逐步解說:建立影像處理網路
本文件示範如何建立執行影像處理之異步消息區塊的網路。
網路會根據其特性決定要根據影像執行的作業。 此範例會 使用數據流 模型,透過網路路由傳送影像。 在資料流程模型中,程式的獨立元件會透過傳送訊息,彼此進行通訊。 當元件收到訊息時,它可以執行一些動作,然後將該動作的結果傳遞給另一個元件。 將此與 控制流程 模型進行比較,其中應用程式會使用控制結構,例如條件語句、迴圈等等,來控制程式中的作業順序。
以數據流為基礎的網路會建立工作的 管線 。 管線的每個階段都會同時執行整體工作的一部分。 以汽車製造的裝配線做比喻。 當每輛車通過組裝線時,一個月臺組裝框架,另一個月臺安裝發動機等等。 通過讓多個車輛同時組裝,組裝線提供比一次組裝完整車輛更好的輸送量。
必要條件
開始本逐步解說之前,請先閱讀下列檔:
我們也建議您先瞭解 GDI+ 的基本概念,再開始本逐步解說。
區段
本逐步解說包含下列各節:
定義影像處理功能
本節顯示影像處理網路用來處理從磁碟讀取的映像的支援函式。
下列函式 GetRGB 和 MakeColor會分別擷取和合併指定色彩的個別元件。
// Retrieves the red, green, and blue components from the given
// color value.
void GetRGB(DWORD color, BYTE& r, BYTE& g, BYTE& b)
{
r = static_cast<BYTE>((color & 0x00ff0000) >> 16);
g = static_cast<BYTE>((color & 0x0000ff00) >> 8);
b = static_cast<BYTE>((color & 0x000000ff));
}
// Creates a single color value from the provided red, green,
// and blue components.
DWORD MakeColor(BYTE r, BYTE g, BYTE b)
{
return (r<<16) | (g<<8) | (b);
}
下列函式 ProcessImage會呼叫指定的 std::function 物件,以轉換 GDI+ Bitmap 物件中每個圖元的色彩值。 函 ProcessImage 式會使用 concurrency::p arallel_for 演算法平行處理位圖的每個數據列。
// Calls the provided function for each pixel in a Bitmap object.
void ProcessImage(Bitmap* bmp, const function<void (DWORD&)>& f)
{
int width = bmp->GetWidth();
int height = bmp->GetHeight();
// Lock the bitmap.
BitmapData bitmapData;
Rect rect(0, 0, bmp->GetWidth(), bmp->GetHeight());
bmp->LockBits(&rect, ImageLockModeWrite, PixelFormat32bppRGB, &bitmapData);
// Get a pointer to the bitmap data.
DWORD* image_bits = (DWORD*)bitmapData.Scan0;
// Call the function for each pixel in the image.
parallel_for (0, height, [&, width](int y)
{
for (int x = 0; x < width; ++x)
{
// Get the current pixel value.
DWORD* curr_pixel = image_bits + (y * width) + x;
// Call the function.
f(*curr_pixel);
}
});
// Unlock the bitmap.
bmp->UnlockBits(&bitmapData);
}
下列函式 Grayscale、、 SepiatoneColorMask和Darken會呼叫 函ProcessImage式,以轉換 物件中Bitmap每個像素的色彩值。 每個函式都會使用 Lambda 運算式來定義一個像素的色彩轉換。
// Converts the given image to grayscale.
Bitmap* Grayscale(Bitmap* bmp)
{
ProcessImage(bmp,
[](DWORD& color) {
BYTE r, g, b;
GetRGB(color, r, g, b);
// Set each color component to the average of
// the original components.
BYTE c = (static_cast<WORD>(r) + g + b) / 3;
color = MakeColor(c, c, c);
}
);
return bmp;
}
// Applies sepia toning to the provided image.
Bitmap* Sepiatone(Bitmap* bmp)
{
ProcessImage(bmp,
[](DWORD& color) {
BYTE r0, g0, b0;
GetRGB(color, r0, g0, b0);
WORD r1 = static_cast<WORD>((r0 * .393) + (g0 *.769) + (b0 * .189));
WORD g1 = static_cast<WORD>((r0 * .349) + (g0 *.686) + (b0 * .168));
WORD b1 = static_cast<WORD>((r0 * .272) + (g0 *.534) + (b0 * .131));
color = MakeColor(min(0xff, r1), min(0xff, g1), min(0xff, b1));
}
);
return bmp;
}
// Applies the given color mask to each pixel in the provided image.
