集合视图支持使用任意布局显示内容。 它们允许轻松开箱即用地创建类似网格的布局,同时支持自定义布局。
集合视图在 UICollectionView 类中提供,是 iOS 6 中的一个新概念,用于介绍使用布局在屏幕上呈现多个项。 向 UICollectionView 提供数据的模式,以创建项并与这些项目进行交互,遵循 iOS 开发中常用的相同委派和数据源模式。
但是,集合视图使用独立于 UICollectionView 本身的布局子系统。 因此,只需提供不同的布局即可轻松更改集合视图的呈现。
iOS 提供了一个名为 UICollectionViewFlowLayout 的布局类,允许创建基于线条的布局(如网格),无需额外工作。 此外,还可以创建自定义布局,允许你想象的任何演示文稿。
UICollectionView 基础知识
UICollectionView 类由三个不同的项组成:
- 单元格 – 每个项的数据驱动视图
- 补充视图 – 与节关联的数据驱动视图。
- 修饰视图 – 布局创建的非数据驱动视图
单元
单元格是表示集合视图所呈现的数据集中的单个项的对象。 每个单元格都是由三个不同的视图组成的 UICollectionViewCell 类的实例,如下图所示:
UICollectionViewCell 类具有以下每个视图的属性:
ContentView– 此视图包含单元格显示的内容。 它在屏幕上以最顶端的 Z 排序呈现。SelectedBackgroundView– Cells 内置了对选择的支持。 此视图用于直观表示已选择单元格。 选择单元格时,它将呈现在ContentView下方。BackgroundView– 单元格还可以显示由BackgroundView呈现的背景。 此视图呈现在SelectedBackgroundView下方。
通过设置 ContentView,使其小于 BackgroundView 和 SelectedBackgroundView,BackgroundView 可用于直观地设置内容框架,而选择单元格时将显示 SelectedBackgroundView,如下所示:
上面的屏幕截图中的单元格是通过从 UICollectionViewCell 继承并分别设置 ContentView、SelectedBackgroundView 和 BackgroundView 属性来创建的,如以下代码所示:
public class AnimalCell : UICollectionViewCell
{
UIImageView imageView;
[Export ("initWithFrame:")]
public AnimalCell (CGRect frame) : base (frame)
{
BackgroundView = new UIView{BackgroundColor = UIColor.Orange};
SelectedBackgroundView = new UIView{BackgroundColor = UIColor.Green};
ContentView.Layer.BorderColor = UIColor.LightGray.CGColor;
ContentView.Layer.BorderWidth = 2.0f;
ContentView.BackgroundColor = UIColor.White;
ContentView.Transform = CGAffineTransform.MakeScale (0.8f, 0.8f);
imageView = new UIImageView (UIImage.FromBundle ("placeholder.png"));
imageView.Center = ContentView.Center;
imageView.Transform = CGAffineTransform.MakeScale (0.7f, 0.7f);
ContentView.AddSubview (imageView);
}
public UIImage Image {
set {
imageView.Image = value;
}
}
}
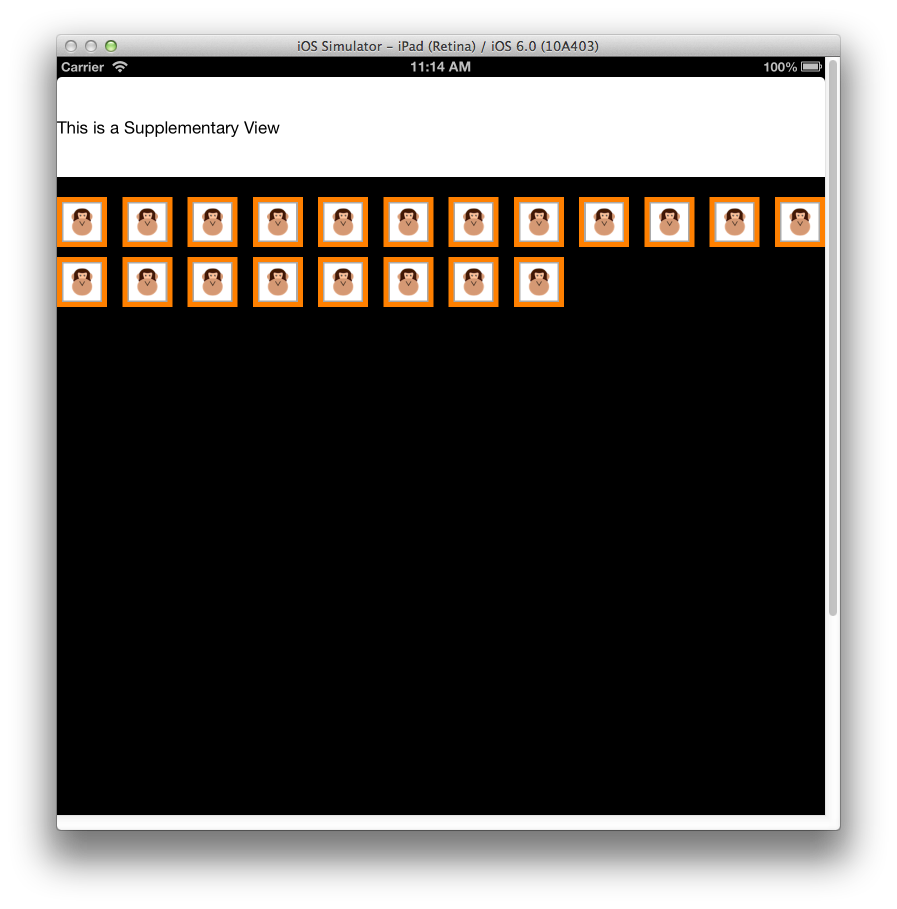
补充视图
补充视图是显示与 UICollectionView 的每个部分关联的信息的视图。 与单元格一样,补充视图是数据驱动的。 当单元格显示数据源中的项数据时,补充视图将显示分区数据,例如书架中的书籍类别或音乐库中的音乐流派。
例如,补充视图可用于显示特定节的标头,如下图所示:
若要使用补充视图,首先需要在 ViewDidLoad 方法中注册它:
CollectionView.RegisterClassForSupplementaryView (typeof(Header), UICollectionElementKindSection.Header, headerId);
然后,需要使用 GetViewForSupplementaryElement 返回视图,通过使用 DequeueReusableSupplementaryView创建,并从 UICollectionReusableView 继承。 以下代码片段将生成上面屏幕截图中显示的补充视图:
public override UICollectionReusableView GetViewForSupplementaryElement (UICollectionView collectionView, NSString elementKind, NSIndexPath indexPath)
{
var headerView = (Header)collectionView.DequeueReusableSupplementaryView (elementKind, headerId, indexPath);
headerView.Text = "Supplementary View";
return headerView;
}
补充视图比页眉和页脚更通用。 它们可以放置在集合视图中的任意位置,并且可以由任何视图组成,使其外观完全可自定义。
修饰视图
修饰视图纯粹是可在一个 UICollectionView 中显示的视觉视图。 与单元格和补充视图不同,它们不是数据驱动的。 它们总是在布局的子类中创建,随后会随着内容布局的变化而变化。 例如,修饰视图可用于显示一个背景视图,该视图与 UICollectionView 中的内容一起滚动,如下所示:
下面的代码片段在示例 CircleLayout 类中将背景更改为红色:
public class MyDecorationView : UICollectionReusableView
{
[Export ("initWithFrame:")]
public MyDecorationView (CGRect frame) : base (frame)
{
BackgroundColor = UIColor.Red;
}
}
数据源
与 iOS 的其他部分(如 UITableView 和 MKMapView)一样,UICollectionView 从 数据源(通过 UICollectionViewDataSource 类在 Xamarin.iOS 中公开)获取其数据。 此类负责向 UICollectionView 提供内容,例如:
- 单元格 - 从
GetCell方法返回。 - 补充视图 - 从
GetViewForSupplementaryElement方法返回。 - 节数 - 从
NumberOfSections方法返回。 如果未实现,则默认值为 1。 - 每个节的项数 - 从
GetItemsCount方法返回。
UICollectionViewController
为方便起见,UICollectionViewController 类可用。这会自动配置为委托,下一部分将讨论,以及其 UICollectionView 视图的数据源。
与 UITableView 一样,UICollectionView 类将仅调用其数据源以获取屏幕上项的单元格。
在屏幕外滚动的单元格放置在队列中以供重复使用,如下图所示:
通过 UICollectionView 和 UITableView 简化了单元格重用。 如果重复使用队列中没有单元格,则不再需要直接在数据源中创建一个单元格,因为单元格已在系统中注册。 如果在调用从重用队列中取消排序时没有可用的单元格,iOS 会根据注册的类型或 nib 自动创建单元格。
同一技术也可用于补充视图。
例如,请考虑注册 AnimalCell 类的以下代码:
static NSString animalCellId = new NSString ("AnimalCell");
CollectionView.RegisterClassForCell (typeof(AnimalCell), animalCellId);
当 UICollectionView 因为它的项位于屏幕上而需要单元格时,UICollectionView 会调用其数据源的 GetCell 方法。 与 UITableView 的工作方式类似,此方法负责从支持数据配置单元格,在本例中为 AnimalCell 类。
以下代码演示返回 AnimalCell 实例的 GetCell 实现:
public override UICollectionViewCell GetCell (UICollectionView collectionView, Foundation.NSIndexPath indexPath)
