使用适用于 Microsoft Agent Framework 的持久任务扩展,可以在 Azure 上的无服务器环境中生成有状态 AI 代理和多代理确定性业务流程。
Azure Functions 是一种无服务器计算服务,可让你按需运行代码,而无需管理基础结构。 持久任务扩展基于此基础来提供持久状态管理,这意味着代理的聊天历史记录和执行状态可靠持久保存,在失败、重启和长时间运行的作中幸存下来。
概述
Durable Agents 将 Agent Framework 的强大功能与 Azure Durable Functions 相结合,以创建以下代理:
- 跨函数调用自动保留状态
- 在失败后恢复 ,而不会丢失会话上下文
- 按需自动缩放
- 协调具有可靠执行保证的多代理工作流
何时使用持久代理
在需要时选择耐用的代理:
- 完全代码控制:部署和管理自己的计算环境,同时保持无服务器优势
- 复杂业务流程:使用可运行数天或数周的确定性可靠工作流协调多个代理
- 事件驱动的编排:与 Azure Functions 触发器(HTTP、计时器、队列等)和用于事件驱动代理程序工作流的绑定进行集成
- 自动聊天状态:代理会话历史记录会自动管理并持久保存,无需在代码中进行显式状态处理
这种无服务器托管方法不同于基于服务的代理托管(例如 Azure AI Foundry 代理服务),后者提供完全托管的基础结构,而无需部署或管理 Azure Functions 应用。 当需要代码优先部署的灵活性以及持久状态管理的可靠性时,持久代理是理想的选择。
在 Azure Functions Flex Consumption 托管计划中托管时,代理可以在不使用时扩展到数千个实例或零个实例,从而只为所需的计算付费。
入门指南
在 .NET Azure Functions 项目中,添加所需的 NuGet 包。
dotnet add package Azure.AI.OpenAI --prerelease
dotnet add package Azure.Identity
dotnet add package Microsoft.Agents.AI.OpenAI --prerelease
dotnet add package Microsoft.Agents.AI.Hosting.AzureFunctions --prerelease
注释
除了这些包,请确保项目使用 2.2.0 或更高版本 的 Microsoft.Azure.Functions.Worker 包。
在 Python Azure Functions 项目中,安装所需的 Python 包。
pip install azure-identity
pip install agent-framework-azurefunctions --pre
无服务器托管
通过持久任务扩展模块,可以在 Azure Functions 中使用内置的 HTTP 终结点和基于协调的调用来部署和托管 Microsoft Agent Framework 代理。 Azure Functions 提供事件驱动的、按调用计费的定价,同时具备自动缩放功能和最少的基础架构管理。
配置持久代理时,持久任务扩展会自动为代理创建 HTTP 终结点,并管理用于存储聊天状态、处理并发请求和协调多代理工作流的所有底层基础结构。
using System;
using Azure.AI.OpenAI;
using Azure.Identity;
using Microsoft.Agents.AI;
using Microsoft.Agents.AI.Hosting.AzureFunctions;
using Microsoft.Azure.Functions.Worker.Builder;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
var endpoint = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT");
var deploymentName = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("AZURE_OPENAI_DEPLOYMENT") ?? "gpt-4o-mini";
// Create an AI agent following the standard Microsoft Agent Framework pattern
AIAgent agent = new AzureOpenAIClient(new Uri(endpoint), new DefaultAzureCredential())
.GetChatClient(deploymentName)
.AsAIAgent(
instructions: "You are good at telling jokes.",
name: "Joker");
// Configure the function app to host the agent with durable thread management
// This automatically creates HTTP endpoints and manages state persistence
using IHost app = FunctionsApplication
.CreateBuilder(args)
.ConfigureFunctionsWebApplication()
.ConfigureDurableAgents(options =>
options.AddAIAgent(agent)
)
.Build();
app.Run();
import os
from agent_framework.azure import AzureOpenAIChatClient, AgentFunctionApp
from azure.identity import DefaultAzureCredential
endpoint = os.getenv("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT")
deployment_name = os.getenv("AZURE_OPENAI_DEPLOYMENT_NAME", "gpt-4o-mini")
# Create an AI agent following the standard Microsoft Agent Framework pattern
agent = AzureOpenAIChatClient(
endpoint=endpoint,
deployment_name=deployment_name,
credential=DefaultAzureCredential()
).as_agent(
instructions="You are good at telling jokes.",
name="Joker"
)
# Configure the function app to host the agent with durable thread management
# This automatically creates HTTP endpoints and manages state persistence
app = AgentFunctionApp(agents=[agent])
具有会话历史记录的有状态代理线程
代理维护在多个交互中持续存在的持久性上下文。 每个线程由唯一的线程 ID 标识,并将完整的会话历史记录存储在由 持久任务计划程序管理的持久存储中。
此模式允许通过进程崩溃和重启保留代理状态的会话连续性,从而允许跨用户线程维护完整的会话历史记录。 持久存储可确保即使 Azure Functions 实例重新启动或缩放到其他实例,对话也会从中断的位置无缝继续。
以下示例演示了对同一线程的多个 HTTP 请求,其中显示了会话上下文的持久化方式:
# First interaction - start a new thread
curl -X POST https://your-function-app.azurewebsites.net/api/agents/Joker/run \
-H "Content-Type: text/plain" \
-d "Tell me a joke about pirates"
# Response includes thread ID in x-ms-thread-id header and joke as plain text
# HTTP/1.1 200 OK
# Content-Type: text/plain
# x-ms-thread-id: @dafx-joker@263fa373-fa01-4705-abf2-5a114c2bb87d
#
# Why don't pirates shower before they walk the plank? Because they'll just wash up on shore later!
# Second interaction - continue the same thread with context
curl -X POST "https://your-function-app.azurewebsites.net/api/agents/Joker/run?thread_id=@dafx-joker@263fa373-fa01-4705-abf2-5a114c2bb87d" \
-H "Content-Type: text/plain" \
-d "Tell me another one about the same topic"
