Belešku
Pristup ovoj stranici zahteva autorizaciju. Možete pokušati da se prijavite ili da promenite direktorijume.
Pristup ovoj stranici zahteva autorizaciju. Možete pokušati da promenite direktorijume.
To deploy your JavaScript-based app to Azure, you move a file or set of files to Azure to be served via an HTTP endpoint. The process of moving the files is called deployment.
Prerequisites
- Azure subscription - create one for free.
- Node.js LTS.
- A GitHub account if you plan to deploy from a GitHub repository.
Deployment methods
Azure offers various deployment methods to suit different needs. Here are some common methods:
| Method | Details |
|---|---|
| Azure Developer CLI | Ideal for developers who prefer command-line tools and need to automate the provisioning and deployment of resources. |
| Visual Studio Code Extensions | Suitable for manual, testing, or infrequent deployments. Requires the relevant Azure extensions installed locally. |
| Azure CLI | Useful for manual or occasional deployments. Requires the Azure CLI installed locally. |
| GitHub Actions | Best for automated or continuous deployments triggered by changes in your GitHub repository. |
Other deployment methods exist, based on the specific service. For example, Azure app service supports a wide variety of deployment methods:
You can redeploy to your App service using any of the provided methods even if you didn't use that method to originally deploy. You may have some configuration before redeploying if you're switching methods.
Azure hosting services for JavaScript apps
Azure provides multiple hosting services optimized for different JavaScript application scenarios:
| Service | Best For | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Azure Static Web Apps | Modern web apps with static frontends (React, Vue, Angular) and optional serverless APIs | Free SSL, global CDN, staging environments on pull requests, integrated authentication |
| Azure App Service | Full-featured web applications and REST APIs | Built-in autoscaling, deployment slots, easy integration with Azure services |
| Azure Functions | Event-driven serverless applications and microservices | Pay-per-execution pricing, automatic scaling, multiple triggers and bindings |
| Azure Container Apps | Containerized applications and microservices | Kubernetes-powered serverless containers, Dapr integration, event-driven scaling |
For more information on choosing the right hosting service, see Hosting applications on Azure.
Build steps
Depending on your application's complexity and deployment needs, you can choose to build your JavaScript app either before or during deployment:
- Build before deployment: For complex or lengthy builds, package your application into a zip file and deploy it. A deployment package allows you to control and test the build before deployment.
- Build during deployment: For simpler builds, use the Azure-provided environment variable SCM_DO_BUILD_DURING_DEPLOYMENT=true to build your app during deployment.
Deployment slots
Deployment slots in Azure App Service allow you to create separate environments for staging and production. The use of slots enables you to test your app in a staging environment before swapping it with the production slot, ensuring a smooth and error-free deployment. Learn more about deployment slots.
Don't use deployment slots to mix deployment purposes. All deployment slots share the app service so you need to make sure the traffic patterns and intended use of all slots are the same. If you need to have a hosted test or stage environment that should be a separate app service.
Deploy with Azure Developer CLI
The Azure Developer CLI (azd) simplifies the process of deploying your app to Azure. Follow these steps:
Install the Azure Developer CLI.
Find an existing project which uses many of the same resources your project uses.
Initialize a local version of the project for use as an infrastructure template for your own project.
azd init --template <template-name>Create the resources and deploy the code to Azure.
azd up
Deploy with Visual Studio Code
To deploy or redeploy your App service app with Visual Studio Code, complete the following steps:
Install the related Azure extensions, for example AzureApp Service or Azure Functions.
Open the Azure explorer. Select the Azure icon in the primary side bar or use the keyboard shortcut (Shift + Alt + A).
In the Resources group, select your subscription and service.
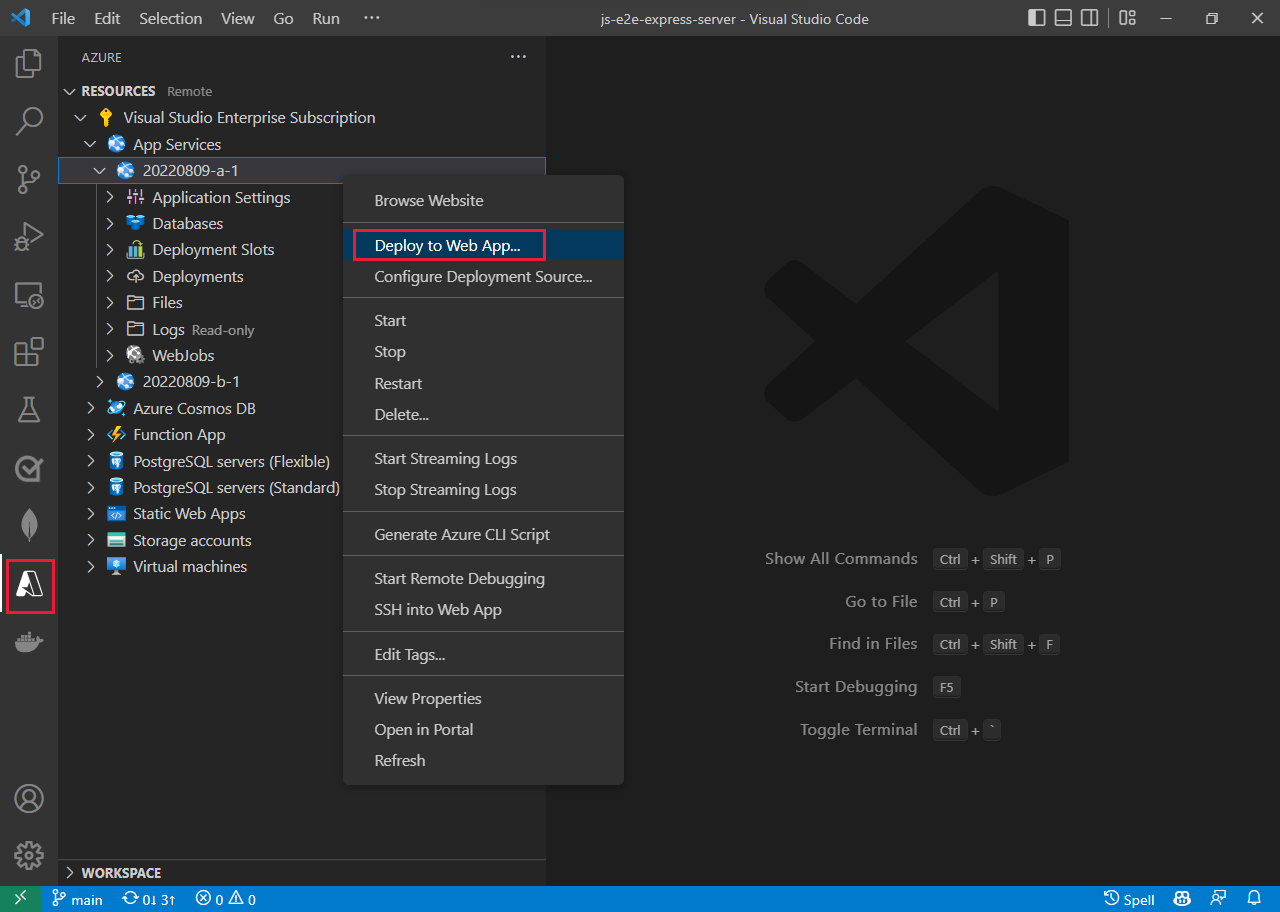
Right-click your service then select Deploy to Web App....
Deploy to Azure Static Web Apps
Azure Static Web Apps is ideal for modern web applications built with JavaScript frameworks. To deploy:
- Install the Azure Static Web Apps extension for Visual Studio Code.
- Build your application locally to ensure it works as expected.
- In Visual Studio Code, open the Azure explorer and find Azure Static Web Apps.
- Right-click on your subscription and select Create Static Web App.
- Follow the prompts to connect your GitHub repository. Azure automatically creates a GitHub Actions workflow.
- Push changes to your repository to trigger automatic deployments.
For more details, see Deploy your web app to Azure Static Web Apps.
Deploy to Azure Container Apps
Azure Container Apps provides serverless container hosting for JavaScript applications. To deploy:
- Containerize your application using Docker. Create a Dockerfile in your project root.
- Build and test your container locally.
- Push your container image to Azure Container Registry.
- Use the Azure Container Apps extension or Azure CLI to create and deploy your container app.
For a complete guide, see JavaScript on Azure Container Apps overview.
Connect to your Azure hosted environment
- For manual or occasional access to your hosted environments, refer to how to view files in your Azure hosted environment.
- For automated or consistent access, consider taking the steps to set up one of the deployment methods.
View files in Azure hosted environment
There are several ways to immediately see the files in your hosted Azure Web app or Function app. If you're using slots in your hosted resource, you need to make sure you are on the correct slot before viewing files.
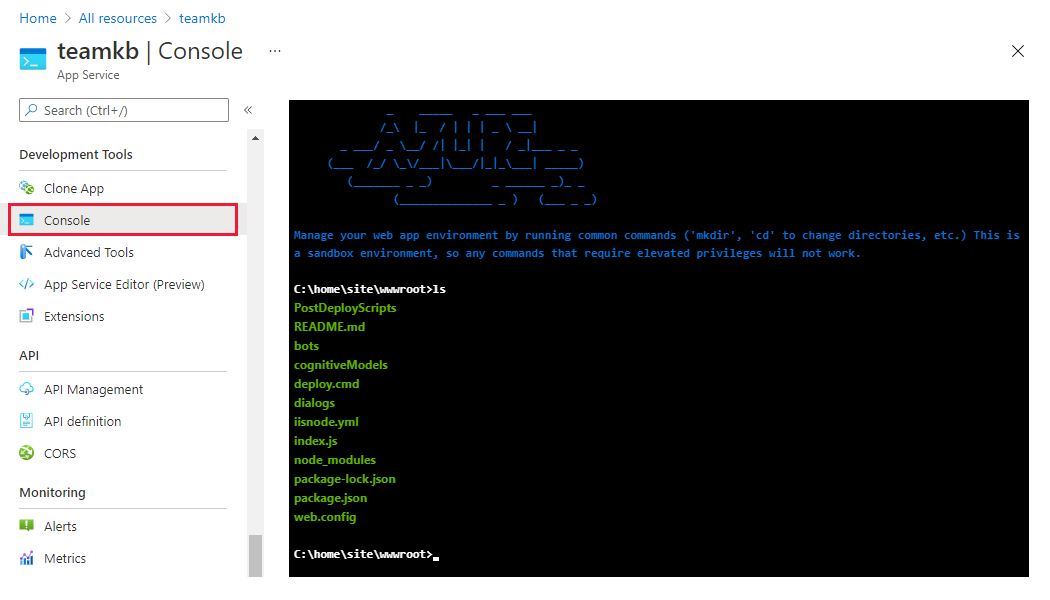
View files in Azure portal - select Console under Development tools for your hosting resource.
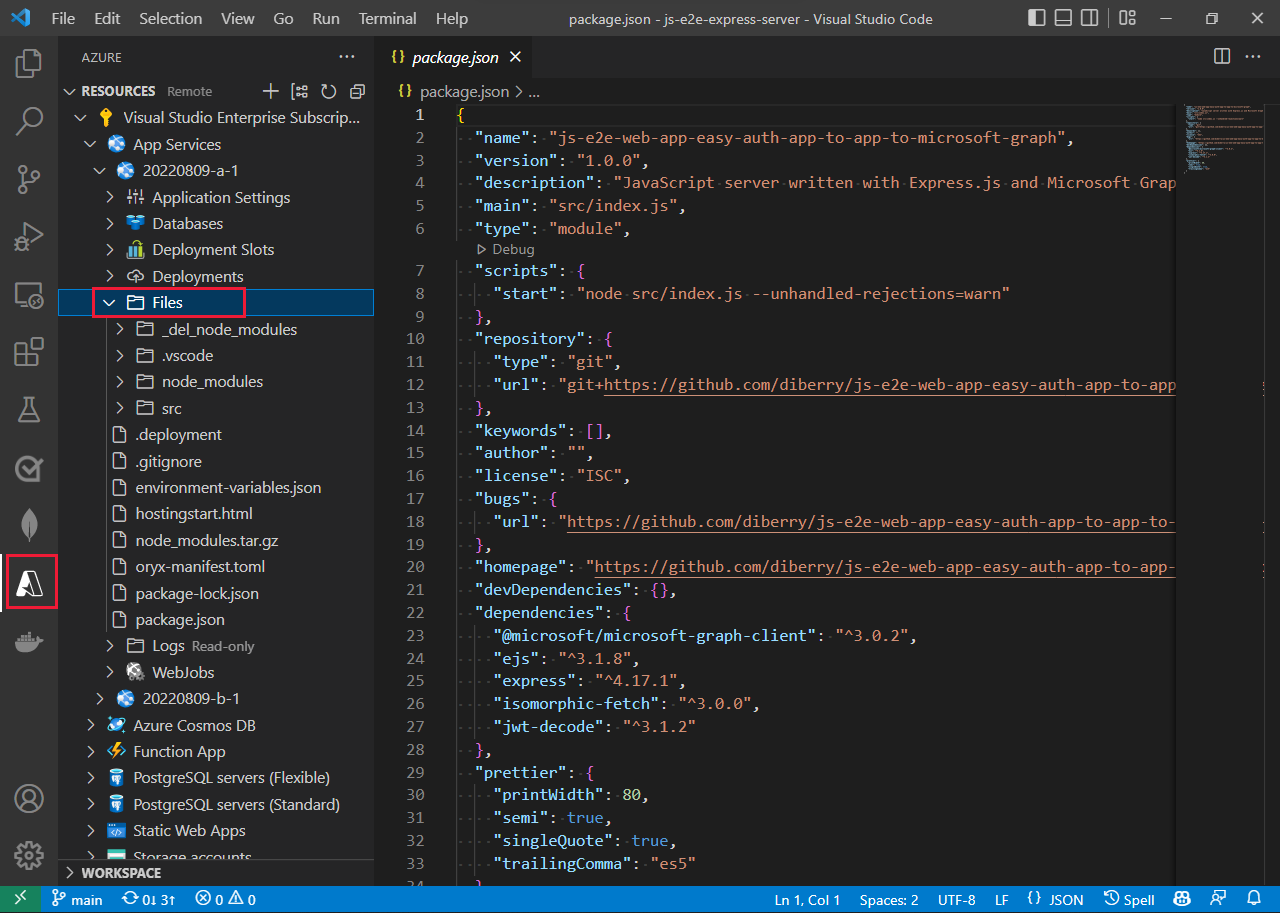
View files in VS Code extension: - select the Azure icon in the Activity bar. In the Resources section, select your subscription and service. The Files node provides a view of your remote files.
- Azure App service and Azure Functions extensions both provide a view of the remote files.
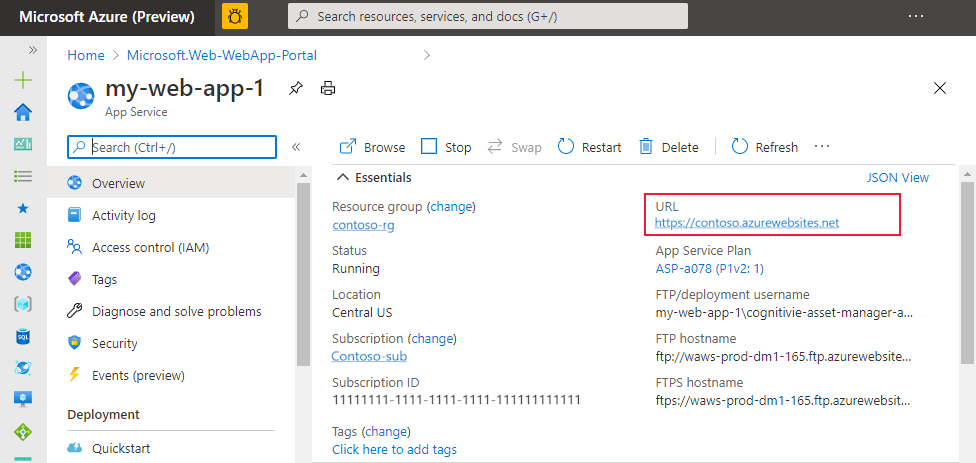
View HTTP endpoint in Azure portal
View your HTTP endpoint from the service's Overview page on the Azure portal.