{
var animalCell = (AnimalCell)collectionView.DequeueReusableCell (animalCellId, indexPath);
var animal = animals [indexPath.Row];
animalCell.Image = animal.Image;
return animalCell;
}
对 DequeReusableCell 的调用是在重新使用队列中取消排队的位置,或者,如果队列中没有单元格,则根据 CollectionView.RegisterClassForCell 调用中注册的类型创建单元格。
在这种情况下,通过注册 AnimalCell 类,iOS 将在内部创建新的 AnimalCell 单元格,并在对单元格取消排队的调用时返回它,之后它将配置动物类中包含的图像,并返回该图像以显示给单元格 UICollectionView。
委托
UICollectionView 类使用类型 UICollectionViewDelegate 的委托来支持与 UICollectionView 中内容的交互。 这样就可以控制:
- 单元格选择 – 确定是否选择了单元格。
- 单元格突出显示 – 确定单元格当前是否被触摸。
- 单元格菜单 – 为单元格显示的菜单,以响应长按手势。
与数据源一样,默认情况下,UICollectionViewController 配置为 UICollectionView 的委托。
单元格突出显示
按下单元格后,单元格将转换为突出显示状态,直到用户从单元格中抬起手指,才会选择该单元格。 这允许在实际选择单元格之前临时更改单元格的外观。 选择后,将显示单元格 SelectedBackgroundView。 下图显示了所选内容发生前突出显示的状态:
若要实现突出显示,可以使用 UICollectionViewDelegate 的 ItemHighlighted 和 ItemUnhighlighted 方法。 例如,以下代码将在突出显示单元格时应用 ContentView 的黄色背景,并在未突出显示时应用白色背景,如下图所示:
public override void ItemHighlighted (UICollectionView collectionView, NSIndexPath indexPath)
{
var cell = collectionView.CellForItem(indexPath);
cell.ContentView.BackgroundColor = UIColor.Yellow;
}
public override void ItemUnhighlighted (UICollectionView collectionView, NSIndexPath indexPath)
{
var cell = collectionView.CellForItem(indexPath);
cell.ContentView.BackgroundColor = UIColor.White;
}
禁用选择
选择默认情况下在 UICollectionView 中启用。 若要禁用选择,请重写 ShouldHighlightItem 并返回 false,如下所示:
public override bool ShouldHighlightItem (UICollectionView collectionView, NSIndexPath indexPath)
{
return false;
}
禁用突出显示后,选择单元格的过程也会被禁用。 此外,还有一个 ShouldSelectItem 方法直接控制选择,尽管如果实现 ShouldHighlightItem 并返回 false,则不会调用 ShouldSelectItem。
ShouldSelectItem 允许在未实现 ShouldHighlightItem 时逐项打开或关闭选择。 它还允许在没有选择的情况下突出显示(如果 ShouldHighlightItem 实现并返回 true),同时 ShouldSelectItem 返回 false。
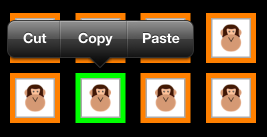
单元格菜单
UICollectionView 中的每个单元格都能够显示允许选择性地剪切、复制和粘贴的菜单。 若要在单元格上创建编辑菜单,请执行以下操作:
- 如果项应显示菜单,请重写
ShouldShowMenu并返回 true。 - 重写
CanPerformAction并返回该项可执行的每个操作的 true,即任何剪切、复制或粘贴操作。 - 重写
PerformAction以执行编辑、粘贴操作的副本。
以下屏幕截图显示按下单元格时菜单:
Layout
UICollectionView 支持布局系统,允许独立于 UICollectionView 本身管理其所有元素、单元格、补充视图和修饰视图的位置。
使用布局系统,应用程序可以支持布局,例如本文中介绍的类似网格的布局,并提供自定义布局。
布局基础知识
UICollectionView 中的布局在继承自 UICollectionViewLayout 的类中定义。 布局实现负责为 UICollectionView 中的每个项创建布局属性。 有两种方法可以创建布局:
- 使用内置
UICollectionViewFlowLayout。 - 通过从
UICollectionViewLayout继承来提供自定义布局。
流布局
UICollectionViewFlowLayout 类提供了一个基于线条的布局,适用于在单元格网格中排列内容,如我们所看到的那样。
若要使用流布局,请执行以下操作:
- 创建
UICollectionViewFlowLayout的实例:
var layout = new UICollectionViewFlowLayout ();
- 将实例传递给
UICollectionView的构造函数:
simpleCollectionViewController = new SimpleCollectionViewController (layout);
这是在网格中布局内容所需的一切。 此外,当方向发生更改时,UICollectionViewFlowLayout 会适当地处理重新排列内容,如下所示:
节内集
为了在 UIContentView 周围提供一些空间,布局具有 UIEdgeInsets 类型的 SectionInset 属性。 例如,以下代码在 UICollectionViewFlowLayout 布局时围绕 UIContentView 的每个部分提供 50 像素的缓冲区:
var layout = new UICollectionViewFlowLayout ();
layout.SectionInset = new UIEdgeInsets (50,50,50,50);
这会导致分区的间距,如下所示:
子类化 UICollectionViewFlowLayout
在直接使用 UICollectionViewFlowLayout 的版本中,还可以对其进行子类化以进一步自定义沿行的内容布局。 例如,这可用于创建不将单元格包装到网格中的布局,而是创建具有水平滚动效果的单个行,如下所示:
若要通过子类化 UICollectionViewFlowLayout 实现此目的,需要:
- 初始化应用于布局本身或构造函数中布局中的所有项的任何布局属性。
- 重写
ShouldInvalidateLayoutForBoundsChange,返回 true,以便在UICollectionView的边界发生更改时,将重新计算单元格的布局。 在这种情况下,使用此方法可确保在滚动期间应用应用于最居中单元格的转换代码。 - 重写
TargetContentOffset以使最中心单元格在滚动停止时贴靠到UICollectionView的中心。 - 重写
LayoutAttributesForElementsInRect以返回UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes的数组。 每个UICollectionViewLayoutAttribute都包含有关如何布局特定项的信息,包括其Center、Size、ZIndex和Transform3D等属性。
以下代码显示了这样的实现:
using System;
using CoreGraphics;
using Foundation;
using UIKit;
using CoreGraphics;
using CoreAnimation;
namespace SimpleCollectionView
{
public class LineLayout : UICollectionViewFlowLayout
{
public const float ITEM_SIZE = 200.0f;
public const int ACTIVE_DISTANCE = 200;
public const float ZOOM_FACTOR = 0.3f;
public LineLayout ()
{
ItemSize = new CGSize (ITEM_SIZE, ITEM_SIZE);
ScrollDirection = UICollectionViewScrollDirection.Horizontal;
SectionInset = new UIEdgeInsets (400,0,400,0);
