Anteckning
Åtkomst till den här sidan kräver auktorisering. Du kan prova att logga in eller ändra kataloger.
Åtkomst till den här sidan kräver auktorisering. Du kan prova att ändra kataloger.
Azure DevOps Server 2022 | Azure DevOps Server 2020 | Azure DevOps Server 2019
Om du har utvecklare på en fjärrplats som delar kod med utvecklare på huvudplatsen kan du spara bandbredd genom att cachelagra versionskontrollfiler på fjärrplatsen. Azure DevOps Proxy Server distribuerar populära versionskontrollfiler från cacheminnet på fjärrplatsen, i stället för att flera utvecklare från fjärrplatsen hämtar samma fil från huvudplatsen. Ditt team på fjärrplatsen fungerar som de alltid har gjort, utan att hantera vilka versionskontrollfiler som läses in i cacheminnet.
För att konfigurera detta installerar och konfigurerar du proxyservern på fjärrplatsen, ansluter proxyservern till programnivån och ansluter sedan versionskontrollfunktionen i Team Explorer till proxyn. Innan du kan börja cachelagrar filer på fjärrplatsen måste du lägga till tjänstkontot för proxyservern till Azure DevOps Server på huvudplatsen.
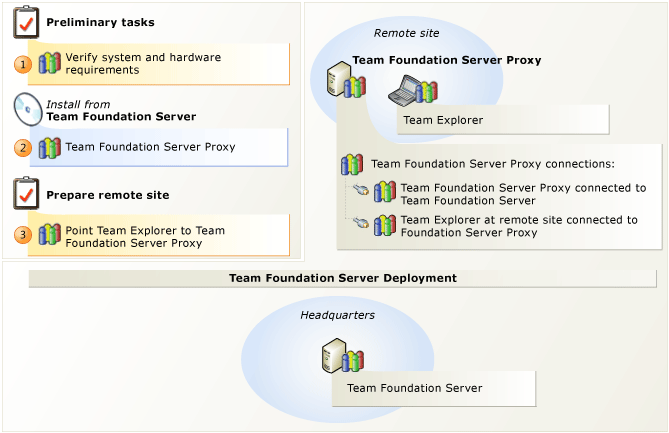
| Steg | Aktivitet | Detaljerade instruktioner |
|---|---|---|

|
Sök efter maskinvara och programvara som stöds. Kontrollera att operativsystemet uppfyller kraven för Azure DevOps Proxy Server och att maskinvaran kan köra den. | Systemkrav för Azure DevOps Proxy Server |

|
Konfigurera Azure DevOps Proxy Server. Installera Azure DevOps Proxy Server. När installationen är klar använder du Azure DevOps Server Configuration Center för att konfigurera proxyservern. |
Kör Azure DevOps Server-installation Konfigurera Azure DevOps Proxy Server med hjälp av Azure DevOps Server Configuration Center |

|
Anslut Team Explorer till Azure DevOps Proxy Server. När du har konfigurerat proxyservern för att ansluta till Azure DevOps Server måste du konfigurera Team Explorer för att komma åt versionskontrollfiler via proxyservern. | Konfigurera versionskontroll för Team Foundation för att använda proxyserver |
Du kan använda följande procedur för att konfigurera Azure DevOps Proxy Server med Azure DevOps Server Configuration Center.
Anteckning
Du kan komma åt Azure DevOps Server Configuration Center på Start-menyn genom att starta Administrationskonsolen för Azure DevOps Server, välja Proxyserver och sedan välja Konfigurera installerade funktioner.
Om du vill följa den här proceduren måste du ha följande behörighetsnivåer:
Medlemskap i säkerhetsgruppen Administratörer på den server där du konfigurerar Azure DevOps Proxy Server.
Medlemskap i gruppen Projektsamlingsadministratörer på Azure DevOps Server.
För Azure DevOps Services måste du antingen vara samlingsadministratör eller hantera proxybehörigheter på proxynamnområdet. Du kan bevilja proxybehörigheter med hjälp av:
tfssecurity /a+ Proxy Proxy Manage <user account> ALLOW /collection:{collection url}Anteckning
Du måste ha en proxyserver på TFS Update 2 eller senare för att kunna använda föregående kommando.
För att konfigurera Azure DevOps Proxy Server måste du ha Azure DevOps Server installerat på ett serveroperativsystem. Mer information finns i Systemkrav för Azure DevOps Server.
Följ dessa steg för att konfigurera Azure DevOps Proxy Server med hjälp av Azure DevOps Server Configuration Center:
Välj Konfigurera Azure DevOps Proxy Server och välj sedan Starta guiden.
Konfigurationsguiden för Azure DevOps Proxy Server visas.
Läs välkomstskärmen och välj sedan Nästa. Om du har en version av TFS 2013-proxyn (den här funktionen fungerar endast med TFS 2013-proxy och framåt) konfigurerad på den här servern uppmanas du att återställa inställningarna. Om du vill konfigurera den här proxyservern med olika resurser väljer du Nej och går vidare till nästa steg. Om du vill ansluta proxyn till samma Azure DevOps Server-servrar väljer du Ja. Azure DevOps Server försöker autentisera. Om Azure DevOps Server har autentiserat alla slutpunkter går du vidare till steg 4.
Om det uppstår problem med en eller flera slutpunkter har du följande felsökningsalternativ för varje misslyckad anslutning:
Anslut: Använd det här alternativet för att manuellt autentisera slutpunkter. Manuell autentisering är ett bra ställe att börja med en misslyckad anslutning.
Hoppa över: Använd det här alternativet för att hoppa över autentisering. Hoppa över är användbart när du ännu inte har lösenordet för att autentisera den här slutpunkten och du vill spara anslutningsinformationen för ett nytt försök senare.
Ta bort: Använd det här alternativet om du vill ta bort slutpunkten helt.
Tips
Mer information om de här alternativen finns i blogginlägget Proxyuppgraderingar: Så här verifierar du överhoppade proxyslutpunkter.
Välj Bläddra och välj sedan den projektsamling som du vill att proxyservern ska ansluta till. Välj Nästa.
Anteckning
Om din projektsamling finns i Azure DevOps Services uppmanas du att autentisera. Ange det Microsoft-konto som du använde för att konfigurera tjänsten.
Under Tjänstkonto väljer du Använd ett systemkonto för att använda Nätverkstjänst eller Använda ett användarkonto för att använda en domän eller ett lokalt konto. Om du använder ett användarkonto måste du ange lösenordet. Om du vill testa kombinationen av användarkonto och lösenord väljer du Testa.
Nätverkstjänst är standardvärdet för proxyservertjänstkontot.
Följande valfria konfigurationer visas under Avancerad konfiguration:
Om du är ansluten till den värdbaserade tjänsten visas Kontonamn här.
När du skapade instansen av Azure DevOps Server på den värdbaserade tjänsten skapades kontonamnet automatiskt åt dig. Det här kontot läggs till i gruppen Proxytjänstkonton för projektsamling i den värdbaserade tjänsten. Om du vill använda ett annat konto anger du kontonamnet och väljer Testa.
Om du vill återställa till standardtjänstkontot som skapas automatiskt väljer du Återställ till standardtjänstkonto. Detta gäller inte längre för Azure DevOps Server 2017 Update 2 och nyare proxyservrar.
Du kan ändra autentiseringsinställningarna. Under Autentiseringsmetod väljer du NTLM för att använda NTLM-autentisering eller Förhandla (Kerberos) för att först försöka använda Kerberos-autentisering, vilket är det säkrare alternativet, och om det misslyckas återgår du till NTLM.
NTLM är standardvärdet.
Välj Nästa.
I Port accepterar du standardvärdet 8081 eller anger ett annat lyssnarportnummer för inkommande anslutningar till Azure DevOps Proxy Server.
8081 är standardvärdet.
Acceptera standardvärdet i Cache Root Directory eller ange sökvägen till en annan plats där cachefiler ska lagras.
Standardvärdet är Drive:\Program Files\TFS 12.0\Version Control Proxy\ _tfs_data
Enheten är bokstaven på den enhet där du vill lagra cachefiler. Du kan ange en mappad nätverksenhet.
Välj Nästa.
På sidan Granska granskar du inställningarna och väljer sedan Nästa.
Guiden verifierar konfigurationen.
Välj Konfigurera för guiden för att tillämpa konfigurationsinställningar.
Välj Nästa på skärmen lyckades för att läsa de detaljerade resultaten på nästa framgångsskärm. Du hittar också en länk till en logg på den här skärmen som innehåller resultatet av konfigurationen.
Välj Stäng två gånger så visas Administrationskonsolen för Azure DevOps Server.
Du kan konfigurera versionskontroll för Team Foundation så att den använder en proxyserver som cachelagrar kopior av versionskontrollfiler på platsen för ett distribuerat team. Du kan minska bandbreddskraven för fjärrutvecklare med hjälp av en proxyserver.
Om du vill följa den här proceduren måste du vara medlem i säkerhetsgruppen Användare på den dator där du konfigurerar Team Explorer.
Så här konfigurerar du Team Explorer för att använda Azure DevOps Proxy Server:
Starta Visual Studio.
På menyn Verktyg väljer du Alternativ.
I dialogrutan Alternativ expanderar du Källkontroll och väljer sedan Plugin-markering.
För plugin-programmet Aktuell källkontroll kontrollerar du att värdet är Visual Studio Team Foundation Server.
Under Källkontroll väljer du Visual Studio Team Foundation Server.
Markera kryssrutan Använd proxyserver för filnedladdningar .
I rutan Proxyservernamn anger du namnet på servern som kör Azure DevOps Proxy Server.
I rutan Port anger du lyssnarporten för Azure DevOps Proxy Server. Som standard lyssnar Azure DevOps Proxy Server efter klientbegäranden på port 8081.
S: Ja. Proxyservern är helt kompatibel med TFS 2010 och TFS 2012. I själva verket är TFS Proxy 2010, TFS Proxy 2012 och proxyservern helt kompatibla med varandra i valfri kombination. Du kan till exempel använda TFS Proxy 2010 med proxyservern eller tvärtom.
F: Har någon version av Azure DevOps Proxy Server förbättringar av cacherensning för att stödja diskar som är större än 1 TB?
S: Ja. Proxyservern har förbättringar av cacherensningen för att stödja stora diskar.
S: Ja. Om en cachelagrad fil skadas på en disk efter att den har lagrats har proxyservern logik för att identifiera skada.
S: Ja.
F: Vad händer med proxycachen när jag uppgraderar från en version av Azure DevOps Proxy Server till en annan?
S: Om du uppgraderar från en tidigare version av Azure DevOps Proxy Server eller TFS Proxy Server bevaras cachen under uppgraderingen. Du kommer att kunna fortsätta att komma åt Azure DevOps Server från fjärranslutna platser direkt, utan prestandapåverkan, eftersom Azure DevOps Server inte behöver återskapa eller fylla i cacheminnet igen.