หมายเหตุ
การเข้าถึงหน้านี้ต้องได้รับการอนุญาต คุณสามารถลอง ลงชื่อเข้าใช้หรือเปลี่ยนไดเรกทอรีได้
การเข้าถึงหน้านี้ต้องได้รับการอนุญาต คุณสามารถลองเปลี่ยนไดเรกทอรีได้
Controlling outbound network access is an important part of an overall network security plan. For example, you may want to limit access to web sites. Or, you may want to limit the outbound IP addresses and ports that can be accessed.
One way you can control outbound network access from an Azure subnet is with Azure Firewall. With Azure Firewall, you can configure:
- Application rules that define fully qualified domain names (FQDNs) that can be accessed from a subnet. The FQDN can also include SQL instances.
- Network rules that define source address, protocol, destination port, and destination address.
Network traffic is subjected to the configured firewall rules when you route your network traffic to the firewall as the subnet default gateway.
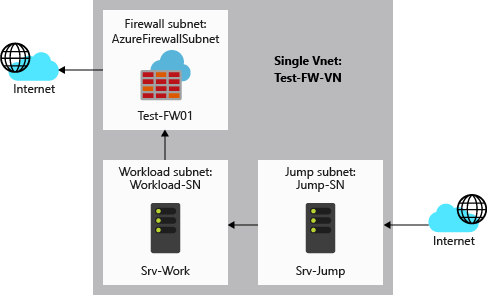
For this article, you create a simplified single VNet with three subnets for easy deployment. For production deployments, a hub and spoke model is recommended. The firewall is in its own VNet. The workload servers are in peered VNets in the same region with one or more subnets.
- AzureFirewallSubnet - the firewall is in this subnet.
- Workload-SN - the workload server is in this subnet. This subnet's network traffic goes through the firewall.
- AzureBastionSubnet - Azure Bastion is in this subnet, providing secure access to the workload server.
In this article, you learn how to:
- Set up a test network environment
- Deploy a firewall
- Create a default route
- Configure an application rule to allow access to www.microsoft.com
- Configure a network rule to allow access to external DNS servers
- Test the firewall
If you prefer, you can complete this procedure using the Azure portal or Azure PowerShell.
If you don't have an Azure account, create a free account before you begin.
Prerequisites
Use the Bash environment in Azure Cloud Shell. For more information, see Get started with Azure Cloud Shell.
If you prefer to run CLI reference commands locally, install the Azure CLI. If you're running on Windows or macOS, consider running Azure CLI in a Docker container. For more information, see How to run the Azure CLI in a Docker container.
If you're using a local installation, sign in to the Azure CLI by using the az login command. To finish the authentication process, follow the steps displayed in your terminal. For other sign-in options, see Authenticate to Azure using Azure CLI.
When you're prompted, install the Azure CLI extension on first use. For more information about extensions, see Use and manage extensions with the Azure CLI.
Run az version to find the version and dependent libraries that are installed. To upgrade to the latest version, run az upgrade.
- This article requires version 2.55.0 or later of the Azure CLI. If using Azure Cloud Shell, the latest version is already installed.
Set up the network
First, create a resource group to contain the resources needed to deploy the firewall. Then create a VNet, subnets, and test servers.
Create a resource group
The resource group contains all the resources for the deployment.
az group create --name Test-FW-RG --location eastus
Create a VNet
This virtual network has three subnets.
Note
The size of the AzureFirewallSubnet subnet is /26. For more information about the subnet size, see Azure Firewall FAQ.
az network vnet create \
--name Test-FW-VN \
--resource-group Test-FW-RG \
--location eastus \
--address-prefix 10.0.0.0/16 \
--subnet-name AzureFirewallSubnet \
--subnet-prefix 10.0.1.0/26
az network vnet subnet create \
--name Workload-SN \
--resource-group Test-FW-RG \
--vnet-name Test-FW-VN \
--address-prefix 10.0.2.0/24
az network vnet subnet create \
--name AzureBastionSubnet \
--resource-group Test-FW-RG \
--vnet-name Test-FW-VN \
--address-prefix 10.0.3.0/26
Create a virtual machine
Create a NIC for Srv-Work with specific DNS server IP addresses and no public IP address to test with.
az network nic create \
--resource-group Test-FW-RG \
--name Srv-Work-NIC \
--vnet-name Test-FW-VN \
--subnet Workload-SN \
--dns-servers <replace with External DNS ip #1> <replace with External DNS ip #2>
Now create the workload virtual machine. The following command creates an Ubuntu Server 22.04 LTS VM with SSH key authentication and installs Nginx. When prompted, save the generated private key to a .pem file for use when connecting through Azure Bastion.
az vm create \
--resource-group Test-FW-RG \
--name Srv-Work \
--location eastus \
--image Ubuntu2204 \
--nics Srv-Work-NIC \
--admin-username azureuser \
--generate-ssh-keys \
--custom-data cloud-init.txt
Create a cloud-init.txt file with the following content to install Nginx:
#cloud-config
package_upgrade: true
packages:
- nginx
runcmd:
- echo '<h1>'$(hostname)'</h1>' | sudo tee /var/www/html/index.html
Note
Azure provides a default outbound access IP for VMs that either aren't assigned a public IP address or are in the backend pool of an internal basic Azure load balancer. The default outbound access IP mechanism provides an outbound IP address that isn't configurable.
