教學課程:在 Azure 監視器中使用 KQL 機器學習功能來偵測和分析異常
Kusto 查詢語言 (KQL) 包括用於時間序列分析、異常偵測、預測和根本原因分析的機器學習運算子、函數和外掛程式。 使用這些 KQL 功能以在 Azure 監視器中執行進階資料分析,而沒有將資料匯出至外部機器學習工具的額外負荷。
在本教學課程中,您會了解如何:
- 建立時間序列
- 識別時間序列中的異常
- 調整異常偵測設定以精簡結果
- 分析異常根本原因
注意
本教學課程提供 Log Analytics 示範環境的連結,而您可以在其中執行 KQL 查詢範例。 不過,您可以在所有使用 KQL 的 Azure 監視器工具中實作相同的 KQL 查詢和主體。
必要條件
- 具有有效訂用帳戶的 Azure 帳戶。 免費建立帳戶。
- 具有記錄資料的工作區。
需要的權限
例如,對於查詢的 Log Analytics 工作區,您必須擁有 Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/query/*/read 權限,如 Log Analytics 讀取器內建角色所提供。
建立時間序列
使用 KQL make-series 運算子來建立時間序列。
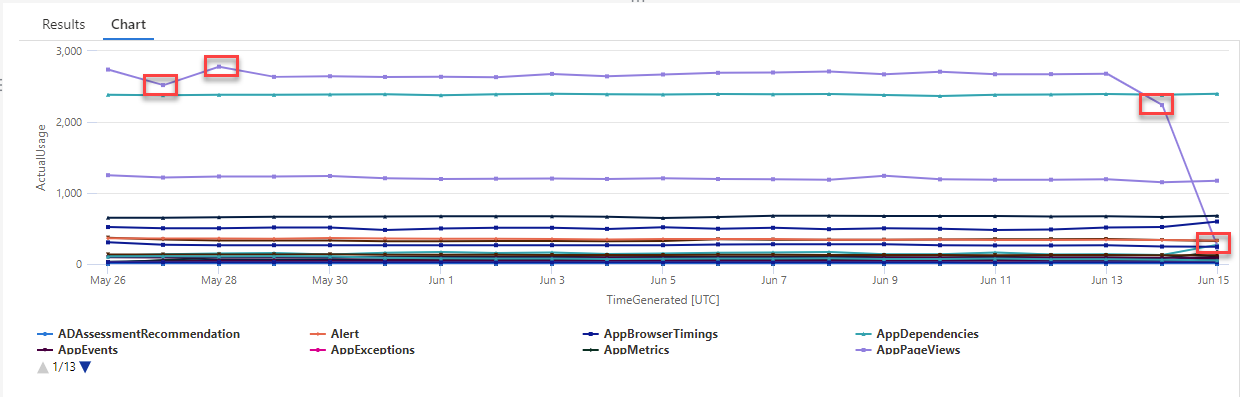
讓我們根據使用量資料表中的記錄來建立時間序列,其中保留工作區中每個資料表每小時擷取的資料量相關資訊,包括可計費和不可計費資料。
此查詢會使用 make-series 來繪製過去 21 天內,工作區中每個資料表每天所擷取的總計費資料量:
let starttime = 21d; // The start date of the time series, counting back from the current date
let endtime = 0d; // The end date of the time series, counting back from the current date
let timeframe = 1d; // How often to sample data
Usage // The table we’re analyzing
| where TimeGenerated between (startofday(ago(starttime))..startofday(ago(endtime))) // Time range for the query, beginning at 12:00 AM of the first day and ending at 12:00 AM of the last day in the time range
| where IsBillable == "true" // Include only billable data in the result set
| make-series ActualUsage=sum(Quantity) default = 0 on TimeGenerated from startofday(ago(starttime)) to startofday(ago(endtime)) step timeframe by DataType // Creates the time series, listed by data type
| render timechart // Renders results in a timechart
在產生的圖表中,您可以清楚地看到一些異常,例如,在 AzureDiagnostics 和 SecurityEvent 資料類型中:
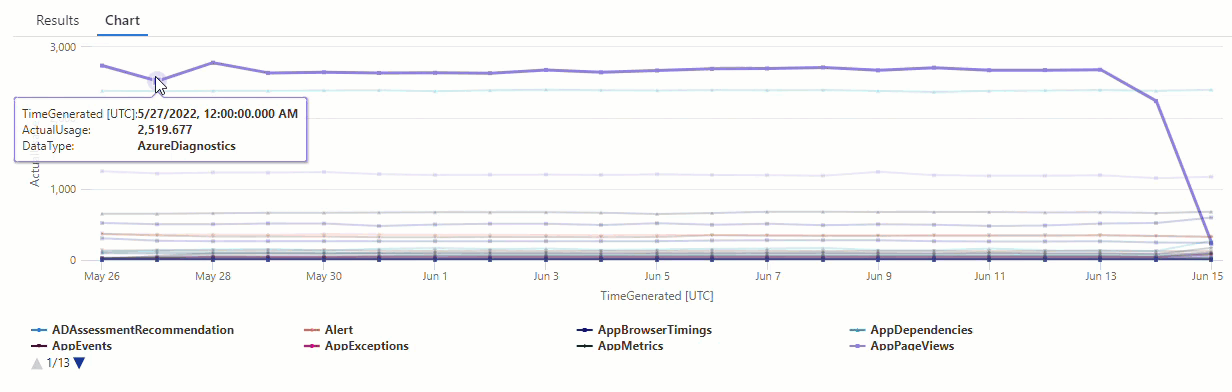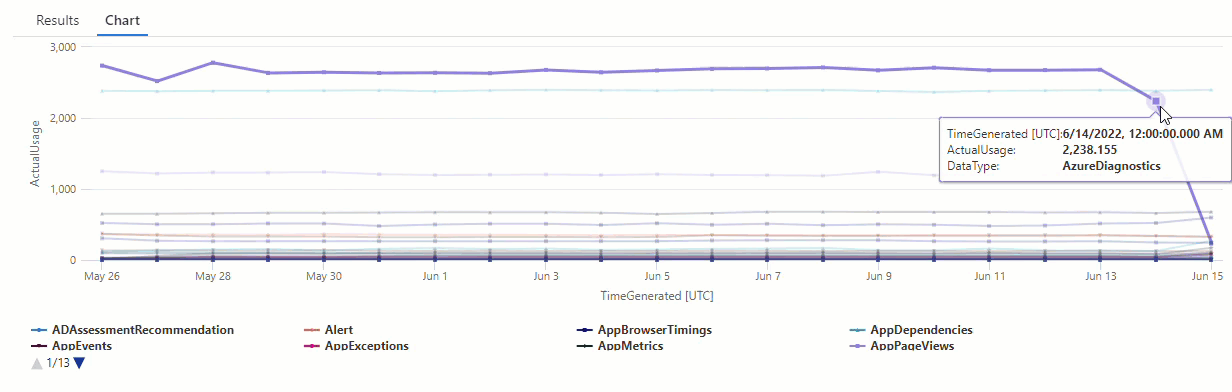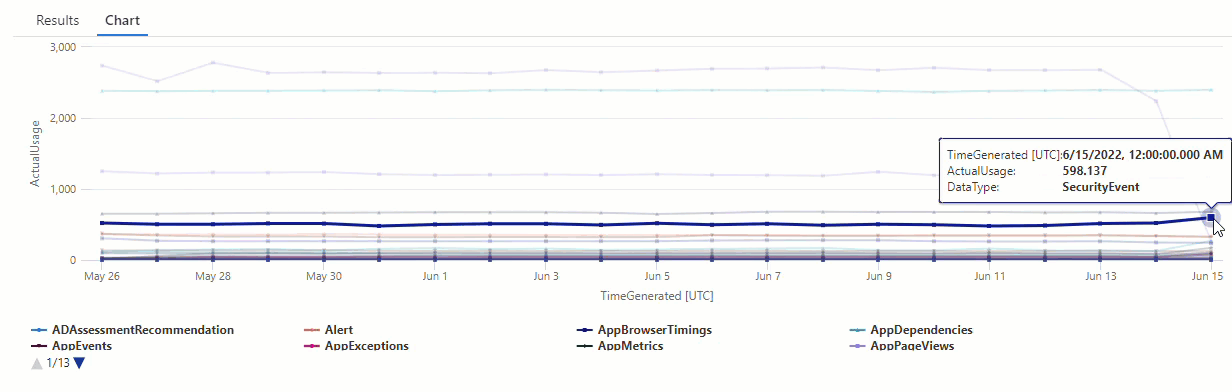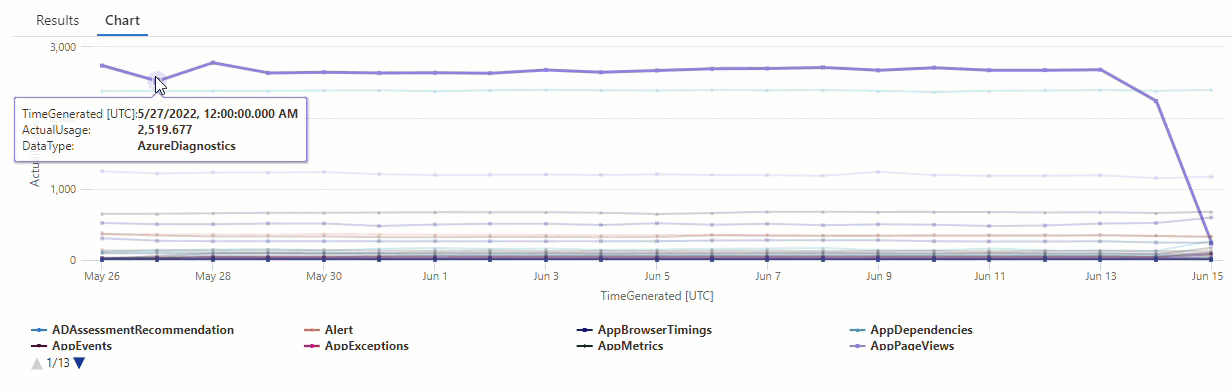
