适用于:  员工租户
员工租户  外部租户(了解详细信息)
外部租户(了解详细信息)
这是本教程系列中的第二个教程,演示如何将适用于 iOS 和 macOS 的 Microsoft 身份验证库(MSAL)添加到 iOS Swift 应用。
在开始之前,请使用此页面顶部的 “选择租户类型 选择器”来选择租户类型。 Microsoft Entra ID 提供两种租户配置:员工和外部。 员工租户配置适用于员工、内部应用和其他组织资源。 外部租户适用于面向客户的应用。
在本教程中,你将:
- 将 MSAL 框架添加到 iOS (Swift) 应用。
- 创建 SDK 实例。
- 配置 Xcode 项目设置。
先决条件
- 在 Microsoft Entra 管理中心注册新的客户端 Web 应用,为 任何组织目录中的帐户和个人Microsoft帐户配置。 有关更多详细信息 ,请参阅注册应用程序 。 在应用程序 概述 页中记录以下值供以后使用:
- 应用程序(客户端)ID
- 目录(租户)ID
- Xcode。
- iOS (Swift) 项目。
添加平台重定向 URL
若要将应用类型指定到应用注册,请执行以下步骤:
- 在“管理”下,选择“身份验证”“添加平台”“iOS/macOS” 。
- 输入项目的捆绑 ID。 如果下载了代码示例,则捆绑 ID 为
com.microsoft.identitysample.MSALiOS。 若要创建自己的项目,请在 Xcode 中选择项目,然后打开“常规”选项卡。此时捆绑标识符会显示在“标识”部分。 - 选择配置并保存出现在MSAL 配置页面的MSAL 配置,以便稍后在配置应用时进行输入。
- 选择“完成”。
将 MSAL 框架添加到 iOS (Swift) 应用
选择以下方式之一在应用中安装 MSAL 库:
可可豆荚
如果使用 CocoaPods,请安装
MSAL,方法是先在项目的 .xcodeproj 文件所在的文件夹中创建名为 podfile 的空文件。 将以下内容添加到podfile:use_frameworks! target '<your-target-here>' do pod 'MSAL' end将
<your-target-here>替换为项目的名称。在终端窗口中导航到包含所创建的 podfile 的文件夹,然后运行 以安装 MSAL 库。
关闭 Xcode,然后打开
<your project name>.xcworkspace,以便在 Xcode 中重新加载项目。
迦太基
如果使用 Carthage,请安装 MSAL,只需将其添加到 Cartfile 即可:
github "AzureAD/microsoft-authentication-library-for-objc" "master"
在终端窗口中,在与更新的 Cartfile 相同的目录中,运行以下命令,让 Carthage 更新项目中的依赖项。
iOS:
carthage update --platform iOS
macOS:
carthage update --platform macOS
手动
还可使用 Git 子模块或查看最新版本,以便在应用程序中将其用作框架。
添加应用注册
接下来,我们将你的应用注册添加到代码中。
首先,将以下导入语句添加到 ViewController.swift 文件和 AppDelegate.swift 或 SceneDelegate.swift 的顶部:
import MSAL
接下来,请在 之前将以下代码添加到 viewDidLoad() 文件中:
// Update the below to your client ID. The below is for running the demo only
let kClientID = "Your_Application_Id_Here"
let kGraphEndpoint = "https://graph.microsoft.com/" // the Microsoft Graph endpoint
let kAuthority = "https://login.microsoftonline.com/common" // this authority allows a personal Microsoft account and a work or school account in any organization's Azure AD tenant to sign in
let kScopes: [String] = ["user.read"] // request permission to read the profile of the signed-in user
var accessToken = String()
var applicationContext : MSALPublicClientApplication?
var webViewParameters : MSALWebviewParameters?
var currentAccount: MSALAccount?
