Create and use orchestration groups in Configuration Manager
Applies to: Configuration Manager (current branch)
An orchestration group gives you the flexibility to update devices based on a percentage, a specific number, or an explicit order. You can also run a PowerShell script before and after the devices run the update deployment.
Members of an orchestration group can be any Configuration Manager client, not just servers. The orchestration group rules apply to the devices for all software update deployments to any collection that contains an orchestration group member. Other deployment behaviors still apply. For example, maintenance windows and deployment schedules.
Create an orchestration group
Verify the prerequisites, permissions, and limitations for orchestration groups.
In the Configuration Manager console, go to the Assets and Compliance workspace, and select the Orchestration Group node.
In the ribbon, select Create Orchestration Group to open the Create Orchestration Group Wizard.
On the General page, give your orchestration group a Name and optionally a Description. Specify your values for the following items:
- Orchestration Group timeout (in minutes): Time limit for all group members to complete update installation.
- Orchestration Group member timeout (in minutes): Time limit for a single device in the group to complete the update installation.
On the Member Selection page, first specify the Site code. Then select Add to add device resources as members of this orchestration group. Search for devices by name, and then Add them. You can also filter your search to a single collection by using Search in Collection. Select OK when you finish adding devices to the selected resources list.
- When selecting resources for the group, only valid clients are shown. Checks are made for verifying the site code, that the client is installed, and that resources aren't duplicated.
On the Rule Selection page, select one of the following options:
Allow a percentage of the machines to be updated at the same time, then select or enter a number for this percentage. Use this setting to allow for future flexibility of the size of the orchestration group. For example, your orchestration group contains 50 devices, and you set this value to 10. During a software update deployment, Configuration Manager allows five devices to simultaneously run the deployment. If you later increase the size of the orchestration group to 100 devices, then 10 devices update at once.
Allow a number of the machines to be updated at the same time, then select or enter a number for this specific count. Use this setting to always limit to a specific number of devices, whatever the overall size of the orchestration group.
Specify the maintenance sequence, then sort the selected resources in the proper order. Use this setting to explicitly define the order in which devices run the software update deployment.
Choose a Pre-installation script and Post-installation script for your orchestration group, if needed, on the Script Picker page.
- Pre-Script: A PowerShell script to run on each device before the deployment runs.
- Post-Script page, enter a PowerShell script to run on each device after the deployment runs and a restart, if required, occurs. The behavior is otherwise the same as the PreScript.
The scripts should return a value of
0for success. Any non-zero value is considered a script failure. Scripts with parameters can't be used and the maximum script length is 50,000 bytes which is 25,000 characters (as we use Unicode encoding). Choose from the following options when adding or modifying a script on the Script Picker page:- Add: Allows you to choose a script to add. Type or paste a PowerShell script into the pane or use one fo the following options:
- Open: Open a specific
.ps1file - Browse: Choose a script that's already approved from the Scripts list. Scripts with parameters will be hidden from the list.
- Clear: Clears the current script in the script pane
- Open: Open a specific
- Edit: Edit the currently selected script
- Delete: Removes the current script
- Script timeout (in seconds): The allowed time in seconds for the script to run before it times out
Complete the wizard.
Warning
- Starting in version 2111, pre and post-scripts require approval to take effect. Editing a script after it's approved will reset the approval state to Waiting for approval. Scripts that don't have approval will not run on clients.
- In version 2103 and later, scripts that have parameters aren't supported and the maximum script length is 50,000 bytes which is 25,000 characters (as we use Unicode encoding).
- For Configuration Manager 2010 and earlier, add scripts to your orchestration groups on the Pre-Script and Post-Script pages.
- Ensure pre-scripts and post-scripts are tested before using them for orchestration groups. The pre-scripts and post-scripts don't timeout and will run until the orchestration group member timeout has been reached. Scripts that have parameters aren't supported and the maximum script length is 5,000 characters.
Approvals for orchestration group scripts
(Introduced in version 2111)
Starting in version 2111, pre and post-scripts for orchestration groups require approval to take effect. If you select a script from a file, author, or modify your own script, approval for the script is required from another admin. When selecting an approved script from the Scripts library, no additional approval is needed. By default, users can't approve a script they've authored. These roles give an additional level of security against running a script without oversight. For ease of testing, you're able to disable script approval for the environment by changing the hierarchy setting.
