从终端 1.15 预览版开始,Windows 终端已开始试验性地支持一些“shell 集成”功能。 这些功能使命令行更易于使用。 在早期版本中,我们启用了 shell 来告知终端当前工作目录是什么。 现在,我们添加了对更多序列的支持,允许 shell 以语义方式将终端输出的各个部分描述为“提示”、“命令”或“输出”。 shell 还可以告知终端某个命令是成功还是失败。
这是从终端 v1.18 开始推出的一些 shell 集成功能的指南。 我们计划在将来基于这些功能构建更多功能,因此希望获得一些有关用户如何使用它们的其他反馈。
注意:从 Terminal 1.21 开始,标记现在是一个稳定的功能。 在 1.21 之前,仅为 Terminal 的预览版启用了标记。 如果你使用的是 1.21 之前的 Terminal 版本,则
showMarksOnScrollbar设置被命名为experimental.showMarksOnScrollbar,autoMarkPrompts被命名为experimental.autoMarkPrompts。
WSL 的工作原理是怎样的?
shell 集成的工作原理是让 shell(或任何命令行应用程序)向终端写入特殊的“转义序列”。 这些转义序列不会输出到终端,而是提供一些元数据供终端用来详细了解应用程序中发生的情况。 通过将这些序列粘贴到 shell 的提示符中,你可以让 shell 不断向终端提供只有 shell 知道的信息。
对于以下序列来说:
-
OSC是字符串"\x1b]"- 一个转义字符,后跟] -
ST是“字符串终止符”,可以是\x1b\(ESC 字符,后跟\),也可以是\x7(BEL 字符) - 空格只是说明性的。
-
<>中的字符串是应由其他值替换的参数。
从终端 v1.18 开始,相关的受支持的 shell 集成序列为:
-
OSC 133 ; A ST(“FTCS_PROMPT”)- 提示开始。 -
OSC 133 ; B ST(“FTCS_COMMAND_START”)- 命令行开始(READ:提示结束)。 -
OSC 133 ; C ST(“FTCS_COMMAND_EXECUTED”)- 命令输出开始/命令行结束。 -
OSC 133 ; D ; <ExitCode> ST(“FTCS_COMMAND_FINISHED”)- 命令结束。ExitCode如果提供了ExitCode,则终端会将0视为“成功”,将其他任何情况视为错误。 如果省略此项,则终端就会让标记保留默认颜色。
如何启用 shell 集成标记
支持这些功能需要 shell 和终端之间的协作。 需要在终端中启用设置才能使用这些新功能,还需要修改 shell 的提示符。
若要在终端中启用这些功能,需要将以下内容添加到设置中:
"profiles":
{
"defaults":
{
// Enable marks on the scrollbar
"showMarksOnScrollbar": true,
// Needed for both pwsh, CMD and bash shell integration
"autoMarkPrompts": true,
// Add support for a right-click context menu
// You can also just bind the `showContextMenu` action
"experimental.rightClickContextMenu": true,
},
}
"actions":
[
// Scroll between prompts
{ "keys": "ctrl+up", "command": { "action": "scrollToMark", "direction": "previous" }, },
{ "keys": "ctrl+down", "command": { "action": "scrollToMark", "direction": "next" }, },
// Add the ability to select a whole command (or its output)
{ "command": { "action": "selectOutput", "direction": "prev" }, },
{ "command": { "action": "selectOutput", "direction": "next" }, },
{ "command": { "action": "selectCommand", "direction": "prev" }, },
{ "command": { "action": "selectCommand", "direction": "next" }, },
]
在 shell 中启用这些标记的方式因 shell 而异。 下面是 CMD、PowerShell 和 Zsh 的教程。
PowerShell (pwsh.exe)
如果你之前从未更改过 PowerShell 提示符,则应先查看 about_Prompts。
我们需要编辑你的 prompt,以确保将有关 CWD 的信息告知终端,并使用适当的标记来标记提示。 PowerShell 还允许我们在序列中包含上一个命令的 133;D 错误代码,这样终端就可以在命令成功或失败时自动着色标记。
将以下内容添加到 PowerShell 配置文件:
$Global:__LastHistoryId = -1
function Global:__Terminal-Get-LastExitCode {
if ($? -eq $True) {
return 0
}
$LastHistoryEntry = $(Get-History -Count 1)
$IsPowerShellError = $Error[0].InvocationInfo.HistoryId -eq $LastHistoryEntry.Id
if ($IsPowerShellError) {
return -1
}
return $LastExitCode
}
function prompt {
# First, emit a mark for the _end_ of the previous command.
$gle = $(__Terminal-Get-LastExitCode);
$LastHistoryEntry = $(Get-History -Count 1)
# Skip finishing the command if the first command has not yet started
if ($Global:__LastHistoryId -ne -1) {
if ($LastHistoryEntry.Id -eq $Global:__LastHistoryId) {
# Don't provide a command line or exit code if there was no history entry (eg. ctrl+c, enter on no command)
$out += "`e]133;D`a"
} else {
$out += "`e]133;D;$gle`a"
}
}
$loc = $($executionContext.SessionState.Path.CurrentLocation);
# Prompt started
$out += "`e]133;A$([char]07)";
# CWD
$out += "`e]9;9;`"$loc`"$([char]07)";
# (your prompt here)
$out += "PWSH $loc$('>' * ($nestedPromptLevel + 1)) ";
# Prompt ended, Command started
$out += "`e]133;B$([char]07)";
$Global:__LastHistoryId = $LastHistoryEntry.Id
return $out
}
哦, 我的 Posh 设置
使用 oh-my-posh? 你需要稍微修改上述内容,以藏匿原始提示,然后将其添加回 shell 集成转义序列的中间。
# initialize oh-my-posh at the top of your profile.ps1
oh-my-posh init pwsh --config "$env:POSH_THEMES_PATH\gruvbox.omp.json" | Invoke-Expression
# then stash away the prompt() that oh-my-posh sets
$Global:__OriginalPrompt = $function:Prompt
function Global:__Terminal-Get-LastExitCode {
if ($? -eq $True) { return 0 }
$LastHistoryEntry = $(Get-History -Count 1)
$IsPowerShellError = $Error[0].InvocationInfo.HistoryId -eq $LastHistoryEntry.Id
if ($IsPowerShellError) { return -1 }
return $LastExitCode
}
function prompt {
$gle = $(__Terminal-Get-LastExitCode);
$LastHistoryEntry = $(Get-History -Count 1)
if ($Global:__LastHistoryId -ne -1) {
if ($LastHistoryEntry.Id -eq $Global:__LastHistoryId) {
$out += "`e]133;D`a"
} else {
$out += "`e]133;D;$gle`a"
}
}
$loc = $($executionContext.SessionState.Path.CurrentLocation);
$out += "`e]133;A$([char]07)";
$out += "`e]9;9;`"$loc`"$([char]07)";
$out += $Global:__OriginalPrompt.Invoke(); # <-- This line adds the original prompt back
$out += "`e]133;B$([char]07)";
$Global:__LastHistoryId = $LastHistoryEntry.Id
return $out
}
命令提示符
命令提示符从 PROMPT 环境变量中源其提示。 CMD.exe 将 $e 读取为 ESC 字符。 遗憾的是,CMD.exe 没有办法在提示中获取上一个命令的返回代码,因此我们无法在 CMD 提示中提供成功/错误信息。
可通过运行以下命令更改当前 CMD.exe 实例的提示:
PROMPT $e]133;D$e\$e]133;A$e\$e]9;9;$P$e\$P$G$e]133;B$e\
也可从命令行为所有未来会话设置变量:
setx PROMPT $e]133;D$e\$e]133;A$e\$e]9;9;$P$e\$P$G$e]133;B$e\
这些示例假定当前 PROMPT 只是 $P$G。 你可以改为选择使用如下所示内容来包装当前提示:
PROMPT $e]133;D$e\$e]133;A$e\$e]9;9;$P$e\%PROMPT%$e]133;B$e\
Bash
可以将以下脚本加载到包含
注释
应该指出,如果PROMPT_COMMAND、PS0、PS1或PS2变量已经被分配给任何非默认值,这可能导致不可预测的结果。 最好先使用“clean”shell 测试脚本,方法是执行 env --ignore-environment bash --noprofile --norc 并溯源描述的文件,如前面所示。
# .bash_profile | .bashrc
function __set_ps1() {
local PS1_TMP="${__PS1_BASE}"
if [ ! -z "${__IS_WT}" ]; then
local __FTCS_CMD_FINISHED='\e]133;D;'"${1}"'\e\\'
PS1_TMP="\[${__FTCS_CMD_FINISHED}\]${__PS1_BASE}"
fi
printf '%s' "${PS1_TMP}"
