你当前正在访问 Microsoft Azure Global Edition 技术文档网站。 如果需要访问由世纪互联运营的 Microsoft Azure 中国技术文档网站,请访问 https://docs.azure.cn。
重要
有关此 SDK 的详细信息,请查看 Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK v4 发行说明、 Maven 存储库、Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK v4 性能提示和 Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK v4 故障排除指南。
重要
由于 Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK v4 最多具有 20 个% 增强的吞吐量、基于 TCP 的直接模式和支持最新的后端服务功能,因此建议下次有机会升级到 v4。 请继续阅读下文,了解详细信息。
更新到最新的 Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK,以充分利用 Azure Cosmos DB 提供的内容 - 一种具有竞争性能的托管非关系数据库服务、五九种可用性、一种类型资源治理等。 本文介绍如何将使用较旧的 Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 的现有 Java 应用程序升级到较新的 Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 4.0 for API for NoSQL。 Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK v4 对应于包 com.azure.cosmos 。 如果要从以下任一 Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 迁移应用程序,可以使用本文档中的说明:
- 同步 Java SDK 2.x.x
- 异步 Java SDK 2.x.x
- Java SDK 3.x.x
Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 和包映射
下表列出了不同的 Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK、包名称和发布信息:
| Java SDK | 发布日期 | 集成 API | Maven Jar | Java 包名称 | API 参考文档 | 发布说明 | 停用日期 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Async 2.x.x | 2018 年 6 月 | Async(RxJava) | com.microsoft.azure::azure-cosmosdb |
com.microsoft.azure.cosmosdb.rx |
API | 发行说明 | 2024 年 8 月 31 日 |
| 同步 2.x.x | 2018 年 9 月 | 同步 | com.microsoft.azure::azure-documentdb |
com.microsoft.azure.cosmosdb |
API | 2024 年 2 月 29 日 | |
| 3.x.x | 2019 年 7 月 | Async(Reactor)/Sync | com.microsoft.azure::azure-cosmos |
com.azure.data.cosmos |
API | - | 2024 年 8 月 31 日 |
| 4.0 | 2020 年 6 月 | Async(Reactor)/同步 | com.azure::azure-cosmos |
com.azure.cosmos |
API | - | - |
SDK 级别实现更改
以下是不同 SDK 之间的主要实现差异:
在 Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 版本 3.x.x 和 4.0 中,RxJava 被替代为 Reactor。
如果不熟悉异步编程或反应式编程,请参阅 Reactor 模式指南 ,了解异步编程和 Project Reactor 简介。 如果过去一直在使用 Azure Cosmos DB Sync Java SDK 2.x.x 或 Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 3.x.x 同步 API,本指南可能很有用。
如果一直在使用 Azure Cosmos DB Async Java SDK 2.x.x,并且打算迁移到 4.0 SDK,请参阅 Reactor vs RxJava 指南 ,了解如何将 RxJava 代码转换为使用 Reactor。
Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK v4 在异步和同步 API 中具有直接连接模式
如果一直在使用 Azure Cosmos DB Sync Java SDK 2.x.x,请注意,基于 TCP 的直接连接模式(而不是 HTTP)在 Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 4.0 中实现,用于异步和同步 API。
API 级别更改
以下是与以前的 SDK(Java SDK 3.x.x、异步 Java SDK 2.x.x 和同步 Java SDK 2.x.x)相比,Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 4.x.x 中的 API 级别更改:
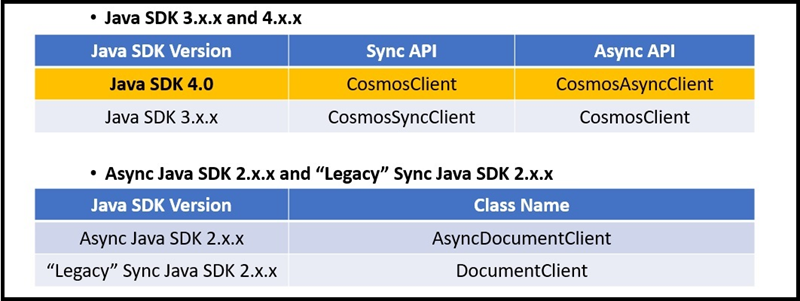
Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 3.x.x 和 4.0 将客户端资源称为
Cosmos<resourceName>。 例如、CosmosClient、CosmosDatabase。CosmosContainer而在版本 2.x.x 中,Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 没有统一的命名方案。Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 3.x.x 和 4.0 提供同步和异步 API。
Java SDK 4.0:所有类都属于同步 API,除非在后面
Async追加Cosmos类名。Java SDK 3.x.x:所有类都属于异步 API,除非在后面
Async追加Cosmos类名。异步 Java SDK 2.x.x:类名称类似于 Sync Java SDK 2.x.x,但名称以 Async 开头。
分层 API 结构
Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 4.0 和 3.x.x 引入了分层 API 结构,以嵌套方式组织客户端、数据库和容器,如以下 4.0 SDK 代码片段所示:
CosmosContainer container = client.getDatabase("MyDatabaseName").getContainer("MyContainerName");
在 Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 版本 2.x.x 中,所有对资源和文档的作都通过客户端实例执行。
表示文档
在 Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 4.0 中,自定义 POJO 和 JsonNodes 是用于从 Azure Cosmos DB 读取和写入文档的两个选项。
在 Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 3.x.x 中,该 CosmosItemProperties 对象由公共 API 公开,并充当文档表示形式。 此类在版本 4.0 中不再公开展示。
导入
Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 4.0 包装以
com.azure.cosmos开始。Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 3.x.x 包以
com.azure.data.cosmos为开头。Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 2.x.x 同步 API 包以
com.microsoft.azure.documentdb开头Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 4.0 将多个类置于嵌套包
com.azure.cosmos.models中。 这些软件包包括:CosmosContainerResponseCosmosDatabaseResponseCosmosItemResponse- 上述所有包的异步 API 对应版本
CosmosContainerPropertiesFeedOptionsPartitionKeyIndexingPolicy-
IndexingMode...等。
Accessors
Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 4.0 公开 get 和 set 方法来访问实例成员。 例如, CosmosContainer 实例具有 container.getId() 和 container.setId() 方法。
这不同于 Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK 3.x.x,其提供了一种流畅的接口。 例如,CosmosSyncContainer 实例的 container.id() 已被重载以用于获取或设置 id 的值。
管理依赖关系冲突
从 Azure Cosmos DB Java SDK V2 升级到 V4 可能会导致依赖项冲突,因为 SDK 使用的库发生了更改。 解决这些冲突需要仔细管理依赖项。
了解新的依赖项:Azure Cosmos DB V4 SDK 有自己的一组依赖项,可能与以前版本中的依赖项不同。 请确保了解以下依赖项:
azure-cosmosreactor-corereactor-nettynetty-handlerguavaslf4j-apijackson-databindjackson-annotationsjackson-corecommons-lang3commons-collections4azure-coreazure-core-http-netty
删除冲突依赖项:首先从
pom.xml文件中删除与早期版本的 SDK 相关的依赖项。 这些依赖项包括azure-cosmosdb以及旧 SDK 可能具有的所有可能的传递依赖项。添加 V4 SDK 依赖项:将 V4 SDK 及其依赖项添加到你的
pom.xml。 下面是一个示例:<dependency> <groupId>com.azure</groupId> <artifactId>azure-cosmos</artifactId> <version>4.x.x</version> <!-- Use the latest version available --> </dependency>检查依赖项冲突:使用 Maven
dependency:tree命令生成依赖项树并识别任何冲突。 运行:mvn dependency:tree查找任何冲突的依赖项版本。 这些冲突通常发生在库(例如
reactor-core、netty-handler、guava和jackson)之间。使用依赖项管理:如果遇到版本冲突,则可能需要使用
<dependencyManagement>节中的pom.xml部分替代有问题的版本。 下面是强制实施特定版本的reactor-core示例:<dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>io.projectreactor</groupId> <artifactId>reactor-core</artifactId> <version>3.x.x</version> <!-- Use a compatible version --> </dependency> <!-- Repeat for any other conflicting dependencies --> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement>排除可传递依赖项:有时,可能需要排除其他依赖项引入的可传递依赖项。 例如,如果另一个库引入冲突的较旧版本的依赖项,则可以将其排除如下:
<dependency> <groupId>some.group</groupId> <artifactId>some-artifact</artifactId> <version>x.x.x</version> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>conflicting.group</groupId> <artifactId>conflicting-artifact</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency>重新生成和测试:进行这些更改后,重新生成项目并对其进行彻底测试,以确保新依赖项正常工作,并且不会发生运行时冲突。
代码片段比较
创建资源
以下代码片段显示了在 4.0、3.x.x 异步、2.x.x 同步和 2.x.x 异步 API 之间创建资源的方式的差异:
// Create Async client.