Bitmap* ColorMask(Bitmap* bmp, DWORD mask)
{
ProcessImage(bmp,
[mask](DWORD& color) {
color = color & mask;
}
);
return bmp;
}
// Darkens the provided image by the given amount.
Bitmap* Darken(Bitmap* bmp, unsigned int percent)
{
if (percent > 100)
throw invalid_argument("Darken: percent must less than 100.");
double factor = percent / 100.0;
ProcessImage(bmp,
[factor](DWORD& color) {
BYTE r, g, b;
GetRGB(color, r, g, b);
r = static_cast<BYTE>(factor*r);
g = static_cast<BYTE>(factor*g);
b = static_cast<BYTE>(factor*b);
color = MakeColor(r, g, b);
}
);
return bmp;
}
下列函式 GetColorDominance也會呼叫 函 ProcessImage 式。 不過,此函式會使用 concurrency::combinable 對象來計算紅色、綠色或藍色元件是否主宰影像,而不是變更每個色彩的值。
// Determines which color component (red, green, or blue) is most dominant
// in the given image and returns a corresponding color mask.
DWORD GetColorDominance(Bitmap* bmp)
{
// The ProcessImage function processes the image in parallel.
// The following combinable objects enable the callback function
// to increment the color counts without using a lock.
combinable<unsigned int> reds;
combinable<unsigned int> greens;
combinable<unsigned int> blues;
ProcessImage(bmp,
[&](DWORD& color) {
BYTE r, g, b;
GetRGB(color, r, g, b);
if (r >= g && r >= b)
reds.local()++;
else if (g >= r && g >= b)
greens.local()++;
else
blues.local()++;
}
);
// Determine which color is dominant and return the corresponding
// color mask.
unsigned int r = reds.combine(plus<unsigned int>());
unsigned int g = greens.combine(plus<unsigned int>());
unsigned int b = blues.combine(plus<unsigned int>());
if (r + r >= g + b)
return 0x00ff0000;
else if (g + g >= r + b)
return 0x0000ff00;
else
return 0x000000ff;
}
下列函式 GetEncoderClsid會擷取編碼器指定MIME類型的類別標識碼。 應用程式會使用此函式來擷取位圖的編碼器。
// Retrieves the class identifier for the given MIME type of an encoder.
int GetEncoderClsid(const WCHAR* format, CLSID* pClsid)
{
UINT num = 0; // number of image encoders
UINT size = 0; // size of the image encoder array in bytes
ImageCodecInfo* pImageCodecInfo = nullptr;
GetImageEncodersSize(&num, &size);
if(size == 0)
return -1; // Failure
pImageCodecInfo = (ImageCodecInfo*)(malloc(size));
if(pImageCodecInfo == nullptr)
return -1; // Failure
GetImageEncoders(num, size, pImageCodecInfo);
for(UINT j = 0; j < num; ++j)
{
if( wcscmp(pImageCodecInfo[j].MimeType, format) == 0 )
{
*pClsid = pImageCodecInfo[j].Clsid;
free(pImageCodecInfo);
return j; // Success
}
}
free(pImageCodecInfo);
return -1; // Failure
}
[靠上]
建立影像處理網路
本節說明如何建立異步消息區塊網路,以在指定目錄中的每個 JPEG (.jpg) 映射上執行影像處理。 網路會執行下列影像處理作業:
對於 Tom 所撰寫的任何影像,請轉換成灰階。
對於任何以紅色做為主要色彩的影像,請移除綠色和藍色元件,然後將它變暗。
若為任何其他影像,請套用敗血症 toning。
網路只會套用符合其中一個條件的第一個影像處理作業。 例如,如果影像是由 Tom 撰寫,且具有紅色做為其主要色彩,則影像只會轉換成灰階。
網路執行每個影像處理作業之後,會將影像儲存到磁碟作為位圖(.bmp) 檔案。
下列步驟示範如何建立可實作此映像處理網路的函式,並將該網路套用至指定目錄中的每個 JPEG 映像。
建立影像處理網路
建立函式
ProcessImages,此函式會採用磁碟上的目錄名稱。void ProcessImages(const wstring& directory) { }在函式中
ProcessImages,建立countdown_event變數。 此逐步解說稍後會顯示 類別countdown_event。// Holds the number of active image processing operations and // signals to the main thread that processing is complete. countdown_event active(0);建立 std::map 物件,使
