opomba,
Dostop do te strani zahteva pooblastilo. Poskusite se vpisati alispremeniti imenike.
Dostop do te strani zahteva pooblastilo. Poskusite lahko spremeniti imenike.
The ML.NET CLI automates model generation for .NET developers.
To use the ML.NET API by itself, (without the ML.NET AutoML CLI) you need to choose a trainer (implementation of a machine learning algorithm for a particular task), and the set of data transformations (feature engineering) to apply to your data. The optimal pipeline will vary for each dataset and selecting the optimal algorithm from all the choices adds to the complexity. Even further, each algorithm has a set of hyperparameters to be tuned. Hence, you can spend weeks and sometimes months on machine learning model optimization trying to find the best combinations of feature engineering, learning algorithms, and hyperparameters.
The ML.NET CLI simplifies this process using automated machine learning (AutoML).
Note
This article refers to ML.NET CLI and ML.NET AutoML, which are currently in preview, and material is subject to change.
What is the ML.NET command-line interface (CLI)?
The ML.NET CLI is a .NET tool. Once installed, you give it a machine learning task and a training dataset, and it generates an ML.NET model, as well as the C# code to run to use the model in your application.
As shown in the following figure, it is simple to generate a high quality ML.NET model (serialized model .zip file) plus the sample C# code to run/score that model. In addition, the C# code to create/train that model is also generated, so that you can research and iterate on the algorithm and settings used for that generated "best model".
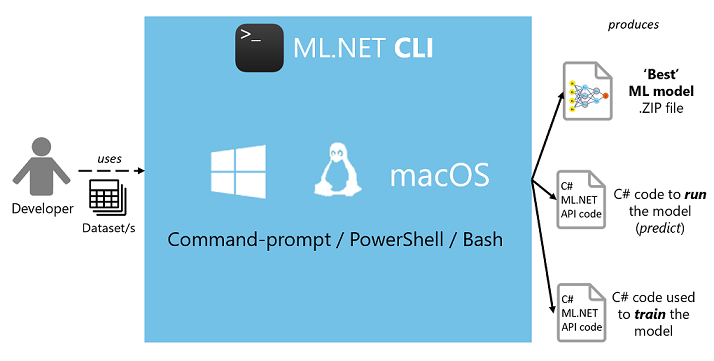
You can generate those assets from your own datasets without coding by yourself, so it also improves your productivity even if you already know ML.NET.
Currently, the ML Tasks supported by the ML.NET CLI are:
- classification
- regression
- recommendation
- image classification
- forecasting
- train
The ML.NET CLI can be installed based on your operating system and its architecture with the following command:
dotnet tool install --global mlnet-<OS>-<ARCH>
For example, the x64 version of Windows can be installed with:
dotnet tool install --global mlnet-win-x64
For more information, see the Install the ML.NET CLI how-to guide.
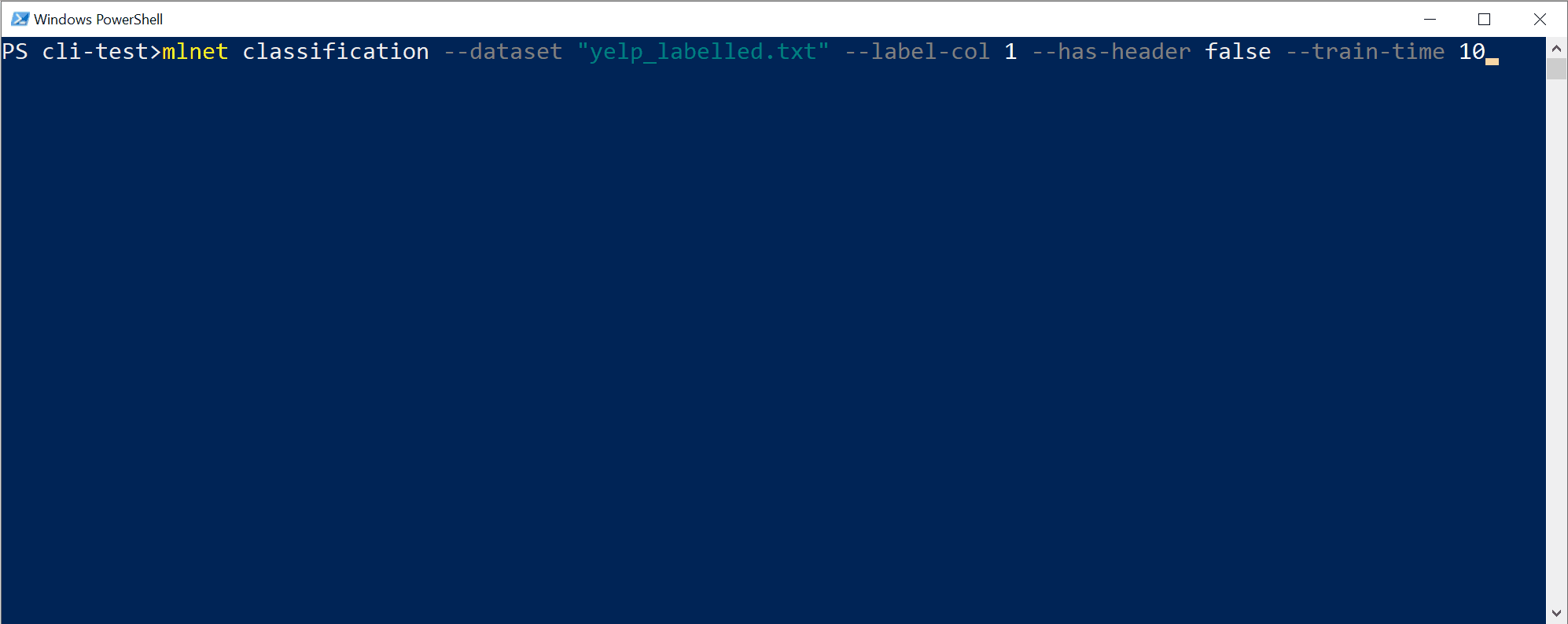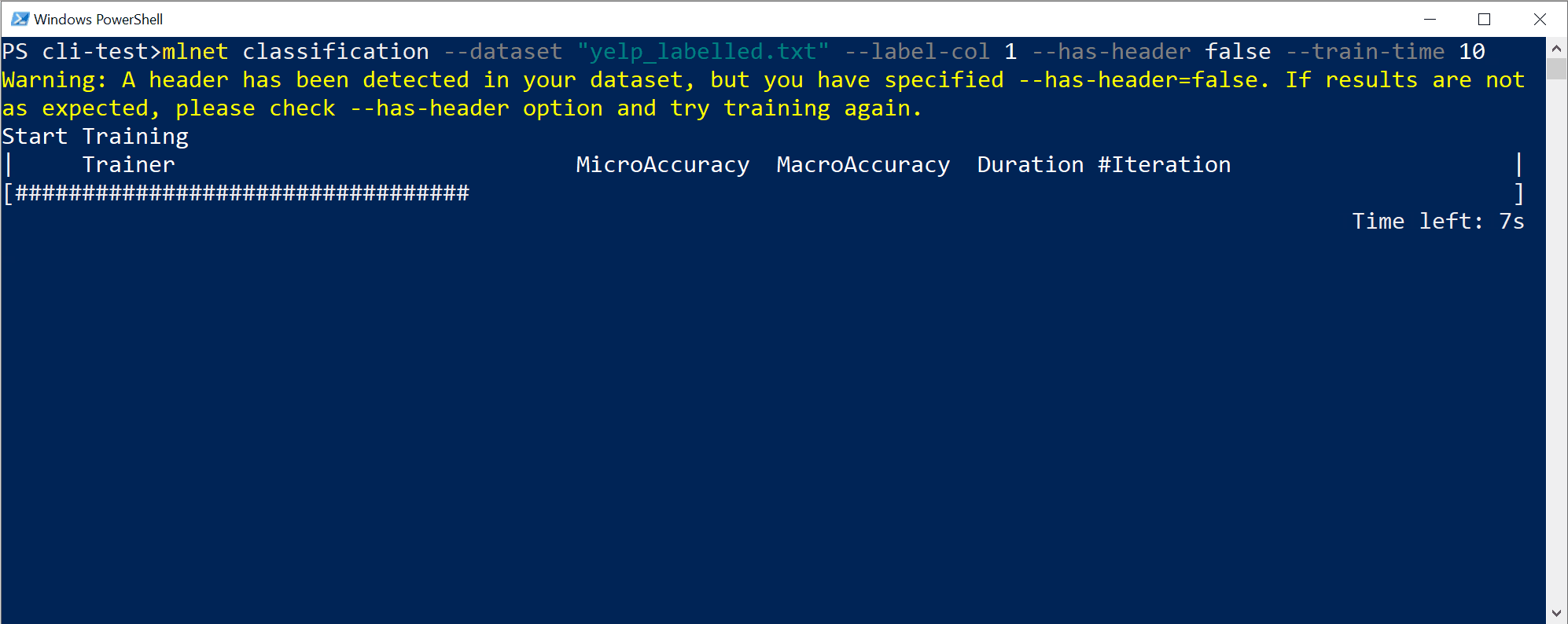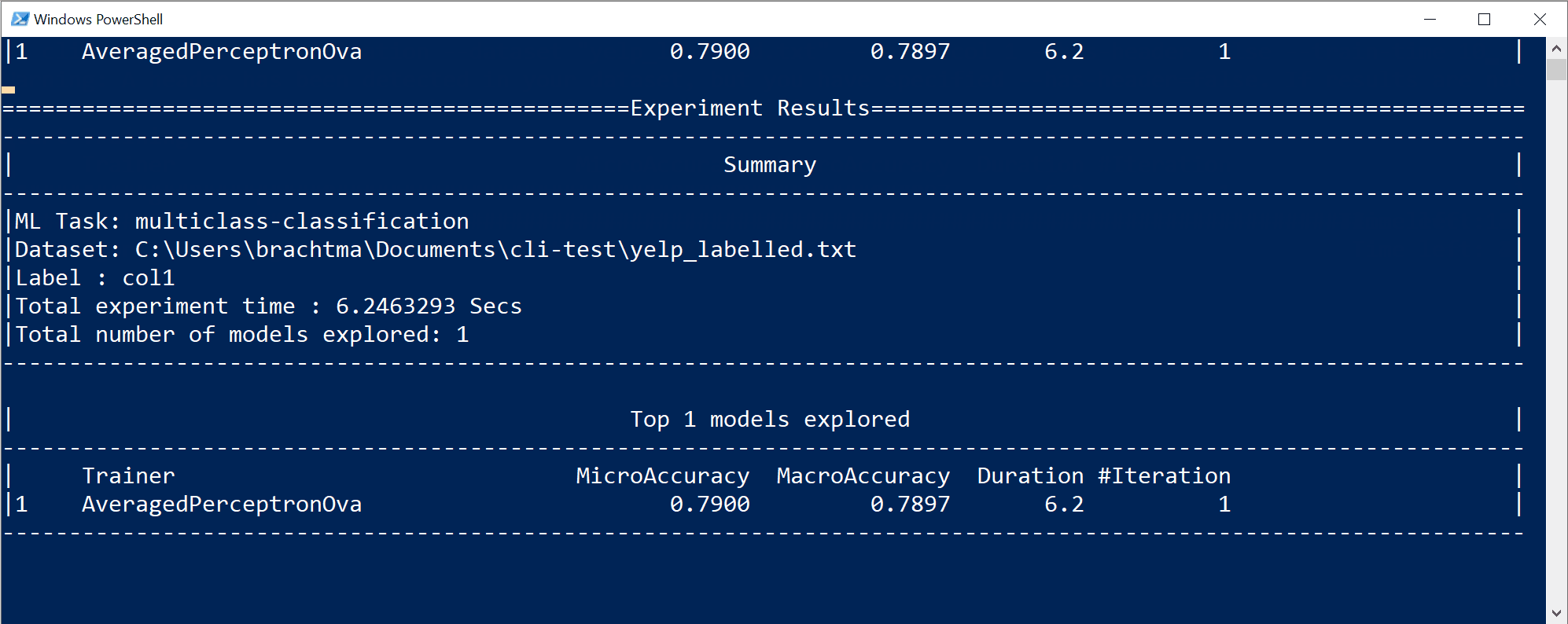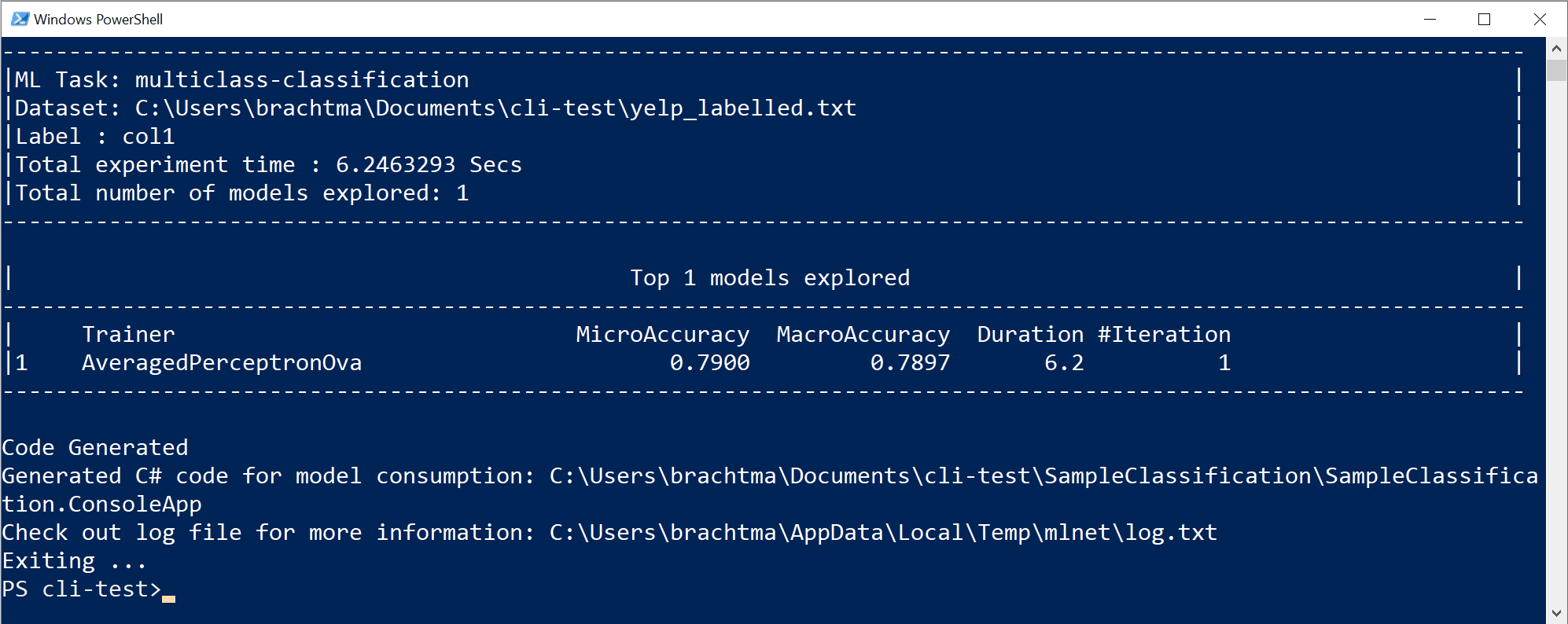
An example of usage (classification scenario):
mlnet classification --dataset "yelp_labelled.txt" --label-col 1 --has-header false --train-time 10
There is also a command where you can train using an mbconfig file. The mbconfig file is created when you start a Model Builder session.
