Give Azure IoT Edge modules access to a device's local storage
Applies to: ![]() IoT Edge 1.5
IoT Edge 1.5 ![]() IoT Edge 1.4
IoT Edge 1.4
Important
IoT Edge 1.5 LTS and IoT Edge 1.4 LTS are supported releases. IoT Edge 1.4 LTS is end of life on November 12, 2024. If you are on an earlier release, see Update IoT Edge.
IoT Edge modules can use storage on the host IoT Edge device itself for improved reliability, especially when operating offline.
Configure system modules to use persistent storage
By default, IoT Edge system modules, IoT Edge agent and IoT Edge hub, store state in the ephemeral file system of their container instance. This state is lost when the container instance is recycled, for example, when module image version or createOptions is updated.
For production scenarios, use a persistent storage location on the host filesystem to store system module state. Doing so improves solution robustness and cloud message delivery guarantees.
To set up system modules to use persistent storage:
For both IoT Edge hub and IoT Edge agent, add an environment variable called StorageFolder that points to a directory in the module.
For both IoT Edge hub and IoT Edge agent, add binds to connect a local directory on the host machine to a directory in the module. For example:
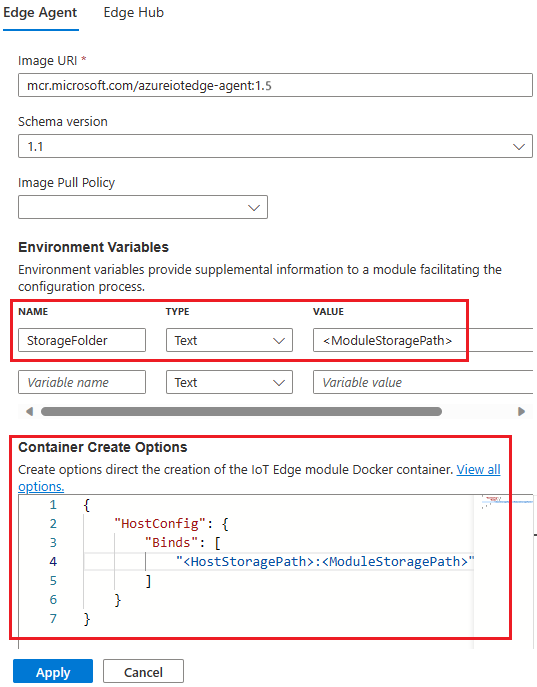
Replace
<HostStoragePath>and<ModuleStoragePath>with your host and module storage path. Both values must be an absolute path and<HostStoragePath>must exist.
You can configure the local storage directly in the deployment manifest. For example, if you want to map the following storage paths:
| Module | Host storage path | Module storage path |
|---|---|---|
| edgeAgent | /srv/edgeAgent | /tmp/edgeAgent |
| edgeHub | /srv/edgeHub | /tmp/edgeHub |
Your deployment manifest would be similar to the following:
"systemModules": {
"edgeAgent": {
"env": {
"StorageFolder": {
"value": "/tmp/edgeAgent"
}
},
"settings": {
"image": "mcr.microsoft.com/azureiotedge-agent:1.5",
"createOptions": "{\"HostConfig\":{\"Binds\":[\"/srv/edgeAgent:/tmp/edgeAgent\"]}}"
},
"type": "docker"
},
"edgeHub": {
"env": {
"StorageFolder": {
"value": "/tmp/edgeHub"
}
},
"restartPolicy": "always",
"settings": {
"image": "mcr.microsoft.com/azureiotedge-hub:1.5",
"createOptions": "{\"HostConfig\":{\"Binds\":[\"/srv/edgeHub:/tmp/edgeHub\"],\"PortBindings\":{\"443/tcp\":[{\"HostPort\":\"443\"}],\"5671/tcp\":[{\"HostPort\":\"5671\"}],\"8883/tcp\":[{\"HostPort\":\"8883\"}]}}}"
},
"status": "running",
"type": "docker"
}
}
Note
If you are using a snap installation, ensure you choose a host storage path that is accessible to the snaps. For example, $HOME/snap/azure-iot-edge/current/modules/.
Automatic host system permissions management
On version 1.4 and newer, there's no need for manually setting ownership or permissions for host storage backing the StorageFolder. Permissions and ownership are automatically managed by the system modules during startup.
Note
Automatic permission management of host bound storage only applies to system modules, IoT Edge agent and Edge hub. For custom modules, manual management of permissions and ownership of bound host storage is required if the custom module container isn't running as root user.
Link module storage to device storage for custom modules
If your custom module requires access to persistent storage on the host file system, use the module's create options to bind a storage folder in module container to a folder on the host machine. For example:
{
"HostConfig": {
"Mounts": [
{
"Target": "<ModuleStoragePath>",
"Source": "<HostStoragePath>",
"Type": "bind",
"ReadOnly": false
}
]
}
}
Replace <HostStoragePath> and <ModuleStoragePath> with your host and module storage path; both values must be an absolute path. Refer to the Docker Engine Mount specification for option details.
Host system permissions
Make sure that the user profile your module is using has the required read, write, and execute permissions to the host system directory. By default, containers run as root user that already has the required permissions. But your module's Dockerfile might specify use of a non-root user in which case host storage permissions must be manually configured.
There are several ways to manage directory permissions on Linux systems, including using chown to change the directory owner and then chmod to change the permissions. For example to allow host storage access to a module running as non-root user ID 1000, use the following commands:
sudo chown 1000 <HostStoragePath>
sudo chmod 700 <HostStoragePath>
Encrypted data in module storage
When modules invoke the IoT Edge daemon's workload API to encrypt data, the encryption key is derived using the module ID and module's generation ID. A generation ID is used to protect secrets if a module is removed from the deployment and then another module with the same module ID is later deployed to the same device. You can view a module's generation ID using the Azure CLI command az iot hub module-identity show.
If you want to share files between modules across generations, they must not contain any secrets or they will fail to be decrypted.
Next steps
For an additional example of accessing host storage from a module, see Store data at the edge with Azure Blob Storage on IoT Edge.