Not
Åtkomst till den här sidan kräver auktorisering. Du kan prova att logga in eller ändra kataloger.
Åtkomst till den här sidan kräver auktorisering. Du kan prova att ändra kataloger.
Det här exemplet visar hur du använder gränssnitten IXMLHTTPRequest2 och IXMLHTTPRequest2Callback tillsammans med uppgifter för att skicka HTTP GET- och POST-begäranden till en webbtjänst i en UWP-app (Universal Windows Platform). Genom att kombinera IXMLHTTPRequest2 med uppgifter kan du skriva kod som består av andra uppgifter. Du kan till exempel använda nedladdningsaktiviteten som en del av en aktivitetskedja. Nedladdningsaktiviteten kan också svara när arbetet avbryts.
Tips/Råd
Du kan också använda C++ REST SDK för att utföra HTTP-begäranden från en UWP-app med C++-appen eller från en C++-skrivbordsapp. Mer information finns i C++ REST SDK (Kodnamn "Casablanca").
Mer information om aktiviteter finns i Aktivitetsparallellitet. Mer information om hur du använder uppgifter i en UWP-app finns i Asynkron programmering i C++ och Skapa asynkrona åtgärder i C++ för UWP-appar.
Det här dokumentet visar först hur du skapar HttpRequest och dess stödklasser. Den visar sedan hur du använder den här klassen från en UWP-app som använder C++ och XAML.
Ett exempel som använder IXMLHTTPRequest2 men inte använder uppgifter finns i Snabbstart: Ansluta med XML HTTP-begäran (IXMLHTTPRequest2).
Tips/Råd
IXMLHTTPRequest2 och IXMLHTTPRequest2Callback är de gränssnitt som vi rekommenderar för användning i en UWP-app. Du kan också anpassa det här exemplet för användning i en skrivbordsapp.
Förutsättningar
UWP-stöd är valfritt i Visual Studio 2017 och senare. Om du vill installera det öppnar du Installationsprogrammet för Visual Studio från Start-menyn i Windows och väljer den version av Visual Studio som du använder. Klicka på knappen Ändra och kontrollera att panelen UWP-utveckling är markerad. Under Valfria komponenter kontrollerar du att C++ UWP Tools är markerat. Använd v141 för Visual Studio 2017 eller v142 för Visual Studio 2019.
Definiera klasserna HttpRequest, HttpRequestBuffersCallback och HttpRequestStringCallback
När du använder IXMLHTTPRequest2 gränssnittet för att skapa webbbegäranden via HTTP implementerar IXMLHTTPRequest2Callback du gränssnittet för att ta emot serversvaret och reagera på andra händelser. Det här exemplet definierar HttpRequest klassen för att skapa webbbegäranden och HttpRequestBuffersCallback klasserna och HttpRequestStringCallback för att bearbeta svar. Klasserna HttpRequestBuffersCallback och HttpRequestStringCallback stöder HttpRequest klassen. Du arbetar bara med HttpRequest klassen från programkoden.
Med GetAsyncmetoderna , PostAsync i HttpRequest klassen kan du starta HTTP GET- respektive POST-åtgärder. Dessa metoder använder HttpRequestStringCallback klassen för att läsa serversvaret som en sträng. Med SendAsync metoderna och ReadAsync kan du strömma stort innehåll i segment. Dessa metoder returnerar concurrency::task för att representera operationen. Metoderna GetAsync och PostAsync skapar task<std::wstring> värde, där wstring delen representerar serverns svar. Metoderna SendAsync och ReadAsync genererar task<void> värden. Dessa uppgifter slutförs när sändnings- och läsåtgärderna slutförs.
Eftersom gränssnitten IXMLHTTPRequest2 fungerar asynkront använder detta exempel samtidighet::task_completion_event för att skapa en uppgift som slutförs efter att återanropsobjektet slutför eller avbryter nedladdningsåtgärden. Klassen HttpRequest skapar en aktivitetsbaserad fortsättning från den här aktiviteten för att ange slutresultatet. Klassen HttpRequest använder en aktivitetsbaserad fortsättning för att säkerställa att fortsättningsaktiviteten körs även om föregående aktivitet genererar ett fel eller avbryts. Mer information om aktivitetsbaserade fortsättningar finns i Aktivitetsparallellitet
För att stödja annullering använder klasserna HttpRequest, HttpRequestBuffersCallbackoch HttpRequestStringCallback annulleringstoken. Klasserna HttpRequestBuffersCallback och HttpRequestStringCallback använder metoden concurrency::cancellation_token::register_callback för att aktivera uppgiftens slutförandehändelse för att svara på annullering. Det här återanropet för avbokning avbryter nedladdningen. Mer information om annullering finns i Annullering.
Så här definierar du HttpRequest-klassen
På huvudmenyn väljer du Arkiv>Nytt>Projekt.
Använd mallen C++ Tom app (Universell Windows) för att skapa ett tomt XAML-appprojekt. I det här exemplet namnges projektet
UsingIXMLHTTPRequest2.Lägg till en rubrikfil med namnet HttpRequest.h i projektet och en källfil med namnet HttpRequest.cpp.
Lägg till den här koden i pch.h:
#include <ppltasks.h> #include <string> #include <sstream> #include <wrl.h> #include <msxml6.h>Lägg till den här koden i HttpRequest.h:
#pragma once #include "pch.h" inline void CheckHResult(HRESULT hResult) { if (hResult == E_ABORT) { concurrency::cancel_current_task(); } else if (FAILED(hResult)) { throw Platform::Exception::CreateException(hResult); } } namespace Web { namespace Details { // Implementation of IXMLHTTPRequest2Callback used when partial buffers are needed from the response. // When only the complete response is needed, use HttpRequestStringCallback instead. class HttpRequestBuffersCallback : public Microsoft::WRL::RuntimeClass< Microsoft::WRL::RuntimeClassFlags<Microsoft::WRL::ClassicCom>, IXMLHTTPRequest2Callback, Microsoft::WRL::FtmBase> { public: HttpRequestBuffersCallback(IXMLHTTPRequest2* httpRequest, concurrency::cancellation_token ct = concurrency::cancellation_token::none()) : request(httpRequest), cancellationToken(ct), responseReceived(false), dataHResult(S_OK), statusCode(200) { // Register a callback function that aborts the HTTP operation when // the cancellation token is canceled. if (cancellationToken != concurrency::cancellation_token::none()) { registrationToken = cancellationToken.register_callback([this]() { if (request != nullptr) { request->Abort(); } }); } dataEvent = concurrency::task_completion_event<void>(); } // Called when the HTTP request is being redirected to a new URL. IFACEMETHODIMP OnRedirect(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, PCWSTR) { return S_OK; } // Called when HTTP headers have been received and processed. IFACEMETHODIMP OnHeadersAvailable(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, DWORD statusCode, PCWSTR reasonPhrase) { HRESULT hr = S_OK; // We must not propagate exceptions back to IXHR2. try { this->statusCode = statusCode; this->reasonPhrase = reasonPhrase; concurrency::critical_section::scoped_lock lock(dataEventLock); dataEvent.set(); } catch (std::bad_alloc&) { hr = E_OUTOFMEMORY; } return hr; } // Called when a portion of the entity body has been received. IFACEMETHODIMP OnDataAvailable(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, ISequentialStream* stream) { HRESULT hr = S_OK; // We must not propagate exceptions back to IXHR2. try { // Store a reference on the stream so it can be accessed by the task. dataStream = stream; // The work must be done as fast as possible, and must not block this thread, // for example, waiting on another event object. Here we simply set an event // that can be processed by another thread. concurrency::critical_section::scoped_lock lock(dataEventLock); dataEvent.set(); } catch (std::bad_alloc&) { hr = E_OUTOFMEMORY; } return hr; } // Called when the entire entity response has been received. IFACEMETHODIMP OnResponseReceived(IXMLHTTPRequest2* xhr, ISequentialStream* responseStream) { responseReceived = true; return OnDataAvailable(xhr, responseStream); } // Called when an error occurs during the HTTP request. IFACEMETHODIMP OnError(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, HRESULT hrError) { HRESULT hr = S_OK; // We must not propagate exceptions back to IXHR2. try { concurrency::critical_section::scoped_lock lock(dataEventLock); dataHResult = hrError; dataEvent.set(); } catch (std::bad_alloc&) { hr = E_OUTOFMEMORY; } return hr; } // Create a task that completes when data is available, in an exception-safe way. concurrency::task<void> CreateDataTask(); HRESULT GetError() const { return dataHResult; } int GetStatusCode() const { return statusCode; } std::wstring const& GetReasonPhrase() const { return