}
function __prompt_command() {
# Must be first in the list otherwise the exit status will be overwritten.
local PS1_EXIT_STATUS=${?}
PS1="$(__set_ps1 ${PS1_EXIT_STATUS})"
}
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# PROMPT (PS0..PS2).
# The given variable might be linked to a function detecting whether `bash`
# actually runs under `Microsoft Terminal` otherwise unexpected garbage might
# be displayed on the user screen.
__IS_WT='true'
printf -v __BASH_V '%d' ${BASH_VERSINFO[*]:0:2}
if [ ${__BASH_V} -ge 44 ]; then
__PS0_BASE=''
fi
# The following assignments reflect the default values.
__PS1_BASE='\s-\v\$ '
__PS2_BASE='> '
if [ ! -z "${__IS_WT}" ]; then
__FTCS_PROMPT='\e]133;A\e\\'
__FTCS_CMD_START='\e]133;B\e\\'
if [ ${__BASH_V} -ge 44 ]; then
__FTCS_CMD_EXECUTED='\e]133;C\e\\'
__PS0_BASE="\[${__FTCS_CMD_EXECUTED}\]"
fi
__PS1_BASE="\[${__FTCS_PROMPT}\]${__PS1_BASE}\[${__FTCS_CMD_START}\]"
# Required, otherwise the `PS2` prefix will split and corrupt a long
# command.
__PS2_BASE=''
fi
PROMPT_COMMAND=__prompt_command
if [ ${__BASH_V} -ge 44 ]; then
PS0="${__PS0_BASE}"
fi
# `PS1` is set with the `__prompt_command` function call.
PS2="${__PS2_BASE}"
