.NET observability with OpenTelemetry
When you run an application, you want to know how well the app is performing and to detect potential problems before they become larger. You can do this by emitting telemetry data such as logs or metrics from your app, then monitoring and analyzing that data.
What is observability?
Observability in the context of a distributed system is the ability to monitor and analyze telemetry about the state of each component, to be able to observe changes in performance, and to diagnose why those changes occur. Unlike debugging, which is invasive and can affect the operation of the application, observability is intended to be transparent to the primary operation and have a small enough performance impact that it can be used continuously.
Observability is commonly done using a combination of:
- Logs, which record individual operations, such as an incoming request, a failure in a specific component, or an order being placed.
- Metrics, which are measuring counters and gauges such as number of completed requests, active requests, widgets that have been sold; or a histogram of the request latency.
- Distributed tracing, which tracks requests and activities across components in a distributed system so that you can see where time is spent and track down specific failures.
Together, logs, metrics, and distributed tracing are sometimes known as the three pillars of observability.
Each pillar might include telemetry data from:
- The .NET runtime, such as the garbage collector or JIT compiler.
- Libraries, such as from Kestrel (the ASP.NET web server) and
HttpClient. - Application-specific telemetry that's emitted by your code.
Observability approaches in .NET
There are a few different ways to achieve observability in .NET applications:
- Explicitly in code, by referencing and using a library such as OpenTelemetry. If you have access to the source code and can rebuild the app, then this is the most powerful and configurable mechanism.
- Out-of-process using EventPipe. Tools such as dotnet-monitor can listen to logs and metrics and then process them without affecting any code.
- Using a startup hook, assemblies can be injected into the process that can then collect instrumentation. An example of this approach is OpenTelemetry .NET Automatic Instrumentation.
What is OpenTelemetry?
OpenTelemetry (OTel) is a cross-platform, open standard for collecting and emitting telemetry data. OpenTelemetry includes:
- APIs for libraries to use to record telemetry data as code is running.
- APIs that app developers use to configure what portion of the recorded data will be sent across the network, where it will be sent to, and how it may be filtered, buffered, enriched, and transformed.
- Semantic conventions provide guidance on naming and content of telemetry data. It is important for the apps that produce telemetry data and the tools that receive the data to agree on what different kinds of data means and what sorts of data are useful so that the tools can provide effective analysis.
- An interface for exporters. Exporters are plugins that allow telemetry data to be transmitted in specific formats to different telemetry backends.
- OTLP wire protocol is a vendor neutral network protocol option for transmitting telemetry data. Some tools and vendors support this protocol in addition to pre-existing proprietary protocols they may have.
Using OTel enables the use of a wide variety of APM systems including open-source systems such as Prometheus and Grafana, Azure Monitor - Microsoft's APM product in Azure, or from the many APM vendors that partner with OpenTelemetry.
There are OpenTelemetry implementations for most languages and platforms, including .NET.
.NET implementation of OpenTelemetry
The .NET OpenTelemetry implementation is a little different from other platforms, as .NET provides logging, metrics, and activity APIs in the framework. That means OTel doesn't need to provide APIs for library authors to use. The .NET OTel implementation uses these platform APIs for instrumentation:
- Microsoft.Extensions.Logging.ILogger<TCategoryName> for logging
- System.Diagnostics.Metrics.Meter for metrics
- System.Diagnostics.ActivitySource and System.Diagnostics.Activity for distributed tracing
Where OTel comes into play is that it collects telemetry from those APIs and other sources (via instrumentation libraries) and then exports them to an application performance monitoring (APM) system for storage and analysis. The benefit that OTel brings as an industry standard is a common mechanism for collection, common schemas and semantics for telemetry data, and an API for how APMs can integrate with OTel. Using OTel means that applications don't need to use APM-specific APIs or data structures; they work against the OTel standard. APMs can either implement an APM specific exporter component or use OTLP, which is a new wire standard for exporting telemetry data to the APM systems.
OpenTelemetry packages
OpenTelemetry in .NET is implemented as a series of NuGet packages that form a couple of categories:
- Core API
- Instrumentation - these packages collect instrumentation from the runtime and common libraries.
- Exporters - these interface with APM systems such as Prometheus, Jaeger, and OTLP.
The following table describes the main packages.
| Package Name | Description |
|---|---|
| OpenTelemetry | Main library that provides the core OTEL functionality |
| OpenTelemetry.Instrumentation.AspNetCore | Instrumentation for ASP.NET Core and Kestrel |
| OpenTelemetry.Instrumentation.GrpcNetClient | Instrumentation for gRPC Client for tracking outbound gRPC calls |
| OpenTelemetry.Instrumentation.Http | Instrumentation for HttpClient and HttpWebRequest to track outbound HTTP calls |
| OpenTelemetry.Instrumentation.SqlClient | Instrumentation for SqlClient used to trace database operations |
| OpenTelemetry.Exporter.Console | Exporter for the console, commonly used to diagnose what telemetry is being exported |
| OpenTelemetry.Exporter.OpenTelemetryProtocol | Exporter using the OTLP protocol |
| OpenTelemetry.Exporter.Prometheus.AspNetCore | Exporter for Prometheus implemented using an ASP.NET Core endpoint |
| OpenTelemetry.Exporter.Zipkin | Exporter for Zipkin tracing |
Examples
This topic is continued with a couple of example walkthroughs for using OpenTelemetry in .NET:
- Example: Use OTLP and the standalone Aspire Dashboard
- Example: Use OpenTelemetry with Azure Monitor and Application Insights
- Example: Use OpenTelemetry with Prometheus, Grafana, and Jaeger
OpenTelemetry in .NET Aspire
.NET Aspire is a set of extensions to .NET to make it easy to create and work with distributed applications. One of the benefits of using .NET Aspire is that telemetry is built in, using the OpenTelemetry libraries for .NET. The default project templates for .NET Aspire contain a ServiceDefaults project, part of which is to setup and configure OTel. The Service Defaults project is referenced and initialized by each service in a .NET Aspire solution.
The Service Defaults project template includes the OTel SDK, ASP.NET, HttpClient and Runtime Instrumentation packages, and those are configured in the Extensions.cs file. For exporting telemetry .NET Aspire includes the OTLP exporter by default so that it can provide telemetry visualization using the Aspire Dashboard.
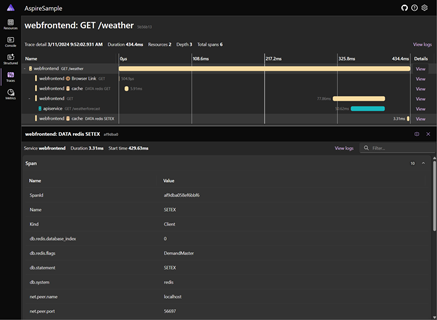
The Aspire Dashboard is designed to bring telemetry observation to the local debug cycle, which enables developers to not only ensure that the applications are producing telemetry, but also use that telemetry to diagnose those applications locally. Being able to observe the calls between services is proving to be just as useful at debug time as in production. The .NET Aspire dashboard is launched automatically when you F5 the AppHost Project from Visual Studio or dotnet run the AppHost project.
For more details on .NET Aspire see:
Reusing Service Defaults project without .NET Aspire Orchestration
Probably the easiest way to configure OTel for ASP.NET projects is to use the Aspire Service Defaults project, even if not using the rest of .NET Aspire such as the AppHost for orchestration. The Service Defaults project is available as a project template via Visual Studio or dotnet new. It configures OTel and sets up the OTLP exporter. You can then use the OTel environment variables to configure the OTLP endpoint to send telemetry to, and provide the resource properties for the application.
The steps to use ServiceDefaults outside .NET Aspire are:
- Add the ServiceDefaults project to the solution using Add New Project in Visual Studio, or use
dotnet new aspire-servicedefaults --output ServiceDefaults - Reference the ServiceDefaults project from your ASP.NET application. In Visual Studio use "Add -> Project Reference" and select the ServiceDefaults project"
- Call its OpenTelemetry setup function as part of your application builder initialization.
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
builder.ConfigureOpenTelemetry();
var app = builder.Build();
app.MapGet("/", () => "Hello World!");
app.Run();
Service Defaults can setup the following additional functionality if required via AddServiceDefaults() or the specific functions:
- Health checks with
/healthand/aliveendpoints - Service discovery which will be a no-op without the rest of .NET Aspire
- Configuring resilience for HttpClient which will retry the request in the case of failures