MinimumLineSpacing = 50.0f;
}
public override bool ShouldInvalidateLayoutForBoundsChange (CGRect newBounds)
{
return true;
}
public override UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes[] LayoutAttributesForElementsInRect (CGRect rect)
{
var array = base.LayoutAttributesForElementsInRect (rect);
var visibleRect = new CGRect (CollectionView.ContentOffset, CollectionView.Bounds.Size);
foreach (var attributes in array) {
if (attributes.Frame.IntersectsWith (rect)) {
float distance = (float)(visibleRect.GetMidX () - attributes.Center.X);
float normalizedDistance = distance / ACTIVE_DISTANCE;
if (Math.Abs (distance) < ACTIVE_DISTANCE) {
float zoom = 1 + ZOOM_FACTOR * (1 - Math.Abs (normalizedDistance));
attributes.Transform3D = CATransform3D.MakeScale (zoom, zoom, 1.0f);
attributes.ZIndex = 1;
}
}
}
return array;
}
public override CGPoint TargetContentOffset (CGPoint proposedContentOffset, CGPoint scrollingVelocity)
{
float offSetAdjustment = float.MaxValue;
float horizontalCenter = (float)(proposedContentOffset.X + (this.CollectionView.Bounds.Size.Width / 2.0));
CGRect targetRect = new CGRect (proposedContentOffset.X, 0.0f, this.CollectionView.Bounds.Size.Width, this.CollectionView.Bounds.Size.Height);
var array = base.LayoutAttributesForElementsInRect (targetRect);
foreach (var layoutAttributes in array) {
float itemHorizontalCenter = (float)layoutAttributes.Center.X;
if (Math.Abs (itemHorizontalCenter - horizontalCenter) < Math.Abs (offSetAdjustment)) {
offSetAdjustment = itemHorizontalCenter - horizontalCenter;
}
}
return new CGPoint (proposedContentOffset.X + offSetAdjustment, proposedContentOffset.Y);
}
}
}
自定义布局
除了使用 UICollectionViewFlowLayout,还可以通过直接从 UICollectionViewLayout 继承来完全自定义布局。
要重写的关键方法是:
PrepareLayout– 用于执行整个布局过程中将使用的初始几何计算。CollectionViewContentSize– 返回用于显示内容的区域的大小。LayoutAttributesForElementsInRect–与前面所示的 UICollectionViewFlowLayout 示例一样,此方法用于向UICollectionView提供有关如何布局每个项的信息。 但是,与UICollectionViewFlowLayout不同,在创建自定义布局时,你可以按自己的方式定位项目。
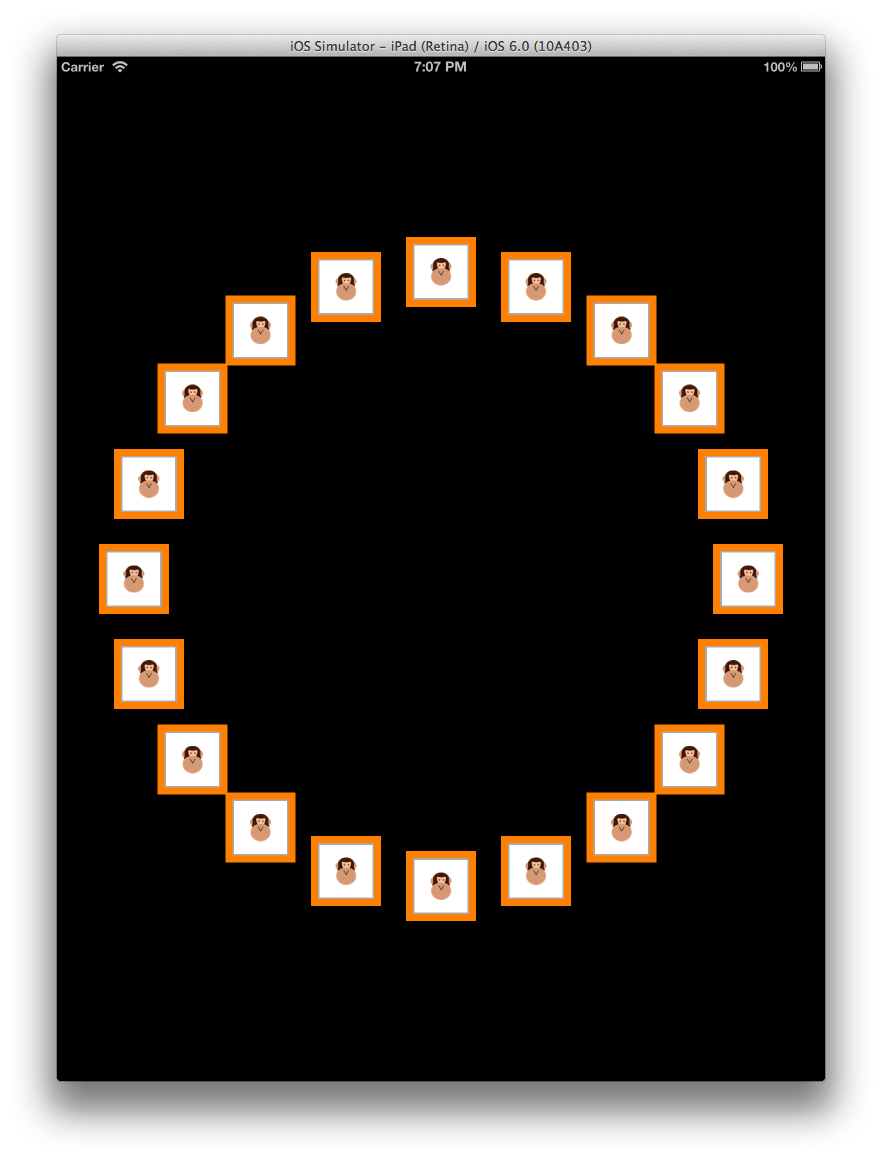
例如,可以在圆形布局中显示相同的内容,如下所示:
布局的强大之处在于,要从类似网格的布局更改为水平滚动布局,然后更改为此圆形布局,只需更改提供给 UICollectionView 的布局类。 UICollectionView 中没有任何内容,其委托或数据源代码完全不会更改。
iOS 9 中的更改
在 iOS 9 中,集合视图 (UICollectionView) 现在通过添加新的默认手势识别器和多个新的支持方法,支持将项重新排序开箱即用。
使用这些新方法,可以轻松地在集合视图中实现拖动重新排序,并可以选择在重新排序过程的任何阶段自定义项目外观。
在本文中,我们将探讨如何在 Xamarin.iOS 应用程序中实现拖放到重新排序,以及 iOS 9 对集合视图控件所做的一些其他更改:
项目重新排序
如上所述,iOS 9 中集合视图的最重要更改之一是现成添加简单的拖放到重新排序功能。
在 iOS 9 中,向集合视图添加重新排序的最快方法是使用 UICollectionViewController。
集合视图控制器现在具有一个 InstallsStandardGestureForInteractiveMovement 属性,该属性添加标准手势识别器,该识别器支持拖动以对集合中的项进行重新排序。
由于默认值为 true,因此只需实现 UICollectionViewDataSource 类的 MoveItem 方法即可支持拖动到重新排序。 例如:
public override void MoveItem (UICollectionView collectionView, NSIndexPath sourceIndexPath, NSIndexPath destinationIndexPath)
{
// Reorder our list of items
...
}
简单重新排序示例
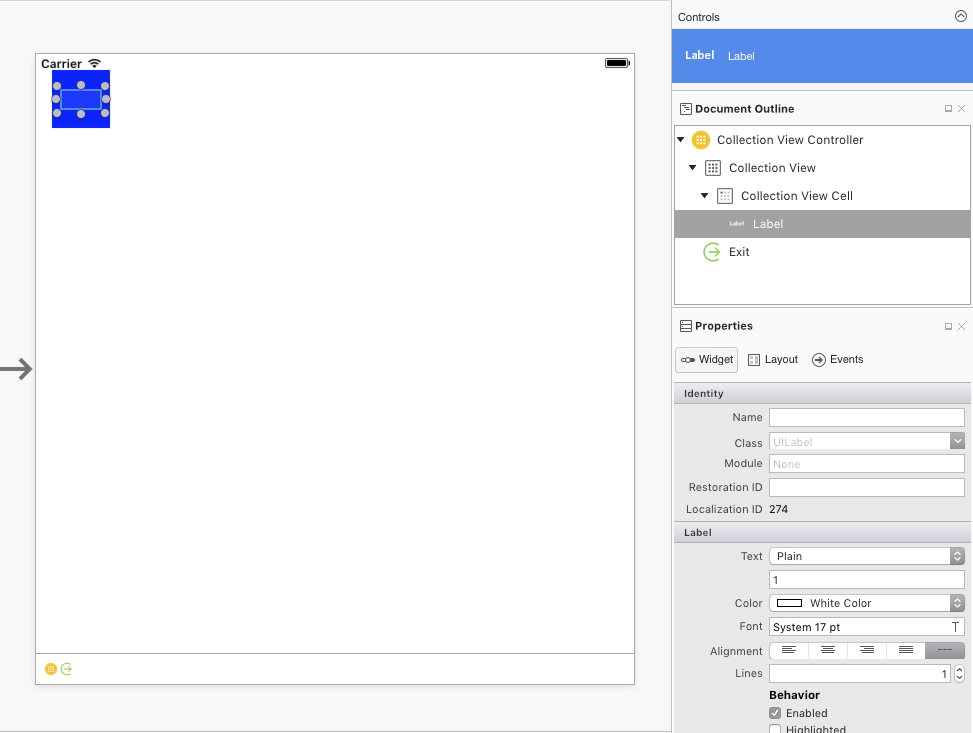
作为一个快速示例,我们来启动新的 Xamarin.iOS 项目并编辑 Main.storyboard 文件。 将 UICollectionViewController 拖到设计图面上:
选择“集合视图”(从文档大纲执行此操作可能最简单)。 在“属性板”的布局选项卡中,设置以下大小,如以下屏幕截图所示:
- 单元格大小:宽度 – 60 |高度 – 60
- 标题大小:宽度 – 0 |高度 – 0
- 页脚大小:宽度 – 0 |高度 – 0
- 最小间距:对于单元格 – 8 |对于行 – 8
- 节内集:顶部 – 16 |底部 – 16 |左 – 16 |右 - 16
接下来,编辑默认单元格:
- 将其背景色更改为蓝色
- 添加标签以充当单元格的标题
- 将重用标识符设置为单元格
添加约束,使标签在单元格中居中并更改大小时保持居中:
在 CollectionViewCell 的 Property Pad 中,将类设置为 TextCollectionViewCell:
将集合可重用视图设置为 Cell:
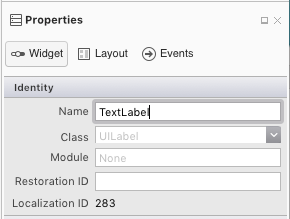
最后,选择标签并将其命名为 TextLabel:
编辑 TextCollectionViewCell 类并添加以下属性:
using System;
using Foundation;
using UIKit;
namespace CollectionView
{
public partial class TextCollectionViewCell : UICollectionViewCell
{
#region Computed Properties
public string Title {
get { return TextLabel.Text; }
set { TextLabel.Text = value; }
}
#endregion
#region Constructors
public TextCollectionViewCell (IntPtr handle) : base (handle)
{
}
#endregion
}
}
此处,标签的 Text 属性作为单元格的标题公开,因此可以从代码中设置它。
向项目添加新的 C# 类,并 WaterfallCollectionSource 调用它。 编辑文件,使其如下所示:
using System;
using Foundation;
using UIKit;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace CollectionView
{
public class WaterfallCollectionSource : UICollectionViewDataSource
{
#region Computed Properties