The default outbound access IP is disabled when one of the following events happens:
- A public IP address is assigned to the VM.
- The VM is placed in the backend pool of a standard load balancer, with or without outbound rules.
- An Azure NAT Gateway resource is assigned to the subnet of the VM.
VMs that you create by using virtual machine scale sets in flexible orchestration mode don't have default outbound access.
For more information about outbound connections in Azure, see Default outbound access in Azure and Use Source Network Address Translation (SNAT) for outbound connections.
Deploy the firewall
Now deploy the firewall into the virtual network.
az network firewall create \
--name Test-FW01 \
--resource-group Test-FW-RG \
--location eastus
az network public-ip create \
--name fw-pip \
--resource-group Test-FW-RG \
--location eastus \
--allocation-method static \
--sku standard
az network firewall ip-config create \
--firewall-name Test-FW01 \
--name FW-config \
--public-ip-address fw-pip \
--resource-group Test-FW-RG \
--vnet-name Test-FW-VN
az network firewall update \
--name Test-FW01 \
--resource-group Test-FW-RG
az network public-ip show \
--name fw-pip \
--resource-group Test-FW-RG
fwprivaddr="$(az network firewall ip-config list --resource-group Test-FW-RG --firewall-name Test-FW01 --query "[?name=='FW-config'].privateIpAddress" --output tsv)"
Note the private IP address. You'll use it later when you create the default route.
Deploy Azure Bastion
Deploy Azure Bastion to securely connect to the Srv-Work virtual machine without requiring public IP addresses or a jump server.
az network public-ip create \
--resource-group Test-FW-RG \
--name bastion-pip \
--sku Standard \
--location eastus
az network bastion create \
--name Test-Bastion \
--public-ip-address bastion-pip \
--resource-group Test-FW-RG \
--vnet-name Test-FW-VN \
--location eastus \
--sku Basic
Note
Azure Bastion deployment can take approximately 10 minutes to complete.
Create a default route
Create a route table, with BGP route propagation disabled
az network route-table create \
--name Firewall-rt-table \
--resource-group Test-FW-RG \
--location eastus \
--disable-bgp-route-propagation true
Create the route.
az network route-table route create \
--resource-group Test-FW-RG \
--name DG-Route \
--route-table-name Firewall-rt-table \
--address-prefix 0.0.0.0/0 \
--next-hop-type VirtualAppliance \
--next-hop-ip-address $fwprivaddr
Associate the route table to the subnet
az network vnet subnet update \
--name Workload-SN \
--resource-group Test-FW-RG \
--vnet-name Test-FW-VN \
--address-prefixes 10.0.2.0/24 \
--route-table Firewall-rt-table
Configure an application rule
The application rule allows outbound access to www.microsoft.com.
az network firewall application-rule create \
--collection-name App-Coll01 \
--firewall-name Test-FW01 \
--name Allow-Microsoft \
--protocols Http=80 Https=443 \
--resource-group Test-FW-RG \
--target-fqdns www.microsoft.com \
--source-addresses 10.0.2.0/24 \
--priority 200 \
--action Allow
Azure Firewall includes a built-in rule collection for infrastructure FQDNs that are allowed by default. These FQDNs are specific for the platform and can't be used for other purposes. For more information, see Infrastructure FQDNs.
Configure a network rule
The network rule allows outbound access to two public DNS IP addresses of your choosing at port 53 (DNS).
az network firewall network-rule create \
--collection-name Net-Coll01 \
--destination-addresses <replace with DNS ip #1> <replace with DNS ip #2> \
--destination-ports 53 \
--firewall-name Test-FW01 \
--name Allow-DNS \
--protocols UDP \
--resource-group Test-FW-RG \
--priority 200 \
--source-addresses 10.0.2.0/24 \
--action Allow
Test the firewall
Now, test the firewall to confirm that it works as expected.
Note the private IP address for the Srv-Work virtual machine:
az vm list-ip-addresses \ --resource-group Test-FW-RG \ --name Srv-WorkIn the Azure portal, navigate to the Srv-Work virtual machine and select Connect > Connect via Bastion.
Provide the username azureuser and upload the private key
.pemfile that was generated when you created the VM. Select Connect to open an SSH session.In the SSH session, run the following commands to test DNS resolution:
nslookup www.google.com nslookup www.microsoft.comBoth commands should return answers, showing that your DNS queries are getting through the firewall.
Run the following commands to test web access:
curl https://www.microsoft.com curl https://www.google.comThe
www.microsoft.comrequest should succeed and return HTML content, while thewww.google.comrequest should fail or time out. This demonstrates that your firewall rules are operating as expected.
So now you've verified that the firewall rules are working:
- You can resolve DNS names using the configured external DNS server.
- You can browse to the one allowed FQDN, but not to any others.
Clean up resources
You can keep your firewall resources for the next tutorial, or if no longer needed, delete the Test-FW-RG resource group to delete all firewall-related resources:
az group delete \
--name Test-FW-RG