Design for data redundancy
Azure Storage always stores multiple copies of your Tailwind Traders data. This redundancy ensures the data is protected from planned and unplanned events. These events can include transient hardware failures, network or power outages, and massive natural disasters. Storage redundancy ensures your storage account meets its availability and durability targets.
Things to know about data redundancy
Review the following characteristics of data redundancy in Azure Storage.
Redundancy is achieved by replicating data to a primary region.
When you create a storage account, you select the primary region for the account.
The primary region supports two replication options: locally redundant storage (LRS) and zone-redundant storage (ZRS).
Replication can also be done for a secondary region. A secondary region is recommended for applications that require high durability.
The paired secondary region is determined based on the primary region and can't be changed.
The secondary region is usually in a geographic location that's distant to the primary region. The distance helps to protect against regional disasters.
The secondary region supports two replication options: geo-redundant storage (GRS) and geo-zone-redundant storage (GZRS).
Redundancy in the primary region
Azure Storage offers two options for how your data is replicated in the primary region: locally redundant storage and zone-redundant storage.
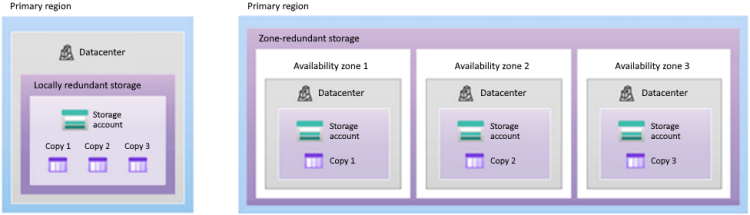
Locally redundant storage is the lowest-cost redundancy option, and offers the least durability. LRS protects your data against server rack and drive failures. However, if the data center fails, all replicas of a storage account that use LRS might be lost or unrecoverable.
Zone-redundant storage replicates synchronously across three Azure availability zones in the primary region. With ZRS, your data is still accessible for both read and write operations even if a zone becomes unavailable.
Redundancy in a secondary region
For applications that require high durability, you can choose to copy the data in your storage account to a secondary region. Azure Storage offers two options for copying your data to a secondary region: geo-redundant storage and geo-zone-redundant storage.

The primary difference between GRS and GZRS is how data is replicated in the primary region. Within the secondary region, data is always replicated synchronously with LRS.
If the primary region becomes unavailable, you can choose to fail over to the secondary region. After the failover has completed, the secondary region becomes the primary region, and you can again read and write data.
Data is replicated to the secondary region asynchronously. A failure that affects the primary region might result in data loss if the primary region can't be recovered.
With GRS or GZRS, the data in the secondary region isn't available for read or write access unless there's a failover to the secondary region. For read access to the secondary region, configure your storage account to use read-access geo-redundant storage (RA-GRS) or read-access geo-zone-redundant storage (RA-GZRS).
Things to consider when using data redundancy
You've reviewed the different options for implementing replication. Data redundancy is accomplished through a primary region and paired secondary region. As you plan the storage accounts and redundancy settings for Tailwind Traders, consider the following factor.
Consider primary replication options. Explore different scenarios for how Tailwind Traders data can be replicated in the primary region. The redundancy options present tradeoffs between lower costs and higher availability. Some business centers can require more data redundancy. Specific departments or regions might work with data that's not sensitive or which doesn't require high durability. You can implement multiple storage accounts with different redundancy to control the overall costs across the organization.
Consider locally redundant storage. Implement LRS for a low cost redundancy solution, but with limited durability. LRS is suited for Tailwind Traders apps that store data that can be easily reconstructed if data loss occurs. LRS is also a good choice for apps that are restricted to replicating data only within a country or region due to data governance requirements.
Consider zone-redundant storage. Choose ZRS for excellent performance, low latency, and resiliency for your data if it becomes temporarily unavailable. Keep in mind that ZRS by itself might not protect your data against a regional disaster where multiple zones are permanently affected.
Consider secondary regions. For applications requiring high durability, you can choose to additionally copy the data in your storage account to a secondary region that is hundreds of miles away from the primary region. If your storage account is copied to a secondary region, then your data is durable even in the case of a complete regional outage or a disaster in which the primary region isn't recoverable.
Consider read access requirements. Identify Tailwind Traders applications that require read access to the replicated data in the secondary region, if the primary region becomes unavailable for any reason. Configure your storage account with read access to the secondary region. Your applications can seamlessly shift to reading data from the secondary region if the primary region becomes unavailable.