Create a stored procedure
Applies to:
SQL Server
Azure SQL Database
Azure SQL Managed Instance
Azure Synapse Analytics
Analytics Platform System (PDW)
This article describes how to create a SQL Server stored procedure by using SQL Server Management Studio and by using the Transact-SQL CREATE PROCEDURE statement.
Permissions
Requires CREATE PROCEDURE permission in the database and ALTER permission on the schema in which the procedure is being created.
Create a stored procedure
You can use the SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) user interface or Transact-SQL in an SSMS query window to create a stored procedure. Always use the latest version of SSMS.
Note
The example stored procedure in this article uses the sample AdventureWorksLT2022 (SQL Server) or AdventureWorksLT (Azure SQL Database) database. For instructions on how to get and use the AdventureWorksLT sample databases, see AdventureWorks sample databases.
Use SQL Server Management Studio
To create a stored procedure in SSMS:
In Object Explorer, connect to an instance of SQL Server or Azure SQL Database.
For more information, see the following quickstarts:
Expand the instance, and then expand Databases.
Expand the database that you want, and then expand Programmability.
Right-click Stored Procedures, and then select New > Stored Procedure. A new query window opens with a template for the stored procedure.
The default stored procedure template has two parameters. If your stored procedure has fewer, more, or no parameters, add or remove parameter lines in the template as appropriate.
On the Query menu, select Specify Values for Template Parameters.
In the Specify Values for Template Parameters dialog box, provide the following information for the Value fields:
- Author: Replace
Namewith your name. - Create Date: Enter today's date.
- Description: Briefly describe what the procedure does.
- Procedure_Name: Replace
ProcedureNamewith the new stored procedure name. - @Param1: Replace
@p1with your first parameter name, such as @ColumnName1. - @Datatype_For_Param1: As appropriate, replace
intwith your first parameter's datatype, such as nvarchar(50). - Default_Value_For_Param1: As appropriate, replace
0with your first parameter's default value, or NULL. - @Param2: Replace
@p2with your second parameter name, such as @ColumnName2. - @Datatype_For_Param2: As appropriate, replace
intwith your second parameter's datatype, such as nvarchar(50). - Default_Value_For_Param2: As appropriate, replace
0with your second parameter's default value, or NULL.
The following screenshot shows the completed dialog box for the example stored procedure:
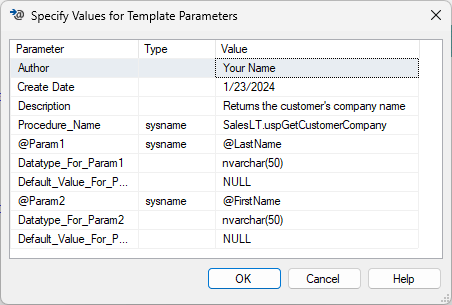
- Author: Replace
Select OK.
In the Query Editor, replace the SELECT statement with the query for your procedure.
The following code shows the completed CREATE PROCEDURE statement for the example stored procedure:
-- ======================================================= -- Create Stored Procedure Template for Azure SQL Database -- ======================================================= SET ANSI_NULLS ON GO SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON GO -- ============================================= -- Author: My Name -- Create Date: 01/23/2024 -- Description: Returns the customer's company name. -- ============================================= CREATE PROCEDURE SalesLT.uspGetCustomerCompany ( -- Add the parameters for the stored procedure here @LastName nvarchar(50) = NULL, @FirstName nvarchar(50) = NULL ) AS BEGIN -- SET NOCOUNT ON added to prevent extra result sets from -- interfering with SELECT statements. SET NOCOUNT ON -- Insert statements for procedure here SELECT FirstName, LastName, CompanyName FROM SalesLT.Customer WHERE FirstName = @FirstName AND LastName = @LastName; END GOTo test the syntax, on the Query menu, select Parse. Correct any errors.
Select Execute from the toolbar. The procedure is created as an object in the database.
To see the new procedure listed in Object Explorer, right-click Stored Procedures and select Refresh.
To run the procedure:
In Object Explorer, right-click the stored procedure name and select Execute Stored Procedure.
In the Execute Procedure window, enter values for all parameters, and then select OK. For detailed instructions, see Execute a stored procedure.
For example, to run the
SalesLT.uspGetCustomerCompanysample procedure, enter Cannon for the @LastName parameter and Chris for the @FirstName parameter, and then select OK. The stored procedure runs, and returnsFirstNameChris,LastNameCannon, andCompanyNameOutdoor Sporting Goods.
Important
Validate all user input. Don't concatenate user input before you validate it. Never execute a command constructed from unvalidated user input.
Use Transact-SQL
To create a procedure in the SSMS Query Editor:
In SSMS, connect to an instance of SQL Server or Azure SQL Database.
Select New Query from the toolbar.
Input the following code into the query window, replacing
<ProcedureName>, the names and data types of any parameters, and the SELECT statement with your own values.CREATE PROCEDURE <ProcedureName> @<ParameterName1> <data type>, @<ParameterName2> <data type> AS SET NOCOUNT ON; SELECT <your SELECT statement>; GOFor example, the following statement creates the same stored procedure in the
AdventureWorksLTdatabase as the previous example, with a slightly different procedure name.CREATE PROCEDURE SalesLT.uspGetCustomerCompany1 @LastName nvarchar(50), @FirstName nvarchar(50) AS SET NOCOUNT ON; SELECT FirstName, LastName, CompanyName FROM SalesLT.Customer WHERE FirstName = @FirstName AND LastName = @LastName; GOSelect Execute from the toolbar to execute the query. The stored procedure is created.
To run the stored procedure, enter an EXECUTE statement in a new query window, providing values for any parameters, and then select Execute. For detailed instructions, see Execute a stored procedure.