Bitmap物件與其源檔名稱產生關聯。// Maps Bitmap objects to their original file names. map<Bitmap*, wstring> bitmap_file_names;新增下列程式代碼來定義影像處理網路的成員。
// // Create the nodes of the network. // // Loads Bitmap objects from disk. transformer<wstring, Bitmap*> load_bitmap( [&](wstring file_name) -> Bitmap* { Bitmap* bmp = new Bitmap(file_name.c_str()); if (bmp != nullptr) bitmap_file_names.insert(make_pair(bmp, file_name)); return bmp; } ); // Holds loaded Bitmap objects. unbounded_buffer<Bitmap*> loaded_bitmaps; // Converts images that are authored by Tom to grayscale. transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> grayscale( [](Bitmap* bmp) { return Grayscale(bmp); }, nullptr, [](Bitmap* bmp) -> bool { if (bmp == nullptr) return false; // Retrieve the artist name from metadata. UINT size = bmp->GetPropertyItemSize(PropertyTagArtist); if (size == 0) // Image does not have the Artist property. return false; PropertyItem* artistProperty = (PropertyItem*) malloc(size); bmp->GetPropertyItem(PropertyTagArtist, size, artistProperty); string artist(reinterpret_cast<char*>(artistProperty->value)); free(artistProperty); return (artist.find("Tom ") == 0); } ); // Removes the green and blue color components from images that have red as // their dominant color. transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> colormask( [](Bitmap* bmp) { return ColorMask(bmp, 0x00ff0000); }, nullptr, [](Bitmap* bmp) -> bool { if (bmp == nullptr) return false; return (GetColorDominance(bmp) == 0x00ff0000); } ); // Darkens the color of the provided Bitmap object. transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> darken([](Bitmap* bmp) { return Darken(bmp, 50); }); // Applies sepia toning to the remaining images. transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> sepiatone( [](Bitmap* bmp) { return Sepiatone(bmp); }, nullptr, [](Bitmap* bmp) -> bool { return bmp != nullptr; } ); // Saves Bitmap objects to disk. transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> save_bitmap([&](Bitmap* bmp) -> Bitmap* { // Replace the file extension with .bmp. wstring file_name = bitmap_file_names[bmp]; file_name.replace(file_name.rfind(L'.') + 1, 3, L"bmp"); // Save the processed image. CLSID bmpClsid; GetEncoderClsid(L"image/bmp", &bmpClsid); bmp->Save(file_name.c_str(), &bmpClsid); return bmp; }); // Deletes Bitmap objects. transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> delete_bitmap([](Bitmap* bmp) -> Bitmap* { delete bmp; return nullptr; }); // Decrements the event counter. call<Bitmap*> decrement([&](Bitmap* _) { active.signal(); });新增下列程式代碼以連線網路。
// // Connect the network. // load_bitmap.link_target(&loaded_bitmaps); loaded_bitmaps.link_target(&grayscale); loaded_bitmaps.link_target(&colormask); colormask.link_target(&darken); loaded_bitmaps.link_target(&sepiatone); loaded_bitmaps.link_target(&decrement); grayscale.link_target(&save_bitmap); darken.link_target(&save_bitmap); sepiatone.link_target(&save_bitmap); save_bitmap.link_target(&delete_bitmap); delete_bitmap.link_target(&decrement);新增下列程式代碼,以將目錄內每個 JPEG 檔案的完整路徑傳送至網路的前端。