// Building an async client is still a sync operation.
CosmosAsyncClient client = new CosmosClientBuilder()
.endpoint("your.hostname")
.key("yourmasterkey")
.consistencyLevel(ConsistencyLevel.EVENTUAL)
.buildAsyncClient();
// Create database with specified name
client.createDatabaseIfNotExists("YourDatabaseName")
.flatMap(databaseResponse -> {
testDatabaseAsync = client.getDatabase("YourDatabaseName");
// Container properties - name and partition key
CosmosContainerProperties containerProperties =
new CosmosContainerProperties("YourContainerName", "/id");
// Provision manual throughput
ThroughputProperties throughputProperties = ThroughputProperties.createManualThroughput(400);
// Create container
return database.createContainerIfNotExists(containerProperties, throughputProperties);
}).flatMap(containerResponse -> {
testContainerAsync = database.getContainer("YourContainerName");
return Mono.empty();
}).subscribe();
项目操作
以下代码片段显示了在 4.0、3.x.x 异步、2.x.x 同步和 2.x.x 异步 API 之间执行项作的方式的差异:
// Container is created. Generate many docs to insert.
int number_of_docs = 50000;
ArrayList<JsonNode> docs = generateManyDocs(number_of_docs);
// Insert many docs into container...
Flux.fromIterable(docs)
.flatMap(doc -> testContainerAsync.createItem(doc))
.subscribe(); // ...Subscribing triggers stream execution.
索引
以下代码片段显示了在 4.0、3.x.x 异步、2.x.x 同步和 2.x.x 异步 API 之间创建索引的方式的差异:
CosmosContainerProperties containerProperties = new CosmosContainerProperties(containerName, "/lastName");
// Custom indexing policy
IndexingPolicy indexingPolicy = new IndexingPolicy();
indexingPolicy.setIndexingMode(IndexingMode.CONSISTENT);
// Included paths
List<IncludedPath> includedPaths = new ArrayList<>();
includedPaths.add(new IncludedPath("/*"));
indexingPolicy.setIncludedPaths(includedPaths);
// Excluded paths
List<ExcludedPath> excludedPaths = new ArrayList<>();
excludedPaths.add(new ExcludedPath("/name/*"));
indexingPolicy.setExcludedPaths(excludedPaths);
containerProperties.setIndexingPolicy(indexingPolicy);
ThroughputProperties throughputProperties = ThroughputProperties.createManualThroughput(400);
database.createContainerIfNotExists(containerProperties, throughputProperties);
CosmosAsyncContainer containerIfNotExists = database.getContainer(containerName);
存储过程
以下代码片段显示了在 4.0、3.x.x 异步、2.x.x 同步和 2.x.x 异步 API 之间创建存储过程的方式的差异:
logger.info("Creating stored procedure...\n");
String sprocId = "createMyDocument";
String sprocBody = "function createMyDocument() {\n" +
"var documentToCreate = {\"id\":\"test_doc\"}\n" +
"var context = getContext();\n" +
"var collection = context.getCollection();\n" +
"var accepted = collection.createDocument(collection.getSelfLink(), documentToCreate,\n" +
" function (err, documentCreated) {\n" +
"if (err) throw new Error('Error' + err.message);\n" +
"context.getResponse().setBody(documentCreated.id)\n" +
"});\n" +
"if (!accepted) return;\n" +
"}";
CosmosStoredProcedureProperties storedProcedureDef = new CosmosStoredProcedureProperties(sprocId, sprocBody);
container.getScripts()
.createStoredProcedure(storedProcedureDef,
new CosmosStoredProcedureRequestOptions()).block();
// ...