接下來,我們將使用 KQL 函數來列出時間序列中的所有異常。
注意
如需 make-series 語法和使用方式的詳細資訊,請參閱 make-series 運算子。
尋找時間序列異常
series_decompose_anomalies() 函數會採用一系列值作為輸入,並擷取異常。
讓我們提供時間序列查詢的結果集作為 series_decompose_anomalies() 函數的輸入:
let starttime = 21d; // Start date for the time series, counting back from the current date
let endtime = 0d; // End date for the time series, counting back from the current date
let timeframe = 1d; // How often to sample data
Usage // The table we’re analyzing
| where TimeGenerated between (startofday(ago(starttime))..startofday(ago(endtime))) // Time range for the query, beginning at 12:00 AM of the first day and ending at 12:00 AM of the last day in the time range
| where IsBillable == "true" // Includes only billable data in the result set
| make-series ActualUsage=sum(Quantity) default = 0 on TimeGenerated from startofday(ago(starttime)) to startofday(ago(endtime)) step timeframe by DataType // Creates the time series, listed by data type
| extend(Anomalies, AnomalyScore, ExpectedUsage) = series_decompose_anomalies(ActualUsage) // Scores and extracts anomalies based on the output of make-series
| mv-expand ActualUsage to typeof(double), TimeGenerated to typeof(datetime), Anomalies to typeof(double),AnomalyScore to typeof(double), ExpectedUsage to typeof(long) // Expands the array created by series_decompose_anomalies()
| where Anomalies != 0 // Returns all positive and negative deviations from expected usage
| project TimeGenerated,ActualUsage,ExpectedUsage,AnomalyScore,Anomalies,DataType // Defines which columns to return
| sort by abs(AnomalyScore) desc // Sorts results by anomaly score in descending ordering
此查詢會傳回所有資料表在過去三周的所有使用異常:
查看查詢結果,即可看到函數:
- 計算每個資料表的預期每日使用量。
- 比較實際每日使用量與預期使用量。
- 將異常分數指派給每個資料點,指出實際使用量與預期使用量的偏差範圍。
- 識別每個資料表中的正 (
1) 和負 (-1) 異常。
注意
如需 series_decompose_anomalies() 語法和使用方式的詳細資訊,請參閱 series_decompose_anomalies()。
調整異常偵測設定以精簡結果
最好檢閱初始查詢結果,並視需要調整查詢。 輸入資料中的極端值可能會影響函數的學習,而且您可能需要調整函數的異常偵測設定,以取得更精確的結果。
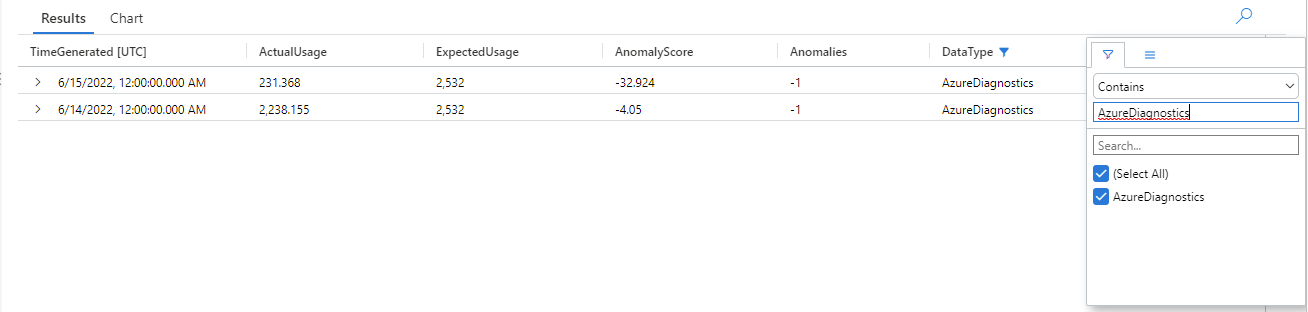
篩選 series_decompose_anomalies() 查詢的結果是否有 AzureDiagnostics 資料類型異常:
結果顯示 6 月 14 日和 6 月 15 日這兩個異常。 將這些結果與第一個 make-series 查詢中的圖表進行比較,而您可以在 5 月 27 日和 28 日看到其他異常:
結果中出現差異的原因是 series_decompose_anomalies() 函數針對預期的使用量值進行異常評分,而函數根據輸入系列中的完整值範圍來進行計算。
若要從函數取得更精簡的結果,請從函數的學習程序中排除 6 月 15 日的使用量 (這是與系列中其他值相較之下的極端值)。
series_decompose_anomalies() 函數的語法為:
series_decompose_anomalies (Series[Threshold,Seasonality,Trend,Test_points,AD_method,Seasonality_threshold])
Test_points 指定要從學習 (迴歸) 程序中排除的序列結尾點數。
若要排除最後一個資料點,請將 Test_points 設定為 1:
let starttime = 21d; // Start date for the time series, counting back from the current date
let endtime = 0d; // End date for the time series, counting back from the current date
let timeframe = 1d; // How often to sample data
Usage // The table we’re analyzing
| where TimeGenerated between (startofday(ago(starttime))..startofday(ago(endtime))) // Time range for the query, beginning at 12:00 AM of the first day and ending at 12:00 AM of the last day in the time range
| where IsBillable == "true" // Includes only billable data in the result set
| make-series ActualUsage=sum(Quantity) default = 0 on TimeGenerated from startofday(ago(starttime)) to startofday(ago(endtime)) step timeframe by DataType // Creates the time series, listed by data type