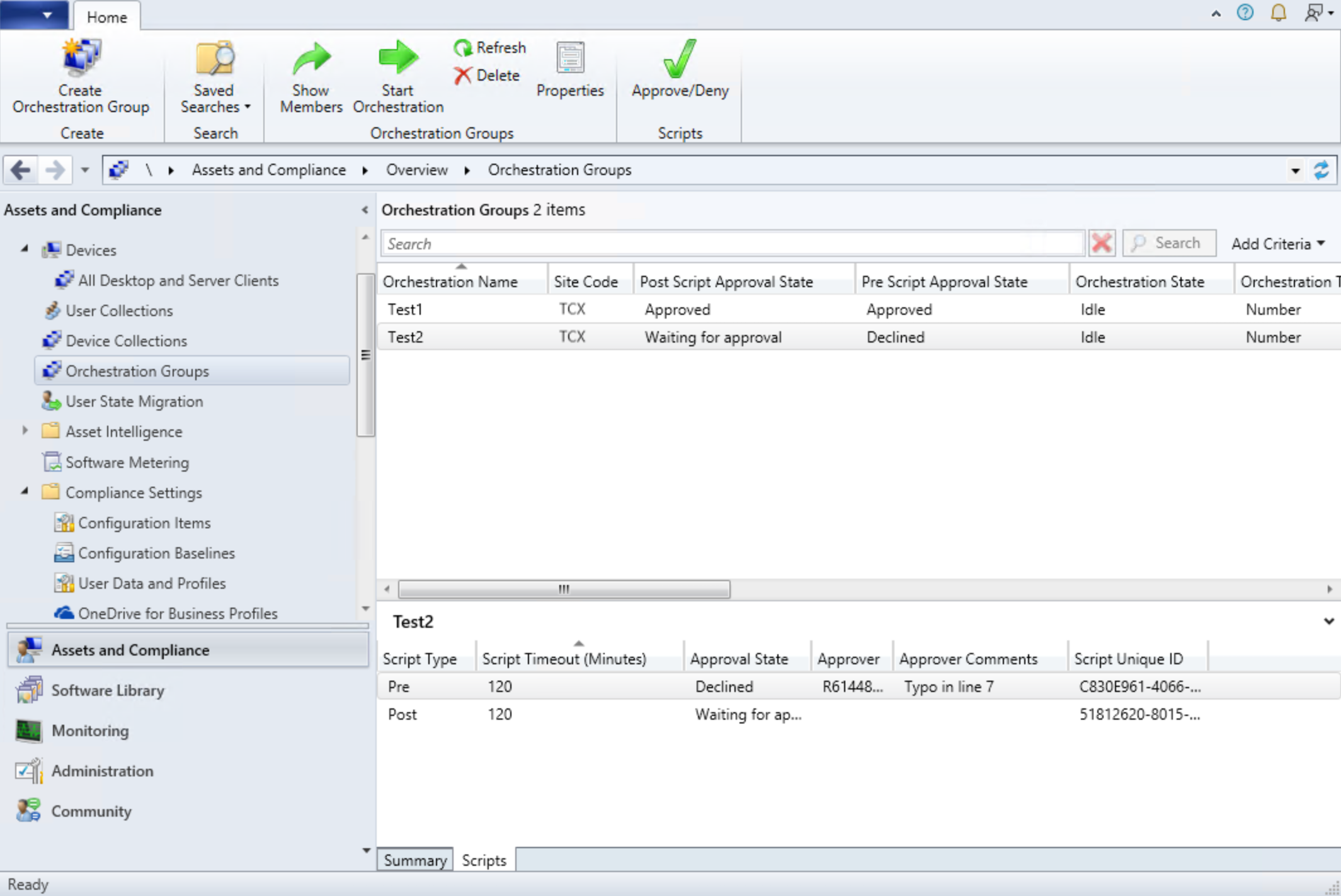
To assist you with script approval, the following two tabs were added to the details pane for Orchestration Groups in version 2111:
- Summary: Contains information about the selected orchestration group, including the Approval State of scripts.
- Scripts: Lists information about pre and post-scripts, including the timeout, approver, and approval state for each script.
Approval states for pre and post-scripts
The approval state for each of the scripts is displayed in the Scripts tab. Editing a script after it's approved will reset the approval state. The Approval State for each script is defined below:
- Approved: The script is approved. Approval is granted from either of the following ways:
- Selecting a script from the list of approved PowerShell scripts
- Manual approval of the script by selecting Approve from the ribbon or the right-click menu.
- Waiting for approval: The script is pending approval. Scripts that are written or edited directly in the code editor, or imported from a
.ps1file will start in this approval state. - Declined: The script was denied during the approval process.
Warning
Editing a script after it's approved will reset the approval state to Waiting for approval. This also means that the previously approved version of the script will not run if you start orchestration on the group while that script is in the Waiting for approval state. Scripts that don't have approval will not run on clients.
Tip
One way to update a script without any interruption is to create a new script in the Scripts library and get approval. Then choose the approved script from the library when you edit an orchestration group's pre or post-script. The already approved new script will replace the existing script immediately.
Permissions for approving scripts
Approving scripts for orchestration groups requires one of the following security roles:
- Full Administrator
- Operations Administrator
Approve or deny a script for an orchestration group
- From the Configuration Manager console, go to the Assets and Compliance workspace > Overview > Orchestration Groups.
- Select an orchestration group and then select the Scripts tab for the group.
- Select one of the scripts and choose Approve/Deny from either the ribbon or the right-click menu.
- Review the script from the Script Details page in the Approve or Deny Script wizard. Select Next when you're finished reviewing the script.
- On the Script Approval page in the wizard, select Approve or Deny. If needed, enter in a comment to be displayed in the Scripts detail pane.
- Complete the wizard to finish the approval process.
