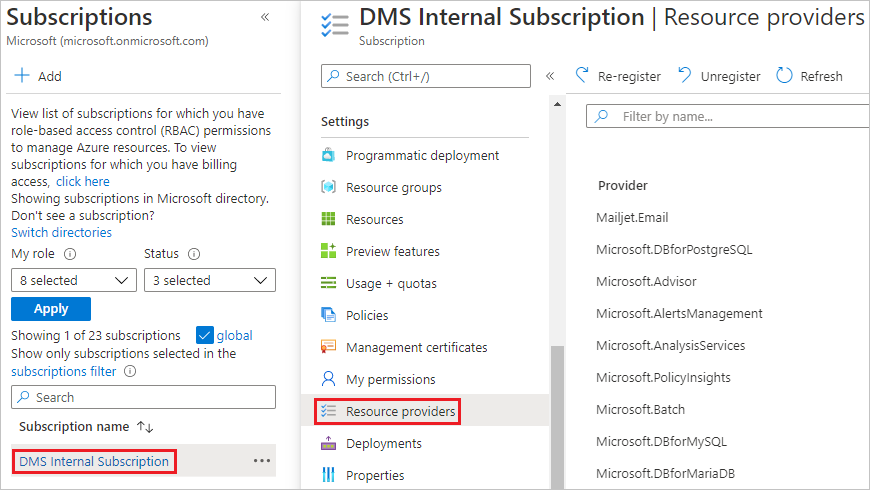
Select the subscription in which you want to create the instance of Azure Database Migration Service, and then select Resource providers.
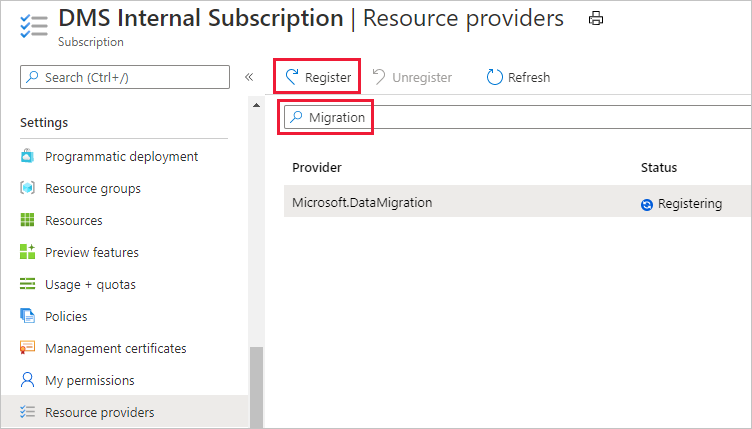
Search for migration, and then select Register for Microsoft.DataMigration.
Create an Azure Database Migration Service instance
In the Azure portal menu or on the Home page, select Create a resource. Search for and select Azure Database Migration Service.