涵盖所有提示变量的种类bash(PS0、PS1和PS2),并通过必要的序列实现完整的 shell 集成。
此外,${HOME}/.inputrc 还可能需要进行调整,以删除“编辑模式通知”和“修改行”标识。
# .inputrc
set mark-modified-lines Off
set show-mode-in-prompt Off
如果一切正确完成,应如下所示:
$ env --ignore-environment bash --noprofile --norc
bash-5.2$ . /tmp/msft-terminal-bash.sh
bash-5.2$ echo "|${PS0}|"
|\[\e]133;C\e\\\]|
bash-5.2$ echo "|${PS1}|"
|\[\e]133;D;0\e\\\]\[\e]133;A\e\\\]\s-\v\$ \[\e]133;B\e\\\]|
bash-5.2$ echo "|${PS2}|"
||
注意:没有在这里看到你喜欢的 shell? 如果你已清楚,可随意为你喜欢的 shell 提供一个解决方案!
Shell 集成功能
在同一工作目录中打开新选项卡
在滚动条中显示每个命令的标记
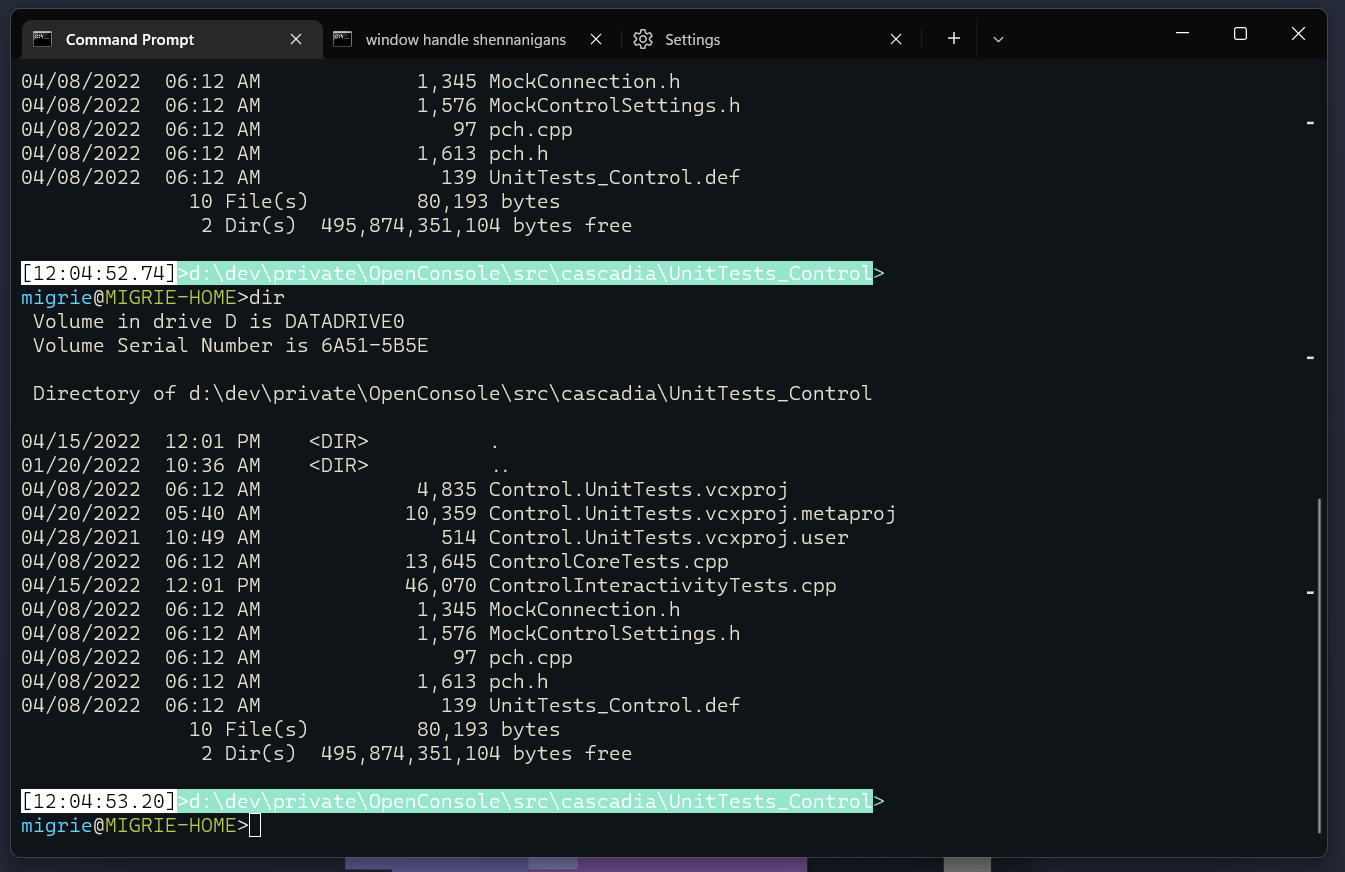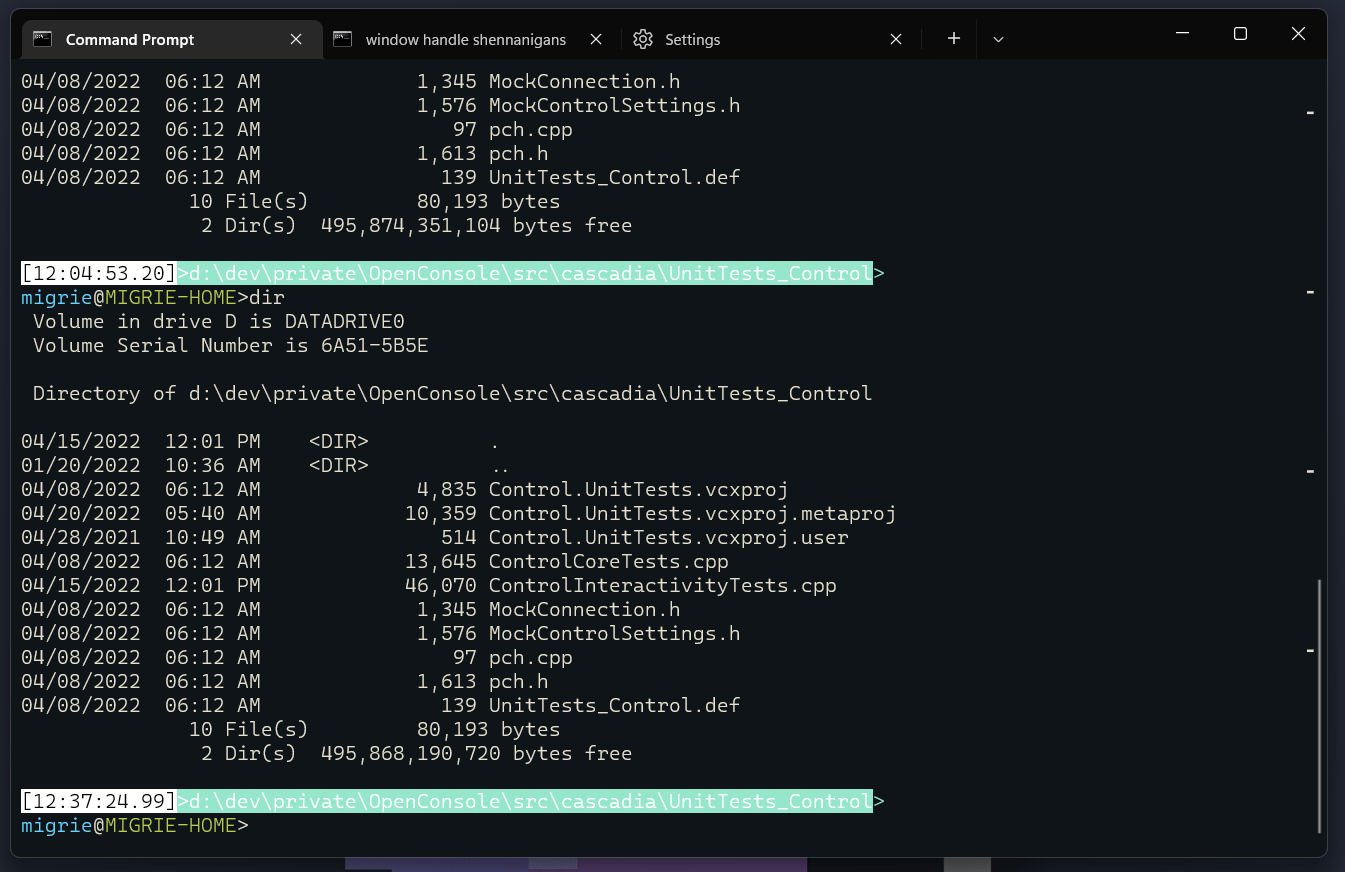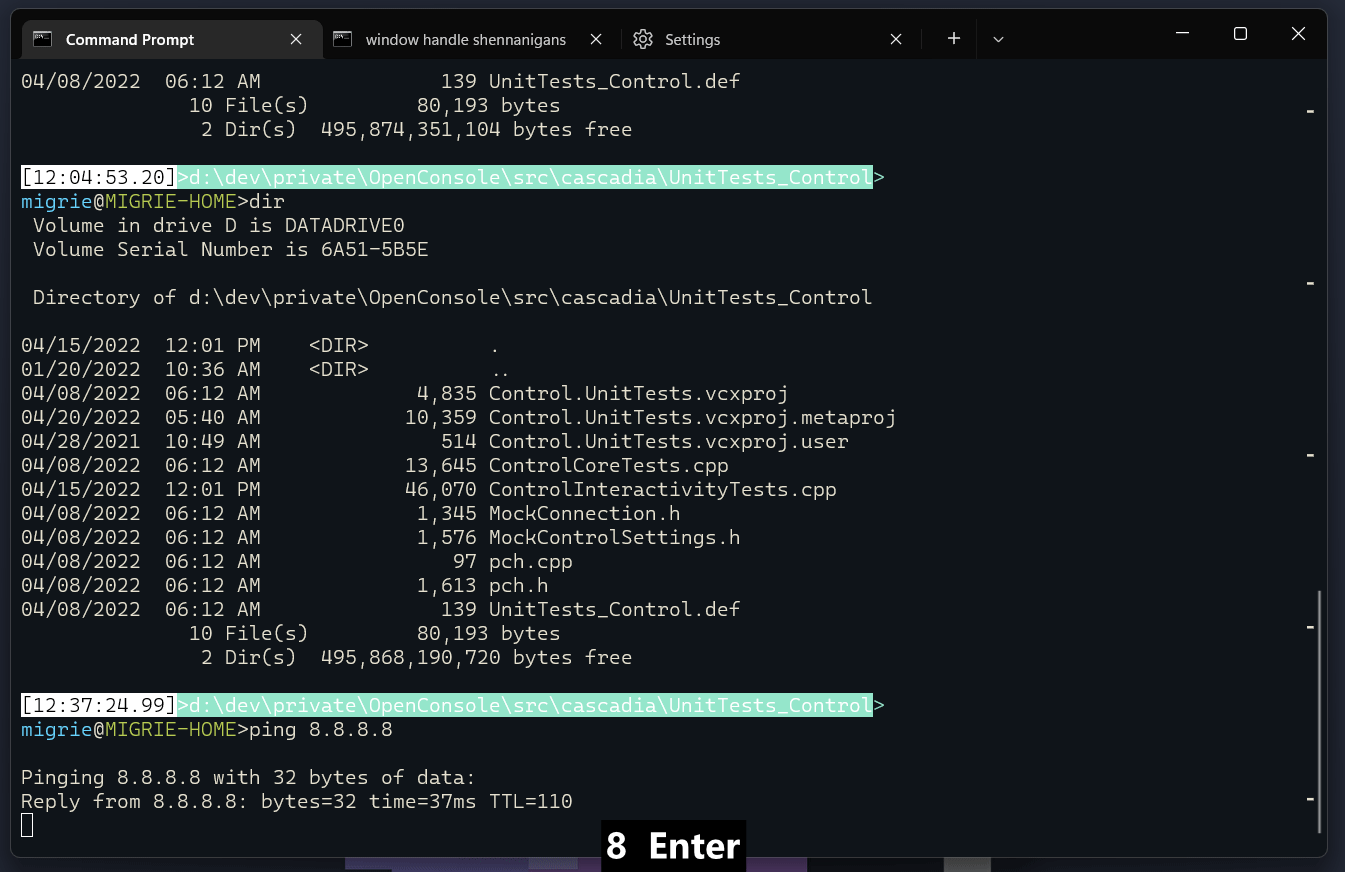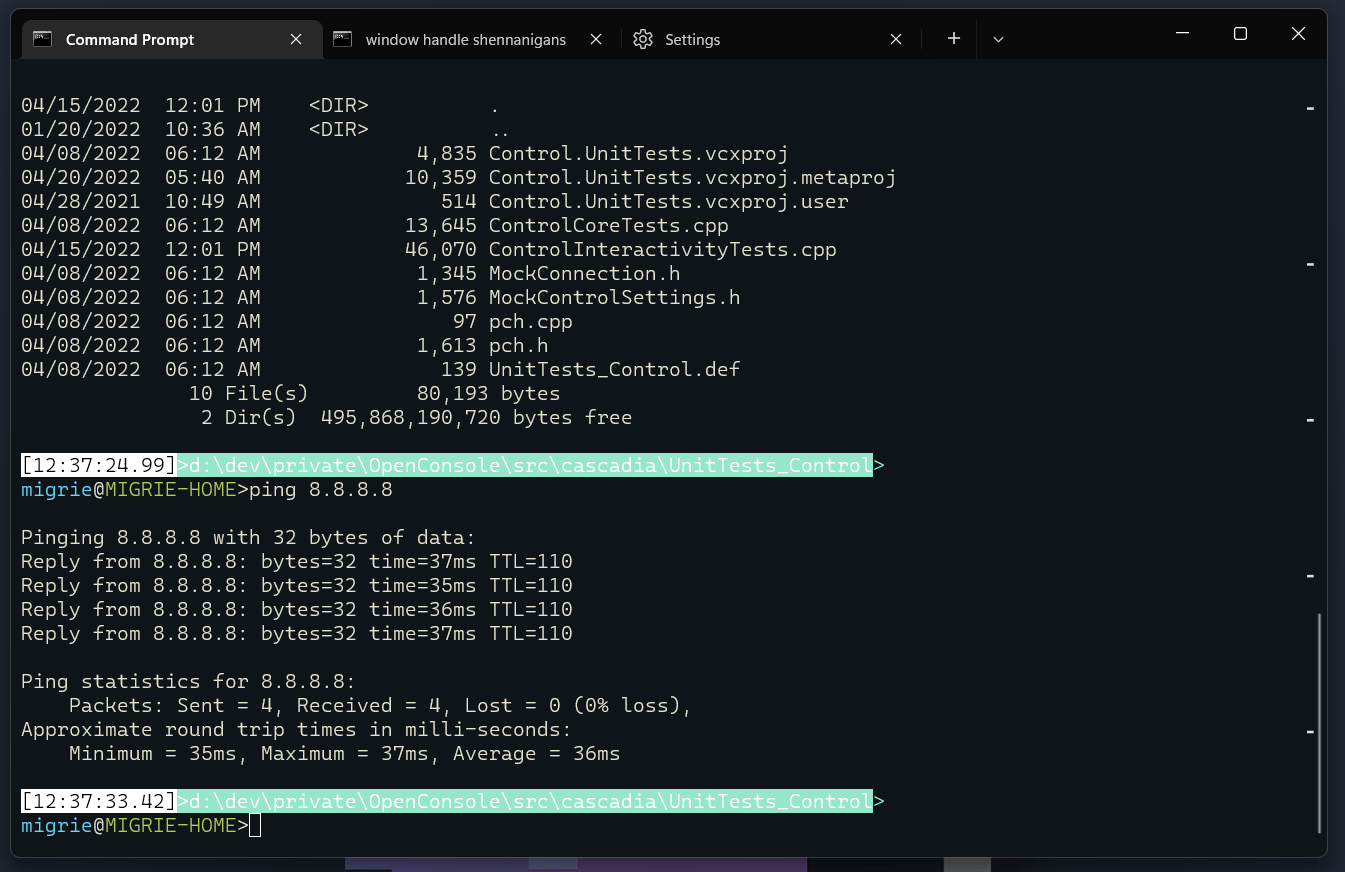
在命令之间自动跳转
这使用 scrollToMark 操作,因为我们在前面已定义了它们。
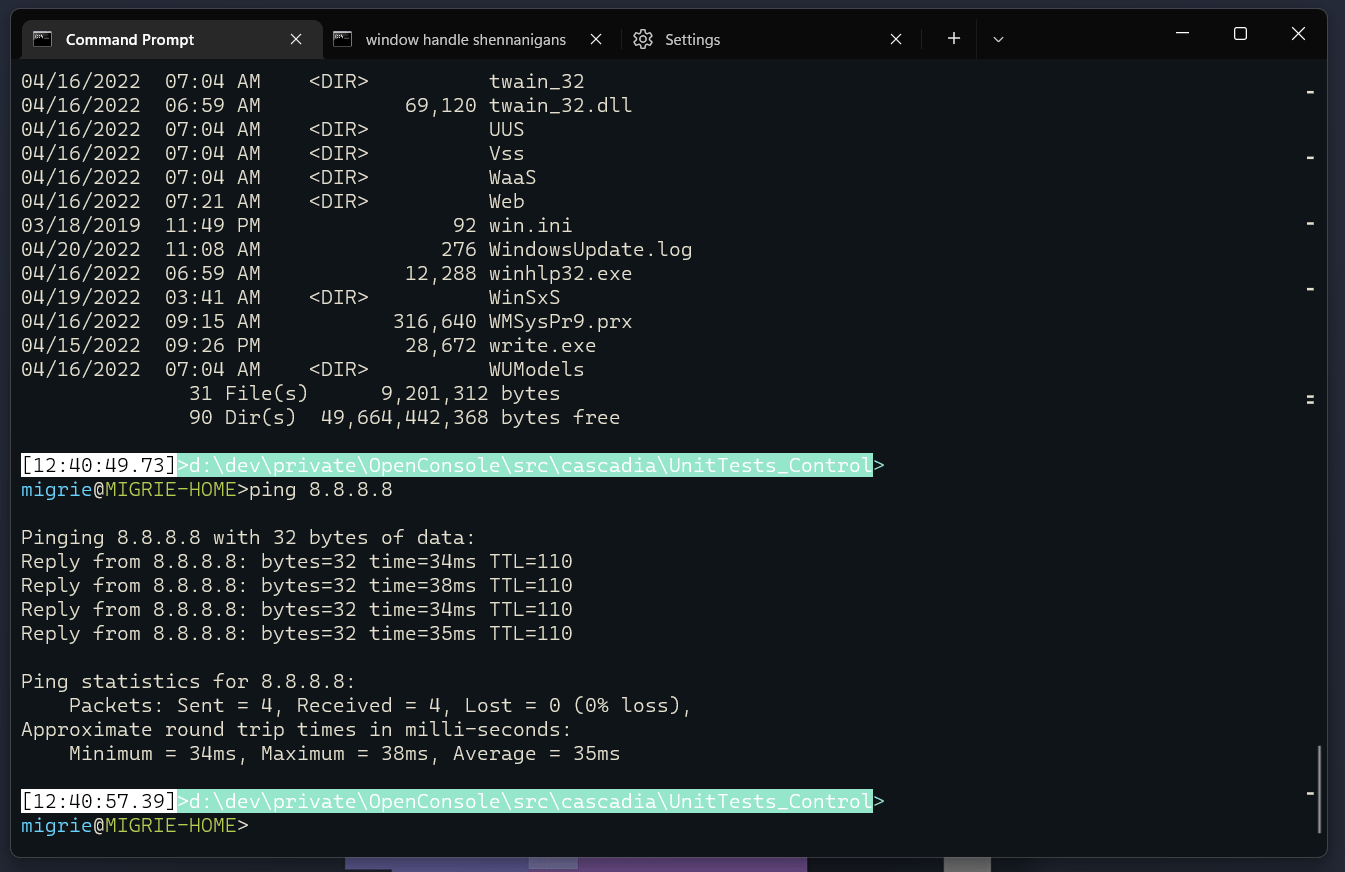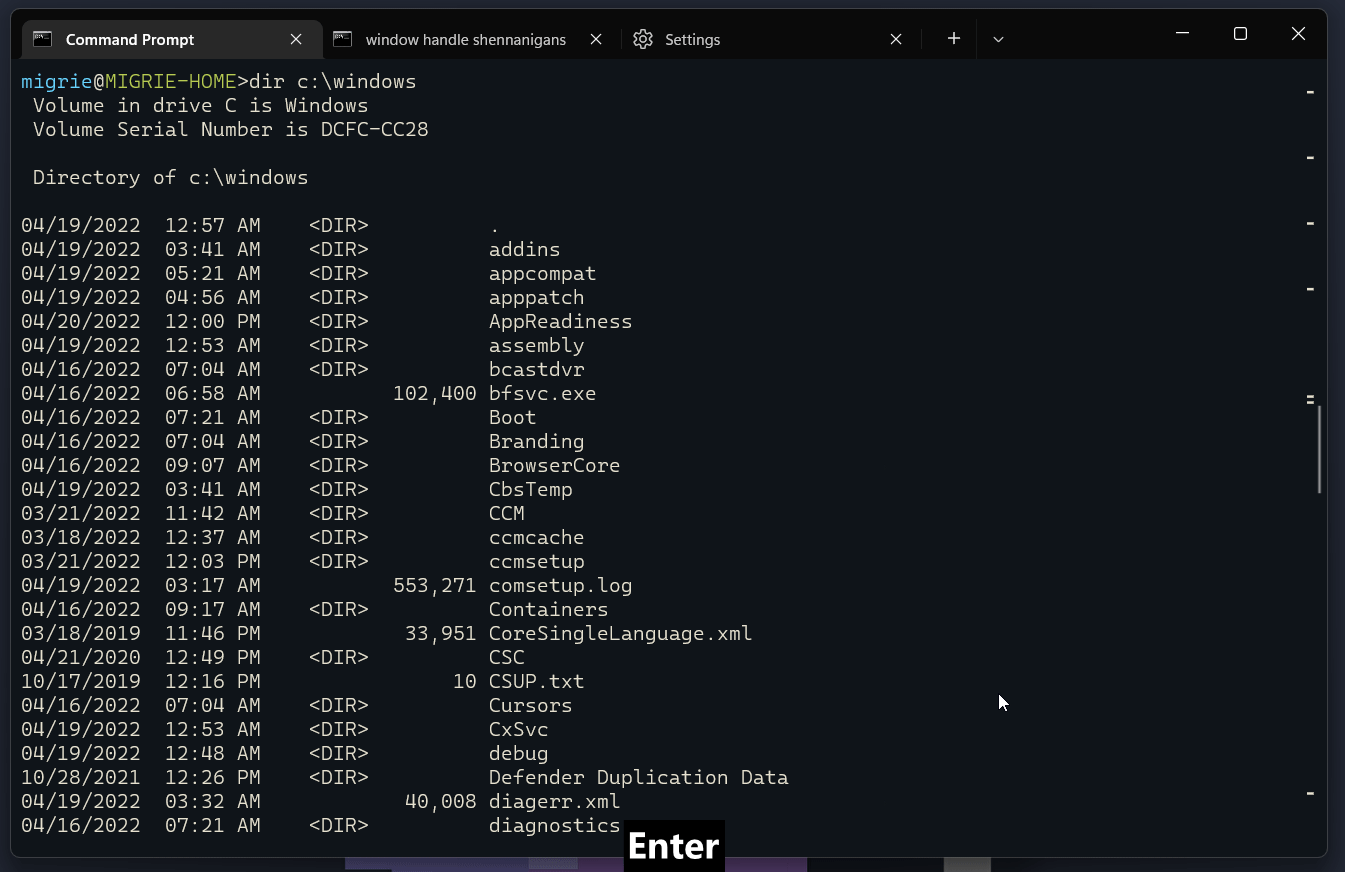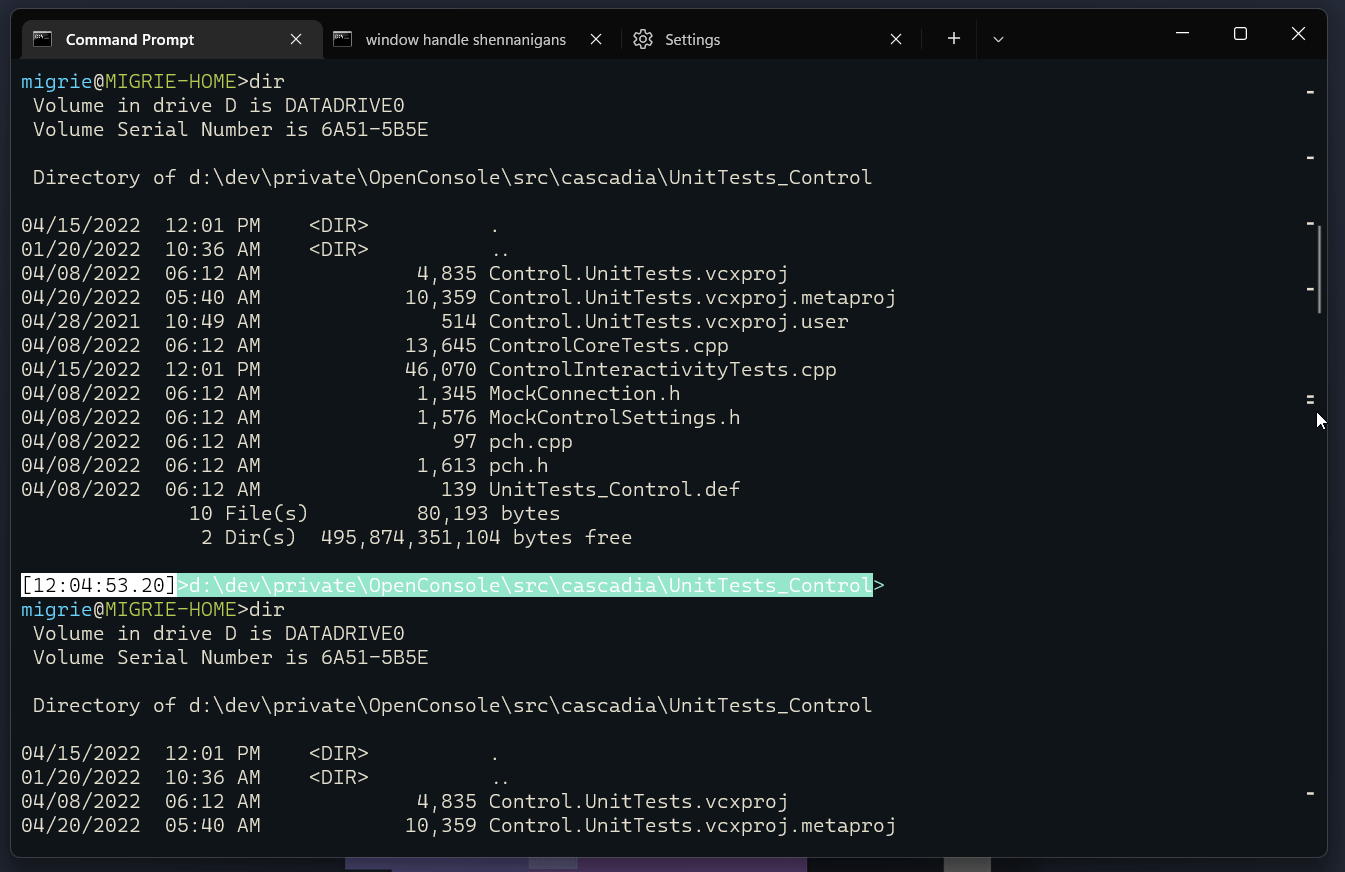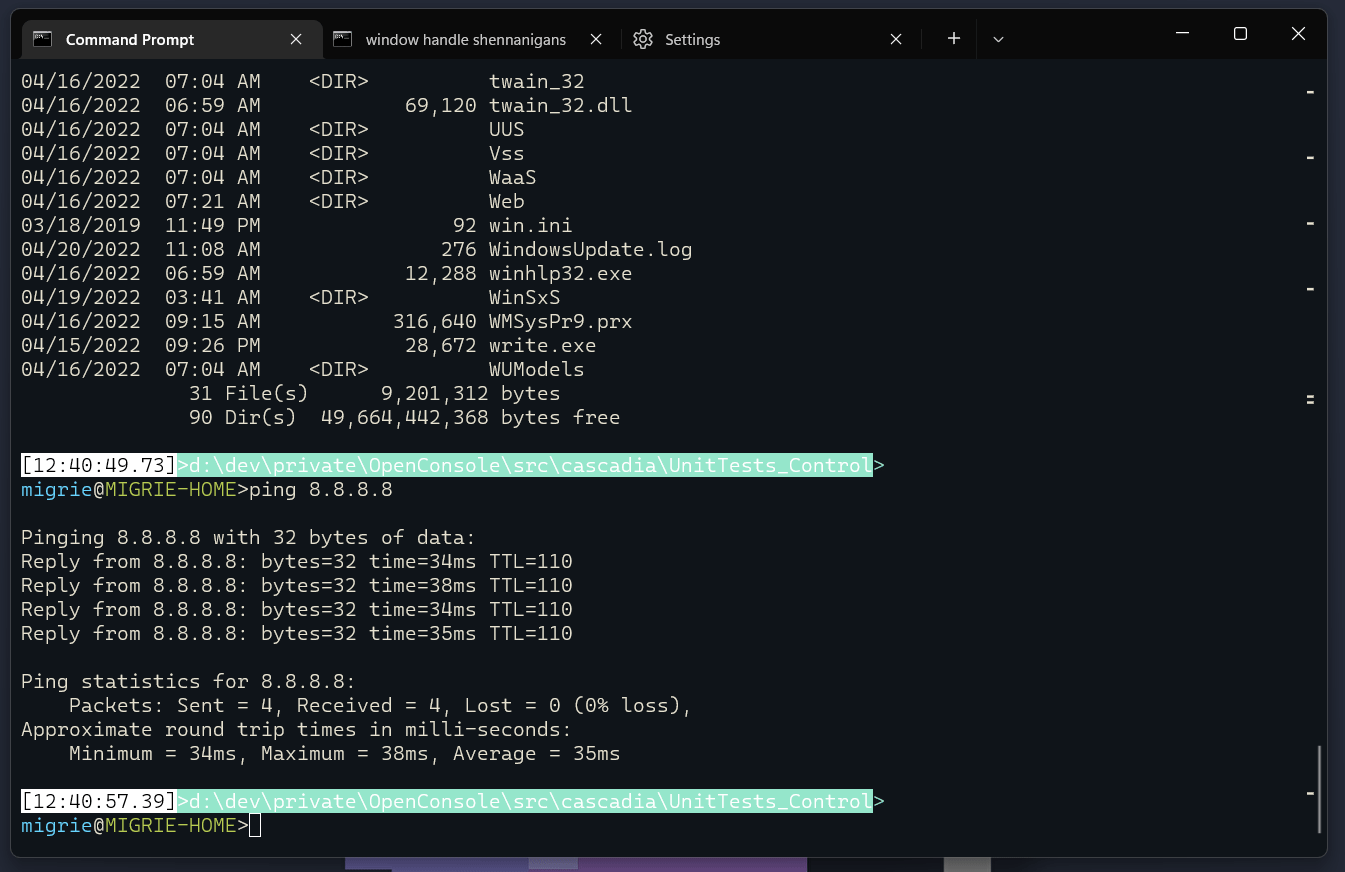
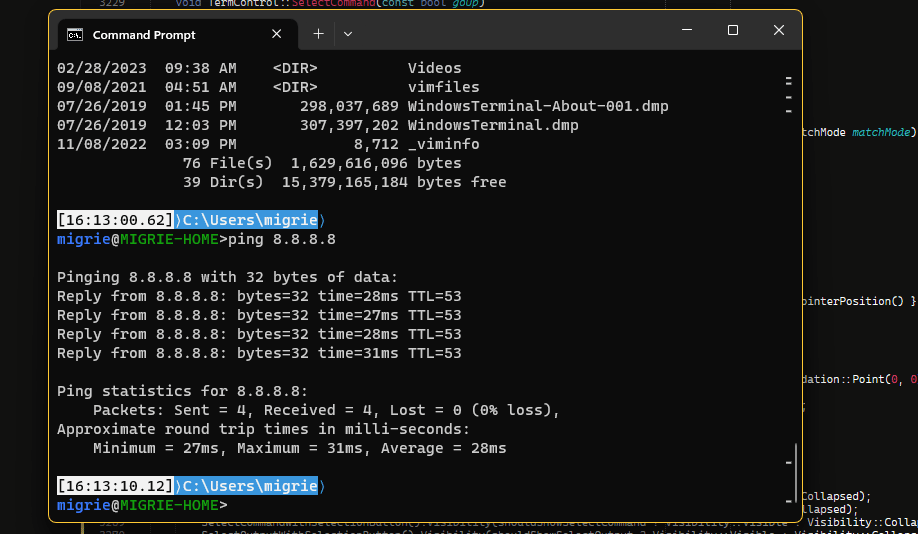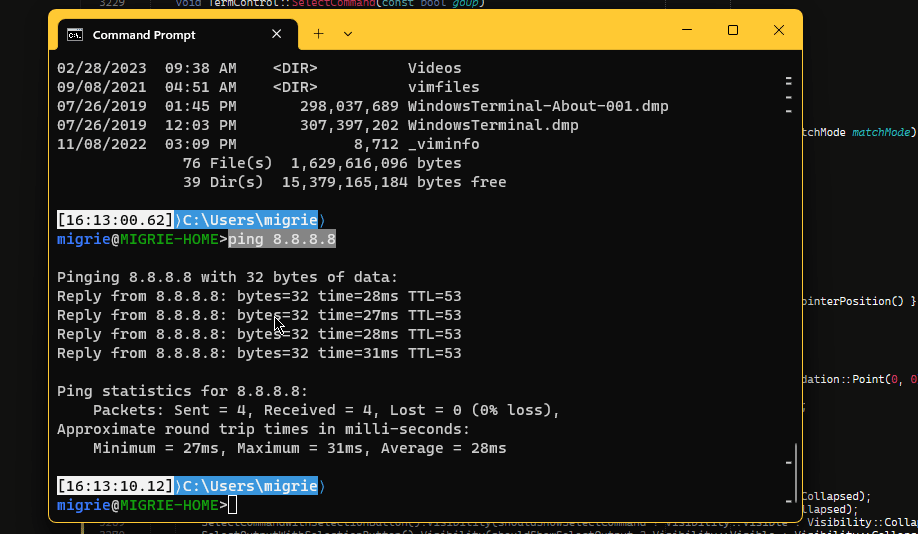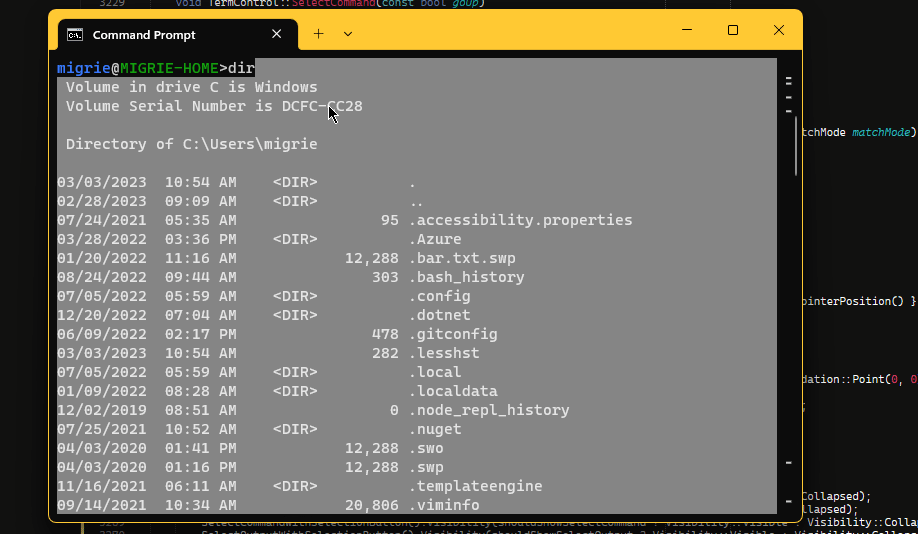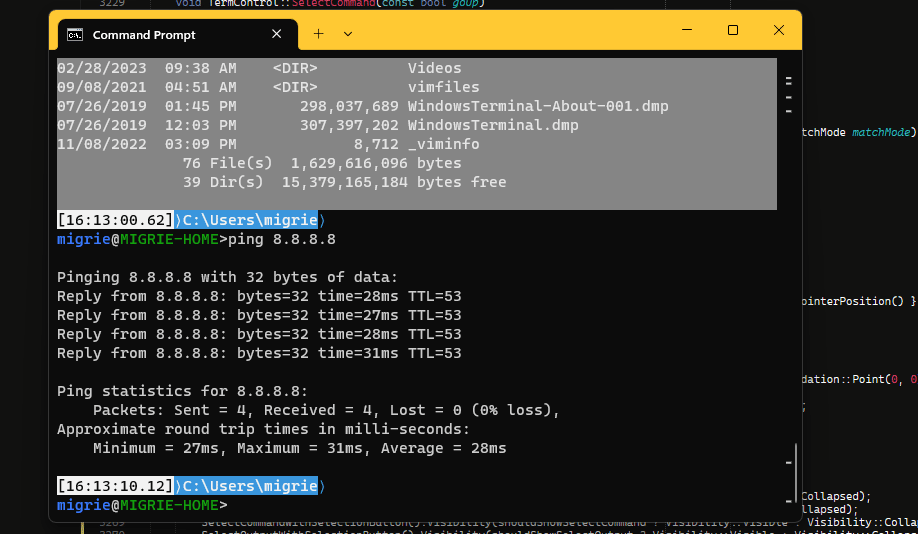
选择命令的整个输出
在此 gif 中,我们使用绑定到 selectOutput 的 ctrl+g 操作来选择命令的整个输出。
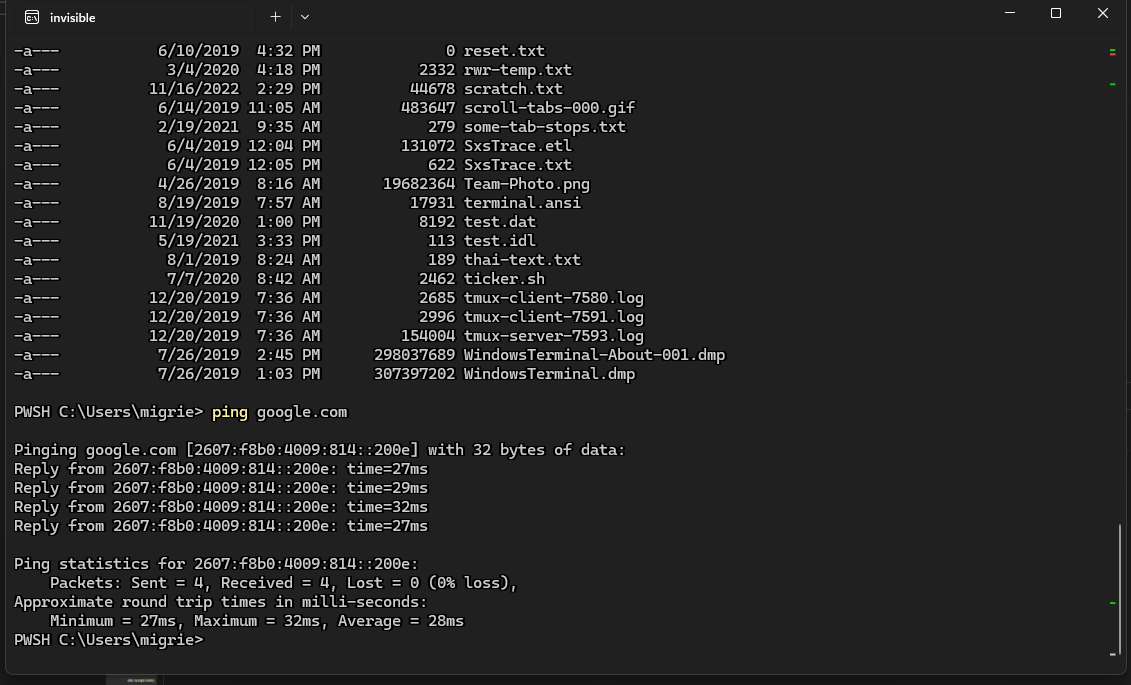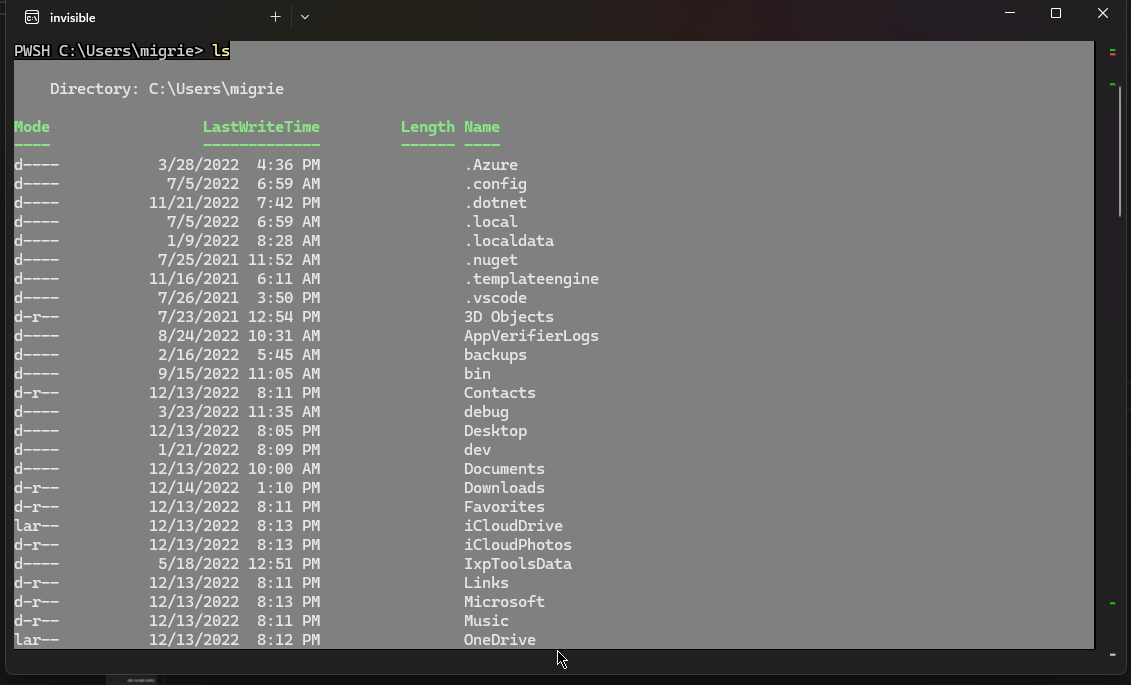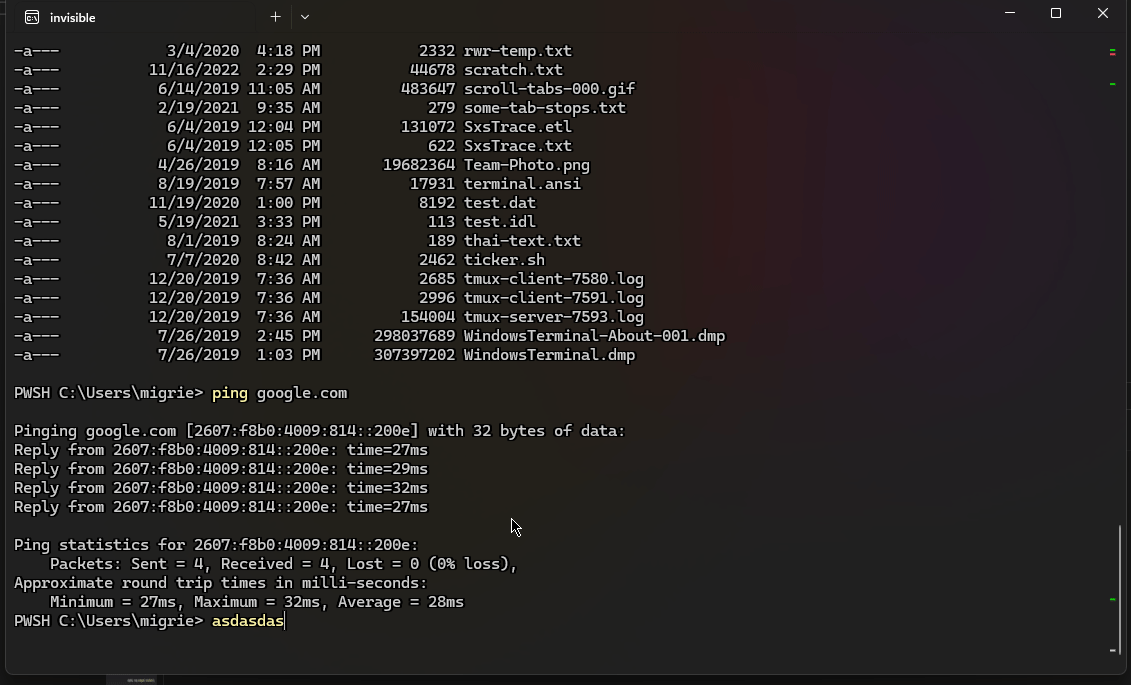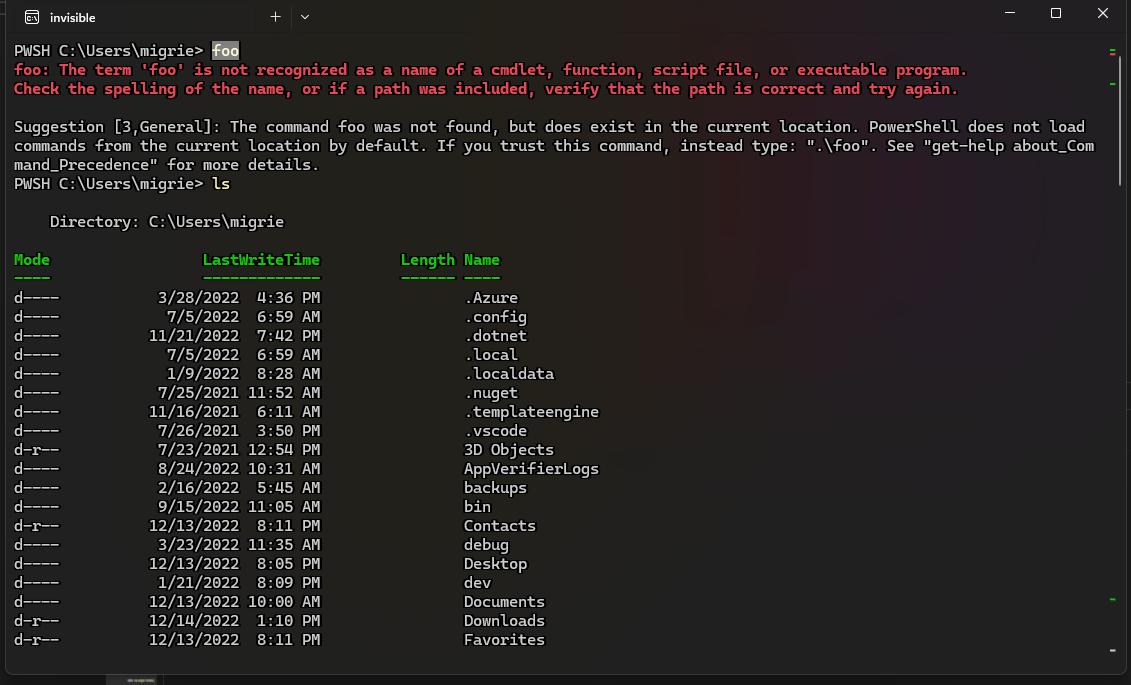
下面的代码使用 experimental.rightClickContextMenu 设置在 Terminal 中启用一个右键单击上下文菜单。 启用该菜单和 shell 集成后,你可以右键单击某个命令来选择整个命令或其输出。
最近的命令建议
启用 shell 集成后,可以将“建议”UI 配置为还显示最近的命令。

可以使用以下操作打开此菜单:
{
"command": { "action": "showSuggestions", "source": "recentCommands", "useCommandline": true },
},
(有关详细信息,请参阅建议文档)