You can run it the same way on Windows PowerShell, macOS/Linux bash, or Windows CMD. However, tabular auto-completion (parameter suggestions) won't work on Windows CMD.
Output assets generated
The ML task commands in the CLI generate the following assets in the output folder:
- C# solution with:
- A console app to run/score the generated model (to make predictions in your end-user apps with that model).
- A console app with the training code used to generate that model (for learning purposes or model retraining).
- This serialized model ("best model") is also provided as a compressed .zip file that's ready to use for running predictions.
- An mbconfig file, which contains configuration data that lets you open the model in Model Builder.
- Log file with information of all iterations/sweeps across the multiple algorithms evaluated, including their detailed configuration/pipeline.
The first two assets can directly be used in your end-user apps (for example, ASP.NET Core web apps, services, and desktop apps) to make predictions with that generated ML model.
The third asset, the training code, shows you what ML.NET API code was used by the CLI to train the generated model, so you can retrain your model and investigate and iterate on which specific trainer/algorithm and hyperparameters were selected by the CLI and AutoML under the covers.
Understanding the quality of the model
When you generate a 'best model' with the CLI tool, you see quality metrics (such as accuracy and R-Squared) as appropriate for the ML task you're targeting.
Here those metrics are summarized grouped by ML task so you can understand the quality of your auto-generated 'best model'.
Metrics for Classification models
The following image displays the classification metrics list for the top five models found by the CLI:
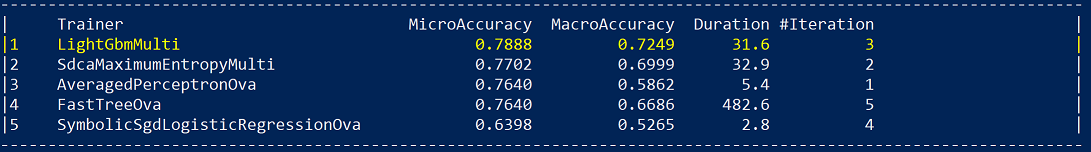
Accuracy is a popular metric for classification problems, however accuracy isn't always the best metric to select the best model from as explained in the following references. There are cases where you need to evaluate the quality of your model with additional metrics.
To explore and understand the metrics that are output by the CLI, see Evaluation metrics for classification.
Metrics for Regression and Recommendation models
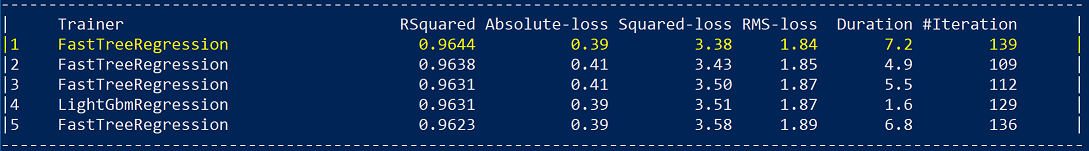
A regression model fits the data well if the differences between the observed values and the model's predicted values are small and unbiased. Regression can be evaluated with certain metrics.
You'll see a similar list of metrics for the top five quality models found by the CLI, except in this case, the top five are related to a regression ML task:
To explore and understand the metrics that are output by the CLI, see Evaluation metrics for regression.
