How to use Data Wrangler on Spark DataFrames
Data Wrangler, a notebook-based tool for exploratory data analysis, now supports both Spark DataFrames and pandas DataFrames. It generates PySpark code, in addition to Python code. For a general overview of Data Wrangler, covering how to explore and transform pandas DataFrames, visit the the main tutorial. This tutorial shows how to use Data Wrangler to explore and transform Spark DataFrames.
Prerequisites
Get a Microsoft Fabric subscription. Or, sign up for a free Microsoft Fabric trial.
Sign in to Microsoft Fabric.
Use the experience switcher on the bottom left side of your home page to switch to Fabric.
Limitations
- Custom code operations are currently supported only for pandas DataFrames.
- The Data Wrangler display works best on large monitors, although you can minimize or hide different portions of the interface, to accommodate smaller screens.
Launching Data Wrangler with a Spark DataFrame
Users can open Spark DataFrames in Data Wrangler directly from a Microsoft Fabric notebook, by navigating to the same dropdown prompt where pandas DataFrames are displayed. A list of active Spark DataFrames appears in the dropdown beneath the list of active pandas variables.
This code snippet creates a Spark DataFrame with the same sample data used in the pandas Data Wrangler tutorial:
import pandas as pd
# Read a CSV into a Spark DataFrame
sdf = spark.createDataFrame(pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/plotly/datasets/master/titanic.csv"))
display(sdf)
In the notebook ribbon "Home" tab, use the Data Wrangler dropdown prompt to browse active DataFrames available for editing. Select the one you wish to open in Data Wrangler.
Tip
Data Wrangler cannot be opened while the notebook kernel is busy. An executing cell must finish its execution before Data Wrangler can launch, as shown in this screenshot:
Choosing custom samples
Data Wrangler automatically converts Spark DataFrames to pandas samples for performance reasons. However, all the code that the tool generates is ultimately translated to PySpark when it exports back to the notebook. As with any pandas DataFrame, you can customize the default sample. To open a custom sample of any active DataFrame with Data Wrangler, select "Choose custom sample" from the dropdown, as shown in this screenshot:
This launches a pop-up with options to specify the size of the desired sample (number of rows) and the sampling method (first records, last records, or a random set), as shown in this screenshot:
Viewing summary statistics
When Data Wrangler loads, it displays an informational banner above the preview grid. This banner explains that Spark DataFrames are temporarily converted to pandas samples, but all generated code is ultimately be converted to PySpark. Past that, using Data Wrangler on Spark DataFrames is no different from using it on pandas DataFrames. A descriptive overview in the "Summary" panel displays information about the sample's dimensions, missing values, and more. Selection of any column in the Data Wrangler grid prompts the "Summary" panel to update and display descriptive statistics about that specific column. Quick insights about every column are also available in its header.
Tip
Column-specific statistics and visuals (both in the "Summary" panel and in the column headers) depend on the column datatype. For instance, a binned histogram of a numeric column will appear in the column header only if the column is cast as a numeric type, as shown in this screenshot:
Browsing data-cleaning operations
A searchable list of data-cleaning steps can be found in the "Operations" panel. From the "Operations" panel, selection of a data-cleaning step prompts you to provide a target column or columns, along with any necessary parameters to complete the step. For example, the prompt to numerically scale a column requires a new range of values, as shown in this screenshot:
Tip
You can apply a smaller selection of operations from the menu of each column header, as shown in this screenshot:
Previewing and applying operations
The Data Wrangler display grid automatically previews the results of a selected operation, and the corresponding code automatically appears in the panel below the grid. To commit the previewed code, select "Apply" in either place. To delete the previewed code and try a new operation, select "Discard" as shown in this screenshot:
Once an operation is applied, the Data Wrangler display grid and summary statistics update to reflect the results. The code appears in the running list of committed operations, located in the "Cleaning steps" panel, as shown in this screenshot:
Tip
You can always undo the most recently applied step. In the "Cleaning steps" panel, a trash can icon will appear if you hover your cursor over that most recently applied step, as shown in this screenshot:
This table summarizes the operations that Data Wrangler currently supports:
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| Sort | Sort a column in ascending or descending order |
| Filter | Filter rows based on one or more conditions |
| One-hot encode | Create new columns for each unique value in an existing column, indicating the presence or absence of those values per row |
| One-hot encode with delimiter | Split and one-hot encode categorical data using a delimiter |
| Change column type | Change the data type of a column |
| Drop column | Delete one or more columns |
| Select column | Choose one or more columns to keep, and delete the rest |
| Rename column | Rename a column |
| Drop missing values | Remove rows with missing values |
| Drop duplicate rows | Drop all rows that have duplicate values in one or more columns |
| Fill missing values | Replace cells with missing values with a new value |
| Find and replace | Replace cells with an exact matching pattern |
| Group by column and aggregate | Group by column values and aggregate results |
| Strip whitespace | Remove whitespace from the beginning and end of text |
| Split text | Split a column into several columns based on a user-defined delimiter |
| Convert text to lowercase | Convert text to lowercase |
| Convert text to uppercase | Convert text to UPPERCASE |
| Scale min/max values | Scale a numerical column between a minimum and maximum value |
| Flash Fill | Automatically create a new column based on examples derived from an existing column |
Modify your display
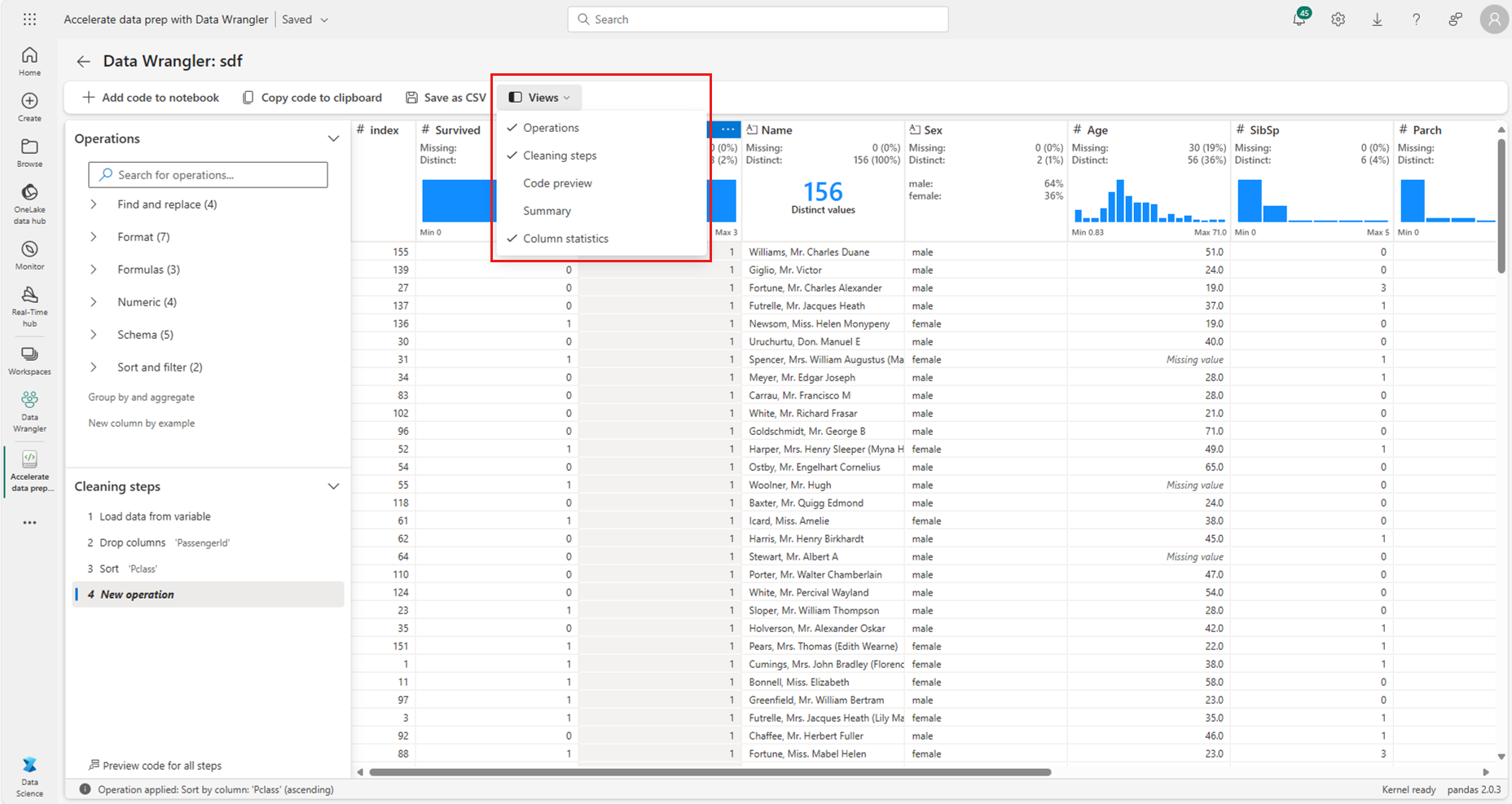
At any time, you can customize the interface with the "Views" tab in the toolbar located above the Data Wrangler display grid. This can hide or show different panes based on your preferences and screen size, as shown in this screenshot:
Saving and exporting code
The toolbar above the Data Wrangler display grid provides options to save the generated code. You can copy the code to the clipboard, or export it to the notebook as a function. For Spark DataFrames, all the code generated on the pandas sample is translated to PySpark before it lands back in the notebook. Before Data Wrangler closes, the tool displays a preview of the translated PySpark code, and it provides an option to export the intermediate pandas code as well.
Tip
Data Wrangler generates code that is applied only when you manually run the new cell, and it won't overwrite your original DataFrame, as shown in this screenshot:
The code is converted to PySpark, as shown in this screenshot:
You can then run that exported code, as shown in this screenshot:
Related content
- For an overview of Data Wrangler, visit this companion article
- To try out Data Wrangler in Visual Studio Code, head to Data Wrangler in VS Code
- Did we miss a feature you need? Let us know! Suggest it at the Fabric Ideas forum