On the Azure Database Migration Service screen, select Create.
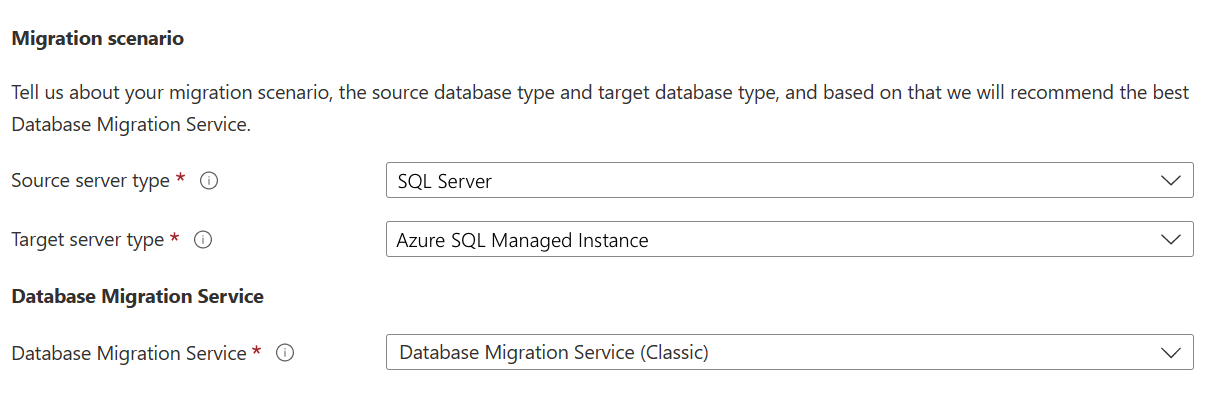
Select the appropriate Source server type and Target server type, and choose the Database Migration Service (Classic) option.
On the Create Migration Service basics screen:
- Select the subscription.
- Create a new resource group or choose an existing one.
- Specify a name for the instance of the Azure Database Migration Service.
- Select the location in which you want to create the instance of Azure Database Migration Service.
- Choose Azure as the service mode.
- Select a pricing tier. For more information on costs and pricing tiers, see the pricing page.
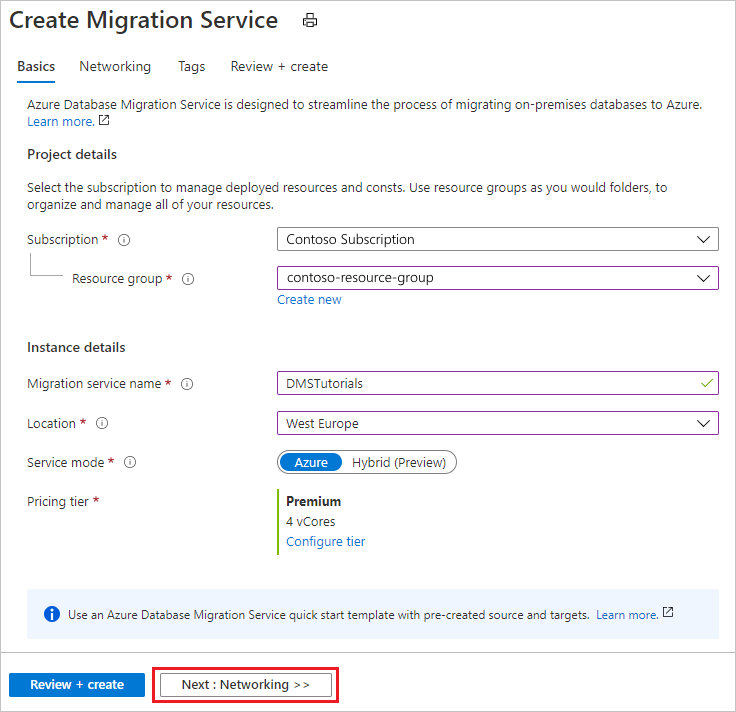
- Select Next: Networking.
On the Create Migration Service networking screen:
- Select an existing virtual network or create a new one. The virtual network provides Azure Database Migration Service with access to the source server and the target instance. For more information about how to create a virtual network in the Azure portal, see the article Create a virtual network using the Azure portal.
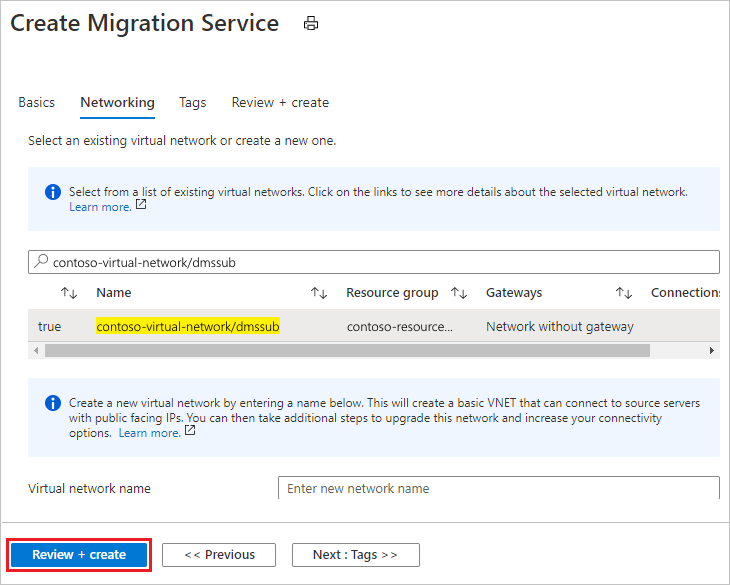
Select Review + Create to review the details and then select Create to create the service.
After a few moments, your instance of the Azure Database Migration service is created and ready to use:

Create a migration project
After the service is created, locate it within the Azure portal, open it, and then create a new migration project.
In the Azure portal, select All services, search for Azure Database Migration Service, and then select Azure Database Migration Services.

On the Azure Database Migration Services screen, search for the name of Azure Database Migration Service instance that you created, select the instance, and then select + New Migration Project.
On the New migration project screen, specify a name for the project, in the Source server type text box, select PostgreSQL, in the Target server type text box, select Azure Database for PostgreSQL.
In the Migration activity type section, select Online data migration.
Alternately, you can choose Create project only to create the migration project now and execute the migration later.
Select Create and run activity, to successfully use Azure Database Migration Service to migrate data.
Specify source details
On the Add Source Details screen, specify the connection details for the source PostgreSQL instance.
Specify target details
On the Target details screen, specify the connection details for the target Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible server, which is the preprovisioned instance to which the schema was deployed by using pg_dump.
Select Next:Select databases, and then on the Select databases screen, map the source and the target database for migration.
If the target database contains the same database name as the source database, Azure Database Migration Service selects the target database by default.
Select Next:Select tables, and then on the Select tables screen, select the required tables that need to be migrated.
Select Next:Configure migration settings, and then on the Configure migration settings screen, accept the default values.
On the Migration summary screen, in the Activity name text box, specify a name for the migration activity, and then review the summary to ensure that the source and target details match what you previously specified.
Run the migration
Select Start migration.
The migration activity window appears, and the Status of the activity should update to show as Backup in Progress.
Monitor the migration
On the migration activity screen, select Refresh to update the display until the Status of the migration shows as Complete.
When the migration is complete, under Database Name, select a specific database to get to the migration status for Full data load and Incremental data sync operations.
Note
Full data load shows the initial load migration status, while Incremental data sync shows change data capture (CDC) status.
Perform migration cutover
After the initial Full load is completed, the databases are marked Ready to cutover.
When you're ready to complete the database migration, select Start Cutover.
Wait until the Pending changes counter shows
0to ensure that all incoming transactions to the source database are stopped, select the Confirm checkbox, and then select Apply.When the database migration status shows Completed, recreate sequences (if applicable), and connect your applications to the new target instance of Azure Database for PostgreSQL.