Integrate API Management with Service Fabric in Azure
Deploying Azure API Management with Service Fabric is an advanced scenario. API Management is useful when you need to publish APIs with a rich set of routing rules for your back-end Service Fabric services. Cloud applications typically need a front-end gateway to provide a single point of ingress for users, devices, or other applications. In Service Fabric, a gateway can be any stateless service designed for traffic ingress such as an ASP.NET Core application, Event Hubs, IoT Hub, or Azure API Management.
This article shows you how to set up Azure API Management with Service Fabric to route traffic to a back-end service in Service Fabric. When you're finished, you have deployed API Management to a VNET, configured an API operation to send traffic to back-end stateless services. To learn more about Azure API Management scenarios with Service Fabric, see the overview article.
Note
We recommend that you use the Azure Az PowerShell module to interact with Azure. To get started, see Install Azure PowerShell. To learn how to migrate to the Az PowerShell module, see Migrate Azure PowerShell from AzureRM to Az.
Availability
Important
This feature is available in the Premium and Developer tiers of API Management due to the required virtual network support.
Prerequisites
Before you begin:
- If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account
- Install Azure PowerShell or Azure CLI.
- Create a secure Windows cluster in a network security group.
- If you deploy a Windows cluster, set up a Windows development environment. Install Visual Studio 2019 and the Azure development, ASP.NET and web development, and .NET Core cross-platform development workloads. Then set up a .NET development environment.
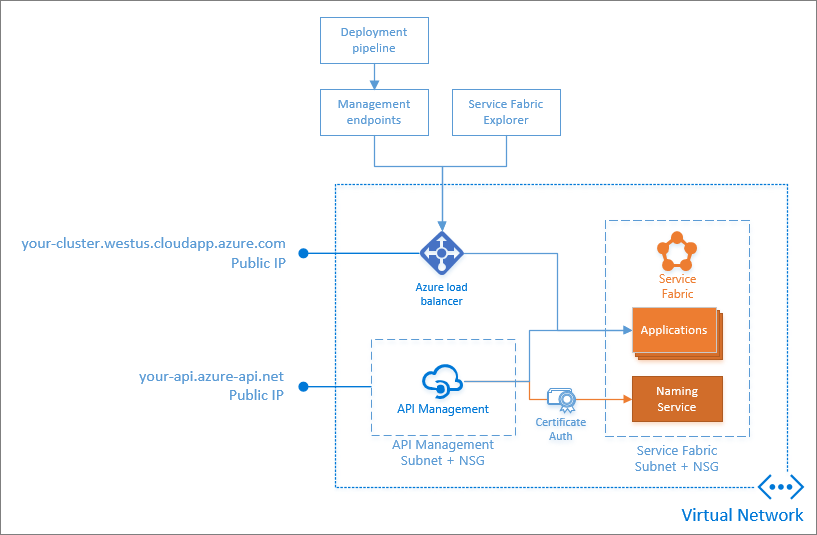
Network topology
Now that you have a secure Windows cluster on Azure, deploy API Management to the virtual network (VNET) in the subnet and NSG designated for API Management. For this article, the API Management Resource Manager template is pre-configured to use the names of the VNET, subnet, and NSG that you set up in the Windows cluster tutorial This article deploys the following topology to Azure in which API Management and Service Fabric are in subnets of the same Virtual Network:
Sign in to Azure and select your subscription
Sign in to your Azure account select your subscription before you execute Azure commands.
Connect-AzAccount
Get-AzSubscription
Set-AzContext -SubscriptionId <guid>
az login
az account set --subscription <guid>
Deploy a Service Fabric back-end service
Before configuring API Management to route traffic to a Service Fabric back-end service, first you need a running service to accept requests.
Create a basic stateless ASP.NET Core Reliable Service using the default Web API project template. This creates an HTTP endpoint for your service, which you expose through Azure API Management.
Start Visual Studio as Administrator and create an ASP.NET Core service:
In Visual Studio, select File -> New Project.
Select the Service Fabric Application template under Cloud and name it "ApiApplication".
Select the stateless ASP.NET Core service template and name the project "WebApiService".
Select the Web API ASP.NET Core 2.1 project template.
Once the project is created, open
PackageRoot\ServiceManifest.xmland remove thePortattribute from the endpoint resource configuration:<Resources> <Endpoints> <Endpoint Protocol="http" Name="ServiceEndpoint" Type="Input" /> </Endpoints> </Resources>Removing the port allows Service Fabric to specify a port dynamically from the application port range, opened through the Network Security Group in the Cluster Resource Manager template, allowing traffic to flow to it from API Management.
Press F5 in Visual Studio to verify the web API is available locally.
Open Service Fabric Explorer and drill down to a specific instance of the ASP.NET Core service to see the base address the service is listening on. Add
/api/valuesto the base address and open it in a browser, which invokes the Get method on the ValuesController in the Web API template. It returns the default response that is provided by the template, a JSON array that contains two strings:["value1", "value2"]`This is the endpoint that you expose through API Management in Azure.
Finally, deploy the application to your cluster in Azure. In Visual Studio, right-click the Application project and select Publish. Provide your cluster endpoint (for example,
mycluster.southcentralus.cloudapp.azure.com:19000) to deploy the application to your Service Fabric cluster in Azure.
An ASP.NET Core stateless service named fabric:/ApiApplication/WebApiService should now be running in your Service Fabric cluster in Azure.
Download and understand the Resource Manager templates
Download and save the following Resource Manager templates and parameters file:
The network-apim.json template deploys a new subnet and network security group in the virtual network where the Service Fabric cluster is deployed.
The following sections describe the resources being defined by the apim.json template. For more information, follow the links to the template reference documentation within each section. The configurable parameters defined in the apim.parameters.json parameters file are set later in this article.
Microsoft.ApiManagement/service
Microsoft.ApiManagement/service describes the API Management service instance: name, SKU or tier, resource group location, publisher information, and virtual network.
Microsoft.ApiManagement/service/certificates
Microsoft.ApiManagement/service/certificates configures API Management security. API Management must authenticate with your Service Fabric cluster for service discovery using a client certificate that has access to your cluster. This article uses the same certificate specified previously when creating the Windows cluster, which by default can be used to access your cluster.
This article uses the same certificate for client authentication and cluster node-to-node security. You may use a separate client certificate if you have one configured to access your Service Fabric cluster. Provide the name, password, and data (base-64 encoded string) of the private key file (.pfx) of the cluster certificate that you specified when creating your Service Fabric cluster.
Microsoft.ApiManagement/service/backends
Microsoft.ApiManagement/service/backends describes the backend service that traffic is forwarded to.
For Service Fabric backends, the Service Fabric cluster is the backend instead of a specific Service Fabric service. This allows a single policy to route to more than one service in the cluster. The url field here is a fully qualified service name of a service in your cluster that all requests are routed to by default if no service name is specified in a backend policy. You may use a fake service name, such as "fabric:/fake/service" if you do not intend to have a fallback service. resourceId specifies the cluster management endpoint. clientCertificateThumbprint and serverCertificateThumbprints identify certificates used to authenticate with the cluster.
Microsoft.ApiManagement/service/products
Microsoft.ApiManagement/service/products creates a product. In Azure API Management, a product contains one or more APIs as well as a usage quota and the terms of use. Once a product is published, developers can subscribe to the product and begin to use the product's APIs.
Enter a descriptive displayName and description for the product. For this article, a subscription is required but subscription approval by an admin is not. This product state is "published" and is visible to subscribers.
Microsoft.ApiManagement/service/apis
Microsoft.ApiManagement/service/apis creates an API. An API in API Management represents a set of operations that can be invoked by client applications. Once the operations are added, the API is added to a product and can be published. Once an API is published, it can be subscribed to and used by developers.
- displayName can be any name for your API. For this article, use "Service Fabric App".
- name provides a unique and descriptive name for the API, such as "service-fabric-app". It is displayed in the developer and publisher portals.
- serviceUrl references the HTTP service implementing the API. API management forwards requests to this address. For Service Fabric backends, this URL value is not used. You can put any value here. For this article, for example "http://servicefabric".
- path is appended to the base URL for the API management service. The base URL is common for all APIs hosted by an API Management service instance. API Management distinguishes APIs by their suffix and therefore the suffix must be unique for every API for a given publisher.
- protocols determine which protocols can be used to access the API. For this article, list http and https.
- path is a suffix for the API. For this article, use "myapp".
Microsoft.ApiManagement/service/apis/operations
Microsoft.ApiManagement/service/apis/operations Before an API in API Management can be used, operations must be added to the API. External clients use an operation to communicate with the ASP.NET Core stateless service running in the Service Fabric cluster.
To add a front-end API operation, fill out the values:
- displayName and description describe the operation. For this article, use "Values".
- method specifies the HTTP verb. For this article, specify GET.
- urlTemplate is appended to the base URL of the API and identifies a single HTTP operation. For this article, use
/api/valuesif you added the .NET backend service orgetMessageif you added the Java backend service. By default, the URL path specified here is the URL path sent to the backend Service Fabric service. If you use the same URL path here that your service uses, such as "/api/values", then the operation works without further modification. You may also specify a URL path here that is different from the URL path used by your backend Service Fabric service, in which case you also need to specify a path rewrite in your operation policy later.
Microsoft.ApiManagement/service/apis/policies
Microsoft.ApiManagement/service/apis/policies creates a backend policy, which ties everything together. This is where you configure the backend Service Fabric service to which requests are routed. You can apply this policy to any API operation. For more information, see Policies overview.
The backend configuration for Service Fabric provides the following request routing controls:
- Service instance selection by specifying a Service Fabric service instance name, either hardcoded (for example,
"fabric:/myapp/myservice") or generated from the HTTP request (for example,"fabric:/myapp/users/" + context.Request.MatchedParameters["name"]). - Partition resolution by generating a partition key using any Service Fabric partitioning scheme.
- Replica selection for stateful services.
- Resolution retry conditions that allow you to specify the conditions for re-resolving a service location and resending a request.
policyContent is the Json escaped XML contents of the policy. For this article, create a backend policy to route requests directly to the .NET or Java stateless service deployed earlier. Add a set-backend-service policy under inbound policies. Replace the sf-service-instance-name value with fabric:/ApiApplication/WebApiService if you previously deployed the .NET backend service, or fabric:/EchoServerApplication/EchoServerService if you deployed the Java service. backend-id references a backend resource, in this case the Microsoft.ApiManagement/service/backends resource defined in the apim.json template. backend-id can also reference another backend resource created using the API Management APIs. For this article, set backend-id to the value of the service_fabric_backend_name parameter.
<policies>
<inbound>
<base/>
<set-backend-service
backend-id="servicefabric"
sf-service-instance-name="service-name"
sf-resolve-condition="@(context.LastError?.Reason == "BackendConnectionFailure")" />
</inbound>
<backend>
<base/>
</backend>
<outbound>
<base/>
</outbound>
</policies>
For a full set of Service Fabric back-end policy attributes, refer to the API Management back-end documentation
Set parameters and deploy API Management
Fill in the following empty parameters in the apim.parameters.json for your deployment.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| apimInstanceName | sf-apim |
| apimPublisherEmail | myemail@contosos.com |
| apimSku | Developer |
| serviceFabricCertificateName | sfclustertutorialgroup320171031144217 |
| certificatePassword | q6D7nN%6ck@6 |
| serviceFabricCertificateThumbprint | C4C1E541AD512B8065280292A8BA6079C3F26F10 |
| serviceFabricCertificate | <base-64 encoded string> |
| url_path | /api/values |
| clusterHttpManagementEndpoint | https://mysfcluster.southcentralus.cloudapp.azure.com:19080 |
| inbound_policy | <XML string> |
certificatePassword and serviceFabricCertificateThumbprint must match the cluster certificate used to set up the cluster.
serviceFabricCertificate is the certificate as a base-64 encoded string, which can be generated using the following script:
$bytes = [System.IO.File]::ReadAllBytes("C:\mycertificates\sfclustertutorialgroup220171109113527.pfx");
$b64 = [System.Convert]::ToBase64String($bytes);
[System.Io.File]::WriteAllText("C:\mycertificates\sfclustertutorialgroup220171109113527.txt", $b64);
In inbound_policy, replace the sf-service-instance-name value with fabric:/ApiApplication/WebApiService if you previously deployed the .NET backend service, or fabric:/EchoServerApplication/EchoServerService if you deployed the Java service. backend-id references a backend resource, in this case the Microsoft.ApiManagement/service/backends resource defined in the apim.json template. backend-id can also reference another backend resource created using the API Management APIs. For this article, set backend-id to the value of the service_fabric_backend_name parameter.
<policies>
<inbound>
<base/>
<set-backend-service
backend-id="servicefabric"
sf-service-instance-name="service-name"
sf-resolve-condition="@(context.LastError?.Reason == "BackendConnectionFailure")" />
</inbound>
<backend>
<base/>
</backend>
<outbound>
<base/>
</outbound>
</policies>
Use the following script to deploy the Resource Manager template and parameter files for API Management:
$groupname = "sfclustertutorialgroup"
$clusterloc="southcentralus"
$templatepath="C:\clustertemplates"
New-AzResourceGroupDeployment -ResourceGroupName $groupname -TemplateFile "$templatepath\network-apim.json" -TemplateParameterFile "$templatepath\network-apim.parameters.json" -Verbose
New-AzResourceGroupDeployment -ResourceGroupName $groupname -TemplateFile "$templatepath\apim.json" -TemplateParameterFile "$templatepath\apim.parameters.json" -Verbose
ResourceGroupName="sfclustertutorialgroup"
az deployment group create --name ApiMgmtNetworkDeployment --resource-group $ResourceGroupName --template-file network-apim.json --parameters @network-apim.parameters.json
az deployment group create --name ApiMgmtDeployment --resource-group $ResourceGroupName --template-file apim.json --parameters @apim.parameters.json
Test it
You can now try sending a request to your back-end service in Service Fabric through API Management directly from the Azure portal.
In the API Management service, select API.
In the Service Fabric App API you created in the previous steps, select the Test tab and then the Values operation.
Click the Send button to send a test request to the backend service. You should see an HTTP response similar to:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Transfer-Encoding: chunked Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8 Vary: Origin Ocp-Apim-Trace-Location: https://apimgmtstodhwklpry2xgkdj.blob.core.windows.net/apiinspectorcontainer/PWSQOq_FCDjGcaI1rdMn8w2-2?sv=2015-07-08&sr=b&sig=MhQhzk%2FEKzE5odlLXRjyVsgzltWGF8OkNzAKaf0B1P0%3D&se=2018-01-28T01%3A04%3A44Z&sp=r&traceId=9f8f1892121e445ea1ae4d2bc8449ce4 Date: Sat, 27 Jan 2018 01:04:44 GMT ["value1", "value2"]
Clean up resources
A cluster is made up of other Azure resources in addition to the cluster resource itself. The simplest way to delete the cluster and all the resources it consumes is to delete the resource group.
Sign in to Azure and select the subscription ID with which you want to remove the cluster. You can find your subscription ID by logging in to the Azure portal. Delete the resource group and all the cluster resources using the Remove-AzResourceGroup cmdlet.
$ResourceGroupName = "sfclustertutorialgroup"
Remove-AzResourceGroup -Name $ResourceGroupName -Force
ResourceGroupName="sfclustertutorialgroup"
az group delete --name $ResourceGroupName
Next steps
Learn more about using API Management.
You can also use the Azure portal to create and manage Service Fabric backends for API Management.