Enum Support - EF Designer
Note
EF5 Onwards Only - The features, APIs, etc. discussed in this page were introduced in Entity Framework 5. If you are using an earlier version, some or all of the information does not apply.
This video and step-by-step walkthrough shows how to use enum types with the Entity Framework Designer. It also demonstrates how to use enums in a LINQ query.
This walkthrough will use Model First to create a new database, but the EF Designer can also be used with the Database First workflow to map to an existing database.
Enum support was introduced in Entity Framework 5. To use the new features like enums, spatial data types, and table-valued functions, you must target .NET Framework 4.5. Visual Studio 2012 targets .NET 4.5 by default.
In Entity Framework, an enumeration can have the following underlying types: Byte, Int16, Int32, Int64 , or SByte.
Watch the Video
This video shows how to use enum types with the Entity Framework Designer. It also demonstrates how to use enums in a LINQ query.
Presented By: Julia Kornich
Pre-Requisites
You will need to have Visual Studio 2012, Ultimate, Premium, Professional, or Web Express edition installed to complete this walkthrough.
Set up the Project
- Open Visual Studio 2012
- On the File menu, point to New, and then click Project
- In the left pane, click Visual C#, and then select the Console template
- Enter EnumEFDesigner as the name of the project and click OK
Create a New Model using the EF Designer
- Right-click the project name in Solution Explorer, point to Add, and then click New Item
- Select Data from the left menu and then select ADO.NET Entity Data Model in the Templates pane
- Enter EnumTestModel.edmx for the file name, and then click Add
- On the Entity Data Model Wizard page, select Empty Model in the Choose Model Contents dialog box
- Click Finish
The Entity Designer, which provides a design surface for editing your model, is displayed.
The wizard performs the following actions:
- Generates the EnumTestModel.edmx file that defines the conceptual model, the storage model, and the mapping between them. Sets the Metadata Artifact Processing property of the .edmx file to Embed in Output Assembly so the generated metadata files get embedded into the assembly.
- Adds a reference to the following assemblies: EntityFramework, System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations, and System.Data.Entity.
- Creates EnumTestModel.tt and EnumTestModel.Context.tt files and adds them under the .edmx file. These T4 template files generate the code that defines the DbContext derived type and POCO types that map to the entities in the .edmx model.
Add a New Entity Type
- Right-click an empty area of the design surface, select Add -> Entity, the New Entity dialog box appears
- Specify Department for the type name and specify DepartmentID for the key property name, leave the type as Int32
- Click OK
- Right-click the entity and select Add New -> Scalar Property
- Rename the new property to Name
- Change the type of the new property to Int32 (by default, the new property is of String type) To change the type, open the Properties window and change the Type property to Int32
- Add another scalar property and rename it to Budget, change the type to Decimal
Add an Enum Type
In the Entity Framework Designer, right-click the Name property, select Convert to enum

In the Add Enum dialog box type DepartmentNames for the Enum Type Name, change the Underlying Type to Int32, and then add the following members to the type: English, Math, and Economics

Press OK
Save the model and build the project
Note
When you build, warnings about unmapped entities and associations may appear in the Error List. You can ignore these warnings because after we choose to generate the database from the model, the errors will go away.
If you look at the Properties window, you will notice that the type of the Name property was changed to DepartmentNames and the newly added enum type was added to the list of types.
If you switch to the Model Browser window, you will see that the type was also added to the Enum Types node.
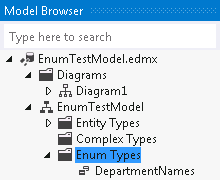
Note
You can also add new enum types from this window by clicking the right mouse button and selecting Add Enum Type. Once the type is created it will appear in the list of types and you would be able to associate with a property
Generate Database from Model
Now we can generate a database that is based on the model.
- Right-click an empty space on the Entity Designer surface and select Generate Database from Model
- The Choose Your Data Connection Dialog Box of the Generate Database Wizard is displayed Click the New Connection button Specify (localdb)\mssqllocaldb for the server name and EnumTest for the database and click OK
- A dialog asking if you want to create a new database will pop up, click Yes.
- Click Next and the Create Database Wizard generates data definition language (DDL) for creating a database The generated DDL is displayed in the Summary and Settings Dialog Box Note, that the DDL does not contain a definition for a table that maps to the enumeration type
- Click Finish Clicking Finish does not execute the DDL script.
- The Create Database Wizard does the following: Opens the EnumTest.edmx.sql in T-SQL Editor Generates the store schema and mapping sections of the EDMX file Adds connection string information to the App.config file
- Click the right mouse button in T-SQL Editor and select Execute The Connect to Server dialog appears, enter the connection information from step 2 and click Connect
- To view the generated schema, right-click on the database name in SQL Server Object Explorer and select Refresh
Persist and Retrieve Data
Open the Program.cs file where the Main method is defined. Add the following code into the Main function. The code adds a new Department object to the context. It then saves the data. The code also executes a LINQ query that returns a Department where the name is DepartmentNames.English.
using (var context = new EnumTestModelContainer())
{
context.Departments.Add(new Department{ Name = DepartmentNames.English });
context.SaveChanges();
var department = (from d in context.Departments
where d.Name == DepartmentNames.English
select d).FirstOrDefault();
Console.WriteLine(
"DepartmentID: {0} and Name: {1}",
department.DepartmentID,
department.Name);
}
Compile and run the application. The program produces the following output:
DepartmentID: 1 Name: English
To view data in the database, right-click on the database name in SQL Server Object Explorer and select Refresh. Then, click the right mouse button on the table and select View Data.
Summary
In this walkthrough we looked at how to map enum types using the Entity Framework Designer and how to use enums in code.