public WaterfallCollectionView CollectionView { get; set;}
public List<int> Numbers { get; set; } = new List<int> ();
#endregion
#region Constructors
public WaterfallCollectionSource (WaterfallCollectionView collectionView)
{
// Initialize
CollectionView = collectionView;
// Init numbers collection
for (int n = 0; n < 100; ++n) {
Numbers.Add (n);
}
}
#endregion
#region Override Methods
public override nint NumberOfSections (UICollectionView collectionView) {
// We only have one section
return 1;
}
public override nint GetItemsCount (UICollectionView collectionView, nint section) {
// Return the number of items
return Numbers.Count;
}
public override UICollectionViewCell GetCell (UICollectionView collectionView, NSIndexPath indexPath)
{
// Get a reusable cell and set {~~it's~>its~~} title from the item
var cell = collectionView.DequeueReusableCell ("Cell", indexPath) as TextCollectionViewCell;
cell.Title = Numbers [(int)indexPath.Item].ToString();
return cell;
}
public override bool CanMoveItem (UICollectionView collectionView, NSIndexPath indexPath) {
// We can always move items
return true;
}
public override void MoveItem (UICollectionView collectionView, NSIndexPath sourceIndexPath, NSIndexPath destinationIndexPath)
{
// Reorder our list of items
var item = Numbers [(int)sourceIndexPath.Item];
Numbers.RemoveAt ((int)sourceIndexPath.Item);
Numbers.Insert ((int)destinationIndexPath.Item, item);
}
#endregion
}
}
此类将是集合视图的数据源,并为集合中的每个单元格提供信息。
请注意,MoveItem 方法的实现允许对集合中的项目进行拖动重排序。
将另一个新的 C# 类添加到项目,并 WaterfallCollectionDelegate 调用它。 编辑此文件,使其如下所示:
using System;
using Foundation;
using UIKit;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace CollectionView
{
public class WaterfallCollectionDelegate : UICollectionViewDelegate
{
#region Computed Properties
public WaterfallCollectionView CollectionView { get; set;}
#endregion
#region Constructors
public WaterfallCollectionDelegate (WaterfallCollectionView collectionView)
{
// Initialize
CollectionView = collectionView;
}
#endregion
#region Overrides Methods
public override bool ShouldHighlightItem (UICollectionView collectionView, NSIndexPath indexPath) {
// Always allow for highlighting
return true;
}
public override void ItemHighlighted (UICollectionView collectionView, NSIndexPath indexPath)
{
// Get cell and change to green background
var cell = collectionView.CellForItem(indexPath);
cell.ContentView.BackgroundColor = UIColor.FromRGB(183,208,57);
}
public override void ItemUnhighlighted (UICollectionView collectionView, NSIndexPath indexPath)
{
// Get cell and return to blue background
var cell = collectionView.CellForItem(indexPath);
cell.ContentView.BackgroundColor = UIColor.FromRGB(164,205,255);
}
#endregion
}
}
这将充当集合视图的委托。 在用户与集合视图中交互时,已重写方法以突出显示单元格。
将最后一个 C# 类添加到项目,并 WaterfallCollectionView 调用它。 编辑此文件,使其如下所示:
using System;
using UIKit;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Foundation;
namespace CollectionView
{
[Register("WaterfallCollectionView")]
public class WaterfallCollectionView : UICollectionView
{
#region Constructors
public WaterfallCollectionView (IntPtr handle) : base (handle)
{
}
#endregion
#region Override Methods
public override void AwakeFromNib ()
{
base.AwakeFromNib ();
// Initialize
DataSource = new WaterfallCollectionSource(this);
Delegate = new WaterfallCollectionDelegate(this);
}
#endregion
}
}
请注意,从其情节提要(或 .xib 文件)构造集合视图时,将设置上面创建的 DataSource 和 Delegate。
再次编辑 Main.storyboard 文件,然后选择集合视图并切换到属性。 将类设置为上面定义的自定义 WaterfallCollectionView 类:
保存对 UI 所做的更改并运行应用。 如果用户从列表中选择一个项并将其拖动到新位置,则其他项将在它们移出项目的方式时自动进行动画处理。 当用户将项置于新位置时,它将坚持该位置。 例如:
使用自定义手势识别器
如果无法使用 UICollectionViewController 并且必须使用常规 UIViewController,或者如果要更好地控制拖放手势,则可以创建自己的自定义手势识别器,并在视图加载时将其添加到集合视图中。 例如:
public override void ViewDidLoad ()
{
base.ViewDidLoad ();
// Create a custom gesture recognizer
var longPressGesture = new UILongPressGestureRecognizer ((gesture) => {
// Take action based on state
switch(gesture.State) {
case UIGestureRecognizerState.Began:
var selectedIndexPath = CollectionView.IndexPathForItemAtPoint(gesture.LocationInView(View));
if (selectedIndexPath !=null) {
CollectionView.BeginInteractiveMovementForItem(selectedIndexPath);
}
break;
case UIGestureRecognizerState.Changed:
CollectionView.UpdateInteractiveMovementTargetPosition(gesture.LocationInView(View));
break;
case UIGestureRecognizerState.Ended:
CollectionView.EndInteractiveMovement();
break;
default:
CollectionView.CancelInteractiveMovement();
break;
}
});
// Add the custom recognizer to the collection view
CollectionView.AddGestureRecognizer(longPressGesture);
}
下面我们将使用添加到集合视图的几个新方法来实现和控制拖动操作:
BeginInteractiveMovementForItem- 标记移动操作的开始。UpdateInteractiveMovementTargetPosition- 在更新项目的位置时发送。EndInteractiveMovement- 标记项移动的末尾。CancelInteractiveMovement- 标记取消移动操作的用户。
运行应用程序时,拖动操作将与集合视图附带的默认拖动手势识别器完全相同。
自定义布局和重新排序
在 iOS 9 中,添加了多个新方法,用于在集合视图中使用拖放到重新排序和自定义布局。 若要浏览此功能,让我们向集合添加自定义布局。
首先,向项目添加名为 WaterfallCollectionLayout 的新 C# 类。 对其进行编辑,使其如下所示:
using System;
using Foundation;
using UIKit;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using CoreGraphics;
namespace CollectionView
{
[Register("WaterfallCollectionLayout")]
public class WaterfallCollectionLayout : UICollectionViewLayout
{
#region Private Variables
private int columnCount = 2;
private nfloat minimumColumnSpacing = 10;
private nfloat minimumInterItemSpacing = 10;
private nfloat headerHeight = 0.0f;
private nfloat footerHeight = 0.0f;
private UIEdgeInsets sectionInset = new UIEdgeInsets(0, 0, 0, 0);
private WaterfallCollectionRenderDirection itemRenderDirection = WaterfallCollectionRenderDirection.ShortestFirst;
private Dictionary<nint,UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes> headersAttributes = new Dictionary<nint, UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes>();
private Dictionary<nint,UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes> footersAttributes = new Dictionary<nint, UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes>();
private List<CGRect> unionRects = new List<CGRect>();
private List<nfloat> columnHeights = new List<nfloat>();
private List<UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes> allItemAttributes = new List<UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes>();
private List<List<UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes>> sectionItemAttributes = new List<List<UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes>>();
private nfloat unionSize = 20;
#endregion
#region Computed Properties
[Export("ColumnCount")]
public int ColumnCount {
get { return columnCount; }
set {
WillChangeValue ("ColumnCount");
columnCount = value;
DidChangeValue ("ColumnCount");
InvalidateLayout ();
}
}
[Export("MinimumColumnSpacing")]
public nfloat MinimumColumnSpacing {
get { return minimumColumnSpacing; }
set {
WillChangeValue ("MinimumColumnSpacing");
minimumColumnSpacing = value;
DidChangeValue ("MinimumColumnSpacing");
InvalidateLayout ();
}
}
[Export("MinimumInterItemSpacing")]
public nfloat MinimumInterItemSpacing {
get { return minimumInterItemSpacing; }
set {
WillChangeValue ("MinimumInterItemSpacing");
minimumInterItemSpacing = value;
DidChangeValue ("MinimumInterItemSpacing");
InvalidateLayout ();
}
}
[Export("HeaderHeight")]
public nfloat HeaderHeight {
get { return headerHeight; }
set {
WillChangeValue ("HeaderHeight");
headerHeight = value;
DidChangeValue ("HeaderHeight");
InvalidateLayout ();
}
}
[Export("FooterHeight")]
public nfloat FooterHeight {
get { return footerHeight; }
set {
WillChangeValue ("FooterHeight");
footerHeight = value;
DidChangeValue ("FooterHeight");
InvalidateLayout ();
}
}
[Export("SectionInset")]
public UIEdgeInsets SectionInset {
get { return sectionInset; }
set {
WillChangeValue ("SectionInset");
sectionInset = value;
DidChangeValue ("SectionInset");
InvalidateLayout ();
}
}
[Export("ItemRenderDirection")]
public WaterfallCollectionRenderDirection ItemRenderDirection {
get { return itemRenderDirection; }
set {
WillChangeValue ("ItemRenderDirection");
itemRenderDirection = value;
DidChangeValue ("ItemRenderDirection");
InvalidateLayout ();
}
}
#endregion
#region Constructors
public WaterfallCollectionLayout ()
{
}
public WaterfallCollectionLayout(NSCoder coder) : base(coder) {
}
#endregion
#region Public Methods
public nfloat ItemWidthInSectionAtIndex(int section) {
var width = CollectionView.Bounds.Width - SectionInset.Left - SectionInset.Right;
return (nfloat)Math.Floor ((width - ((ColumnCount - 1) * MinimumColumnSpacing)) / ColumnCount);
}
#endregion
#region Override Methods
public override void PrepareLayout ()
{
base.PrepareLayout ();
// Get the number of sections
var numberofSections = CollectionView.NumberOfSections();
if (numberofSections == 0)
return;
// Reset collections
headersAttributes.Clear ();
footersAttributes.Clear ();
unionRects.Clear ();
columnHeights.Clear ();
allItemAttributes.Clear ();
sectionItemAttributes.Clear ();
// Initialize column heights
for (int n = 0; n < ColumnCount; n++) {
columnHeights.Add ((nfloat)0);
}
// Process all sections
nfloat top = 0.0f;
var attributes = new UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes ();
var columnIndex = 0;
for (nint section = 0; section < numberofSections; ++section) {
// Calculate section specific metrics
var minimumInterItemSpacing = (MinimumInterItemSpacingForSection == null) ? MinimumColumnSpacing :
MinimumInterItemSpacingForSection (CollectionView, this, section);
// Calculate widths
var width = CollectionView.Bounds.Width - SectionInset.Left - SectionInset.Right;
var itemWidth = (nfloat)Math.Floor ((width - ((ColumnCount - 1) * MinimumColumnSpacing)) / ColumnCount);
// Calculate section header
var heightHeader = (HeightForHeader == null) ? HeaderHeight :
HeightForHeader (CollectionView, this, section);
if (heightHeader > 0) {
attributes = UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes.CreateForSupplementaryView (UICollectionElementKindSection.Header, NSIndexPath.FromRowSection (0, section));
attributes.Frame = new CGRect (0, top, CollectionView.Bounds.Width, heightHeader);
headersAttributes.Add (section, attributes);
allItemAttributes.Add (attributes);
top = attributes.Frame.GetMaxY ();
}
top += SectionInset.Top;
for (int n = 0; n < ColumnCount; n++) {
columnHeights [n] = top;
}
// Calculate Section Items
var itemCount = CollectionView.NumberOfItemsInSection(section);
List<UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes> itemAttributes = new List<UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes> ();
for (nint n = 0; n < itemCount; n++) {
var indexPath = NSIndexPath.FromRowSection (n, section);
columnIndex = NextColumnIndexForItem (n);
var xOffset = SectionInset.Left + (itemWidth + MinimumColumnSpacing) * (nfloat)columnIndex;
var yOffset = columnHeights [columnIndex];
var itemSize = (SizeForItem == null) ? new CGSize (0, 0) : SizeForItem (CollectionView, this, indexPath);
nfloat itemHeight = 0.0f;
if (itemSize.Height > 0.0f && itemSize.Width > 0.0f) {
itemHeight = (nfloat)Math.Floor (itemSize.Height * itemWidth / itemSize.Width);
}
attributes = UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes.CreateForCell (indexPath);
attributes.Frame = new CGRect (xOffset, yOffset, itemWidth, itemHeight);
itemAttributes.Add (attributes);
allItemAttributes.Add (attributes);
columnHeights [columnIndex] = attributes.Frame.GetMaxY () + MinimumInterItemSpacing;
}
sectionItemAttributes.Add (itemAttributes);
// Calculate Section Footer
nfloat footerHeight = 0.0f;
columnIndex = LongestColumnIndex();
top = columnHeights [columnIndex] - MinimumInterItemSpacing + SectionInset.Bottom;
footerHeight = (HeightForFooter == null) ? FooterHeight : HeightForFooter(CollectionView, this, section);
if (footerHeight > 0) {
attributes = UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes.CreateForSupplementaryView (UICollectionElementKindSection.Footer, NSIndexPath.FromRowSection (0, section));
attributes.Frame = new CGRect (0, top, CollectionView.Bounds.Width, footerHeight);
footersAttributes.Add (section, attributes);
allItemAttributes.Add (attributes);
top = attributes.Frame.GetMaxY ();
}
for (int n = 0; n < ColumnCount; n++) {
columnHeights [n] = top;
}
}
var i =0;
var attrs = allItemAttributes.Count;
while(i < attrs) {
var rect1 = allItemAttributes [i].Frame;
i = (int)Math.Min (i + unionSize, attrs) - 1;
