How to secure a single-page web application with non-interactive sign-in
Secure a single-page web application with Microsoft Entra ID, even when the user isn't able to sign in to Microsoft Entra ID.
To create this non-interactive authentication flow, first create an Azure Function secure web service that's responsible for acquiring access tokens from Microsoft Entra ID. This web service is exclusively available only to your single-page web application.
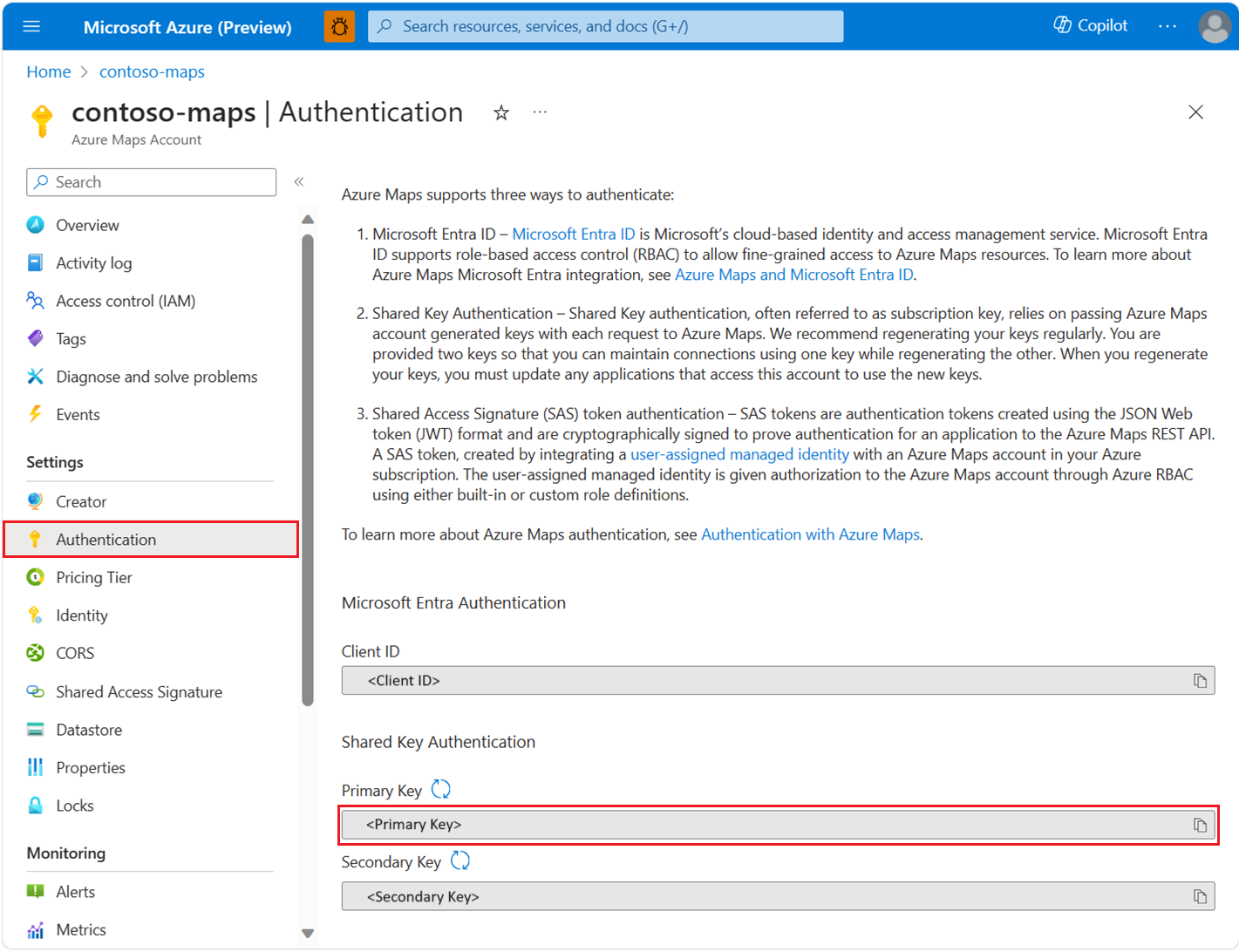
To view your Azure Maps account authentication details in the Azure portal:
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Navigate to the Azure portal menu. Select All resources, and then select your Azure Maps account.
