Напомена
Приступ овој страници захтева ауторизацију. Можете покушати да се пријавите или промените директоријуме.
Приступ овој страници захтева ауторизацију. Можете покушати да промените директоријуме.
You can use Microsoft Dynamics Lifecycle Services (LCS) to perform a refresh of the database to a sandbox user acceptance testing (UAT) environment. A database refresh lets you copy the transactional and financial reporting databases of your production environment into the target, sandbox UAT environment. If you have another sandbox environment, you can also copy the databases from that environment to your target, sandbox UAT environment.
Important
Copying production data during business hours or peak hours could have an impact on the production system. It's highly recommended to do the refresh database operation during off-peak hours and limit only one refresh operation at a time.
Copying production data to your sandbox environment for the purpose of production reporting isn't supported.
Self-service database refresh
With the goal of providing Data Application Lifecycle Management (also referred to as DataALM) capabilities to our customers without relying on human or manual processes, the Lifecycle Services team has introduced an automated Refresh database action. This process is outlined below:
- Visit your target sandbox on the Environment Details page, and click the Maintain > Move database menu option.
- Select the Refresh database option and choose your source environment.
- Note the warnings and review the list of data elements that aren't copied from the source environment.
- The refresh operation begins immediately.
Refresh operation failed
If there's a failure, the refresh operation automatically rolls back. Your target sandbox environment is restored to the state it was before the refresh began. This is made possible by the Azure SQL point-in-time restore capability to restore the database. This is often required if a customization that is present in the target sandbox can't complete a database synchronization with the newly refreshed data.
To determine the root cause of the failure, use the Environment change history page to download the logs for the failed operation.
Data elements that aren't copied during refresh
The information in this section lists certain elements of the database that aren't copied over to the target environment during a database refresh operation.
When refreshing a production environment to a sandbox environment or a sandbox to another sandbox environment
- Email addresses in the LogisticsElectronicAddress table.
- SMTP Relay server in the SysEmailParameters table.
- Print Management settings in the PrintMgmtSettings and PrintMgmtDocInstance tables.
- All users except the admin are set to Disabled status.
- Dimension log and cache status tables including DIMENSIONHASHMESSAGELOG, DIMENSIONDATAINTEGRITYLOG, DIMENSIONVALUERENAMEAUDIT, DIMENSIONVALUEDELETEAUDIT, DIMENSIONATTRIBUTEVALUECOMBINATIONSTATUS, DIMENSIONATTRIBUTEVALUEGROUPSTATUS, DIMENSIONDATAENTITYSFKCACHE, DIMENSIONREFERENCES.
When refreshing from sandbox environment to production environment
This is also referred to as Golden configuration promotion.
- Batch job history is stored in the BatchJobHistory, BatchHistory, and BatchConstraintHistory tables.
These elements are removed for all database refresh operations
- Environment-specific records in the SysServerConfig, SysServerSessions, SysCorpNetPrinters, SysClientSessions, BatchServerConfig, and BatchServerGroup tables.
- All files stored in Azure blob storage. This includes document attachments (from the DocuValue and DocuDeletedValue tables) and custom Microsoft Office templates (from the DocuTemplate table).
- All batch jobs are set to Withhold status.
- All users will have their partition value reset to the "initial" partition record ID.
- All Microsoft-encrypted fields are cleared, because they can't be decrypted on a different database server. An example is the Password field in the SysEmailSMTPPassword table.
- Maintenance mode settings are disabled even if it was enabled in source.
- Dual-write configuration. To set up a new link on the target environment after this operation is successful, see Enable Power Platform Integration.
- Any change-tracking on entities are disabled.
- Service endpoints for business events and data events are removed.
Some of these elements aren't copied because they're environment-specific. Examples include BatchServerConfig and SysCorpNetPrinters records. Other elements aren't copied because of the volume of support tickets. For example, duplicate emails might be sent because Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is still enabled in the UAT environment, invalid integration messages might be sent because batch jobs are still enabled, and users might be enabled before admins can perform post-refresh cleanup activities.
Environment administrator
The System Administrator account in the target environment (UserId of 'Admin') is reset to the value found in the web.config file on the target. This should be the same value as that of the Administrator from Lifecycle Services. To preview which account this is, visit your target sandbox Environment Details page in LCS. The value of the Environment Administrator field that was selected when the environment was first deployed is updated to be the System Administrator in the transactional database. This also means that the tenant of the environment is that of the Environment Administrator.
If you have used the Admin User Provisioning Tool on your environment to change the web.config file to a different value, it might not match what is in Lifecycle Services. If you require a different account to be used, you need to deallocate and delete the target sandbox, and redeploy selecting another account. After this, you can perform another refresh database action to restore the data.
An environment can't be refreshed from one tenant to another. This restriction applies even to .onmicrosoft.com tenants. You should make sure that the admin accounts in the source and target environments are from the same tenant domain.
Conditions of a database refresh
The following is the list of requirements and conditions of operation for a database refresh:
- A refresh performs a delete operation on the original target database.
- The target environment is available until the database copy has reached the target server. After that point, the environment is offline until the refresh process is completed.
- The refresh affects only the application and Financial Reporting databases.
- No file stored in Azure blob storage is copied from one environment to another. This includes document attachments and custom Microsoft Office templates. These documents won't be changed and remains in their current state.
- All users except the Admin user and other internal service user accounts are unavailable. This process allows the Admin user to delete or obfuscate data before allowing other users back into the system.
- The Admin user must make required configuration changes, such as reconnecting integration endpoints to specific services or URLs.
- All data management framework with recurring import and export jobs must be fully processed and stopped in the target system prior to initiating the restore. In addition, we recommend that you select the database from the source after all recurring import and export jobs have been fully processed. This ensures there are no orphaned files in Azure storage from either system. This is important because orphaned files can't be processed after the database is restored in the target environment. After the restore, the integration jobs can be resumed.
- Any user with a role of Project owner or Environment manager in LCS has access to the SQL and machine credentials for all nonproduction environments.
- The databases must be hosted in the same Azure geographic region, unless the databases are Spartan-managed. Databases are Spartan-managed when you see 'spartan' as part of the fully qualified SQL server address.
- The allocated database capacity of the source environment must be less than the maximum database capacity of the target environment.
Steps to complete after a database refresh for environments that use Commerce functionality
Important
When a Commerce headquarters database (previously called AOS database) is migrated, the associated Commerce Scale Units (CSUs) are not moved. In several cases, depending on the features that are in use, a CSU redeployment may be required. Redeployment must then be followed by a full synchronization of data to the CSU. In extreme scenarios where data discrepancies still exist, the final action is to delete the CSU, deploy a fresh CSU to replace it, and then perform a full synchronization of data to the new CSU.
Some environment-specific records are not included in automated database movement operations and require additional steps. These include the following:
- Commerce self-service installer references.
- Commerce Scale Unit channel database configuration records.
If you copy a database between environments, Commerce capabilities in the destination environment won't be fully functional until you perform the following additional steps.
Initialize Commerce Scale Units
If you're moving a database to a sandbox user acceptance testing (UAT) or production environment, you must Initialize Commerce Scale Unit after the database movement operation is complete. The Commerce Scale Unit's association from the source environment won't copy over to the destination environment.
Synchronize Commerce self-service installers
To be able to access Commerce self-service installers in headquarters, you must Synchronize self-service installers after the database movement operation is complete.
Important
The environment reprovisioning step has now been fully automated as part of database movement operations, and no longer needs to be run manually. The environment reprovisioning tool is still available in the asset library, but is only required for restoring a database to a development environment running Commerce version 10.0.37 or earlier. For development environments running Commerce version 10.0.38 and later, the environment reprovisioning tool doesn't apply because these environments use a sealed CSU.
To run the environment reprovisioning tool on the destination environment, run the following steps:
- In your project's Asset Library, in the Software deployable packages section, select Import.
- From the list of shared assets, select the Environment Reprovisioning Tool.
- On the Environment details page for your destination environment, select Maintain > Apply updates.
- Select the Environment Reprovisioning tool that you uploaded earlier, and then select Apply to apply the package.
- Monitor the progress of the package deployment.
For more information about how to apply a deployable package, see Create deployable packages of models. For more information about how to manually apply a deployable package, see Install deployable packages from the command line.
Reactivate POS devices
If you use point of sale (POS) devices, you must activate the POS devices again after you import a database. Previously activated devices in the destination environment will no longer function. For more information, see Point of sale device activation.
Known issues
The Restore operation fails if the sandbox customizations are incompatible with production data
Even if a customization is successfully added to the sandbox environment (that is, the customer's AOT deployable package is successfully installed via LCS), it might not succeed for production data. For example, a customer adds a unique index on Vendor Name to the VendTable table. This customization can be successfully installed if there are no duplicate vendor names in the sandbox environment. However, when the production database is brought in as part of the Restore operation, installation might fail if there are duplicates in the dataset that is inbound to the sandbox environment. Duplicates in this dataset aren't supported. Therefore, you must remove the customization before you can have a successful Restore operation.
Refresh is denied for environments that run Platform update 20 or earlier
The database refresh process can't currently be completed if the environment is running Platform update 20 or earlier. For more information, see the list of currently supported platform updates.
Incompatible version of Financial Reporting between source and target environments
The database refresh process (self-service or via a service request) can't be completed successfully if the version of Financial Reporting in the target environment is earlier than the version in the source environment. To resolve this issue, update both environments so that they have the latest version of Financial Reporting.
To determine the version you have installed in your source and target environments, visit the View detailed version information link on the Environment Details page.
Search for MRApplicationService and ensure that the target environment is greater than or equal to the source environment.
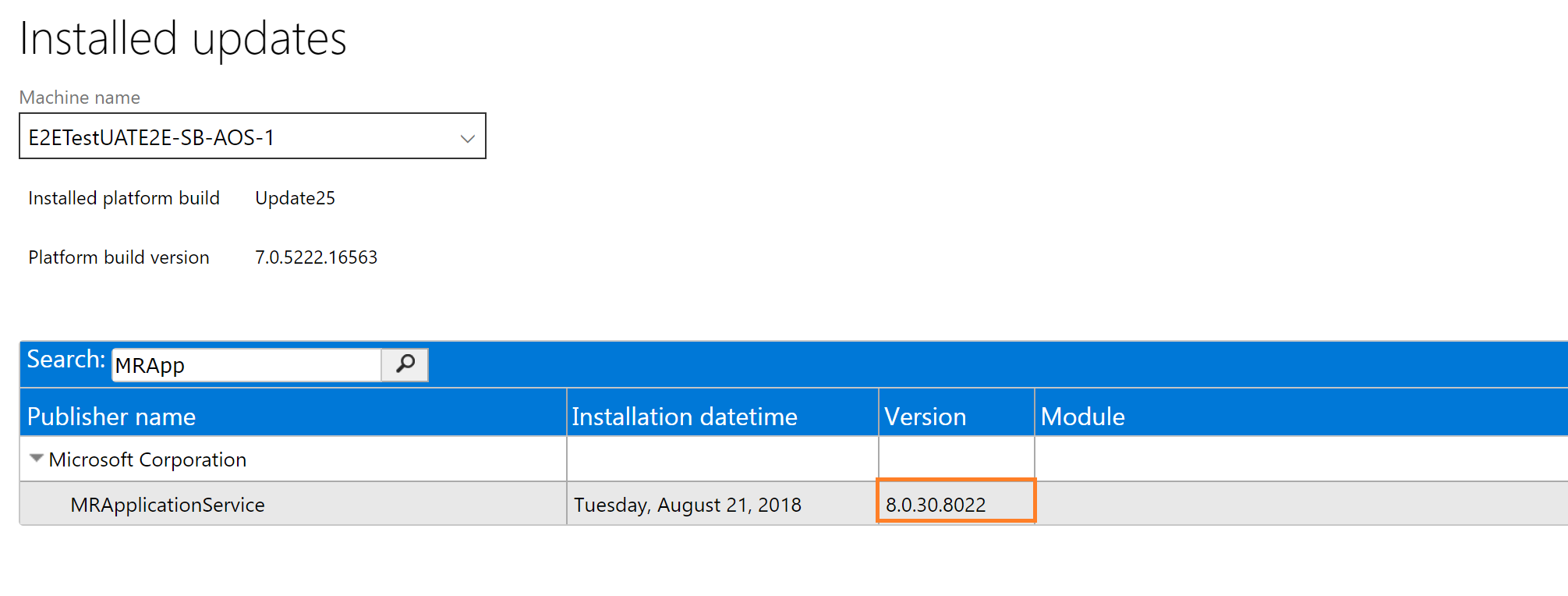
For customers that use version 8.1 or later:
- Go to the Update tiles for your UAT environment. Save the updates to your Project asset library.
- Apply this package to your UAT environment.
- Verify that the error has been resolved.
For customers that use version 8.0 or earlier:
- Review the Environment history of your source environment. Specifically, look for any "Platform and application binary package" that might have been deployed to the source environment and not the target environment.
- Apply this binary package to your target environment.
- Verify that the error has been resolved.
Incompatible application versions between source and target environments
The database refresh process (self-service or via service request) can't be completed if the Application release of your source and target environments aren't the same. This is because the data upgrade process isn't executed by database movement operations such as refresh, and data loss can occur.
When upgrading your sandbox UAT environment to a newer Application version (for example, 7.3 to 8.1), be sure to perform the database refresh action prior to starting the upgrade. After your sandbox is upgraded to the newer version, you can't restore an older production environment database in to the sandbox UAT environment.
Conversely, if your production environment is newer than your target sandbox, you need to either upgrade the target sandbox prior to the refresh or deallocate, delete, and redeploy prior to performing the refresh.