reasonPhrase; } bool IsResponseReceived() const { return responseReceived; } // Copy bytes from the sequential stream into the buffer provided until // we reach the end of one or the other. unsigned int ReadData( _Out_writes_(outputBufferSize) byte* outputBuffer, unsigned int outputBufferSize); private: ~HttpRequestBuffersCallback() { // Unregister the callback. if (cancellationToken != concurrency::cancellation_token::none()) { cancellationToken.deregister_callback(registrationToken); } } // Signals that the download operation was canceled. concurrency::cancellation_token cancellationToken; // Used to unregister the cancellation token callback. concurrency::cancellation_token_registration registrationToken; // The IXMLHTTPRequest2 that processes the HTTP request. Microsoft::WRL::ComPtr<IXMLHTTPRequest2> request; // Task completion event that is set when data is available or error is triggered. concurrency::task_completion_event<void> dataEvent; concurrency::critical_section dataEventLock; // We cannot store the error obtained from IXHR2 in the dataEvent since any value there is first-writer-wins, // whereas we want a subsequent error to override an initial success. HRESULT dataHResult; // Referenced pointer to the data stream. Microsoft::WRL::ComPtr<ISequentialStream> dataStream; // HTTP status code and reason returned by the server. int statusCode; std::wstring reasonPhrase; // Whether the response has been completely received. bool responseReceived; }; }; // Utility class for performing asynchronous HTTP requests. // This class only supports one outstanding request at a time. class HttpRequest { public: HttpRequest(); int GetStatusCode() const { return statusCode; } std::wstring const& GetReasonPhrase() const { return reasonPhrase; } // Whether the response has been completely received, if using ReadAsync(). bool IsResponseComplete() const { return responseComplete; } // Start an HTTP GET on the specified URI. The returned task completes once the entire response // has been received, and the task produces the HTTP response text. The status code and reason // can be read with GetStatusCode() and GetReasonPhrase(). concurrency::task<std::wstring> GetAsync( Windows::Foundation::Uri^ uri, concurrency::cancellation_token cancellationToken = concurrency::cancellation_token::none()); // Start an HTTP POST on the specified URI, using a string body. The returned task produces the // HTTP response text. The status code and reason can be read with GetStatusCode() and GetReasonPhrase(). concurrency::task<std::wstring> PostAsync( Windows::Foundation::Uri^ uri, PCWSTR contentType, IStream* postStream, uint64 postStreamSizeToSend, concurrency::cancellation_token cancellationToken = concurrency::cancellation_token::none()); // Start an HTTP POST on the specified URI, using a stream body. The returned task produces the // HTTP response text. The status code and reason can be read with GetStatusCode() and GetReasonPhrase(). concurrency::task<std::wstring> PostAsync( Windows::Foundation::Uri^ uri, const std::wstring& str, concurrency::cancellation_token cancellationToken = concurrency::cancellation_token::none()); // Send a request but don't return the response. Instead, let the caller read it with ReadAsync(). concurrency::task<void> SendAsync( const std::wstring& httpMethod, Windows::Foundation::Uri^ uri, concurrency::cancellation_token cancellationToken = concurrency::cancellation_token::none()); // Read a chunk of data from the HTTP response, up to a specified length or until we reach the end // of the response, and store the value in the provided buffer. This is useful for large content, // enabling the streaming of the result. concurrency::task<void> ReadAsync( Windows::Storage::Streams::IBuffer^ readBuffer, unsigned int offsetInBuffer, unsigned int requestedBytesToRead); static void CreateMemoryStream(IStream **stream); private: // Start a download of the specified URI using the specified method. The returned task