Under Settings in the left pane, select Authentication.
Three values are created when the Azure Maps account is created. They're used to support two types of authentication in Azure Maps:
- Microsoft Entra authentication: The
Client IDrepresents the account that is to be used for REST API requests. TheClient IDvalue should be stored in application configuration, and then it should be retrieved before making Azure Maps HTTP requests that use Microsoft Entra authentication. - Shared Key Authentication: The
Primary KeyandSecondary Keyare used as the subscription key for Shared Key authentication. Shared Key authentication relies on passing the key generated by the Azure Maps account with each request to Azure Maps. We recommend that you regularly regenerate your keys. To maintain current connections during regeneration, two keys are provided. One key can be in use, while regenerating the other. When you regenerate your keys, you must update any applications that access this account to use the new keys. For more information, see Authentication with Azure Maps
Tip
Azure Maps can support access tokens from user sign-on or interactive flows. You can use interactive flows for a more restricted scope of access revocation and secret management.
Create an Azure function
To create a secured web service application that's responsible for authentication to Microsoft Entra ID:
Create a function in the Azure portal. For more information, see Getting started with Azure Functions.
Configure CORS policy on the Azure function to be accessible by the single-page web application. The CORS policy secures browser clients to the allowed origins of your web application. For more information, see Add CORS functionality.
Add a system-assigned identity on the Azure function to enable creation of a service principal to authenticate to Microsoft Entra ID.
Grant role-based access for the system-assigned identity to the Azure Maps account. For more information, see Grant role-based access.
Write code for the Azure function to obtain Azure Maps access tokens using system-assigned identity with one of the supported mechanisms or the REST protocol. For more information, see Obtain tokens for Azure resources.
Here's an example REST protocol:
GET /MSI/token?resource=https://atlas.microsoft.com/&api-version=2019-08-01 HTTP/1.1 Host: localhost:4141And here's an example response:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Content-Type: application/json { "access_token": "eyJ0eXAi…", "expires_on": "1586984735", "resource": "https://atlas.microsoft.com/", "token_type": "Bearer", "client_id": "..." }Configure security for the Azure function HttpTrigger:
- Create a function access key
- Secure HTTP endpoint for the Azure function in production.
Configure a web application Azure Maps Web SDK.
//URL to custom endpoint to fetch Access token var url = 'https://{App-Name}.azurewebsites.net/api/{Function-Name}?code={API-Key}'; var map = new atlas.Map('myMap', { center: [-122.33, 47.6], zoom: 12, language: 'en-US', view: "Auto", authOptions: { authType: "anonymous", clientId: "<insert>", // azure map account client id getToken: function(resolve, reject, map) { fetch(url).then(function(response) { return response.text(); }).then(function(token) { resolve(token); }); } } }); // use the following events to debug, you can remove them at any time. map.events.add("tokenacquired", function () { console.log("token acquired"); }); map.events.add("error", function (err) { console.log(JSON.stringify(err.error)); });
Grant role-based access for users to Azure Maps
You can grant Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC) by assigning a Microsoft Entra group or security principal to one or more Azure Maps role definitions.
To view the available Azure role definitions for Azure Maps, see View built-in Azure Maps role definitions.
For detailed steps about how to assign an available Azure Maps role to the created managed identity or the service principal, see Assign Azure roles using the Azure portal
To efficiently manage the Azure Maps app and resource access of a large amount of users, see Microsoft Entra groups.
Important
For users to be allowed to authenticate to an application, the users must first be created in Microsoft Entra ID. For more information, see Add or delete users using Microsoft Entra ID.
To learn about how to effectively manage a large directory for users, see Microsoft Entra ID.
Warning
Azure Maps built-in role definitions provide a very large authorization access to many Azure Maps REST APIs. To restrict APIs access to a minimum, see create a custom role definition and assign the system-assigned identity to the custom role definition. This enables the least privilege necessary for the application to access Azure Maps.
Next steps
Further understanding of a single-page application scenario:
Find the API usage metrics for your Azure Maps account:
Explore other samples that show how to integrate Microsoft Entra ID with Azure Maps: