Metadata curation in Microsoft Purview
This article describes how users can update and curate the metadata of an asset in the Microsoft Purview Data Map. Data assets in the map automatically have technical metadata like name and schema, but users can also add other information like descriptions and contacts. This extra information allows other users to better understand data assets so they can discover, govern, and use them.
Who can update metadata?
Users who have the owner role or write permissions on available, live Azure resources can access and edit those resources in free and enterprise account types. For more information about data owner metadata curation, see the data owner curation section on this page.
Users who have data curator permissions on a collection in a Microsoft Purview account can edit the metadata details for all data assets in that collection. This is only available in the enterprise version of Microsoft Purview.
Users who are using the classic Microsoft Purview Unified Catalog and have been assigned to the the data curator role group can edit the metadata details for all data assets in a Microsoft Purview account. For more information, see the role group curation section on this page.
Data owner curation
If a user is a data owner on an available, live Azure resource, they're able to access and manage that asset's metadata in Microsoft Purview. In this case, a 'data owner' isn't limited to users who have the Azure RBAC owner role on a resource. It also applies to users who have certain write permissions on the available Azure resources. The permissions needed are listed in the supported live sources section.
With those permissions, data owners able to update these aspects of a data asset:
- Description
- Contacts
- Column descriptions
Tip
Any of these updates are tracked by Microsoft Purview and can be viewed in data map history.
Role group curation
If a user has been added to the data curator role group in the classic Microsoft Purview Unified Catalog, they're able to access and manage asset metadata in Microsoft Purview depending on the version of Microsoft Purview they're using.
With the free version of Microsoft Purview governance solutions you can update these aspects:
- Display name
- Description
- Contacts
- Column descriptions
- Column names
- Column data types
- Source classifications
- Column classifications