produces the // HTTP response text. The status code and reason can be read with GetStatusCode() and GetReasonPhrase(). concurrency::task<std::wstring> DownloadAsync( PCWSTR httpMethod, PCWSTR uri, concurrency::cancellation_token cancellationToken, PCWSTR contentType, IStream* postStream, uint64 postStreamBytesToSend); // Referenced pointer to the callback, if using SendAsync/ReadAsync. Microsoft::WRL::ComPtr<Details::HttpRequestBuffersCallback> buffersCallback; int statusCode; std::wstring reasonPhrase; // Whether the response has been completely received, if using ReadAsync(). bool responseComplete; }; };Lägg till den här koden i HttpRequest.cpp:
#include "pch.h" #include "HttpRequest.h" #include <robuffer.h> #include <shcore.h> using namespace concurrency; using namespace Microsoft::WRL; using namespace Platform; using namespace std; using namespace Web; using namespace Windows::Foundation; using namespace Windows::Storage::Streams; // Implementation of IXMLHTTPRequest2Callback used when only the complete response is needed. // When processing chunks of response data as they are received, use HttpRequestBuffersCallback instead. class HttpRequestStringCallback : public RuntimeClass<RuntimeClassFlags<ClassicCom>, IXMLHTTPRequest2Callback, FtmBase> { public: HttpRequestStringCallback(IXMLHTTPRequest2* httpRequest, cancellation_token ct = concurrency::cancellation_token::none()) : request(httpRequest), cancellationToken(ct) { // Register a callback function that aborts the HTTP operation when // the cancellation token is canceled. if (cancellationToken != cancellation_token::none()) { registrationToken = cancellationToken.register_callback([this]() { if (request != nullptr) { request->Abort(); } }); } } // Called when the HTTP request is being redirected to a new URL. IFACEMETHODIMP OnRedirect(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, PCWSTR) { return S_OK; } // Called when HTTP headers have been received and processed. IFACEMETHODIMP OnHeadersAvailable(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, DWORD statusCode, PCWSTR reasonPhrase) { HRESULT hr = S_OK; // We must not propagate exceptions back to IXHR2. try { this->statusCode = statusCode; this->reasonPhrase = reasonPhrase; } catch (std::bad_alloc&) { hr = E_OUTOFMEMORY; } return hr; } // Called when a portion of the entity body has been received. IFACEMETHODIMP OnDataAvailable(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, ISequentialStream*) { return S_OK; } // Called when the entire entity response has been received. IFACEMETHODIMP OnResponseReceived(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, ISequentialStream* responseStream) { wstring wstr; HRESULT hr = ReadUtf8StringFromSequentialStream(responseStream, wstr); // We must not propagate exceptions back to IXHR2. try { completionEvent.set(make_tuple<HRESULT, wstring>(move(hr), move(wstr))); } catch (std::bad_alloc&) { hr = E_OUTOFMEMORY; } return hr; } // Simulate the functionality of DataReader.ReadString(). // This is needed because DataReader requires IRandomAccessStream and this // code has an ISequentialStream that does not have a conversion to IRandomAccessStream like IStream does. HRESULT ReadUtf8StringFromSequentialStream(ISequentialStream* readStream, wstring& str) { // Convert the response to Unicode wstring. HRESULT hr; // Holds the response as a Unicode string. wstringstream ss; while (true) { ULONG cb; char buffer[4096]; // Read the response as a UTF-8 string. Since UTF-8 characters are 1-4 bytes long, // we need to make sure we only read an integral number of characters. So we'll // start with 4093 bytes. hr = readStream->Read(buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 3, &cb); if (FAILED(hr) || (cb == 0)) { break; // Error or no more data to process, exit loop. } if (cb == sizeof(buffer) - 3) { ULONG subsequentBytesRead; unsigned int i, cl; // Find the first byte of the last UTF-8 character in the buffer. for (i = cb - 1; (i >= 0) && ((buffer[i] & 0xC0) == 0x80); i--); // Calculate the number of subsequent bytes in the UTF-8 character. if (((unsigned char)buffer[i]) < 0x80) { cl = 1; } else if (((unsigned char)buffer[i]) < 0xE0) { cl = 2; } else if (((unsigned char)buffer[i]) < 0xF0) { cl = 3; } else { cl = 4; } // Read any remaining bytes. if (cb < i + cl) { hr = readStream->Read(buffer + cb, i + cl - cb, &subsequentBytesRead); if (FAILED(hr)) { break; // Error, exit loop. } cb += subsequentBytesRead; } } // First determine the size required to store the Unicode string. int const sizeRequired = MultiByteToWideChar(CP_UTF8, 0, buffer, cb, nullptr, 0); if (sizeRequired == 0) { // Invalid UTF-8. hr = HRESULT_FROM_WIN32(GetLastError()); break; } unique_ptr<char16[]> wstr(new(std::nothrow) char16[sizeRequired + 1]); if (wstr.get() == nullptr) { hr = E_OUTOFMEMORY; break; } // Convert the string from UTF-8 to UTF-16LE. This can never fail, since // the previous call above succeeded. MultiByteToWideChar(CP_UTF8, 0, buffer, cb, wstr.get(), sizeRequired); wstr[sizeRequired] = L'\0'; // Terminate the string. ss << wstr.get(); // Write the string to the stream. } str = SUCCEEDED(hr) ? ss.str() : wstring(); return (SUCCEEDED(hr)) ? S_OK : hr; // Don't return S_FALSE. } // Called when an error occurs during the HTTP request. IFACEMETHODIMP OnError(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, HRESULT hrError) { HRESULT hr = S_OK; // We must not propagate exceptions back to IXHR2. try { completionEvent.set(make_tuple<HRESULT, wstring>(move(hrError), wstring())); } catch (std::bad_alloc&) { hr = E_OUTOFMEMORY; } return hr; } // Retrieves the completion event for the HTTP operation. task_completion_event<tuple<HRESULT, wstring>> const& GetCompletionEvent() const { return completionEvent; } int GetStatusCode() const { return statusCode; } wstring GetReasonPhrase() const { return reasonPhrase; } private: ~HttpRequestStringCallback() { // Unregister the callback. if (cancellationToken != cancellation_token::none()) { cancellationToken.deregister_callback(registrationToken); } } // Signals that the download operation was canceled. cancellation_token cancellationToken; // Used to unregister the cancellation token callback. cancellation_token_registration registrationToken; // The IXMLHTTPRequest2 that processes the HTTP request. ComPtr<IXMLHTTPRequest2> request; // Task completion event that is set when the // download operation completes. task_completion_event<tuple<HRESULT, wstring>> completionEvent; int statusCode; wstring reasonPhrase; }; // Copy bytes from the sequential stream into the buffer provided until // we reach the end of one or the other. unsigned int Web::Details::HttpRequestBuffersCallback::ReadData( _Out_writes_(outputBufferSize) byte* outputBuffer, unsigned int outputBufferSize) { // Lock the data event while doing the read, to ensure that any bytes we don't read will // result in the correct event getting triggered. concurrency::critical_section::scoped_lock lock(dataEventLock); ULONG bytesRead; CheckHResult(dataStream.Get()->Read(outputBuffer, outputBufferSize, &bytesRead)); if (bytesRead < outputBufferSize) { // We need to reset the data event, which we can only do by creating a new one. dataEvent = task_completion_event<void>(); } return bytesRead; } // Create a task that completes when data is available, in an exception-safe way. task<void> Web::Details::HttpRequestBuffersCallback::CreateDataTask() { concurrency::critical_section::scoped_lock lock(dataEventLock); return create_task(dataEvent, cancellationToken); } HttpRequest::HttpRequest() : responseComplete(true), statusCode(200) { } // Start a download of the specified URI using the specified method. The returned task produces the // HTTP response text. The status code and reason can be read with GetStatusCode() and GetReasonPhrase(). task<wstring> HttpRequest::DownloadAsync(PCWSTR httpMethod, PCWSTR uri, cancellation_token cancellationToken, PCWSTR contentType, IStream* postStream, uint64 postStreamSizeToSend) { // Create an IXMLHTTPRequest2 object. ComPtr<IXMLHTTPRequest2> xhr; CheckHResult(CoCreateInstance(CLSID_XmlHttpRequest, nullptr, CLSCTX_INPROC, IID_PPV_ARGS(&xhr))); // Create callback. auto stringCallback = Make<HttpRequestStringCallback>(xhr.Get(), cancellationToken); CheckHResult(stringCallback ? S_OK : E_OUTOFMEMORY); auto completionTask = create_task(stringCallback->GetCompletionEvent()); // Create a request. CheckHResult(xhr->Open(httpMethod, uri, stringCallback.Get(), nullptr, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr)); if (postStream != nullptr && contentType != nullptr) { CheckHResult(xhr->SetRequestHeader(L"Content-Type", contentType)); } // Send the request. CheckHResult(xhr->Send(postStream, postStreamSizeToSend)); // Return a task that completes when the HTTP operation completes. // We pass the callback to the continuation because the lifetime of the // callback must exceed the operation to ensure that cancellation // works correctly. return completionTask.then([this, stringCallback](tuple<HRESULT, wstring> resultTuple) { // If the GET operation failed, throw an Exception. CheckHResult(std::get<0>(resultTuple)); statusCode = stringCallback->GetStatusCode(); reasonPhrase = stringCallback->GetReasonPhrase(); return std::get<1>(resultTuple); }); } // Start an HTTP GET on the specified URI. The returned task completes once the entire response // has been received, and the task produces the HTTP response text. The status code and reason // can be read with GetStatusCode() and GetReasonPhrase(). task<wstring> HttpRequest::GetAsync(Uri^ uri, cancellation_token cancellationToken) { return DownloadAsync(L"GET", uri->AbsoluteUri->Data(), cancellationToken, nullptr, nullptr, 0); } void HttpRequest::CreateMemoryStream(IStream **stream) { auto randomAccessStream = ref new Windows::Storage::Streams::InMemoryRandomAccessStream(); CheckHResult(CreateStreamOverRandomAccessStream(randomAccessStream, IID_PPV_ARGS(stream))); } // Start an HTTP POST on the specified URI, using a string body. The returned task produces the // HTTP response text. The status code and reason can be read with GetStatusCode() and GetReasonPhrase(). task<wstring> HttpRequest::PostAsync(Uri^ uri, const wstring& body, cancellation_token cancellationToken) { int length = 0; ComPtr<IStream> postStream; CreateMemoryStream(&postStream); if (body.length() > 0) { // Get the required buffer size. int size = WideCharToMultiByte(CP_UTF8, // UTF-8 0, // Conversion type body.c_str(), // Unicode string to convert static_cast<int>(body.length()), // Size nullptr, // Output buffer 0, // Output buffer size nullptr, nullptr); CheckHResult((size != 0) ? S_OK : HRESULT_FROM_WIN32(GetLastError())); std::unique_ptr<char[]> tempData(new char[size]); length = WideCharToMultiByte(CP_UTF8, // UTF-8 0, // Conversion type body.c_str(), // Unicode string to convert static_cast<int>(body.length()), // Size tempData.get(), // Output buffer size, // Output buffer size nullptr, nullptr); CheckHResult((length != 0) ? S_OK : HRESULT_FROM_WIN32(GetLastError())); CheckHResult(postStream->Write(tempData.get(), length, nullptr)); } return DownloadAsync(L"POST", uri->AbsoluteUri->Data(), cancellationToken, L"text/plain;charset=utf-8", postStream.Get(), length); } // Start an HTTP POST on the specified URI, using a stream body. The returned task produces the // HTTP response text. The status code and reason can be read with GetStatusCode() and GetReasonPhrase(). task<wstring> HttpRequest::PostAsync(Uri^ uri, PCWSTR contentType, IStream* postStream, uint64 postStreamSizeToSend, cancellation_token cancellationToken) { return DownloadAsync(L"POST", uri->AbsoluteUri->Data(), cancellationToken, contentType, postStream, postStreamSizeToSend); } // Send a request but don't return the response. Instead, let the caller read it with ReadAsync(). task<void> HttpRequest::SendAsync(const wstring& httpMethod, Uri^ uri, cancellation_token