// Traverse all files in the directory. wstring searchPattern = directory; searchPattern.append(L"\\*"); WIN32_FIND_DATA fileFindData; HANDLE hFind = FindFirstFile(searchPattern.c_str(), &fileFindData); if (hFind == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE) return; do { if (!(fileFindData.dwFileAttributes & FILE_ATTRIBUTE_DIRECTORY)) { wstring file = fileFindData.cFileName; // Process only JPEG files. if (file.rfind(L".jpg") == file.length() - 4) { // Form the full path to the file. wstring full_path(directory); full_path.append(L"\\"); full_path.append(file); // Increment the count of work items. active.add_count(); // Send the path name to the network. send(load_bitmap, full_path); } } } while (FindNextFile(hFind, &fileFindData) != 0); FindClose(hFind);等候
countdown_event變量達到零。// Wait for all operations to finish. active.wait();
下表描述網路的成員。
| member | 描述 |
|---|---|
load_bitmap |
並行 ::transformer 物件,從磁碟載入 Bitmap 物件,並將專案新增至 物件, map 以將影像與其源檔名稱產生關聯。 |
loaded_bitmaps |
並行 ::unbounded_buffer 物件,會將載入的影像傳送至影像處理篩選。 |
grayscale |
transformer物件,可將 Tom 所撰寫的影像轉換成灰階。 它會使用影像的元數據來判斷其作者。 |
colormask |
transformer物件,從以紅色做為主要色彩的影像中移除綠色和藍色元件。 |
darken |
物件 transformer ,會將紅色做為主要色彩的影像變暗。 |
sepiatone |
物件 transformer ,套用 sepia toning 至不是由 Tom 撰寫且不是以紅色為主的影像。 |
save_bitmap |
物件 transformer ,會將已處理 image 到磁碟的 儲存為位圖。 save_bitmap 會從物件擷 map 取源檔名稱,並將其擴展名變更為 .bmp。 |
delete_bitmap |
transformer對象,釋放影像的記憶體。 |
decrement |
並行 ::call 物件,做為網路中終端節點。 它會遞 countdown_event 減 物件,以向主要應用程式發出已處理影像的訊號。 |
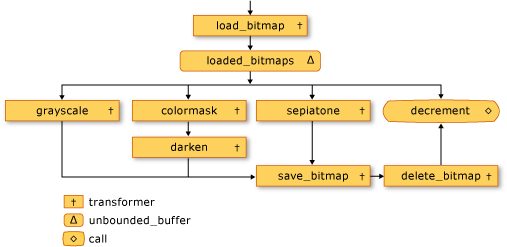
訊息 loaded_bitmaps 緩衝區很重要,因為作為 unbounded_buffer 物件,它會將 Bitmap 物件提供給多個接收者。 當目標區塊接受 Bitmap 物件時, unbounded_buffer 物件不會提供該 Bitmap 物件給任何其他目標。 因此,將對象連結至 unbounded_buffer 對象的順序很重要。 grayscale、 colormask和 sepiatone 訊息區塊都會使用篩選條件只接受特定Bitmap物件。 訊息 decrement 緩衝區是訊息緩衝區的重要目標 loaded_bitmaps ,因為它會接受其他訊息緩衝區拒絕的所有 Bitmap 物件。 需要 unbounded_buffer 物件才能依序傳播訊息。 因此, unbounded_buffer 對象會封鎖,直到新的目標區塊鏈接至該區塊為止,如果目前的目標區塊不接受該訊息,則接受該訊息。
如果您的應用程式要求多個訊息區塊處理訊息,而不只是第一個接受訊息的訊息區塊,您可以使用另一個訊息區塊類型,例如 overwrite_buffer。 類別 overwrite_buffer 一次保存一則訊息,但它會將該訊息傳播至其每個目標。
下圖顯示影像處理網路:
countdown_event此範例中的物件可讓影像處理網路在處理所有影像時通知主要應用程式。 類別 countdown_event 會使用 並行::event 物件,在計數器值達到零時發出訊號。 主要應用程式會在每次將檔名傳送至網路時遞增計數器。 網路終端節點在處理每個映射之後,會遞減計數器。 在主要應用程式周遊指定的目錄之後,它會等候 countdown_event 對象發出其計數器已達到零的訊號。
下列範例顯示 類別 countdown_event :
// A synchronization primitive that is signaled when its
// count reaches zero.
class countdown_event
{
public:
countdown_event(unsigned int count = 0)
: _current(static_cast<long>(count))
{
// Set the event if the initial count is zero.
if (_current == 0L)
_event.set();
}
// Decrements the event counter.
void signal() {
if(InterlockedDecrement(&_current) == 0L) {
_event.set();
}
}
// Increments the event counter.
void add_count() {
if(InterlockedIncrement(&_current) == 1L) {
_event.reset();
}
}
// Blocks the current context until the event is set.