logger.info(String.format("Executing stored procedure %s...\n\n", sprocId));
CosmosStoredProcedureRequestOptions options = new CosmosStoredProcedureRequestOptions();
options.setPartitionKey(new PartitionKey("test_doc"));
container.getScripts()
.getStoredProcedure(sprocId)
.execute(null, options)
.flatMap(executeResponse -> {
logger.info(String.format("Stored procedure %s returned %s (HTTP %d), at cost %.3f RU.\n",
sprocId,
executeResponse.getResponseAsString(),
executeResponse.getStatusCode(),
executeResponse.getRequestCharge()));
return Mono.empty();
}).block();
更改源
以下代码片段显示了在 4.0 和 3.x.x 版本的异步 API 中,更改源操作的执行方式上的差异。
ChangeFeedProcessor changeFeedProcessorInstance =
new ChangeFeedProcessorBuilder()
.hostName(hostName)
.feedContainer(feedContainer)
.leaseContainer(leaseContainer)
.handleChanges((List<JsonNode> docs) -> {
logger.info("--->setHandleChanges() START");
for (JsonNode document : docs) {
try {
//Change Feed hands the document to you in the form of a JsonNode
//As a developer you have two options for handling the JsonNode document provided to you by Change Feed
//One option is to operate on the document in the form of a JsonNode, as shown below. This is great
//especially if you do not have a single uniform data model for all documents.
logger.info("---->DOCUMENT RECEIVED: " + OBJECT_MAPPER.writerWithDefaultPrettyPrinter()
.writeValueAsString(document));
//You can also transform the JsonNode to a POJO having the same structure as the JsonNode,
//as shown below. Then you can operate on the POJO.
CustomPOJO pojo_doc = OBJECT_MAPPER.treeToValue(document, CustomPOJO.class);
logger.info("----=>id: " + pojo_doc.getId());
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
logger.info("--->handleChanges() END");
})
.buildChangeFeedProcessor();
// ...
changeFeedProcessorInstance.start()
.subscribeOn(Schedulers.boundedElastic())
.subscribe();
容器级生存时间(TTL)
以下代码片段显示了如何在 4.0、3.x.x 异步、2.x.x 同步和 2.x.x 异步 API 之间为容器中的数据创建生存时间的差异:
CosmosAsyncContainer container;
// Create a new container with TTL enabled with default expiration value
CosmosContainerProperties containerProperties = new CosmosContainerProperties("myContainer", "/myPartitionKey");
containerProperties.setDefaultTimeToLiveInSeconds(90 * 60 * 60 * 24);
ThroughputProperties throughputProperties = ThroughputProperties.createManualThroughput(400);
database.createContainerIfNotExists(containerProperties, throughputProperties).block();
container = database.getContainer("myContainer");
项目级生存时间(TTL)
以下代码片段显示了如何为项创建生存时间在 4.0、3.x.x 异步、2.x.x 同步和 2.x.x 异步 API 之间的差异:
// Include a property that serializes to "ttl" in JSON
class SalesOrder
{
private String id;
private String customerId;
private Integer ttl;
public SalesOrder(String id, String customerId, Integer ttl) {
this.id = id;
this.customerId = customerId;
this.ttl = ttl;
}
public String getId() {return this.id;}
public void setId(String new_id) {this.id = new_id;}
public String getCustomerId() {return this.customerId;}
public void setCustomerId(String new_cid) {this.customerId = new_cid;}
public Integer getTtl() {return this.ttl;}
public void setTtl(Integer new_ttl) {this.ttl = new_ttl;}
//...
}
// Set the value to the expiration in seconds
SalesOrder salesOrder = new SalesOrder(
"SO05",
"CO18009186470",
60 * 60 * 24 * 30 // Expire sales orders in 30 days
);
后续步骤
- 使用 V4 SDK 生成 Java 应用以管理用于 NoSQL 数据的 Azure Cosmos DB
- 了解 基于 Reactor 的 Java SDK
- 了解如何通过 Reactor 与 RxJava 对比指南,将 RxJava 异步代码转换为 Reactor 异步代码。
- 尝试为迁移到 Azure Cosmos DB 进行容量规划?
- 如果你只知道现有数据库群集中的 vCore 和服务器数量,请阅读根据 vCore 或 vCPU 数量估算请求单位数
- 若知道当前数据库工作负载的典型请求速率,请阅读使用 Azure Cosmos DB 容量计划工具估算请求单位