你修改的唯一值是被分配给 kClientID 作为你的 应用程序 ID 的值。 此值是你在本教程开头用于注册应用程序的步骤中保存的 MSAL 配置数据的一部分。
创建 SDK 实例
若要在项目中创建 MSAL 实例,请执行以下步骤:
将 ViewController 方法添加到 initMSAL 类:
func initMSAL() throws {
guard let authorityURL = URL(string: kAuthority) else {
self.updateLogging(text: "Unable to create authority URL")
return
}
let authority = try MSALAADAuthority(url: authorityURL)
let msalConfiguration = MSALPublicClientApplicationConfig(clientId: kClientID, redirectUri: nil, authority: authority)
self.applicationContext = try MSALPublicClientApplication(configuration: msalConfiguration)
self.initWebViewParams()
}
仍在 ViewController 类中,在 initMSAL 方法后面,添加 initWebViewParams 方法:
iOS 代码:
func initWebViewParams() {
self.webViewParameters = MSALWebviewParameters(authPresentationViewController: self)
}
macOS 代码:
func initWebViewParams() {
self.webViewParameters = MSALWebviewParameters()
}
配置 Xcode 项目设置
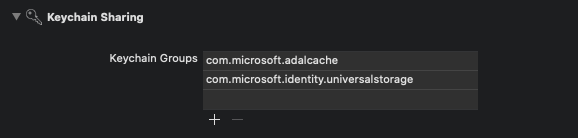
向项目 签名和功能添加新的密钥链组。 密钥链组在 iOS 上应为 com.microsoft.adalcache,在 macOS 上应为 com.microsoft.identity.universalstorage。
仅对于 iOS,配置 URL 方案
在此步骤中需注册 CFBundleURLSchemes,以便用户在登录后可重定向回应用。 另外,LSApplicationQueriesSchemes 也允许应用使用 Microsoft Authenticator。
在 Xcode 中将 Info.plist 作为源代码文件打开,在 部分中添加以下命令。 将 [BUNDLE_ID] 替换为你之前使用的值。 如果已下载代码,则捆绑包标识符为 com.microsoft.identitysample.MSALiOS。 若要创建自己的项目,请在 Xcode 中选择项目,然后打开“常规”选项卡。此时捆绑标识符会显示在“标识”部分。
<key>CFBundleURLTypes</key>
<array>
<dict>
<key>CFBundleURLSchemes</key>
<array>
<string>msauth.[BUNDLE_ID]</string>
</array>
</dict>
</array>
<key>LSApplicationQueriesSchemes</key>
<array>
<string>msauthv2</string>
<string>msauthv3</string>
</array>
仅对于 macOS,配置应用沙盒
- 转到 Xcode 项目设置 >“功能”选项卡>“应用沙盒”
- 选中“传出连接(客户端)”复选框。
后续步骤
这是本教程系列中的第二个教程,演示如何将适用于 iOS 和 macOS 的 Microsoft 身份验证库(MSAL)添加到 iOS Swift 应用。
在开始之前,请使用此页面顶部的 “选择租户类型 选择器”来选择租户类型。 Microsoft Entra ID 提供两种租户配置:员工和外部。 员工租户配置适用于员工、内部应用和其他组织资源。 外部租户适用于面向客户的应用。
在本教程中,你将;
- 将 MSAL 框架添加到 iOS (Swift) 应用。
- 创建 SDK 实例。
先决条件
- 在 Microsoft Entra 管理中心注册新的客户端 Web 应用,为 任何组织目录中的帐户和个人Microsoft帐户配置。 有关更多详细信息 ,请参阅注册应用程序 。 在应用程序 概述 页中记录以下值供以后使用:
- 应用程序(客户端)ID
- 目录(租户)ID
- Xcode。
- iOS (Swift) 项目。
添加平台重定向 URL
若要将应用类型指定到应用注册,请执行以下步骤:
- 在“管理”下,选择“身份验证”“添加平台”“iOS/macOS” 。
- 输入项目的捆绑 ID。 如果下载了代码示例,则捆绑 ID 为
com.microsoft.identitysample.MSALiOS。 若要创建自己的项目,请在 Xcode 中选择项目,然后打开“常规”选项卡。此时捆绑标识符会显示在“标识”部分。 - 选择配置并保存出现在MSAL 配置页面的MSAL 配置,以便稍后在配置应用时进行输入。
- 选择“完成”。
启用公共客户端流
若要将应用标识为公共客户端,请执行以下步骤:
在 管理中,选择 身份验证。
在“高级设置”下,对于“允许公共客户端流”,选择“是”。
选择 保存 以保存更改。
将 MSAL 框架添加到 iOS (Swift) 应用
MSAL 身份验证 SDK 用于使用标准 OAuth2 和 OpenID Connect 将身份验证集成到应用中。 它允许使用Microsoft标识登录用户或应用。 若要将 MSAL 添加到 iOS (Swift) 项目,请执行以下步骤:
- 在 Xcode 中打开 iOS 项目。
- 从“文件”菜单中选择“添加包依赖项...”。
- 输入
https://github.com/AzureAD/microsoft-authentication-library-for-objc为包 URL,然后选择 “添加包”
更新捆绑标识符
在 Apple 生态系统中,捆绑标识符是应用程序的唯一标识符。 若要更新项目中的捆绑标识符,请执行以下步骤:
打开项目设置。 在“标识”部分输“捆绑标识符”。
右键单击Info.plist,然后选择打开为>源代码。
在 dict 根节点下,将
Enter_the_bundle_Id_Here替换为你在门户中使用的“捆绑 ID”。 请注意字符串中的msauth.前缀。<key>CFBundleURLTypes</key> <array> <dict> <key>CFBundleURLSchemes</key> <array> <string>msauth.Enter_the_Bundle_Id_Here</string> </array> </dict> </array>
创建 SDK 实例
若要在项目中创建 MSAL 实例,请执行以下步骤:
将 MSAL 库导入视图控制器中,通过在
import MSAL类顶部添加ViewController。通过在
applicationContext函数前面添加以下代码,将viewDidLoad()成员变量添加到 ViewController 类:var applicationContext : MSALPublicClientApplication? var webViewParameters : MSALWebviewParameters?代码声明两个变量:
applicationContext存储实例的MSALPublicClientApplication变量,以及webViewParameters存储实例的MSALWebviewParameters变量。MSALPublicClientApplication是 MSAL 提供的用于处理公共客户端应用程序的类。MSALWebviewParametersMSAL 提供的类定义用于配置身份验证过程中使用的 Web 视图的参数。将以下代码添加到视图
viewDidLoad()函数:do { try self.initMSAL() } catch let error { self.updateLogging(text: "Unable to create Application Context \(error)") }代码尝试初始化 MSAL,处理过程中发生的任何错误。 如果发生错误,它会使用错误的详细信息更新日志记录。
添加以下代码以创建
initMSAL()函数,该函数用于初始化 MSAL:func initMSAL() throws { guard let authorityURL = URL(string: Configuration.kAuthority) else { self.updateLogging(text: "Unable to create authority URL") return } let authority = try MSALCIAMAuthority(url: authorityURL) let msalConfiguration = MSALPublicClientApplicationConfig(clientId: Configuration.kClientID, redirectUri: Configuration.kRedirectUri, authority: authority) self.applicationContext = try MSALPublicClientApplication(configuration: msalConfiguration) }此代码初始化适用于 iOS 的 MSAL。 它首先尝试使用提供的 Configuration.kAuthority 字符串为权威创建一个 URL。 如果成功,它将基于该 URL 创建一个 MSAL 权威对象。 然后,它根据给定的客户端 ID、重定向 URI 和授权机构配置
MSALPublicClientApplication。 如果已正确设置所有配置,则会使用配置的MSALPublicClientApplication初始化应用程序上下文。 如果过程中发生任何错误,则会引发错误。创建 Configuration.swift 文件并添加以下配置:
import Foundation @objcMembers class Configuration { static let kTenantSubdomain = "Enter_the_Tenant_Subdomain_Here" // Update the below to your client ID you received in the portal. static let kClientID = "Enter_the_Application_Id_Here" static let kRedirectUri = "Enter_the_Redirect_URI_Here" static let kProtectedAPIEndpoint = "Enter_the_Protected_API_Full_URL_Here" static let kScopes = ["Enter_the_Protected_API_Scopes_Here"] static let kAuthority = "https://\(kTenantSubdomain).ciamlogin.com" }此 Swift 配置代码定义了一个名为
Configuration并标记为@objcMembers的类。 它包括与身份验证设置相关的各种配置参数的静态常量。 这些参数包括 租户子域、 客户端 ID、 重定向 URI、 受保护的 API 终结点和 范围。 这些配置常量应使用特定于应用程序的设置的适当值进行更新。查找占位符:
-
查找
Enter_the_Application_Id_Here并将其替换为之前注册的应用的应用程序(客户端)ID。 -
Enter_the_Redirect_URI_Here并将其替换为之前添加平台重定向 URL 时下载的 MSAL 配置文件中的 kRedirectUri 值。 -
Enter_the_Protected_API_Scopes_Here并将其替换为前面记录的范围。 如果尚未记录任何范围,可以将此范围列表留空。 -
Enter_the_Tenant_Subdomain_Here并将其替换为 Directory (tenant) 子域。 例如,如果租户主域名是contoso.onmicrosoft.com,请使用contoso。 如果不知道租户子域,请了解如何 阅读租户详细信息。
-
查找
使用自定义 URL 域(可选)
使用自定义域对身份验证 URL 进行完全品牌化。 从用户的角度来看,用户在身份验证过程中仍然停留在您的域名上,而不会被重定向到 ciamlogin.com 域名。
使用以下步骤使用自定义域:
使用启用外部租户中应用的自定义 URL 域名中的步骤,为您的外部租户启用自定义 URL 域名。
打开 Configuration.swift 文件:
- 将属性的值
kAuthority更新为 https://Enter_the_Custom_Domain_Here/Enter_the_Tenant_ID_Here. 将Enter_the_Custom_Domain_Here替换为您的自定义 URL 域,并将Enter_the_Tenant_ID_Here替换为您的租户 ID。 如果没有租户 ID,请了解如何读取租户详细信息。
- 将属性的值
对 Configuration.swift 文件进行更改后,如果自定义 URL 域 login.contoso.com,并且租户 ID 为 aaaabb-0000-cccc-1111-dd222eeee,则文件应类似于以下代码片段:
import Foundation
@objcMembers
class Configuration {
static let kTenantSubdomain = "login.contoso.com"
// Update the below to your client ID you received in the portal.
static let kClientID = "Enter_the_Application_Id_Here"
static let kRedirectUri = "Enter_the_Redirect_URI_Here"
static let kProtectedAPIEndpoint = "Enter_the_Protected_API_Full_URL_Here"
static let kScopes = ["Enter_the_Protected_API_Scopes_Here"]
static let kAuthority = "https://\(kTenantSubdomain)/aaaabbbb-0000-cccc-1111-dddd2222eeee"
}