Define Hyper-V Replica
While Contoso prepares to virtualize and migrate its workloads, as the Windows Server administrator, you need to determine an appropriate BCDR solution. With this solution, operations could continue and data could be recovered if a natural disaster occurs, such as an earthquake, flooding, or fire. You'll start this process by learning about Hyper-V Replica.
Overview of Hyper-V Replica
Hyper-V failover clusters are used to make virtual machines (VMs) highly available, but they're typically limited to a single location. Multi-site clusters usually depend on specialized hardware and can be complicated and expensive to implement. If a natural disaster such as an earthquake or a flood occurred, all server infrastructure at the affected location could be lost.
One possible solution is to periodically copy the VM manually. You also can back up the VM and its storage. Although this solution achieves the desired result, it's resource intensive and time-consuming. In addition, because you perform backups only periodically, the backup is seldom as current as the running VM.
You can use Hyper-V Replica to implement an affordable BCDR solution for a virtual environment:
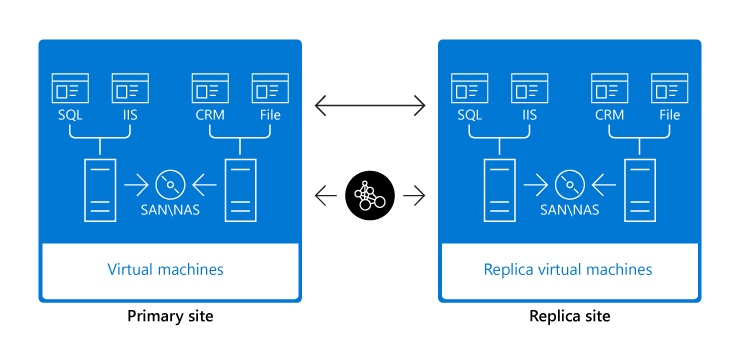
Hyper-V Replica can protect against data loss from site outage by copying a live VM as a replica VM from one location to another. If the site that contains the primary VM becomes unavailable, the replica VM is available to keep workloads available.
If necessary, you can use Hyper-V Replica to extend replication of the offline copy to a third location.
If your organization only has a single location available, you can still use Hyper-V Replica to replicate VMs to a partner organization in another location, to a hosting provider, or to Microsoft Azure.
Hyper-V Replica can have the following two instances of a single VM residing on different Hyper-V hosts:
- The main, actively running VM, which is called a primary VM.
- An offline copy of the primary VM, which is called a replica VM.
If failure occurs at the primary server site, you can use Hyper-V Replica to perform a failover of the VM(s) to the replica server at a secondary server site. This will incur minimal downtime.
Prerequisites for Hyper-V Replica implementation
Before implementing Hyper-V Replica, ensure that the virtualization infrastructure has the following prerequisites:
- A supported version of Windows Server with the Hyper-V role installed at both the primary and replica locations.
- Sufficient storage on both the primary and replica Hyper-V hosts to store and run all VMs, such as the local VMs and the replicated VMs. Replicated VMs are in a turned-off state and start only if you perform a failover.
- Sufficient storage for the log files that contain the changes at the primary location. Although log files get purged after they are replicated, if there are issues with network connectivity, log files could fill up the storage.
- Network connectivity between the locations that are hosting the primary and the replica Hyper-V hosts. Connectivity can be through a wide area network (WAN) or a local area network (LAN) link.
- Firewall rules to allow replication between the primary and replica sites. When you install the Hyper-V role, Hyper-V Replica HTTP Listener (TCP-In) and Hyper-V Replica HTTPS Listener (TCP-In) rules are added to Windows Defender Firewall. Before you can use Hyper-V Replica, you must enable one or both rules on the replica Hyper-V host.
- Authentication certification or Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) infrastructure requirements, depending on which type of authentication you plan to use:
- If you plan to use certificate-based authentication, you need an X.509v3 certificate from a trusted certification authority to support mutual authentication at both Hyper-V hosts. When you use certificate-based authentication, Hyper-V hosts can be in different AD DS forests.
- If you plan to use Kerberos authentication, both Hyper-V hosts need to be joined to the same AD DS forest.
Important
Hyper-V Replica isn't a high-availability technology, it's a disaster-recovery technology. High availability primarily removes single points of failure, so that services are always, or nearly always, available. Because it's a disaster recovery technology, Hyper-V Replica intervenes when high availability fails. Hyper-V Replica doesn't have an automatic failover option.
Hyper-V Replica high-level architecture
When you configure a VM for replication, Hyper-V Replica performs an initial replication and then creates a copy of the VM on the second Hyper-V host at the recovery site. The replicated VM stays turned off until you initiate a failover; meanwhile, the primary VM keeps running. Changes in the primary VM are written in a log file that's periodically replicated and applied to the replica.
Hyper-V Replica has the components detailed in the following table.
| Hyper-V Replica Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Replication engine | The replication engine manages the initial replication, replication configuration details, replication of delta changes, and failover and test failover operations. It also tracks VM and storage mobility events and takes appropriate actions when necessary. |
| Change tracking module | The change tracking module tracks changes that occur to the VM on a source Hyper-V host. The change tracking module tracks write operations to the virtual hard disks (VHDs). It does this regardless of where the VHDs are stored, whether they are stored locally on a storage area network (SAN), on network-attached storage (NAS), on a Server Message Block version 3 (SMB3) or newer share, or on a Cluster Shared Volume (CSV). |
| Network module | The network module provides a secure and efficient way to transfer VM data between Hyper-V hosts. By default, the network module minimizes traffic by compressing data. It can also encrypt data when HTTPS and certification-based authentication are used. |
| Hyper-V Replica Broker | Hyper-V Replica Broker is used only when a Hyper-V host is a node in a failover cluster. Hyper-V Replica Broker enables you to use Hyper-V Replica with highly available VMs that can move between cluster nodes. The Hyper-V Replica Broker role does this by querying the cluster database, then redirects all requests to the cluster node where the VM is currently running. |
| Management tools | You can configure and manage Hyper-V Replica with tools such as Hyper-V Manager and Windows PowerShell. Use Failover Cluster Manager for all VM management and Hyper-V Replica configurations when the source or the replica Hyper-V hosts are part of a Hyper-V failover cluster. |
Important
Hyper-V replica works at the host level and is workload and application agnostic. This means that you can use Site Recovery for any operating system that Hyper-V supports, and to protect all kinds of workloads, including Windows or Linux environments such as:
- Microsoft SharePoint Server
- Microsoft Dynamics CRM
- Microsoft SQL Server
- Internet Information Services (IIS)
- Third-party applications