# Agent remembers the pirate context from the first message and responds with plain text
# What's a pirate's favorite letter? You'd think it's R, but it's actually the C!
代理状态在持久存储中维护,允许跨多个实例执行分布式执行。 任何实例都可以在中断或失败后恢复代理的运行,确保持续运行。
确定性多代理业务流程
持久任务扩展支持构建使用 Azure Durable Functions 业务流程协调多个代理的确定性工作流。
业务流程 是基于代码的工作流,以可靠的方式协调多个作(例如代理调用、外部 API 调用或计时器)。 确定性 意味着业务流程代码在发生故障后重播时执行的方式相同,使工作流可靠且可调试 — 重播业务流程历史记录时,可以看到每个步骤中发生的确切情况。
协调过程能够可靠地执行,在代理调用之间经受住失败,并提供可预测且可重复的过程。 这使得它们非常适合需要有保证的执行顺序和容错的复杂多代理方案。
顺序业务流程
在顺序多代理模式中,专用代理按特定顺序执行,其中每个代理的输出都可能会影响下一个代理的执行。 此模式支持基于代理响应的条件逻辑和分支。
在业务流程中使用代理时,必须使用 context.GetAgent() API 获取一个 DurableAIAgent 实例,该实例是标准 AIAgent 类型的一个特殊子类,用于包装你的一个已注册代理。 封装 DurableAIAgent 类确保持久业务流程框架能够正确跟踪和检查点代理程序调用。
using Microsoft.Azure.Functions.Worker;
using Microsoft.DurableTask;
using Microsoft.Agents.AI.DurableTask;
[Function(nameof(SpamDetectionOrchestration))]
public static async Task<string> SpamDetectionOrchestration(
[OrchestrationTrigger] TaskOrchestrationContext context)
{
Email email = context.GetInput<Email>();
// Check if the email is spam
DurableAIAgent spamDetectionAgent = context.GetAgent("SpamDetectionAgent");
AgentSession spamSession = await spamDetectionAgent.CreateSessionAsync();
AgentResponse<DetectionResult> spamDetectionResponse = await spamDetectionAgent.RunAsync<DetectionResult>(
message: $"Analyze this email for spam: {email.EmailContent}",
session: spamSession);
DetectionResult result = spamDetectionResponse.Result;
if (result.IsSpam)
{
return await context.CallActivityAsync<string>(nameof(HandleSpamEmail), result.Reason);
}
// Generate response for legitimate email
DurableAIAgent emailAssistantAgent = context.GetAgent("EmailAssistantAgent");
AgentSession emailSession = await emailAssistantAgent.CreateSessionAsync();
AgentResponse<EmailResponse> emailAssistantResponse = await emailAssistantAgent.RunAsync<EmailResponse>(
message: $"Draft a professional response to: {email.EmailContent}",
session: emailSession);
return await context.CallActivityAsync<string>(nameof(SendEmail), emailAssistantResponse.Result.Response);
}
在编排中使用代理时,必须使用方法 app.get_agent() 来获取持久代理实例,后者是您注册的代理的一个特殊包装器。 持久代理包装器可确保通过持久业务流程框架正确跟踪和检查代理调用。
import azure.durable_functions as df
from typing import cast
from agent_framework.azure import AgentFunctionApp
from pydantic import BaseModel
class SpamDetectionResult(BaseModel):
is_spam: bool
reason: str
class EmailResponse(BaseModel):
response: str
app = AgentFunctionApp(agents=[spam_detection_agent, email_assistant_agent])
@app.orchestration_trigger(context_name="context")
def spam_detection_orchestration(context: df.DurableOrchestrationContext):
email = context.get_input()
# Check if the email is spam
spam_agent = app.get_agent(context, "SpamDetectionAgent")
spam_thread = spam_agent.create_session()
spam_result_raw = yield spam_agent.run(
messages=f"Analyze this email for spam: {email['content']}",
session=spam_thread,
response_format=SpamDetectionResult
)
spam_result = cast(SpamDetectionResult, spam_result_raw.get("structured_response"))
if spam_result.is_spam:
result = yield context.call_activity("handle_spam_email", spam_result.reason)
return result
# Generate response for legitimate email
email_agent = app.get_agent(context, "EmailAssistantAgent")
email_thread = email_agent.create_session()
email_response_raw = yield email_agent.run(
messages=f"Draft a professional response to: {email['content']}",
session=email_thread,
response_format=EmailResponse
)
email_response = cast(EmailResponse, email_response_raw.get("structured_response"))
result = yield context.call_activity("send_email", email_response.response)
return result
编排协调多个代理的工作,能够在代理调用期间承受失败。 编排上下文提供用于检索和与编排中的托管代理交互的方法。
并行业务流程
在并行多代理模式中,可以并发执行多个代理,然后聚合其结果。 此模式可用于同时收集不同的透视或处理独立的子任务。
using Microsoft.Azure.Functions.Worker;
using Microsoft.DurableTask;
using Microsoft.Agents.AI.DurableTask;
[Function(nameof(ResearchOrchestration))]
public static async Task<string> ResearchOrchestration(
[OrchestrationTrigger] TaskOrchestrationContext context)
{
string topic = context.GetInput<string>();
// Execute multiple research agents in parallel
DurableAIAgent technicalAgent = context.GetAgent("TechnicalResearchAgent");
DurableAIAgent marketAgent = context.GetAgent("MarketResearchAgent");
DurableAIAgent competitorAgent = context.GetAgent("CompetitorResearchAgent");
// Start all agent runs concurrently
Task<AgentResponse<TextResponse>> technicalTask =
technicalAgent.RunAsync<TextResponse>($"Research technical aspects of {topic}");
