Authenticated scan for Windows
Applies to:
- Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management
- Microsoft Defender XDR
- Microsoft Defender for Servers Plan 2
Note
To use this feature you'll require Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management Standalone or if you're already a Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Plan 2 customer, the Defender Vulnerability Management add-on.
Authenticated scan for Windows provides the ability to run scans on unmanaged Windows devices. You can remotely target by IP ranges or hostnames and scan Windows services by providing Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management with credentials to remotely access the devices. Once configured the targeted unmanaged devices will be scanned regularly for software vulnerabilities. By default, the scan will run every four hours with options to change this interval or have it only run once.
Security administrators can then see the latest security recommendations and review recently discovered vulnerabilities for the targeted device in the Microsoft Defender portal.
Tip
Did you know you can try all the features in Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management for free? Find out how to sign up for a free trial.
Scanner Installation
Similar to network device authenticated scan, you'll need a scanning device with the scanner installed. If you don't already have the scanner installed, see Install the scanner for steps on how to download and install it.
Note
No changes are required for pre-existing installed scanners.
Pre-requisites
The following section lists the pre-requisites you need to configure to use Authenticated scan for Windows.
Scanning account
A scanning account is required to remotely access the devices. This must be a Group Managed Service Account (gMsa).
Note
We recommend the gMSA account is a least privileged account with only the required scanning permissions and is set to cycle the password regularly.
To create a gMsa account:
On your domain controller in a PowerShell window, run:
New-ADServiceAccount -Name gmsa1 -PrincipalsAllowedToRetrieveManagedPassword scanner-win11-i$ -KerberosEncryptionType RC4, AES128, AES256 -Verbose- gmsa1 stands for the name of the account you are creating, and scanner-win11-I$ stands for the machine name where the scanner agent will run. Only this machine will be able to retrieve the account password. You can provide a comma separated list of machines.
- Modifying an existing account can be done with Get-ADServiceAccount and Set-ADServiceAccount
To Install the AD Service Account, on the machine where the scanner agent will run using an elevated PowerShell window, run:
Install-ADServiceAccount -Identity gmsa1
If your PowerShell doesn't recognize those commands, it probably means you're missing a required PowerShell module. Instructions on how to install the module vary depending on your operating system. For more information, see Getting Started with Group Managed Service Accounts.
Devices to be scanned
Use the table below for guidance on the configurations required, along with the permissions needed for the scanning account, on each device to be scanned:
Note
The below steps are only one recommended way to configure the permissions on each device to be scanned and uses the Performance Monitor Users group. You can also configure the permissions in the following ways:
- Add the account to a different user group and give all the permissions required to that group.
- Give these permissions explicitly to the scanning account.
To configure and apply the permission to a group of devices to be scanned using a group policy, see Configure a group of devices with a group policy.
| Devices to be scanned requirements | Description |
|---|---|
| Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) is enabled | To enable remote Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI):
|
| Scanning account is a member of Performance Monitor Users group | The scanning account must be a member of the Performance Monitor Users group on the device to be scanned. |
| Performance Monitor Users group has 'Enable Account' and 'Remote Enable' permissions on Root/CIMV2 WMI namespace | To verify or enable these permissions:
|
| Performance Monitor Users group should have permissions on DCOM operations | To verify or enable these permissions:
|
Configure a group of devices with a group policy
A group policy will let you bulk apply the configurations required, as well as the permissions required for the scanning account, to a group of devices to be scanned.
Follow these steps on a domain controller to configure a group of devices at the same time:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Create a new Group Policy Object |
|
| Enable Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) | To enable remote Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI):
|
| Allow WMI through the firewall | To allow Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) through the firewall:
|
| Grant permissions to perform DCOM operations | To grant permissions to perform DCOM operations:
|
| Grant permissions to the Root\CIMV2 WMI namespace by running a PowerShell script via group policy: |
|
Example PowerShell script
Use the following PowerShell script as a starting point to grant permissions to the Root\CIMV2 WMI namespace via group policy:
Param ()
Process {
$ErrorActionPreference = "Stop"
$accountSID = "S-1-5-32-558" # Performance Monitor Users built-in group, please change or pass parameter as you wish
$computerName = "."
$remoteparams = @{ComputerName=$computerName}
$invokeparams = @{Namespace="root\cimv2";Path="__systemsecurity=@"} + $remoteParams
$output = Invoke-WmiMethod @invokeparams -Name GetSecurityDescriptor
if ($output.ReturnValue -ne 0) {
throw "GetSecurityDescriptor failed: $($output.ReturnValue)"
}
$acl = $output.Descriptor
$CONTAINER_INHERIT_ACE_FLAG = 0x2
$ACCESS_MASK = 0x21 # Enable Account + Remote Enable
$ace = (New-Object System.Management.ManagementClass("win32_Ace")).CreateInstance()
$ace.AccessMask = $ACCESS_MASK
$ace.AceFlags = $CONTAINER_INHERIT_ACE_FLAG
$trustee = (New-Object System.Management.ManagementClass("win32_Trustee")).CreateInstance()
$trustee.SidString = $accountSID
$ace.Trustee = $trustee
$ACCESS_ALLOWED_ACE_TYPE = 0x0
$ace.AceType = $ACCESS_ALLOWED_ACE_TYPE
$acl.DACL += $ace.psobject.immediateBaseObject
$setparams = @{Name="SetSecurityDescriptor";ArgumentList=$acl.psobject.immediateBaseObject} + $invokeParams
$output = Invoke-WmiMethod @setparams
if ($output.ReturnValue -ne 0) {
throw "SetSecurityDescriptor failed: $($output.ReturnValue)"
}
}
Once the GPO policy is applied to a device, all the required settings will be applied and your gMSA account will be able to access and scan the device.