var rect2 = allItemAttributes [i].Frame;
unionRects.Add (CGRect.Union (rect1, rect2));
i++;
}
}
public override CGSize CollectionViewContentSize {
get {
if (CollectionView.NumberOfSections () == 0) {
return new CGSize (0, 0);
}
var contentSize = CollectionView.Bounds.Size;
contentSize.Height = columnHeights [0];
return contentSize;
}
}
public override UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes LayoutAttributesForItem (NSIndexPath indexPath)
{
if (indexPath.Section >= sectionItemAttributes.Count) {
return null;
}
if (indexPath.Item >= sectionItemAttributes [indexPath.Section].Count) {
return null;
}
var list = sectionItemAttributes [indexPath.Section];
return list [(int)indexPath.Item];
}
public override UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes LayoutAttributesForSupplementaryView (NSString kind, NSIndexPath indexPath)
{
var attributes = new UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes ();
switch (kind) {
case "header":
attributes = headersAttributes [indexPath.Section];
break;
case "footer":
attributes = footersAttributes [indexPath.Section];
break;
}
return attributes;
}
public override UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes[] LayoutAttributesForElementsInRect (CGRect rect)
{
var begin = 0;
var end = unionRects.Count;
List<UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes> attrs = new List<UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes> ();
for (int i = 0; i < end; i++) {
if (rect.IntersectsWith(unionRects[i])) {
begin = i * (int)unionSize;
}
}
for (int i = end - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (rect.IntersectsWith (unionRects [i])) {
end = (int)Math.Min ((i + 1) * (int)unionSize, allItemAttributes.Count);
break;
}
}
for (int i = begin; i < end; i++) {
var attr = allItemAttributes [i];
if (rect.IntersectsWith (attr.Frame)) {
attrs.Add (attr);
}
}
return attrs.ToArray();
}
public override bool ShouldInvalidateLayoutForBoundsChange (CGRect newBounds)
{
var oldBounds = CollectionView.Bounds;
return (newBounds.Width != oldBounds.Width);
}
#endregion
#region Private Methods
private int ShortestColumnIndex() {
var index = 0;
var shortestHeight = nfloat.MaxValue;
var n = 0;
// Scan each column for the shortest height
foreach (nfloat height in columnHeights) {
if (height < shortestHeight) {
shortestHeight = height;
index = n;
}
++n;
}
return index;
}
private int LongestColumnIndex() {
var index = 0;
var longestHeight = nfloat.MinValue;
var n = 0;
// Scan each column for the shortest height
foreach (nfloat height in columnHeights) {
if (height > longestHeight) {
longestHeight = height;
index = n;
}
++n;
}
return index;
}
private int NextColumnIndexForItem(nint item) {
var index = 0;
switch (ItemRenderDirection) {
case WaterfallCollectionRenderDirection.ShortestFirst:
index = ShortestColumnIndex ();
break;
case WaterfallCollectionRenderDirection.LeftToRight:
index = ColumnCount;
break;
case WaterfallCollectionRenderDirection.RightToLeft:
index = (ColumnCount - 1) - ((int)item / ColumnCount);
break;
}
return index;
}
#endregion
#region Events
public delegate CGSize WaterfallCollectionSizeDelegate(UICollectionView collectionView, WaterfallCollectionLayout layout, NSIndexPath indexPath);
public delegate nfloat WaterfallCollectionFloatDelegate(UICollectionView collectionView, WaterfallCollectionLayout layout, nint section);
public delegate UIEdgeInsets WaterfallCollectionEdgeInsetsDelegate(UICollectionView collectionView, WaterfallCollectionLayout layout, nint section);
public event WaterfallCollectionSizeDelegate SizeForItem;
public event WaterfallCollectionFloatDelegate HeightForHeader;
public event WaterfallCollectionFloatDelegate HeightForFooter;
public event WaterfallCollectionEdgeInsetsDelegate InsetForSection;
public event WaterfallCollectionFloatDelegate MinimumInterItemSpacingForSection;
#endregion
}
}
这可用于向集合视图提供自定义的两列瀑布类型布局。
该代码使用键值编码(通过 WillChangeValue 和 DidChangeValue 方法)为此类中的计算属性提供数据绑定。
接下来,编辑 WaterfallCollectionSource 并进行以下更改和添加:
private Random rnd = new Random();
...
public List<nfloat> Heights { get; set; } = new List<nfloat> ();
...