Task<AgentResponse<TextResponse>> marketTask =
marketAgent.RunAsync<TextResponse>($"Research market trends for {topic}");
Task<AgentResponse<TextResponse>> competitorTask =
competitorAgent.RunAsync<TextResponse>($"Research competitors in {topic}");
// Wait for all tasks to complete
await Task.WhenAll(technicalTask, marketTask, competitorTask);
// Aggregate results
string allResearch = string.Join("\n\n",
technicalTask.Result.Result.Text,
marketTask.Result.Result.Text,
competitorTask.Result.Result.Text);
DurableAIAgent summaryAgent = context.GetAgent("SummaryAgent");
AgentResponse<TextResponse> summaryResponse =
await summaryAgent.RunAsync<TextResponse>($"Summarize this research:\n{allResearch}");
return summaryResponse.Result.Text;
}
import azure.durable_functions as df
from agent_framework.azure import AgentFunctionApp
app = AgentFunctionApp(agents=[technical_agent, market_agent, competitor_agent, summary_agent])
@app.orchestration_trigger(context_name="context")
def research_orchestration(context: df.DurableOrchestrationContext):
topic = context.get_input()
# Execute multiple research agents in parallel
technical_agent = app.get_agent(context, "TechnicalResearchAgent")
market_agent = app.get_agent(context, "MarketResearchAgent")
competitor_agent = app.get_agent(context, "CompetitorResearchAgent")
technical_task = technical_agent.run(messages=f"Research technical aspects of {topic}")
market_task = market_agent.run(messages=f"Research market trends for {topic}")
competitor_task = competitor_agent.run(messages=f"Research competitors in {topic}")
# Wait for all tasks to complete
results = yield context.task_all([technical_task, market_task, competitor_task])
# Aggregate results
all_research = "\n\n".join([r.get('response', '') for r in results])
summary_agent = app.get_agent(context, "SummaryAgent")
summary = yield summary_agent.run(messages=f"Summarize this research:\n{all_research}")
return summary.get('response', '')
使用任务列表跟踪并行执行。 自动检查点可确保在聚合期间发生故障时不会重复或丢失已完成的代理执行。
人机循环业务流程
确定性的代理编排可以在人工输入、审批或审查时暂停,而不消耗计算资源。 持久执行使业务流程能够在等待人工响应时等待数天甚至数周。 当与无服务器托管相结合时,所有计算资源在等待期间都会关闭,从而消除计算成本,直到用户提供输入。
using Microsoft.Azure.Functions.Worker;
using Microsoft.DurableTask;
using Microsoft.Agents.AI.DurableTask;
[Function(nameof(ContentApprovalWorkflow))]
public static async Task<string> ContentApprovalWorkflow(
[OrchestrationTrigger] TaskOrchestrationContext context)
{
string topic = context.GetInput<string>();
// Generate content using an agent
DurableAIAgent contentAgent = context.GetAgent("ContentGenerationAgent");
AgentResponse<GeneratedContent> contentResponse =
await contentAgent.RunAsync<GeneratedContent>($"Write an article about {topic}");
GeneratedContent draftContent = contentResponse.Result;
// Send for human review
await context.CallActivityAsync(nameof(NotifyReviewer), draftContent);
// Wait for approval with timeout
HumanApprovalResponse approvalResponse;
try
{
approvalResponse = await context.WaitForExternalEvent<HumanApprovalResponse>(
eventName: "ApprovalDecision",
timeout: TimeSpan.FromHours(24));
}
catch (OperationCanceledException)
{
// Timeout occurred - escalate for review
return await context.CallActivityAsync<string>(nameof(EscalateForReview), draftContent);
}
if (approvalResponse.Approved)
{
return await context.CallActivityAsync<string>(nameof(PublishContent), draftContent);
}
return "Content rejected";
}
import azure.durable_functions as df
from datetime import timedelta
from agent_framework.azure import AgentFunctionApp
app = AgentFunctionApp(agents=[content_agent])
@app.orchestration_trigger(context_name="context")
def content_approval_workflow(context: df.DurableOrchestrationContext):
topic = context.get_input()
# Generate content using an agent
content_agent = app.get_agent(context, "ContentGenerationAgent")
draft_content = yield content_agent.run(
messages=f"Write an article about {topic}"
)
# Send for human review
yield context.call_activity("notify_reviewer", draft_content)
# Wait for approval with timeout
approval_task = context.wait_for_external_event("ApprovalDecision")
timeout_task = context.create_timer(
context.current_utc_datetime + timedelta(hours=24)
)
winner = yield context.task_any([approval_task, timeout_task])
if winner == approval_task:
timeout_task.cancel()
approval_data = approval_task.result
if approval_data.get("approved"):
result = yield context.call_activity("publish_content", draft_content)
return result
return "Content rejected"