Edit or delete an orchestration group
To delete the orchestration group, select it then select Delete in the ribbon or from the right-click menu. To edit an orchestration group, select it then select Properties in the ribbon or from the right-click menu. Change the settings from the following tabs:
General:
- Name: The name of your orchestration group
- Description: Orchestration group description (optional)
- Orchestration Group timeout (in minutes): Time limit for all group members to complete update installation.
- Orchestration Group member timeout (in minutes): Time limit for a single device in the group to complete the update installation.
Member Selection:
- Site Code: Site code for the orchestration group.
- Members: Select Add to select more devices for the orchestration group. Choose Remove to remove the selected device.
Rules Selection:
- Allow a percentage of the machines to be updated at the same time, then select or enter a number for this percentage. Use this setting to allow for future flexibility of the size of the orchestration group. For example, your orchestration group contains 50 devices, and you set this value to 10. During a software update deployment, Configuration Manager allows five devices to simultaneously run the deployment. If you later increase the size of the orchestration group to 100 devices, then 10 devices update at once.
- Allow a number of the machines to be updated at the same time, then select or enter a number for this specific count. Use this setting to always limit to a specific number of devices, whatever the overall size of the orchestration group.
- Specify the maintenance sequence: Sort the selected resources to the proper order. Use this setting to explicitly define the order in which devices run the software update deployment.
Choose a Pre-installation script and Post-installation script for your orchestration group as needed. The script should return a value of
0for success. Any non-zero value is considered a script failure. Scripts with parameters can't be used and the maximum script length is 50,000 bytes which is 25,000 characters (as we use Unicode encoding) .For Configuration Manager version 2103 and later, choose a Pre-installation script and Post-installation script on the Script Picker page. Choose from the following options when adding or modifying a script:
- Add: Allows you to choose a script to add. Type or paste a PowerShell script into the pane or use one fo the following options:
- Open: Open a specific
.ps1file - Browse: Choose a script that's already approved from the Scripts list. Scripts with parameters will be hidden from the list.
- Clear: Clears the current script in the script pane
- Open: Open a specific
- Edit: Edit the currently selected script
- Delete: Removes the current script
- Script timeout (in seconds): The allowed time in seconds for the script to run before it times out
- Add: Allows you to choose a script to add. Type or paste a PowerShell script into the pane or use one fo the following options:
For Configuration Manager version 2010 and earlier, add scripts to your orchestration groups on the Pre-Script and Post-Script tabs.
Warning
- Starting in version 2111, pre and post-scripts require approval to take effect. Editing a script after it's approved will reset the approval state to Waiting for approval. Scripts that don't have approval will not run on clients.
- In version 2103 and later, scripts that have parameters aren't supported and the maximum script length is 50,000 bytes which is 25,000 characters (as we use Unicode encoding) .
- For Configuration Manager 2010 and earlier, add scripts to your orchestration groups on the Pre-Script and Post-Script tabs.
- Ensure pre-scripts and post-scripts are tested before using them for orchestration groups. The pre-scripts and post-scripts don't timeout and will run until the orchestration group member timeout has been reached. Scripts that have parameters aren't supported and the maximum script length is 5,000 characters.
Display orchestration groups and members
From the Assets and Compliance workspace, select the Orchestration Group node. To view members, select an orchestration group and select Show Members in the ribbon. For more information about the available columns for the nodes, see Monitor orchestration groups and members.
Start orchestration
Deploy software updates to a collection that contains the members of the orchestration group.
Orchestration starts when any client in the group tries to install any software update at deadline or during a maintenance window. It starts for the entire group, and makes sure that the devices update by following the orchestration group rules.
You can manually start orchestration by selecting it from the Orchestration Group node, then choosing Start Orchestration from the ribbon or right-click menu.
If needed, select Ignore all applicable windows for the members to start the installation immediately and bypass maintenance windows.
- This option was introduced in Configuration Manager version 2103
If an orchestration group is in a Failed state:
- Determine why the orchestration failed and resolve any issues.
- Reset the orchestration state for group members.
- From the Orchestration Group node, choose the Start Orchestration button to restart orchestration.
Tip
- Orchestration groups only apply to software update deployments. They don't apply to other deployments.
- You can right-click on an Orchestration Group member and select Reset Orchestration Group Member. This allows you to rerun orchestration.
Reset orchestration state for a group member
If you want to rerun orchestration on a group member, you can clear its state such as Complete or Failed. To clear the state, right-click on the Orchestration Group member and select Reset Orchestration Group Member. You can also select Reset Orchestration Group Member from the ribbon. Before resetting the state, you should check the client to see why it failed and correct any issues found.
Automate with Windows PowerShell
You can use the following PowerShell cmdlets to automate some of these tasks:
Get-CMOrchestrationGroup: Use this cmdlet to get an orchestration group object by name or ID. You can use this object to start, remove, or configure the orchestration group.
Invoke-CMOrchestrationGroup: Use this cmdlet to start orchestration.
New-CMOrchestrationGroup: Use this cmdlet to create a new orchestration group.
Remove-CMOrchestrationGroup: Use this cmdlet to remove an orchestration group.
Set-CMOrchestrationGroup: Use this cmdlet to configure an orchestration group.