Recognize architectural components
This reference architecture describes an enterprise-grade, production-level system. To suit your business needs, this configuration can be reduced to a single virtual machine. However, the following components are required:
Virtual network
The Azure Virtual Network service securely connects Azure resources to each other. The virtual network also connects to an on-premises environment via virtual gateway provisioned as part of ExpressRoute or Site-to-Site connection. In a typical VDC design, this virtual gateway resides in the virtual network that serves as the hub of a hub-spoke hierarchy consisting of multiple, peered virtual networks. The spokes represent individual virtual networks hosting the SAP applications and database tiers.
Subnets
Each virtual network is typically divided into separate subnets hosting application (SAP NetWeaver) and database tiers. There might be also extra subnets hosting infrastructure services (such as Active Directory domain controllers) and serving the role of network perimeter (containing jumpbox Azure Virtual Machines) – although these commonly reside in the hub virtual network.
Virtual machines
This architecture uses virtual machines running Linux for the application tier and database tier, grouped as follows:
- Application tier. Includes the Fiori Front-end Server pool, SAP Web Dispatcher pool, application server pool, and SAP Central Services cluster. For high availability of Central Services on Azure Linux virtual machines, a highly available Network File System (NFS) service is required.
- NFS cluster. This architecture uses an NFS server running on a Linux cluster to store data shared between SAP systems. This centralized cluster can be shared across multiple SAP systems. For high availability of the NFS service, the appropriate High Availability Extension for the selected Linux distribution is used.
- SAP HANA. The database tier uses two or more Linux virtual machines in a cluster to achieve high availability. HANA System Replication (HSR) is used to replicate contents between primary and secondary HANA systems. Linux clustering is used to detect system failures and facilitate automatic failover. A storage-based or cloud-based fencing mechanism can be used to ensure the failed system is isolated or shut down to avoid the cluster split-brain condition.
- Jumpbox. Also called a bastion host. This Azure Virtual Machine runs hardened operating system instance that administrators use to connect to the other virtual machines. It can run Windows or Linux. Use a Windows jumpbox to run tools such as HANA Cockpit or HANA Studio.
Load balancers
Both built-in SAP load balancers and Azure load balancer are used to achieve HA. Azure load balancer instances are used to distribute traffic to virtual machines in the application and database tiers.
Availability sets
Virtual machines for all pools and clusters (Web Dispatcher, SAP application servers, Central Services, NFS, and HANA) are grouped into separate availability sets, and at least two virtual machines are provisioned per role. This makes the virtual machines eligible for a higher service level agreement (SLA).
Network interface cards (NICs)
Network interface cards attach virtual machines to a virtual network.
Network security groups (NSGs)
NSGs restrict incoming, outgoing, and intra-subnet traffic in a virtual network.
Virtual gateway
A virtual gateway facilitates extending your on-premises network to the Azure virtual network. ExpressRoute is the recommended service for cross-premises connectivity of SAP deployments in Azure, but a Site-to-Site VPN or Virtual WAN can serve as alternatives.
Disks
Azure Virtual Machine disks provide persistent storage for SAP workloads.
SAP Web Dispatcher pool
The Web Dispatcher component is used as a load balancer for SAP traffic among the SAP application servers. To achieve high availability for the Web Dispatcher component, Azure load balancer is used to implement the parallel Web Dispatcher setup. Web Dispatcher uses in a round-robin configuration for HTTP(S) traffic distribution among the available Web Dispatchers in the load balanced backend pool.
Both SAP Web Dispatcher and Azure Application Gateway solutions work as a reverse proxy, and therefore it would be tempting to use only the Application Gateway. The Web Dispatcher, however, contains unique features to understand the SAP landscape and therefore the Web Dispatcher load balancing has advantages over Application Gateway. The SAP Web Dispatcher decides whether the incoming request should be forwarded to an ABAP or Java Server and the SAP Web Dispatcher carries out the following tasks:
- Checks the session ID to pass subsequent requests for stateful sessions to the processing server (Session-Stickiness).
- Decides whether the request is an ABAP request (e.g. a BSP application) or a Java request (for example, a JSP or a servlet).
- Load Balancing
- HTTPS scheduling or end-to-end SSL
- URL filtering
On the other hand, the Azure Application Gateway offers advanced threat detection and web application firewall, which significantly increase security of the entire landscape, especially if the system is exposed to the internet. Thus, combining both solutions is recommended.
Fiori Front-end Server
The Fiori Front-end Server uses a NetWeaver Gateway (which facilitates exposing SAP application data as an OData service). For small deployments, the gateway can be loaded on the Fiori server. For large deployments, a separate server for the NetWeaver Gateway might be deployed in front of the Fiori Front-end Server pool.