# Timeout occurred - escalate for review
result = yield context.call_activity("escalate_for_review", draft_content)
return result
确定性的代理业务流程可以等待外部事件,在等待人工反馈、幸存故障、重启和延长等待期间时持久保存其状态。 当人工响应到达时,业务流程会自动恢复,完整聊天上下文和执行状态保持不变。
提供人工输入
若要将审批或输入发送到等待的业务流程,请使用 Durable Functions 客户端 SDK 向业务流程实例引发外部事件。 例如,审阅者可能通过一个调用的 Web 表单来批准内容:
await client.RaiseEventAsync(instanceId, "ApprovalDecision", new HumanApprovalResponse
{
Approved = true,
Feedback = "Looks great!"
});
approval_data = {
"approved": True,
"feedback": "Looks great!"
}
await client.raise_event(instance_id, "ApprovalDecision", approval_data)
成本效益
在 Azure Functions Flex Consumption 计划中托管时,具有持久代理的人工循环工作流非常经济高效。 对于等待 24 小时审批的工作流,只需花费几秒钟的执行时间(生成内容、发送通知和处理响应的时间),而不是等待的 24 小时。 在等待期间,不会消耗任何计算资源。
Durable Task Scheduler 的可观测性
Durable Task Scheduler(DTS)是为您的持久代理推荐的耐久后端,能够提供最佳性能、完全托管的基础设施,并通过 UI 仪表板内置可观测性。 虽然 Azure Functions 可以使用其他存储后端(如 Azure 存储),但 DTS 专门针对持久工作负荷进行了优化,并提供卓越的性能和监视功能。
代理会话见解
- 对话历史记录:查看每个代理会话的完整聊天历史记录,包括任何时间点的所有消息、工具调用和聊天上下文
- 任务计时:监视完成特定任务和代理交互所需的时间
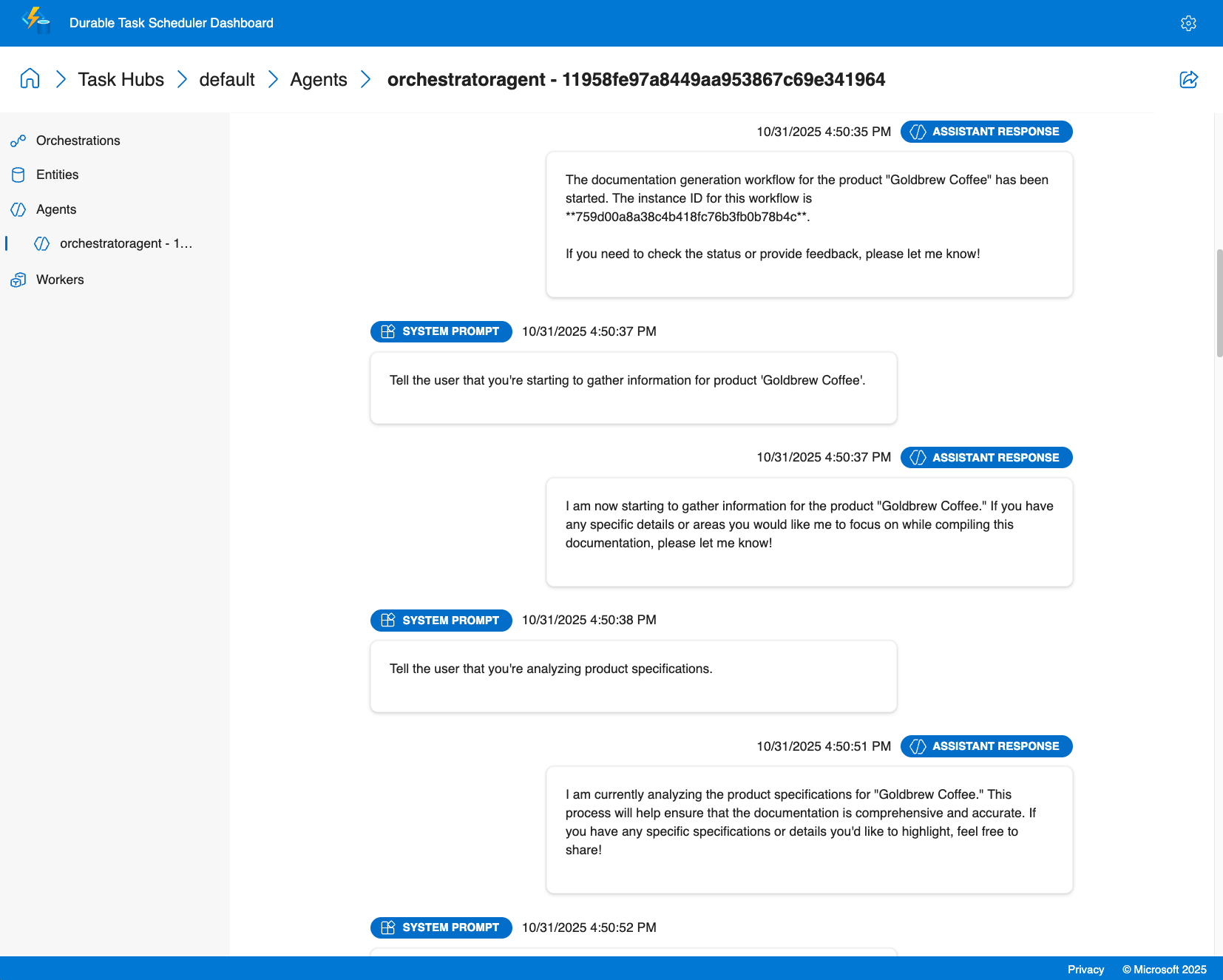
业务流程见解
- 多代理可视化:在调用多个专用代理时查看执行流,该代理具有并行执行和条件分支的可视表示形式
- 执行历史记录:访问详细的执行日志
- 实时监视:跟踪整个部署中的活动业务流程、排队的工作项和代理状态
- 性能指标:监视代理响应时间、令牌使用情况和业务流程持续时间

调试功能
- 查看结构化代理输出和工具调用结果
- 跟踪工具调用及其结果
- 监视人机循环方案的外部事件处理
利用仪表板,可以准确了解代理正在执行的作、快速诊断问题,并根据实际执行数据优化性能。
教程:创建并运行持久代理
本教程介绍如何使用适用于 Microsoft Agent Framework 的持久任务扩展创建和运行 Durable AI 代理。 你将生成一个 Azure Functions 应用,该应用托管具有内置 HTTP 终结点的有状态代理,并了解如何使用 Durable Task Scheduler 仪表板对其进行监视。
先决条件
开始之前,请确保具备以下先决条件:
- .NET 9.0 SDK 或更高版本
- Azure Functions Core Tools v4.x
- Azure 开发工具 CLI (azd)
- 已安装的Azure CLI并且已进行身份验证
- 已安装并运行 Docker Desktop(用于使用 Azurite 和 Durable Task Scheduler 模拟器进行本地开发)
- 有权创建资源的 Azure 订阅
注释
Microsoft .NET 的所有主动支持版本都支持代理框架。 出于此示例的目的,我们建议使用 .NET 9 SDK 或更高版本。
- Python 3.10 或更高版本
- Azure Functions Core Tools v4.x
- Azure 开发工具 CLI (azd)
- 已安装的Azure CLI并且已进行身份验证
- 已安装并运行 Docker Desktop(用于使用 Azurite 和 Durable Task Scheduler 模拟器进行本地开发)
- 有权创建资源的 Azure 订阅
下载快速入门项目
使用 Azure 开发人员 CLI 从持久代理快速入门模板初始化新项目。
为项目创建新目录并导航到它:
mkdir MyDurableAgent cd MyDurableAgent
从模板初始化项目:
azd init --template durable-agents-quickstart-dotnet当系统提示输入环境名称时,请输入一个名称,如下所示
my-durable-agent。
这会下载包含所有必要文件的快速入门项目,包括 Azure Functions 配置、代理代码和基础结构作为代码模板。
为项目创建新目录并导航到它:
mkdir MyDurableAgent cd MyDurableAgent
从模板初始化项目:
azd init --template durable-agents-quickstart-python当系统提示输入环境名称时,请输入一个名称,如下所示
my-durable-agent。创建和激活虚拟环境:
python3 -m venv .venv source .venv/bin/activate
安装所需的包:
python -m pip install -r requirements.txt
这会下载包含所有必要文件的快速入门项目,包括 Azure Functions 配置、代理代码和基础结构作为代码模板。 它还准备具有所需依赖项的虚拟环境。
预配 Azure 资源
使用 Azure 开发人员 CLI 为持久代理创建所需的 Azure 资源。
预配基础结构:
azd provision此命令创建:
- 具有 gpt-4o-mini 部署的 Azure OpenAI 服务
- 具有弹性消耗托管计划的 Azure Functions 应用
- 用于 Azure Functions 运行时环境和持久存储的 Azure 存储帐户
- 用于管理代理状态的持久任务调度程序实例(消费计划)
- 必要的网络和标识配置
出现提示时,选择 Azure 订阅并选择资源的位置。
预配过程需要几分钟时间。 完成后,azd 会将已创建的资源信息存储在环境中。
查看代理代码
现在,让我们检查定义持久化代理的代码。
打开 Program.cs 以查看代理配置:
using Azure.AI.OpenAI;
using Azure.Identity;
using Microsoft.Agents.AI;
using Microsoft.Agents.AI.Hosting.AzureFunctions;
using Microsoft.Azure.Functions.Worker.Builder;
using Microsoft.Extensions.AI;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
using OpenAI;
var endpoint = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT")
?? throw new InvalidOperationException("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT environment variable is not set");
var deploymentName = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("AZURE_OPENAI_DEPLOYMENT") ?? "gpt-4o-mini";
// Create an AI agent following the standard Microsoft Agent Framework pattern
AIAgent agent = new AzureOpenAIClient(new Uri(endpoint), new DefaultAzureCredential())
.GetChatClient(deploymentName)
.AsAIAgent(
instructions: "You are a helpful assistant that can answer questions and provide information.",
name: "MyDurableAgent");
using IHost app = FunctionsApplication
.CreateBuilder(args)
.ConfigureFunctionsWebApplication()
.ConfigureDurableAgents(options => options.AddAIAgent(agent))
.Build();
app.Run();
此代码:
- 从环境变量中检索 Azure OpenAI 配置。
- 使用 Azure 凭据创建 Azure OpenAI 客户端。
- 使用说明和名称创建 AI 代理。
- 将 Azure Functions 应用配置为使用持久线程管理来托管代理。
打开 function_app.py 以查看代理配置:
import os
from agent_framework.azure import AzureOpenAIChatClient, AgentFunctionApp
from azure.identity import DefaultAzureCredential
endpoint = os.getenv("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT")
if not endpoint:
raise ValueError("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT is not set.")
deployment_name = os.getenv("AZURE_OPENAI_DEPLOYMENT_NAME", "gpt-4o-mini")
# Create an AI agent following the standard Microsoft Agent Framework pattern
agent = AzureOpenAIChatClient(
endpoint=endpoint,
deployment_name=deployment_name,
credential=DefaultAzureCredential()
).as_agent(
instructions="You are a helpful assistant that can answer questions and provide information.",
name="MyDurableAgent"
)
# Configure the function app to host the agent with durable thread management
app = AgentFunctionApp(agents=[agent])
此代码:
- 从环境变量中检索 Azure OpenAI 配置。
- 使用 Azure 凭据创建 Azure OpenAI 客户端。
- 使用说明和名称创建 AI 代理。
- 将 Azure Functions 应用配置为使用持久线程管理来托管代理。
代理现已准备好托管在 Azure Functions 中。 持久任务扩展会自动创建 HTTP 终结点以与代理交互,并跨多个请求管理会话状态。
配置本地设置
local.settings.json根据项目中包含的示例文件创建用于本地开发的文件。
复制示例设置文件:
cp local.settings.sample.json local.settings.json
从预配的资源获取 Azure OpenAI 端点:
azd env get-value AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT打开
local.settings.json并将<your-resource-name>值中的AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT替换为上一命令中的端点。
你的 local.settings.json 应该如下显示:
{
"IsEncrypted": false,
"Values": {
// ... other settings ...
"AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT": "https://your-openai-resource.openai.azure.com",
"AZURE_OPENAI_DEPLOYMENT": "gpt-4o-mini",
"TASKHUB_NAME": "default"
}
}
注释
该文件 local.settings.json 仅用于本地开发,不会部署到 Azure。 对于生产部署,这些设置由基础结构模板自动在 Azure Functions 应用中配置。
启动本地开发依赖项
若要在本地运行持久代理,需要启动两个服务:
- Azurite:模拟 Azure 存储服务(由 Azure Functions 用于管理触发器和内部状态)。
- 持久任务调度程序(DTS)模拟器:管理持久状态(会话历史记录、协调状态)和代理的调度
启动 Azurite
Azurite 在本地模拟 Azure 存储服务。 Azure Functions 使用它来管理内部状态。 需要在新的终端窗口中运行此功能,并在开发和测试持久代理时使其保持运行。
打开新的终端窗口并拉取 Azurite Docker 映像:
docker pull mcr.microsoft.com/azure-storage/azurite在终端窗口中启动 Azurite:
docker run -p 10000:10000 -p 10001:10001 -p 10002:10002 mcr.microsoft.com/azure-storage/azuriteAzurite 将启动和侦听 Blob(10000)、队列(10001)和表(10002)服务的默认端口。
在开发和测试持久代理时,请保持此终端窗口打开。
小窍门
有关 Azurite 的详细信息,包括替代安装方法,请参阅 使用 Azurite 模拟器进行本地 Azure 存储开发。
启动持久任务计划程序模拟器
DTS 模拟器提供用于管理代理状态和业务流程的持久后端。 它存储会话历史记录,并确保代理的状态在重启时保持。 它还触发持久协调器和代理。 需要在单独的新终端窗口中运行此功能,并在开发和测试持久代理时使其保持运行状态。
打开另一个新的终端窗口并拉取 DTS 模拟器 Docker 映像:
docker pull mcr.microsoft.com/dts/dts-emulator:latest运行 DTS 模拟器:
docker run -p 8080:8080 -p 8082:8082 mcr.microsoft.com/dts/dts-emulator:latest此命令启动模拟器并公开:
- 端口 8080:Durable Task Scheduler 的 gRPC 终结点(由 Functions 应用使用)
- 端口 8082:管理仪表板
仪表板将在
http://localhost:8082可用。
在开发和测试持久代理时,请保持此终端窗口打开。
小窍门
若要详细了解 DTS 模拟器,包括如何配置多个任务中心和访问仪表板,请参阅 使用 Durable Task Scheduler 进行开发。
运行函数应用
现在,你已准备好使用持久代理运行 Azure Functions 应用。
在新终端窗口中(使 Azurite 和 DTS 模拟器在单独的窗口中保持运行),导航到项目目录。
启动 Azure Functions 运行时:
func start你应该看到显示函数应用正在运行的输出,其中包含代理的 HTTP 端点:
Functions: http-MyDurableAgent: [POST] http://localhost:7071/api/agents/MyDurableAgent/run dafx-MyDurableAgent: entityTrigger
这些终结点自动管理聊天状态 - 无需自行创建或管理线程对象。
在本地测试代理
现在,可以使用 HTTP 请求与持久代理交互。 代理跨多个请求维护会话状态,从而启用多轮对话。
开始新对话
创建新线程并发送第一条消息:
curl -i -X POST http://localhost:7071/api/agents/MyDurableAgent/run \
-H "Content-Type: text/plain" \
-d "What are three popular programming languages?"
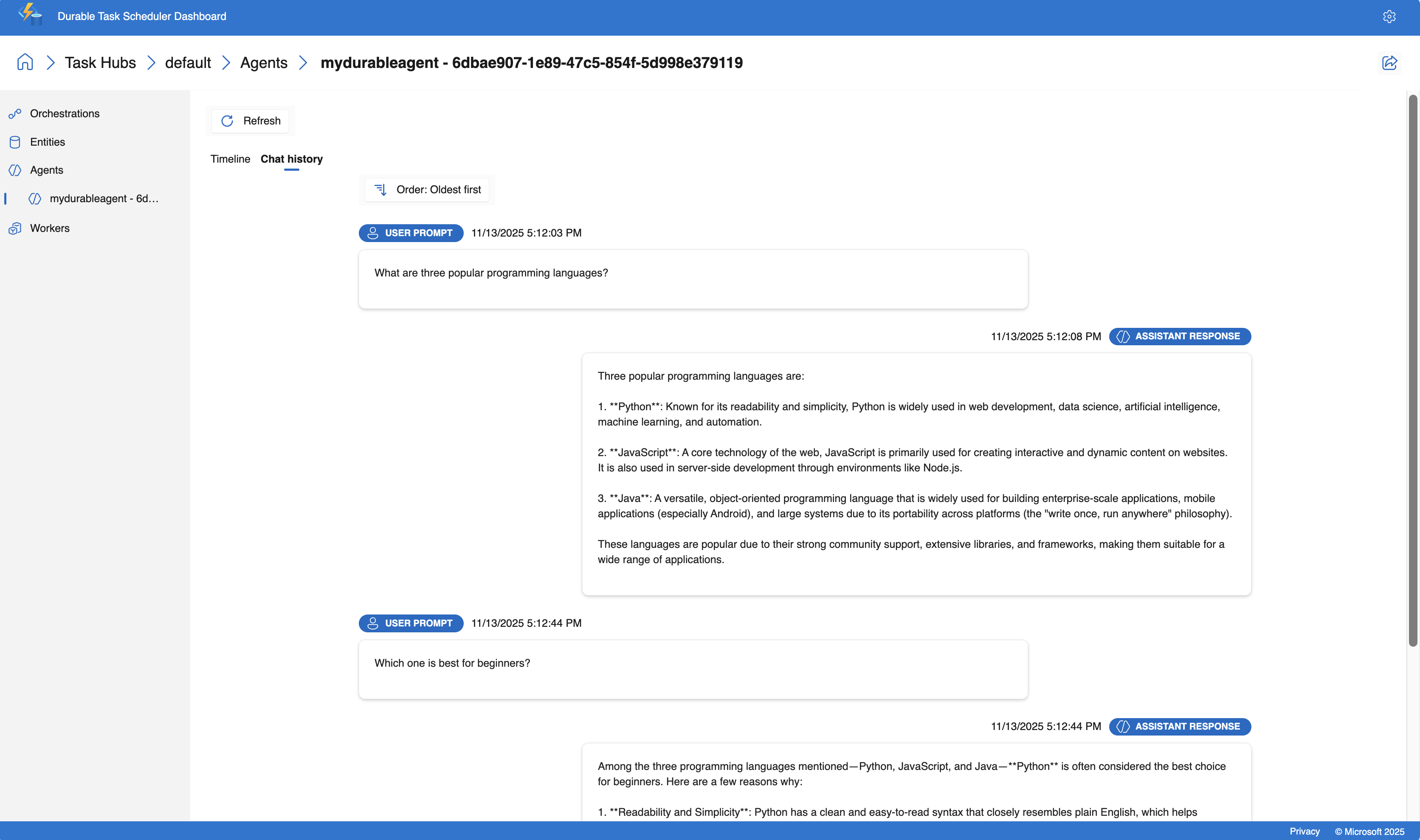
示例响应(请注意 x-ms-thread-id 标头包含线程 ID):
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: text/plain
x-ms-thread-id: @dafx-mydurableagent@263fa373-fa01-4705-abf2-5a114c2bb87d
Content-Length: 189
Three popular programming languages are Python, JavaScript, and Java. Python is known for its simplicity and readability, JavaScript powers web interactivity, and Java is widely used in enterprise applications.
将线程 ID 从 x-ms-thread-id 标头中(例如,@dafx-mydurableagent@263fa373-fa01-4705-abf2-5a114c2bb87d)保存以供下一个请求使用。
继续对话
请通过将线程 ID 作为查询参数,向同一线程发送后续消息:
curl -X POST "http://localhost:7071/api/agents/MyDurableAgent/run?thread_id=@dafx-mydurableagent@263fa373-fa01-4705-abf2-5a114c2bb87d" \
-H "Content-Type: text/plain" \
-d "Which one is best for beginners?"
将 @dafx-mydurableagent@263fa373-fa01-4705-abf2-5a114c2bb87d 替换为上一响应标头 x-ms-thread-id 中的实际线程 ID。
示例响应:
Python is often considered the best choice for beginners among those three. Its clean syntax reads almost like English, making it easier to learn programming concepts without getting overwhelmed by complex syntax. It's also versatile and widely used in education.
请注意,代理会记住上一条消息(三种编程语言)中的上下文,而无需再次指定它们。 由于持久任务计划程序持久存储会话状态,因此即使重新启动函数应用或会话由其他实例恢复,此历史记录也会持续。
使用 Durable Task Scheduler 控制面板进行监控
Durable 任务调度程序提供内置仪表板,用于监控和调试您的持久代理。 仪表板提供对代理操作、会话历史记录和执行流程的深入可视化。
访问仪表板
在 Web 浏览器中打开本地 DTS 模拟器
http://localhost:8082的仪表板。从列表中选择 默认 任务中心以查看其详细信息。
选择右上角的齿轮图标以打开设置,并确保选中“预览功能”下的“启用代理”页面选项。
浏览代理对话
在仪表板中,导航到 “代理 ”选项卡。
从列表中选择持久化代理线程(例如
mydurableagent - 263fa373-fa01-4705-abf2-5a114c2bb87d)。你将看到代理线程的详细视图,包括包含所有消息和响应的完整会话历史记录。
仪表板提供了一个时间线视图,可帮助你了解聊天流。 关键信息包括:
- 每个交互的时间戳和持续时间
- 提示和响应内容
- 使用的令牌数
小窍门
DTS 仪表板提供实时更新,让您可以在通过 HTTP 终端与其交互时监控代理的行为。
部署到 Azure 云
在本地测试持久代理后,请将其部署到 Azure。
部署应用程序:
azd deploy此命令打包应用程序并将其部署到预配期间创建的 Azure Functions 应用。
等待部署完成。 输出将确认代理在 Azure 中运行时。
测试已部署的代理
部署后,测试在 Azure 中运行的代理。
获取函数密钥
Azure Functions 需要一个 API 密钥,用于生产中 HTTP 触发的函数:
API_KEY=`az functionapp function keys list --name $(azd env get-value AZURE_FUNCTION_NAME) --resource-group $(azd env get-value AZURE_RESOURCE_GROUP) --function-name http-MyDurableAgent --query default -o tsv`
在 Azure 中启动新对话
创建新线程并将第一条消息发送到已部署的代理:
curl -i -X POST "https://$(azd env get-value AZURE_FUNCTION_NAME).azurewebsites.net/api/agents/MyDurableAgent/run?code=$API_KEY" \
-H "Content-Type: text/plain" \
-d "What are three popular programming languages?"
请注意响应标头中返回的 x-ms-thread-id 线程 ID。
在 Azure 中继续对话
在同一线程中发送后续消息。 将 <thread-id> 替换为来自上一响应的线程 ID。
THREAD_ID="<thread-id>"
curl -X POST "https://$(azd env get-value AZURE_FUNCTION_NAME).azurewebsites.net/api/agents/MyDurableAgent/run?code=$API_KEY&thread_id=$THREAD_ID" \
-H "Content-Type: text/plain" \
-d "Which is easiest to learn?"
代理在 Azure 中维护会话上下文,就像在本地一样,演示代理状态的持久性。
监视已部署的代理
可以使用 Azure 中的 Durable Task Scheduler 仪表板监视已部署的代理。
获取 Durable Task Scheduler 实例的名称:
azd env get-value DTS_NAME打开 Azure 门户 并搜索上一步中的 Durable Task Scheduler 名称。
在持久任务计划程序资源的概述窗格中,从列表中选择 默认 任务中心。
选择任务中心页面顶部的 “打开仪表板 ”以打开监视仪表板。
像使用本地模拟器一样查看代理的对话。
Azure 托管的仪表板提供与本地模拟器相同的调试和监视功能,使你能够检查对话历史记录、跟踪工具调用和分析生产环境中的性能。
教程:协调持久代理
本教程介绍如何使用扇出/扇入模式协调多个持久 AI 代理。 你将扩展 上一教程 中的持久代理,以创建处理用户问题的多代理系统,然后将响应同时转换为多种语言。
了解业务流程模式
您将构建的编排遵循以下流程:
- 用户输入 - 来自用户的问题或消息
-
主代理 - 第一个教程中的
MyDurableAgent处理问题 - 扇出 - 主代理的响应同时发送到两个翻译代理
- 翻译代理 - 两个专业代理翻译响应(法语和西班牙语)
- 汇聚 - 结果被聚合为一个包含原始响应和翻译的 JSON 响应
此模式可实现并发处理,从而减少与顺序转换相比的总响应时间。
在启动时注册代理
要在持久化编排中正确使用代理程序,请在应用程序启动时对其进行注册。 它们可以在编排执行中使用。
请将 Program.cs 更新以将翻译代理与现有 MyDurableAgent 代理一起注册:
using System;
using Azure.AI.OpenAI;
using Azure.Identity;
using Microsoft.Agents.AI;
using Microsoft.Agents.AI.Hosting.AzureFunctions;
using Microsoft.Azure.Functions.Worker.Builder;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
using OpenAI;
using OpenAI.Chat;
// Get the Azure OpenAI configuration
string endpoint = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT")
?? throw new InvalidOperationException("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT is not set.");
string deploymentName = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("AZURE_OPENAI_DEPLOYMENT")
?? "gpt-4o-mini";
// Create the Azure OpenAI client
AzureOpenAIClient client = new(new Uri(endpoint), new DefaultAzureCredential());
ChatClient chatClient = client.GetChatClient(deploymentName);
// Create the main agent from the first tutorial
AIAgent mainAgent = chatClient.AsAIAgent(
instructions: "You are a helpful assistant that can answer questions and provide information.",
name: "MyDurableAgent");
// Create translation agents
AIAgent frenchAgent = chatClient.AsAIAgent(
instructions: "You are a translator. Translate the following text to French. Return only the translation, no explanations.",
name: "FrenchTranslator");
AIAgent spanishAgent = chatClient.AsAIAgent(
instructions: "You are a translator. Translate the following text to Spanish. Return only the translation, no explanations.",
name: "SpanishTranslator");
// Build and configure the Functions host
using IHost app = FunctionsApplication
.CreateBuilder(args)
.ConfigureFunctionsWebApplication()
.ConfigureDurableAgents(options =>
{
// Register all agents for use in orchestrations and HTTP endpoints
options.AddAIAgent(mainAgent);
options.AddAIAgent(frenchAgent);
options.AddAIAgent(spanishAgent);
})
.Build();
app.Run();
请将 function_app.py 更新以将翻译代理与现有 MyDurableAgent 代理一起注册:
import os
from azure.identity import DefaultAzureCredential
from agent_framework.azure import AzureOpenAIChatClient, AgentFunctionApp
# Get the Azure OpenAI configuration
endpoint = os.getenv("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT")
if not endpoint:
raise ValueError("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT is not set.")
deployment_name = os.getenv("AZURE_OPENAI_DEPLOYMENT", "gpt-4o-mini")
# Create the Azure OpenAI client
chat_client = AzureOpenAIChatClient(
endpoint=endpoint,
deployment_name=deployment_name,
credential=DefaultAzureCredential()
)
# Create the main agent from the first tutorial
main_agent = chat_client.as_agent(
instructions="You are a helpful assistant that can answer questions and provide information.",
name="MyDurableAgent"
)
# Create translation agents
french_agent = chat_client.as_agent(
instructions="You are a translator. Translate the following text to French. Return only the translation, no explanations.",
name="FrenchTranslator"
)
spanish_agent = chat_client.as_agent(
instructions="You are a translator. Translate the following text to Spanish. Return only the translation, no explanations.",
name="SpanishTranslator"
)
# Create the function app and register all agents
app = AgentFunctionApp(agents=[main_agent, french_agent, spanish_agent])
创建编排函数
编排函数协调多个代理之间的工作流。 它从持久化上下文中检索已注册的代理程序并协调其执行,首先调用主代理程序,然后同时分发到翻译代理程序。
在项目目录中创建一 AgentOrchestration.cs 个名为的新文件:
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.Agents.AI;
using Microsoft.Agents.AI.DurableTask;
using Microsoft.Azure.Functions.Worker;
using Microsoft.DurableTask;
namespace MyDurableAgent;
public static class AgentOrchestration
{
// Define a strongly-typed response structure for agent outputs
public sealed record TextResponse(string Text);
[Function("agent_orchestration_workflow")]
public static async Task<Dictionary<string, string>> AgentOrchestrationWorkflow(
[OrchestrationTrigger] TaskOrchestrationContext context)
{
var input = context.GetInput<string>() ?? throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(context), "Input cannot be null");
// Step 1: Get the main agent's response
DurableAIAgent mainAgent = context.GetAgent("MyDurableAgent");
AgentResponse<TextResponse> mainResponse = await mainAgent.RunAsync<TextResponse>(input);
string agentResponse = mainResponse.Result.Text;
// Step 2: Fan out - get the translation agents and run them concurrently
DurableAIAgent frenchAgent = context.GetAgent("FrenchTranslator");
DurableAIAgent spanishAgent = context.GetAgent("SpanishTranslator");
Task<AgentResponse<TextResponse>> frenchTask = frenchAgent.RunAsync<TextResponse>(agentResponse);
Task<AgentResponse<TextResponse>> spanishTask = spanishAgent.RunAsync<TextResponse>(agentResponse);
// Step 3: Wait for both translation tasks to complete (fan-in)
await Task.WhenAll(frenchTask, spanishTask);
// Get the translation results
TextResponse frenchResponse = (await frenchTask).Result;
TextResponse spanishResponse = (await spanishTask).Result;
// Step 4: Combine results into a dictionary
var result = new Dictionary<string, string>
{
["original"] = agentResponse,
["french"] = frenchResponse.Text,
["spanish"] = spanishResponse.Text
};
return result;
}
}
将协调函数添加到 function_app.py 文件中。
import azure.durable_functions as df
@app.orchestration_trigger(context_name="context")
def agent_orchestration_workflow(context: df.DurableOrchestrationContext):
"""
Orchestration function that coordinates multiple agents.
Returns a dictionary with the original response and translations.
"""
input_text = context.get_input()
# Step 1: Get the main agent's response
main_agent = app.get_agent(context, "MyDurableAgent")
main_response = yield main_agent.run(input_text)
agent_response = main_response.text
# Step 2: Fan out - get the translation agents and run them concurrently
french_agent = app.get_agent(context, "FrenchTranslator")
spanish_agent = app.get_agent(context, "SpanishTranslator")
parallel_tasks = [
french_agent.run(agent_response),
spanish_agent.run(agent_response)
]
# Step 3: Wait for both translation tasks to complete (fan-in)
translations = yield context.task_all(parallel_tasks) # type: ignore
# Step 4: Combine results into a dictionary
result = {
"original": agent_response,
"french": translations[0].text,
"spanish": translations[1].text
}
return result
测试业务流程
确保第一个教程中的本地开发依赖项仍在运行:
- 一个终端窗口中的 Azurite
- 在另一个终端窗口中持久任务计划程序模拟器
在本地开发依赖项正在运行的情况下:
在新终端窗口中启动 Azure Functions 应用:
func startDurable Functions 扩展会自动创建用于管理编排的内置 HTTP 终结点。 使用内置 API 启动编排:
curl -X POST http://localhost:7071/runtime/webhooks/durabletask/orchestrators/agent_orchestration_workflow \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '"\"What are three popular programming languages?\""'
响应包括用于管理编排实例的 URL:
{ "id": "abc123def456", "statusQueryGetUri": "http://localhost:7071/runtime/webhooks/durabletask/instances/abc123def456", "sendEventPostUri": "http://localhost:7071/runtime/webhooks/durabletask/instances/abc123def456/raiseEvent/{eventName}", "terminatePostUri": "http://localhost:7071/runtime/webhooks/durabletask/instances/abc123def456/terminate", "purgeHistoryDeleteUri": "http://localhost:7071/runtime/webhooks/durabletask/instances/abc123def456" }使用
statusQueryGetUri查询编排状态(将abc123def456替换为你的实际实例 ID):curl http://localhost:7071/runtime/webhooks/durabletask/instances/abc123def456
轮询状态终结点,直到
runtimeStatus是Completed。 当你完成后,你将看到编排输出,其中包括主代理的响应及其翻译:{ "name": "agent_orchestration_workflow", "instanceId": "abc123def456", "runtimeStatus": "Completed", "output": { "original": "Three popular programming languages are Python, JavaScript, and Java. Python is known for its simplicity...", "french": "Trois langages de programmation populaires sont Python, JavaScript et Java. Python est connu pour sa simplicité...", "spanish": "Tres lenguajes de programación populares son Python, JavaScript y Java. Python es conocido por su simplicidad..." } }
在仪表板中监控编排情况
Durable 任务调度器仪表板提供对编排的可见性:
在浏览器中打开
http://localhost:8082。选择“默认”任务中心。
选择“编排”选项卡。
在列表中查找编排实例。
选择要查看的实例:
- 编排时间线
- 主代理执行后,随后并发执行转换代理
- 每个代理执行过程(MyDurableAgent,然后是法语和西班牙语翻译器)
- 可视化扇出和扇入模式
- 每个步骤的计时和持续时间
将业务流程部署到 Azure
使用 Azure 开发人员 CLI 部署更新的应用程序:
azd deploy
这会使用新的业务流程函数和其他代理将更新的代码部署到第一个教程中创建的 Azure Functions 应用。
测试已部署的业务流程
部署后,在 Azure 中测试正在运行的编排。
获取持久扩展的系统密钥:
SYSTEM_KEY=$(az functionapp keys list --name $(azd env get-value AZURE_FUNCTION_NAME) --resource-group $(azd env get-value AZURE_RESOURCE_GROUP) --query "systemKeys.durabletask_extension" -o tsv)
使用内置 API 启动编排:
curl -X POST "https://$(azd env get-value AZURE_FUNCTION_NAME).azurewebsites.net/runtime/webhooks/durabletask/orchestrators/agent_orchestration_workflow?code=$SYSTEM_KEY" \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '"\"What are three popular programming languages?\""'
- 使用从响应中提取的
statusQueryGetUri进行轮询以完成,并使用翻译查看结果。
后续步骤
其他资源: