Deploy and call custom APIs from workflows in Azure Logic Apps
Applies to: Azure Logic Apps (Consumption)
After you create your own APIs to use in your logic app workflows, you need to deploy those APIs before you can call them. You can deploy your APIs as web apps, but consider deploying your APIs as API apps, which make your job easier when you build, host, and consume APIs in the cloud and on premises. You don't have to change any code in your APIs - just deploy your code to an API app. You can host your APIs on Azure App Service, a platform-as-a-service (PaaS) offering that provides highly scalable, easy API hosting.
Although you can call any API from a logic app workflow, for the best experience, add Swagger metadata that describes your API's operations and parameters. This Swagger document helps your API integrate more easily and work better with logic app workflows.
Deploy your API as a web app or API app
Before you can call your custom API from a logic app workflow, deploy your API as a web app or API app to Azure App Service. To make your Swagger document readable by your workflow, set the API definition properties and turn on cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) for your web app or API app.
In the Azure portal, select your web app or API app.
In the app menu that opens, under API, select API definition. Set the API definition location to the URL for your swagger.json file.
Usually, the URL appears in this format:
https://{name}.azurewebsites.net/swagger/docs/v1)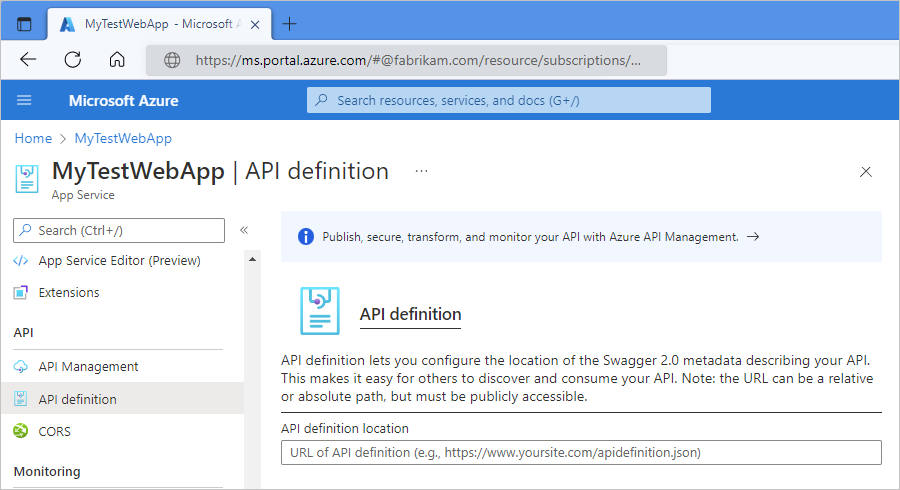
Under API, select CORS. Set the CORS policy for Allowed origins to '*' (allow all).
This setting permits requests from the workflow designer.

For more information, review Host a RESTful API with CORS in Azure App Service.
Call your custom API from logic app workflows
After you set up the API definition properties and CORS, your custom API's triggers and actions should be available for you to include in your logic app workflow.
To view websites that have OpenAPI URLs, you can browse your subscription websites in the workflow designer.
To view available actions and inputs by pointing at a Swagger document, use the HTTP + Swagger action.
To call any API, including APIs that don't have or expose a Swagger document, you can always create a request with the HTTP action.