| extend(Anomalies, AnomalyScore, ExpectedUsage) = series_decompose_anomalies(ActualUsage,1.5,-1,'avg',1) // Scores and extracts anomalies based on the output of make-series, excluding the last value in the series - the Threshold, Seasonality, and Trend input values are the default values for the function
| mv-expand ActualUsage to typeof(double), TimeGenerated to typeof(datetime), Anomalies to typeof(double),AnomalyScore to typeof(double), ExpectedUsage to typeof(long) // Expands the array created by series_decompose_anomalies()
| where Anomalies != 0 // Returns all positive and negative deviations from expected usage
| project TimeGenerated,ActualUsage,ExpectedUsage,AnomalyScore,Anomalies,DataType // Defines which columns to return
| sort by abs(AnomalyScore) desc // Sorts results by anomaly score in descending ordering
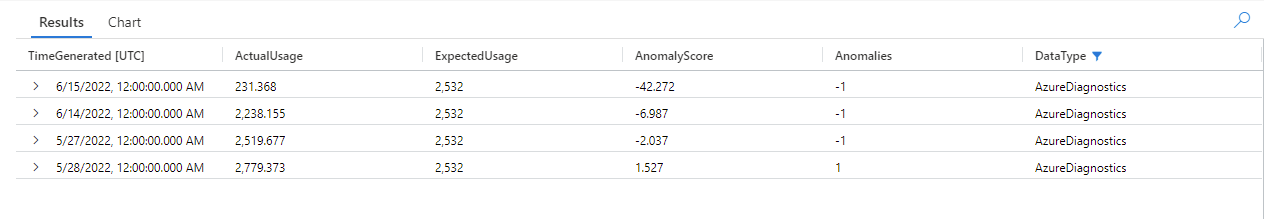
篩選 AzureDiagnostics 資料類型的結果:
第一個 make-series 查詢中圖表內的所有異常現在都會出現在結果集中。
分析異常根本原因
比較預期值與異常值,可協助您瞭解兩個集合之間的差異原因。
KQL diffpatterns() 外掛程式會比較兩個相同結構的資料集,並找出可描述兩個資料集之間差異的模式。
此查詢會比較 6 月 15 日的 AzureDiagnostics 使用量 (在我們的範例中為極端值) 與其他天數的資料表使用量:
let starttime = 21d; // Start date for the time series, counting back from the current date
let endtime = 0d; // End date for the time series, counting back from the current date
let anomalyDate = datetime_add('day',-1, make_datetime(startofday(ago(endtime)))); // Start of day of the anomaly date, which is the last full day in the time range in our example (you can replace this with a specific hard-coded anomaly date)
AzureDiagnostics
| extend AnomalyDate = iff(startofday(TimeGenerated) == anomalyDate, "AnomalyDate", "OtherDates") // Adds calculated column called AnomalyDate, which splits the result set into two data sets – AnomalyDate and OtherDates
| where TimeGenerated between (startofday(ago(starttime))..startofday(ago(endtime))) // Defines the time range for the query
| project AnomalyDate, Resource // Defines which columns to return
| evaluate diffpatterns(AnomalyDate, "OtherDates", "AnomalyDate") // Compares usage on the anomaly date with the regular usage pattern
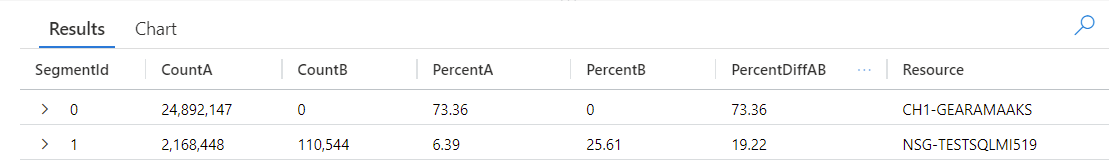
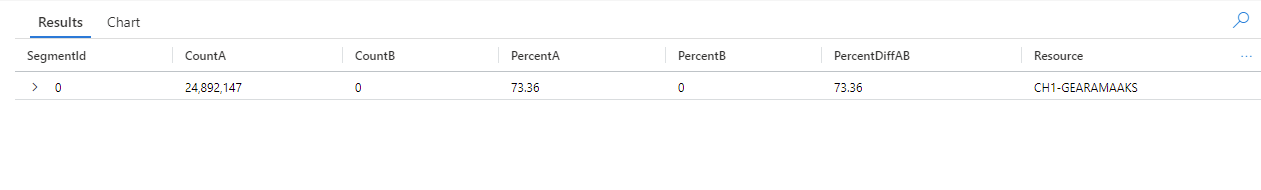
此查詢會將資料表中的每個項目都識別為在 AnomalyDate (6 月 15 日) 或 OtherDates 重複執行。 diffpatterns() 外掛程式接著會分割這些資料集 - 稱為 A (在我們的範例中為 OtherDates) 和 B (在我們的範例中為 AnomalyDate),並傳回一些模式,而這些模式會貢獻兩個集合的差異:
查看查詢結果,您可以看到下列差異:
- 在查詢時間範圍的所有其他天數,來自 CH1-GEARAMAAKS 資源的擷取有 24,892,147 個執行個體,而且 6 月 15 日未從此資源擷取資料。 CH1-GEARAMAAKS 資源中的資料占查詢時間範圍內其他天數之擷取總數的 73.36%,而占 6 月 15 日之擷取總數的 0%。
- 在查詢時間範圍的所有其他天數,來自 NSG-TESTSQLMI519 資源的擷取有 2,168,448 個執行個體,而且 6 月 15 日從此資源擷取 110,544 個執行個體。 NSG-TESTSQLMI519 資源中的資料占查詢時間範圍內其他天數之擷取總數的 6.39%,而占 6 月 15 日之擷取的 25.61%。
請注意,平均而言,在 20 天內會從 NSG-TESTSQLMI519 資源擷取 108,422 個執行個體,而這些執行個體構成「其他天數」期間 (將 2,168,448 除以 20)。 因此,6 月 15 日從 NSG-TESTSQLMI519 資源的擷取與其他天數來自此資源的擷取並無明顯不同。 不過,因為 CH1-GEARAMAAKS 在 6 月 15 日沒有擷取,所以 NSG-TESTSQLMI519 的擷取會比其他天數的擷取明顯構成異常日期擷取總數較大的百分比。
PercentDiffAB 資料行顯示 A 與 B 之間的絕對百分比點差異 (|PercentA - PercentB|),而這是兩個集合之間差異的主要量值。 根據預設,diffpatterns() 外掛程式會傳回兩個資料集之間超過 5% 的差異,但您可以調整此閾值。 例如,若只要傳回兩個資料集之間等於或超過 20% 的差異,您可以在上述查詢中設定 | evaluate diffpatterns(AnomalyDate, "OtherDates", "AnomalyDate", "~", 0.20)。 查詢現在只會傳回一個結果:
注意
如需 diffpatterns() 語法和使用方式的詳細資訊,請參閱差異模式外掛程式。
下一步
深入了解:
意見反應
即將登場:在 2024 年,我們將逐步淘汰 GitHub 問題作為內容的意見反應機制,並將它取代為新的意見反應系統。 如需詳細資訊,請參閱:https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback。
提交並檢視相關的意見反應