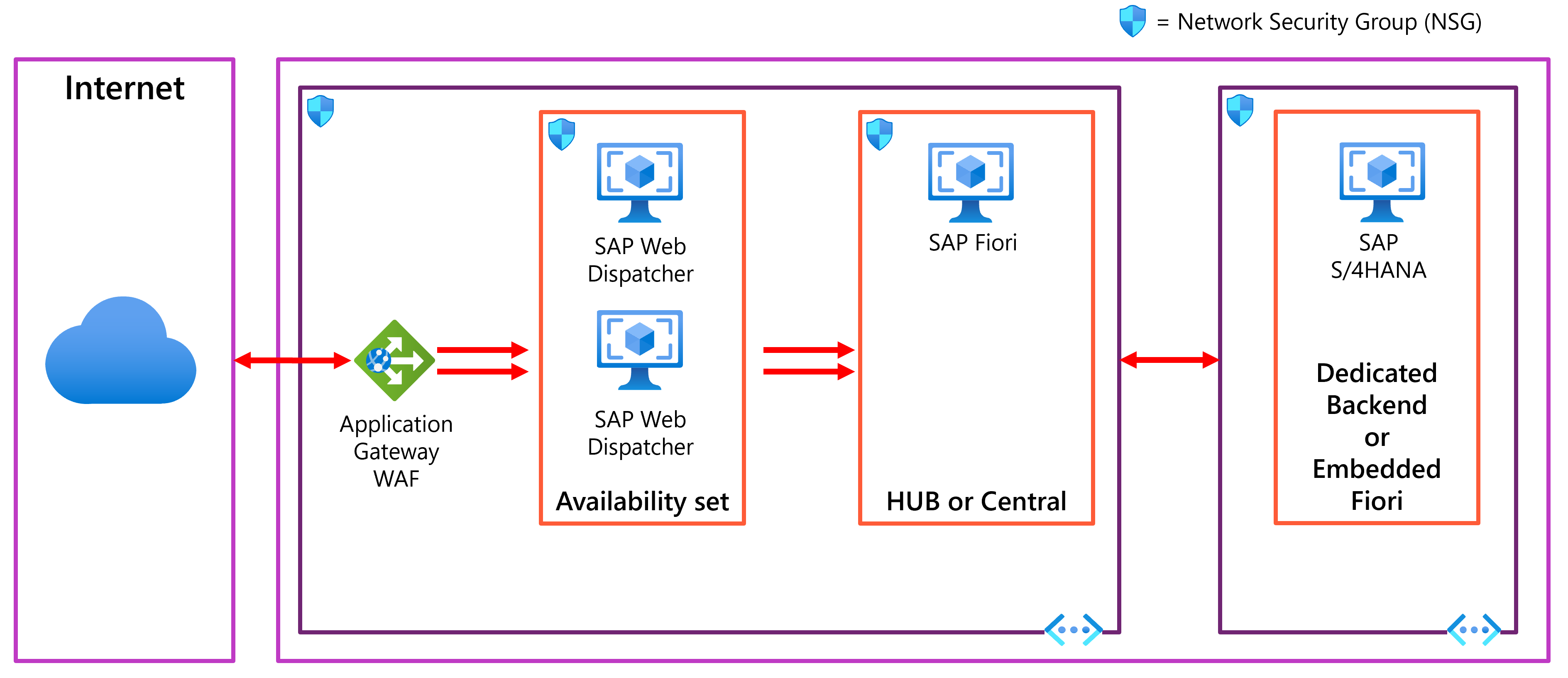
SAP Central Services cluster
The Central Services is a potential single point of failure (SPOF) when deployed to a single virtual machine — a typical deployment when high availability isn't a requirement. To implement a high availability solution, deploy multiple Central Services instances and configure them as members of a failover cluster with a shared disk or a file share providing highly available storage accessible by all cluster nodes. As mentioned earlier, Azure doesn't support natively shared disks, but you can use third-party solutions (such as SIOS DataKeeper Cluster Edition, which replicates synchronously independent disks owned by individual cluster nodes) to implement this functionality on Azure Virtual Machines running Linux or Windows Server. For Linux accessible shares, you can use highly available NFS deployment of Azure Virtual Machines.
Database servers
The database tier uses two or more Linux virtual machines in a cluster to achieve high availability. HANA System Replication (HSR) is used to replicate contents between primary and secondary HANA systems. Linux clustering is used to detect system failures and facilitate automatic failover. A storage-based or cloud-based fencing mechanism can be used to ensure the failed system is isolated or shut down to avoid the cluster split-brain condition.
Application servers pool
To provide high availability of application servers, simply deploy the primary application server and one or more extra application servers. To manage logon groups for ABAP application servers, the SMLG transaction is used. It uses the load balancing function within the message server of the Central Services to distribute workload among SAP application servers pool for SAPGUIs and RFC traffic. The application server connection to the highly available Central Services is through the cluster virtual network name.