教程:使用 R 预测牛油果价格
本教程介绍了 Microsoft Fabric 中 Synapse 数据科学工作流的端到端示例。 它使用 R 分析并可视化美国牛油果价格,以便构建预测未来牛油果价格的机器学习模型。
本教程涵盖以下步骤:
- 加载默认库
- 加载数据
- 自定义数据
- 将新包添加到会话
- 分析和可视化数据
- 模型

先决条件
获取 Microsoft Fabric 订阅。 或者注册免费的 Microsoft Fabric 试用版。
登录 Microsoft Fabric。
使用主页左侧的体验切换器切换到 Synapse 数据科学体验。
打开或创建笔记本。 请参阅如何使用 Microsoft Fabric 笔记本,了解如何操作。
通过将语言选项设置为 Spark (R) 来更改主要语言。
将笔记本附加到湖屋。 选择左侧的“添加”以添加现有湖屋或创建湖屋。
加载库
使用默认 R 运行时中的库:
library(tidyverse)
library(lubridate)
library(hms)
加载数据
从 Internet 上下载的 .csv 文件读取鳄梨价格:
df <- read.csv('https://synapseaisolutionsa.blob.core.windows.net/public/AvocadoPrice/avocado.csv', header = TRUE)
head(df,5)
操作该数据
首先,为列指定友好名称。
# To use lowercase
names(df) <- tolower(names(df))
# To use snake case
avocado <- df %>%
rename("av_index" = "x",
"average_price" = "averageprice",
"total_volume" = "total.volume",
"total_bags" = "total.bags",
"amount_from_small_bags" = "small.bags",
"amount_from_large_bags" = "large.bags",
"amount_from_xlarge_bags" = "xlarge.bags")
# Rename codes
avocado2 <- avocado %>%
rename("PLU4046" = "x4046",
"PLU4225" = "x4225",
"PLU4770" = "x4770")
head(avocado2,5)
更改数据类型,删除不需要的列,并添加总消耗量:
# Convert data
avocado2$year = as.factor(avocado2$year)
avocado2$date = as.Date(avocado2$date)
avocado2$month = factor(months(avocado2$date), levels = month.name)
avocado2$average_price =as.numeric(avocado2$average_price)
avocado2$PLU4046 = as.double(avocado2$PLU4046)
avocado2$PLU4225 = as.double(avocado2$PLU4225)
avocado2$PLU4770 = as.double(avocado2$PLU4770)
avocado2$amount_from_small_bags = as.numeric(avocado2$amount_from_small_bags)
avocado2$amount_from_large_bags = as.numeric(avocado2$amount_from_large_bags)
avocado2$amount_from_xlarge_bags = as.numeric(avocado2$amount_from_xlarge_bags)
# Remove unwanted columns
avocado2 <- avocado2 %>%
select(-av_index,-total_volume, -total_bags)
# Calculate total consumption
avocado2 <- avocado2 %>%
mutate(total_consumption = PLU4046 + PLU4225 + PLU4770 + amount_from_small_bags + amount_from_large_bags + amount_from_xlarge_bags)
安装新包
使用内联包安装将新包添加到会话:
install.packages(c("repr","gridExtra","fpp2"))
加载所需的库。
library(tidyverse)
library(knitr)
library(repr)
library(gridExtra)
library(data.table)
分析和可视化数据
按地区比较传统(非有机)牛油果价格:
options(repr.plot.width = 10, repr.plot.height =10)
# filter(mydata, gear %in% c(4,5))
avocado2 %>%
filter(region %in% c("PhoenixTucson","Houston","WestTexNewMexico","DallasFtWorth","LosAngeles","Denver","Roanoke","Seattle","Spokane","NewYork")) %>%
filter(type == "conventional") %>%
select(date, region, average_price) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = reorder(region, -average_price, na.rm = T), y = average_price)) +
geom_jitter(aes(colour = region, alpha = 0.5)) +
geom_violin(outlier.shape = NA, alpha = 0.5, size = 1) +
geom_hline(yintercept = 1.5, linetype = 2) +
geom_hline(yintercept = 1, linetype = 2) +
annotate("rect", xmin = "LosAngeles", xmax = "PhoenixTucson", ymin = -Inf, ymax = Inf, alpha = 0.2) +
geom_text(x = "WestTexNewMexico", y = 2.5, label = "My top 5 cities!", hjust = 0.5) +
stat_summary(fun = "mean") +
labs(x = "US city",
y = "Avocado prices",
title = "Figure 1. Violin plot of nonorganic avocado prices",
subtitle = "Visual aids: \n(1) Black dots are average prices of individual avocados by city \n between January 2015 and March 2018. \n(2) The plot is ordered descendingly.\n(3) The body of the violin becomes fatter when data points increase.") +
theme_classic() +
theme(legend.position = "none",
axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 25, vjust = 0.65),
plot.title = element_text(face = "bold", size = 15)) +
scale_y_continuous(lim = c(0, 3), breaks = seq(0, 3, 0.5))
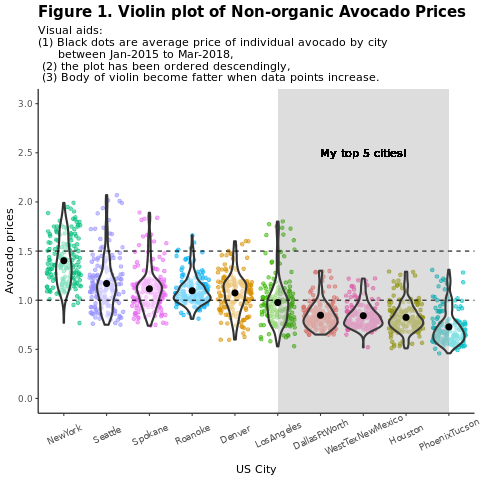
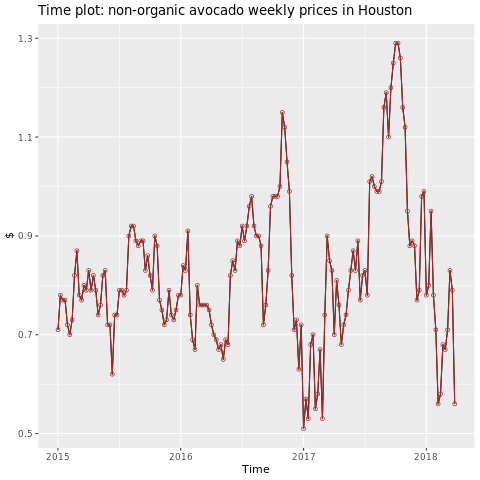
重点关注休斯顿地区。
library(fpp2)
conv_houston <- avocado2 %>%
filter(region == "Houston",
type == "conventional") %>%
group_by(date) %>%
summarise(average_price = mean(average_price))
# Set up ts
conv_houston_ts <- ts(conv_houston$average_price,
start = c(2015, 1),
frequency = 52)
# Plot
autoplot(conv_houston_ts) +
labs(title = "Time plot: nonorganic avocado weekly prices in Houston",
y = "$") +
geom_point(colour = "brown", shape = 21) +
geom_path(colour = "brown")
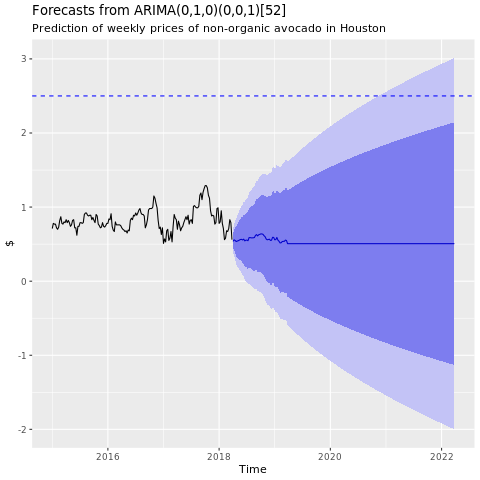
训练机器学习模型
根据自动回归集成移动平均线 (ARIMA) 为休斯顿地区构建价格预测模型:
conv_houston_ts_arima <- auto.arima(conv_houston_ts,
d = 1,
approximation = F,
stepwise = F,
trace = T)
checkresiduals(conv_houston_ts_arima)
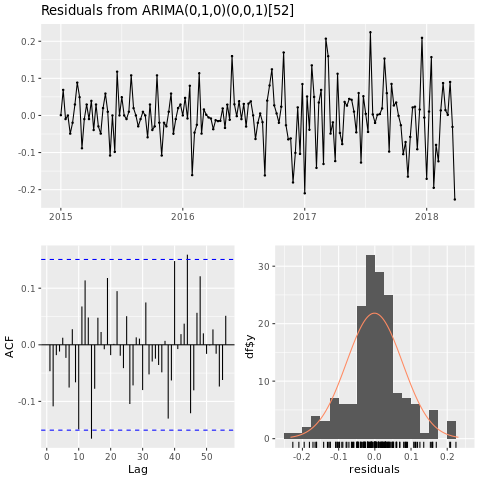
显示休斯顿 ARIMA 模型的预测图:
conv_houston_ts_arima_fc <- forecast(conv_houston_ts_arima, h = 208)
autoplot(conv_houston_ts_arima_fc) + labs(subtitle = "Prediction of weekly prices of nonorganic avocados in Houston",
y = "$") +
geom_hline(yintercept = 2.5, linetype = 2, colour = "blue")