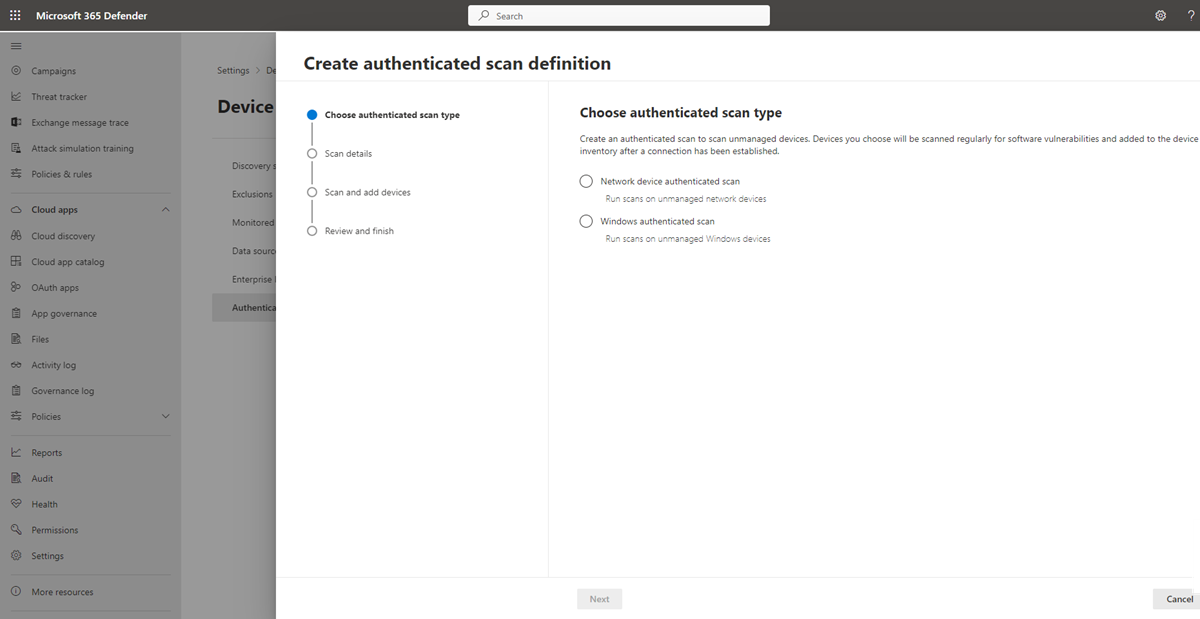
Configure a new authenticated scan
To configure a new authenticated scan:
Go to Settings > Device discovery > Authenticated scans in the Microsoft Defender portal.
Select Add new scan and choose Windows authenticated scan and select Next.
Enter a Scan name.
Select the Scanning device: The onboarded device you'll use to scan the unmanaged devices.
Enter the Target (range): The IP address ranges or hostnames you want to scan. You can either enter the addresses or import a CSV file. Importing a file will override any manually added addresses.
Select the Scan interval: By default, the scan will run every four hours, you can change the scan interval or have it only run once, by selecting 'Do not repeat'.
Choose your Authentication method - there are two options to choose from:
- Kerberos (preferred)
- Negotiate
Note
Negotiate option will fallback to NTLM in cases where Kerberos fails. Using NTLM is not recommended as it is not a secure protocol.
Enter the credentials Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management will use to remotely access the devices:
- Use azure KeyVault: If you manage your credentials in Azure KeyVault you can enter the Azure KeyVault URL and Azure KeyVault secret name to be accessed by the scanning device to provide credentials
- For the Azure KeyVault secret value use gMSA account details in the format Domain;Username
Select Next to run or skip the test scan. For more information on test scans, see Scan and add network devices.
Select Next to review the settings and then select Submit to create your new authenticated scan.
Note
As the authenticated scanner currently uses an encryption algorithm that is not compliant with Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS), the scanner can't operate when an organization enforces the use of FIPS compliant algorithms.
To allow algorithms that are not compliant with FIPS, set the following value in the registry for the devices where the scanner will run: Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\FipsAlgorithmPolicy with a DWORD value named Enabled and value of 0x0
FIPS compliant algorithms are only used in relation to departments and agencies of the United States federal government.
Authenticated scan for Windows APIs
You can use APIs to create a new scan and view all existing configured scans in your organization. For more information, see:
- Get all scan definitions
- Add, delete or update a scan definition
- Get all scan agents
- Get scan agent by Id
- Get scan history by definition
- Get scan history by session