void wait() {
_event.wait();
}
private:
// The current count.
volatile long _current;
// The event that is set when the counter reaches zero.
event _event;
// Disable copy constructor.
countdown_event(const countdown_event&);
// Disable assignment.
countdown_event const & operator=(countdown_event const&);
};
[靠上]
完整範例
下列程式碼顯示完整範例。 函 wmain 式會管理 GDI+ 連結庫,並呼叫 函 ProcessImages 式來處理目錄中的 Sample Pictures JPEG 檔案。
// image-processing-network.cpp
// compile with: /DUNICODE /EHsc image-processing-network.cpp /link gdiplus.lib
#include <windows.h>
#include <gdiplus.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <agents.h>
#include <ppl.h>
using namespace concurrency;
using namespace Gdiplus;
using namespace std;
// Retrieves the red, green, and blue components from the given
// color value.
void GetRGB(DWORD color, BYTE& r, BYTE& g, BYTE& b)
{
r = static_cast<BYTE>((color & 0x00ff0000) >> 16);
g = static_cast<BYTE>((color & 0x0000ff00) >> 8);
b = static_cast<BYTE>((color & 0x000000ff));
}
// Creates a single color value from the provided red, green,
// and blue components.
DWORD MakeColor(BYTE r, BYTE g, BYTE b)
{
return (r<<16) | (g<<8) | (b);
}
// Calls the provided function for each pixel in a Bitmap object.
void ProcessImage(Bitmap* bmp, const function<void (DWORD&)>& f)
{
int width = bmp->GetWidth();
int height = bmp->GetHeight();
// Lock the bitmap.
BitmapData bitmapData;
Rect rect(0, 0, bmp->GetWidth(), bmp->GetHeight());
bmp->LockBits(&rect, ImageLockModeWrite, PixelFormat32bppRGB, &bitmapData);
// Get a pointer to the bitmap data.
DWORD* image_bits = (DWORD*)bitmapData.Scan0;
// Call the function for each pixel in the image.
parallel_for (0, height, [&, width](int y)
{
for (int x = 0; x < width; ++x)
{
// Get the current pixel value.
DWORD* curr_pixel = image_bits + (y * width) + x;
// Call the function.
f(*curr_pixel);
}
});
// Unlock the bitmap.
bmp->UnlockBits(&bitmapData);
}
// Converts the given image to grayscale.
Bitmap* Grayscale(Bitmap* bmp)
{
ProcessImage(bmp,
[](DWORD& color) {
BYTE r, g, b;
GetRGB(color, r, g, b);
// Set each color component to the average of
// the original components.
BYTE c = (static_cast<WORD>(r) + g + b) / 3;
color = MakeColor(c, c, c);
}
);
return bmp;
}
// Applies sepia toning to the provided image.
Bitmap* Sepiatone(Bitmap* bmp)
{
ProcessImage(bmp,
[](DWORD& color) {
BYTE r0, g0, b0;
GetRGB(color, r0, g0, b0);
WORD r1 = static_cast<WORD>((r0 * .393) + (g0 *.769) + (b0 * .189));
WORD g1 = static_cast<WORD>((r0 * .349) + (g0 *.686) + (b0 * .168));
WORD b1 = static_cast<WORD>((r0 * .272) + (g0 *.534) + (b0 * .131));
color = MakeColor(min(0xff, r1), min(0xff, g1), min(0xff, b1));
}
);
return bmp;
}
// Applies the given color mask to each pixel in the provided image.
Bitmap* ColorMask(Bitmap* bmp, DWORD mask)
{
ProcessImage(bmp,
[mask](DWORD& color) {
color = color & mask;
}
);
return bmp;
}
// Darkens the provided image by the given amount.
Bitmap* Darken(Bitmap* bmp, unsigned int percent)
{
if (percent > 100)
throw invalid_argument("Darken: percent must less than 100.");
double factor = percent / 100.0;
ProcessImage(bmp,
[factor](DWORD& color) {
BYTE r, g, b;
GetRGB(color, r, g, b);
r = static_cast<BYTE>(factor*r);
g = static_cast<BYTE>(factor*g);
b = static_cast<BYTE>(factor*b);
color = MakeColor(r, g, b);
}
);
return bmp;
}
// Determines which color component (red, green, or blue) is most dominant
// in the given image and returns a corresponding color mask.
DWORD GetColorDominance(Bitmap* bmp)
{
// The ProcessImage function processes the image in parallel.
// The following combinable objects enable the callback function
// to increment the color counts without using a lock.
combinable<unsigned int> reds;
combinable<unsigned int> greens;
combinable<unsigned int> blues;
ProcessImage(bmp,
[&](DWORD& color) {
BYTE r, g, b;
GetRGB(color, r, g, b);
if (r >= g && r >= b)
reds.local()++;
else if (g >= r && g >= b)
greens.local()++;
else
blues.local()++;
}
);
// Determine which color is dominant and return the corresponding
// color mask.
unsigned int r = reds.combine(plus<unsigned int>());
unsigned int g = greens.combine(plus<unsigned int>());
unsigned int b = blues.combine(plus<unsigned int>());
if (r + r >= g + b)
return 0x00ff0000;
else if (g + g >= r + b)
return 0x0000ff00;
else
return 0x000000ff;
}
// Retrieves the class identifier for the given MIME type of an encoder.
int GetEncoderClsid(const WCHAR* format, CLSID* pClsid)
{
UINT num = 0; // number of image encoders
UINT size = 0; // size of the image encoder array in bytes
ImageCodecInfo* pImageCodecInfo = nullptr;
GetImageEncodersSize(&num, &size);
if(size == 0)
return -1; // Failure
pImageCodecInfo = (ImageCodecInfo*)(malloc(size));
if(pImageCodecInfo == nullptr)
return -1; // Failure
GetImageEncoders(num, size, pImageCodecInfo);
for(UINT j = 0; j < num; ++j)
{
if( wcscmp(pImageCodecInfo[j].MimeType, format) == 0 )
{
*pClsid = pImageCodecInfo[j].Clsid;
free(pImageCodecInfo);
return j; // Success
}
}
free(pImageCodecInfo);
return -1; // Failure
}
// A synchronization primitive that is signaled when its
// count reaches zero.
class countdown_event
{
public:
countdown_event(unsigned int count = 0)
: _current(static_cast<long>(count))
{
// Set the event if the initial count is zero.
if (_current == 0L)
_event.set();
}
// Decrements the event counter.
void signal() {
if(InterlockedDecrement(&_current) == 0L) {
_event.set();
}
}
// Increments the event counter.
void add_count() {
if(InterlockedIncrement(&_current) == 1L) {
_event.reset();
}
}
// Blocks the current context until the event is set.
void wait() {
_event.wait();
}
private:
// The current count.
volatile long _current;
// The event that is set when the counter reaches zero.
event _event;
// Disable copy constructor.
countdown_event(const countdown_event&);
// Disable assignment.
countdown_event const & operator=(countdown_event const&);
};
// Demonstrates how to set up a message network that performs a series of
// image processing operations on each JPEG image in the given directory and
// saves each altered image as a Windows bitmap.
void ProcessImages(const wstring& directory)
{
// Holds the number of active image processing operations and
// signals to the main thread that processing is complete.
countdown_event active(0);
// Maps Bitmap objects to their original file names.
map<Bitmap*, wstring> bitmap_file_names;
//
// Create the nodes of the network.
//
// Loads Bitmap objects from disk.
transformer<wstring, Bitmap*> load_bitmap(
[&](wstring file_name) -> Bitmap* {
Bitmap* bmp = new Bitmap(file_name.c_str());
if (bmp != nullptr)
bitmap_file_names.insert(make_pair(bmp, file_name));
return bmp;
}
);
// Holds loaded Bitmap objects.
unbounded_buffer<Bitmap*> loaded_bitmaps;
// Converts images that are authored by Tom to grayscale.
transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> grayscale(
[](Bitmap* bmp) {
return Grayscale(bmp);
},
nullptr,
[](Bitmap* bmp) -> bool {
if (bmp == nullptr)
return false;
// Retrieve the artist name from metadata.