With the enterprise version of Microsoft Purview, after extending live view, or registering and scanning an asset, you can edit all the other aspects of that asset, including adding glossary terms.
Tip
Any of these updates are tracked by Microsoft Purview and can be viewed in data map history.
Collection-level role curation
If a user has been given the data curator role on a collection in the Microsoft Purview Data Map, they're able to access and manage metadata for any assets in that collection.
Note
A user can only be assigned the data curator role on a collection in the enterprise version of Microsoft Purview.
With the data curator role, a user can update aspects of their data assets depending on the kind of asset it is.
If an asset is only available as a live view asset you can edit:
- Display name
- Description
- Contacts
- Column descriptions
- Column names
- Column data types
- Source classifications
- Column classifications
Once an asset has had live view extended for all users, or if an asset has been registered and scanned, you can edit all the other aspects of an asset, including adding glossary terms.
How to edit assets
In the Microsoft Purview portal (or the classic Microsoft Purview governance portal) search or browse for a data source or asset.
Select the asset to view details.
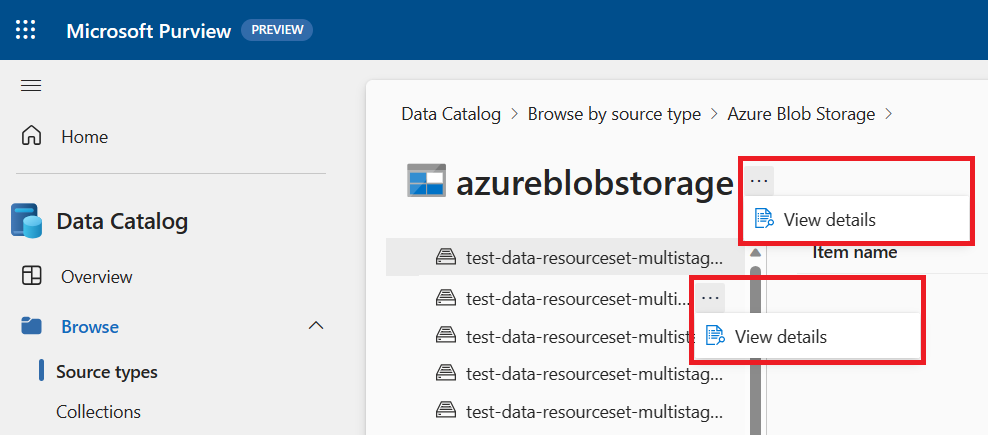
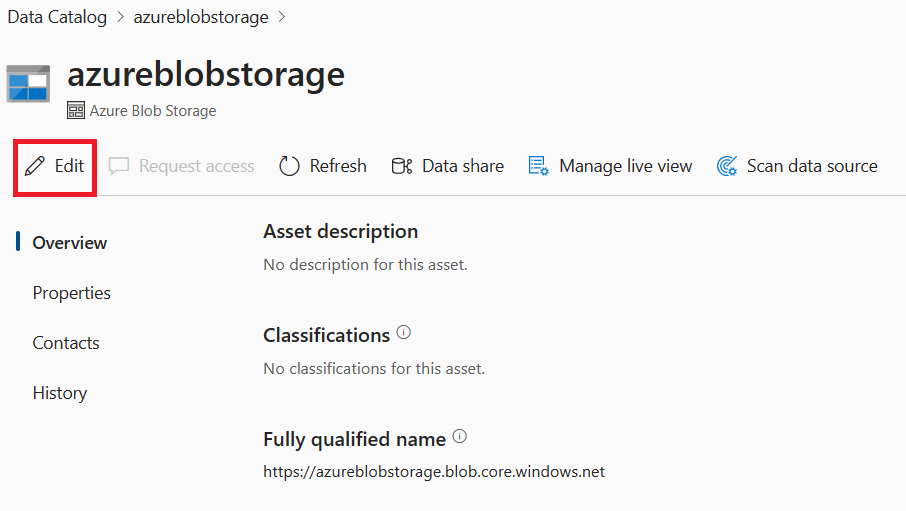
Select Edit.
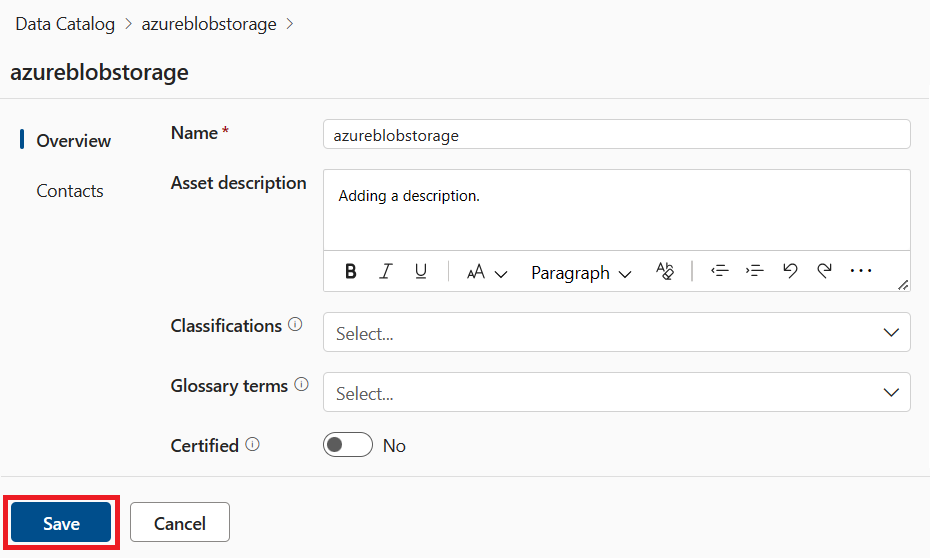
Make any changes to the metadata, and select Save when you're finished.
For more information about editing assets, including rich text editing for descriptions, see the [manage assets in the Unified Catalog article]classic-catalog-asset-details.md).
Supported live sources
| Data source | Owner permission |
|---|---|
| Azure SQL Database | "Microsoft.Sql/servers/write", "Microsoft.Sql/servers/databases/write", "Microsoft.Authorization/roleAssignments/write" |
| Azure Blob Storage | "Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/write", "Microsoft.Authorization/roleAssignments/write" |
| Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 | "Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/write", "Microsoft.Authorization/roleAssignments/write" |
Limitations
These are the current limitations for metadata curation in Microsoft Purview:
- When a user in the data curator role group edits a live mode asset for the first time, it will not work. If you edit a second time with a different edit than the first attempt, then it works.