cancellationToken) { // Create an IXMLHTTPRequest2 object. ComPtr<IXMLHTTPRequest2> xhr; CheckHResult(CoCreateInstance(CLSID_XmlHttpRequest, nullptr, CLSCTX_INPROC, IID_PPV_ARGS(&xhr))); // Create callback. buffersCallback = Make<Web::Details::HttpRequestBuffersCallback>(xhr.Get(), cancellationToken); CheckHResult(buffersCallback ? S_OK : E_OUTOFMEMORY); ComPtr<IXMLHTTPRequest2Callback> xhrCallback; CheckHResult(buffersCallback.As(&xhrCallback)); // Open and send the request. CheckHResult(xhr->Open(httpMethod.c_str(), uri->AbsoluteUri->Data(), xhrCallback.Get(), nullptr, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr)); responseComplete = false; CheckHResult(xhr->Send(nullptr, 0)); // Return a task that completes when the HTTP operation completes. // Since buffersCallback holds a reference on the callback, the lifetime of the callback will exceed // the operation and ensure that cancellation works correctly. return buffersCallback->CreateDataTask().then([this]() { CheckHResult(buffersCallback->GetError()); statusCode = buffersCallback->GetStatusCode(); reasonPhrase = buffersCallback->GetReasonPhrase(); }); } // Read a chunk of data from the HTTP response, up to a specified length or until we reach the end // of the response, and store the value in the provided buffer. This is useful for large content, // enabling the streaming of the result. task<void> HttpRequest::ReadAsync(Windows::Storage::Streams::IBuffer^ readBuffer, unsigned int offsetInBuffer, unsigned int requestedBytesToRead) { if (offsetInBuffer + requestedBytesToRead > readBuffer->Capacity) { throw ref new InvalidArgumentException(); } // Return a task that completes when a read completes. // We pass the callback to the continuation because the lifetime of the // callback must exceed the operation to ensure that cancellation // works correctly. return buffersCallback->CreateDataTask().then([this, readBuffer, offsetInBuffer, requestedBytesToRead]() { CheckHResult(buffersCallback->GetError()); // Get a pointer to the location to copy data into. ComPtr<IBufferByteAccess> bufferByteAccess; CheckHResult(reinterpret_cast<IUnknown*>(readBuffer)->QueryInterface(IID_PPV_ARGS(&bufferByteAccess))); byte* outputBuffer; // Returned internal pointer, do not free this value. CheckHResult(bufferByteAccess->Buffer(&outputBuffer)); // Copy bytes from the sequential stream into the buffer provided until // we reach the end of one or the other. readBuffer->Length = buffersCallback->ReadData(outputBuffer + offsetInBuffer, requestedBytesToRead); if (buffersCallback->IsResponseReceived() && (readBuffer->Length < requestedBytesToRead)) { responseComplete = true; } }); }
Använda HttpRequest-klassen i en UWP-app
Det här avsnittet visar hur du HttpRequest använder klassen i en UWP-app. Appen innehåller en indataruta som definierar en URL-resurs och knappkommandon som utför GET- och POST-åtgärder samt ett knappkommando som avbryter den aktuella åtgärden.
Så här använder du HttpRequest-klassen
I MainPage.xaml definierar du StackPanel-elementet enligt följande.
<StackPanel HorizontalAlignment="Left" Width="440" Background="{StaticResource ApplicationPageBackgroundThemeBrush}"> <TextBox x:Name="InputTextBox" TextWrapping="Wrap" Text="http://www.fourthcoffee.com/"/> <StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal"> <Button x:Name="GetButton" Content="Get" Background="Green" Click="GetButton_Click"/> <Button x:Name="PostButton" Content="Post" Background="Blue" Click="PostButton_Click"/> <Button x:Name="CancelButton" Content="Cancel" Background="Red" IsEnabled="False" Click="CancelButton_Click"/> <ProgressRing x:Name="ResponseProgressRing" /> </StackPanel> <TextBlock x:Name="ResponseTextBlock" TextWrapping="Wrap"/> </StackPanel>Lägg till det här
#includedirektivet i MainPage.xaml.h:#include "HttpRequest.h"I MainPage.xaml.h, lägg till dessa
privatemedlemsvariabler tillMainPageklassen.// Produces HTTP requets. Web::HttpRequest m_httpRequest; // Enables us to cancel the active HTTP request. concurrency::cancellation_token_source m_cancelHttpRequestSource;I MainPage.xaml.h ska du deklarera metoden
privateProcessHttpRequest:// Displays the result of the provided HTTP request on the UI. void ProcessHttpRequest(concurrency::task<std::wstring> httpRequest);Lägg till följande
usinginstruktioner i MainPage.xaml.cpp:using namespace concurrency; using namespace std; using namespace Web;I MainPage.xaml.cpp implementerar du
GetButton_Click,PostButton_ClickochCancelButton_Clickmetoderna förMainPageklassen.void MainPage::GetButton_Click(Object^ sender, RoutedEventArgs^ e) { // Create a new cancellation token source for the web request. m_cancelHttpRequestSource = cancellation_token_source(); // Set up the GET request parameters. auto uri = ref new Uri(InputTextBox->Text); auto token = m_cancelHttpRequestSource.get_token(); // Send the request and then update the UI. ProcessHttpRequest(m_httpRequest.GetAsync(uri, token)); } void MainPage::PostButton_Click(Object^ sender, RoutedEventArgs^ e) { // Create a new cancellation token source for the web request. m_cancelHttpRequestSource = cancellation_token_source(); // Set up the POST request parameters. auto uri = ref new Uri(InputTextBox->Text); wstring postData(L"This is sample POST data."); auto token = m_cancelHttpRequestSource.get_token(); // Send the request and then update the UI. ProcessHttpRequest(m_httpRequest.PostAsync(uri, postData, token)); } void MainPage::CancelButton_Click(Object^ sender, RoutedEventArgs^ e) { // Disable the Cancel button. // It will be re-enabled during the next web request. CancelButton->IsEnabled = false; // Initiate cancellation. m_cancelHttpRequestSource.cancel(); }Tips/Råd
Om din app inte kräver stöd för annullering, skicka samtidighet::cancellation_token::none till
HttpRequest::GetAsyncochHttpRequest::PostAsyncmetoderna.Implementera metoden i
MainPage::ProcessHttpRequestMainPage.xaml.cpp.// Displays the result of the provided HTTP request on the UI. void MainPage::ProcessHttpRequest(task<wstring> httpRequest) { // Enable only the Cancel button. GetButton->IsEnabled = false; PostButton->IsEnabled = false; CancelButton->IsEnabled = true; // Clear the previous response and start the progress ring. ResponseTextBlock->Text = ""; ResponseProgressRing->IsActive = true; // Create a continuation that shows the results on the UI. // The UI must be updated on the ASTA thread. // Therefore, schedule the continuation to run on the current context. httpRequest.then([this](task<wstring> previousTask) { try { // // Show the result on the UI. wstring response = previousTask.get(); if (m_httpRequest.GetStatusCode() == 200) { // The request succeeded. Show the response. ResponseTextBlock->Text = ref new String(response.c_str()); } else { // The request failed. Show the status code and reason. wstringstream ss; ss << L"The server returned " << m_httpRequest.GetStatusCode() << L" (" << m_httpRequest.GetReasonPhrase() << L')'; ResponseTextBlock->Text = ref new String(ss.str().c_str()); } } catch (const task_canceled&) { // Indicate that the operation was canceled. ResponseTextBlock->Text = "The operation was canceled"; } catch (Exception^ e) { // Indicate that the operation failed. ResponseTextBlock->Text = "The operation failed"; // TODO: Handle the error further. (void)e; } // Enable the Get and Post buttons. GetButton->IsEnabled = true; PostButton->IsEnabled = true; CancelButton->IsEnabled = false; // Stop the progress ring. ResponseProgressRing->IsActive = false; }, task_continuation_context::use_current()); }Under Linker i projektegenskaperna anger du
shcore.libochmsxml6.lib.
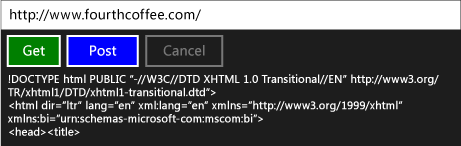
Här är appen som körs:
Nästa steg
Genomgång av samtidighetskörning
Se även
Uppgiftsparallellitet
Annullering i PPL
Asynkron programmering i C++
Skapa asynkrona åtgärder i C++ för UWP-appar
Snabbstart: Ansluta med XML HTTP Request (IXMLHTTPRequest2)task Class (Concurrency Runtime)
task_completion_event class