UINT size = bmp->GetPropertyItemSize(PropertyTagArtist);
if (size == 0)
// Image does not have the Artist property.
return false;
PropertyItem* artistProperty = (PropertyItem*) malloc(size);
bmp->GetPropertyItem(PropertyTagArtist, size, artistProperty);
string artist(reinterpret_cast<char*>(artistProperty->value));
free(artistProperty);
return (artist.find("Tom ") == 0);
}
);
// Removes the green and blue color components from images that have red as
// their dominant color.
transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> colormask(
[](Bitmap* bmp) {
return ColorMask(bmp, 0x00ff0000);
},
nullptr,
[](Bitmap* bmp) -> bool {
if (bmp == nullptr)
return false;
return (GetColorDominance(bmp) == 0x00ff0000);
}
);
// Darkens the color of the provided Bitmap object.
transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> darken([](Bitmap* bmp) {
return Darken(bmp, 50);
});
// Applies sepia toning to the remaining images.
transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> sepiatone(
[](Bitmap* bmp) {
return Sepiatone(bmp);
},
nullptr,
[](Bitmap* bmp) -> bool { return bmp != nullptr; }
);
// Saves Bitmap objects to disk.
transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> save_bitmap([&](Bitmap* bmp) -> Bitmap* {
// Replace the file extension with .bmp.
wstring file_name = bitmap_file_names[bmp];
file_name.replace(file_name.rfind(L'.') + 1, 3, L"bmp");
// Save the processed image.
CLSID bmpClsid;
GetEncoderClsid(L"image/bmp", &bmpClsid);
bmp->Save(file_name.c_str(), &bmpClsid);
return bmp;
});
// Deletes Bitmap objects.
transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> delete_bitmap([](Bitmap* bmp) -> Bitmap* {
delete bmp;
return nullptr;
});
// Decrements the event counter.
call<Bitmap*> decrement([&](Bitmap* _) {
active.signal();
});
//
// Connect the network.
//
load_bitmap.link_target(&loaded_bitmaps);
loaded_bitmaps.link_target(&grayscale);
loaded_bitmaps.link_target(&colormask);
colormask.link_target(&darken);
loaded_bitmaps.link_target(&sepiatone);
loaded_bitmaps.link_target(&decrement);
grayscale.link_target(&save_bitmap);
darken.link_target(&save_bitmap);
sepiatone.link_target(&save_bitmap);
save_bitmap.link_target(&delete_bitmap);
delete_bitmap.link_target(&decrement);
// Traverse all files in the directory.
wstring searchPattern = directory;
searchPattern.append(L"\\*");
WIN32_FIND_DATA fileFindData;
HANDLE hFind = FindFirstFile(searchPattern.c_str(), &fileFindData);
if (hFind == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE)
return;
do
{
if (!(fileFindData.dwFileAttributes & FILE_ATTRIBUTE_DIRECTORY))
{
wstring file = fileFindData.cFileName;
// Process only JPEG files.
if (file.rfind(L".jpg") == file.length() - 4)
{
// Form the full path to the file.
wstring full_path(directory);
full_path.append(L"\\");
full_path.append(file);
// Increment the count of work items.
active.add_count();
// Send the path name to the network.
send(load_bitmap, full_path);
}
}
}
while (FindNextFile(hFind, &fileFindData) != 0);
FindClose(hFind);
// Wait for all operations to finish.
active.wait();
}
int wmain()
{
GdiplusStartupInput gdiplusStartupInput;
ULONG_PTR gdiplusToken;
// Initialize GDI+.
GdiplusStartup(&gdiplusToken, &gdiplusStartupInput, nullptr);
// Perform image processing.
// TODO: Change this path if necessary.
ProcessImages(L"C:\\Users\\Public\\Pictures\\Sample Pictures");
// Shutdown GDI+.
GdiplusShutdown(gdiplusToken);
}
下圖顯示範例輸出。 每個來源影像都高於其對應的修改影像。

Lighthouse 由 Tom Alphin 撰寫,因此會轉換成灰階。 Chrysanthemum、 Desert、 Koala和 Tulips 具有紅色做為主要色彩,因此移除藍色和綠色元件並變暗。 Hydrangeas、 Jellyfish和 Penguins 符合預設準則,因此會以陰性為基底。
[靠上]
編譯程式碼
複製範例程式代碼,並將其貼到 Visual Studio 專案中,或貼到名為 image-processing-network.cpp 的檔案中,然後在 Visual Studio 命令提示字元視窗中執行下列命令。
cl.exe /DUNICODE /EHsc image-processing-network.cpp /link gdiplus.lib