public WaterfallCollectionSource (WaterfallCollectionView collectionView)
{
// Initialize
CollectionView = collectionView;
// Init numbers collection
for (int n = 0; n < 100; ++n) {
Numbers.Add (n);
Heights.Add (rnd.Next (0, 100) + 40.0f);
}
}
这将为列表中显示的每个项创建随机高度。
接下来,编辑 WaterfallCollectionView 类并添加以下帮助程序属性:
public WaterfallCollectionSource Source {
get { return (WaterfallCollectionSource)DataSource; }
}
这样可以更轻松地从自定义布局获取数据源(和项高度)。
最后,编辑视图控制器并添加以下代码:
public override void AwakeFromNib ()
{
base.AwakeFromNib ();
var waterfallLayout = new WaterfallCollectionLayout ();
// Wireup events
waterfallLayout.SizeForItem += (collectionView, layout, indexPath) => {
var collection = collectionView as WaterfallCollectionView;
return new CGSize((View.Bounds.Width-40)/3,collection.Source.Heights[(int)indexPath.Item]);
};
// Attach the custom layout to the collection
CollectionView.SetCollectionViewLayout(waterfallLayout, false);
}
这会创建自定义布局的实例,设置事件以提供每个项的大小,并将新布局附加到集合视图。
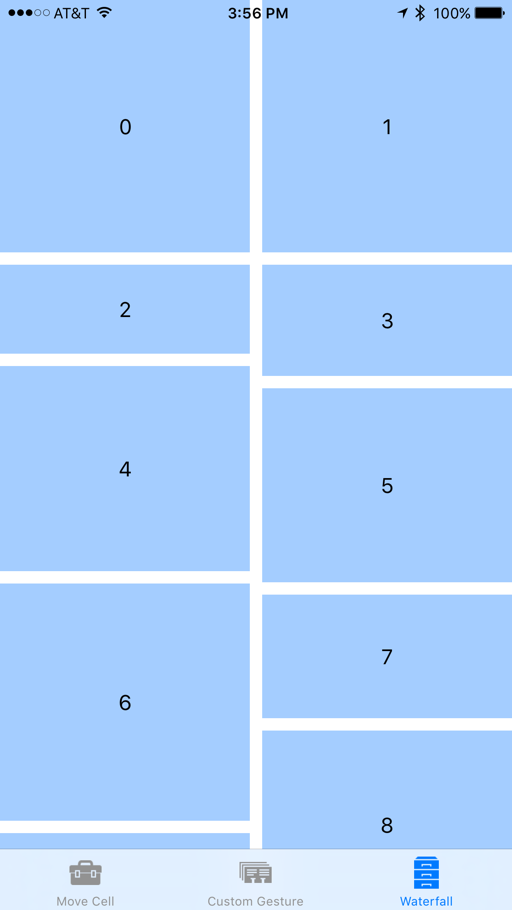
如果再次运行 Xamarin.iOS 应用,则集合视图现在将如下所示:
我们仍然可以像以前一样拖动到重新排序项,但是这些项现在将更改大小以适应其新位置(删除它们)。
集合视图更改
在以下部分中,我们将详细查看 iOS 9 对集合视图中每个类所做的更改。
UICollectionView
对 iOS 9 的类进行了 UICollectionView 以下更改或添加:
BeginInteractiveMovementForItem– 标记拖动操作的开始。CancelInteractiveMovement– 通知集合视图用户已取消拖动操作。EndInteractiveMovement– 通知集合视图用户已完成拖动操作。GetIndexPathsForVisibleSupplementaryElements– 返回indexPath集合视图部分的页眉或页脚。GetSupplementaryView– 返回给定的页眉或页脚。GetVisibleSupplementaryViews– 返回所有可见页眉和页脚的列表。UpdateInteractiveMovementTargetPosition– 通知集合视图用户已移动或正在移动拖动操作中的项。
UICollectionViewController
iOS 9 中的 UICollectionViewController 类进行了以下更改或添加:
InstallsStandardGestureForInteractiveMovement– 如果true,将使用自动支持拖放到重新排序的新手势识别器。CanMoveItem– 如果给定的项可以重新排序,通知集合视图。GetTargetContentOffset– 用于获取给定集合视图项的偏移量。GetTargetIndexPathForMove– 获取拖动操作的给定项的indexPath。MoveItem– 移动列表中的给定项的顺序。
UICollectionViewDataSource
对 iOS 9 中的 UICollectionViewDataSource 类进行了以下更改或添加:
CanMoveItem– 如果给定的项可以重新排序,通知集合视图。MoveItem– 移动列表中的给定项的顺序。
UICollectionViewDelegate
对 iOS 9 中的 UICollectionViewDelegate 类进行了以下更改或添加:
GetTargetContentOffset– 用于获取给定集合视图项的偏移量。GetTargetIndexPathForMove– 获取拖动操作的给定项的indexPath。
UICollectionViewFlowLayout
对 iOS 9 中的 UICollectionViewFlowLayout 类进行了以下更改或添加:
SectionFootersPinToVisibleBounds– 将分区页脚粘附到可见的集合视图边界。SectionHeadersPinToVisibleBounds– 将节标题粘附到可见的集合视图边界。
UICollectionViewLayout
对 iOS 9 中的 UICollectionViewLayout 类进行了以下更改或添加:
GetInvalidationContextForEndingInteractiveMovementOfItems– 当用户完成拖动或取消拖动操作时,返回拖动操作末尾的失效上下文。GetInvalidationContextForInteractivelyMovingItems– 返回拖动操作开始时的失效上下文。GetLayoutAttributesForInteractivelyMovingItem– 获取拖动项时给定项的布局属性。GetTargetIndexPathForInteractivelyMovingItem– 返回拖动项时位于给定点的项的indexPath。
UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes
对 iOS 9 中的 UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes 类进行了以下更改或添加:
CollisionBoundingPath– 在拖动操作期间返回两个项目的碰撞路径。CollisionBoundsType– 返回在拖动操作期间发生的碰撞类型(作为UIDynamicItemCollisionBoundsType)。
UICollectionViewLayoutInvalidationContext
对 iOS 9 中的 UICollectionViewLayoutInvalidationContext 类进行了以下更改或添加:
InteractiveMovementTarget– 返回拖动操作的目标项。PreviousIndexPathsForInteractivelyMovingItems– 返回拖动以重新排序操作中涉及的其他项的indexPaths。TargetIndexPathsForInteractivelyMovingItems– 返回由于拖放到重新排序操作而重新排序的项的indexPaths。
UICollectionViewSource
对 iOS 9 中的 UICollectionViewSource 类进行了以下更改或添加:
CanMoveItem– 如果给定的项可以重新排序,通知集合视图。GetTargetContentOffset– 返回将通过拖放到重新排序操作移动的项的偏移量。GetTargetIndexPathForMove– 返回将在拖放到重新排序操作期间移动的项的indexPath。MoveItem– 移动列表中的给定项的顺序。
总结
本文介绍了 iOS 9 中集合视图的更改,并介绍了如何在 Xamarin.iOS 中实现它们。 它介绍了如何在集合视图中实现简单的拖放到重新排序操作;将自定义手势识别器与拖动重新排序配合使用;以及拖放到重新排序如何影响自定义集合视图布局。