從 .NET Framework 4.5 開始,Windows Workflow Foundation (WF) 支援 C# 表達式。 以 .NET Framework 4.5 為目標的 Visual Studio 2012 中建立的新 C# 工作流程專案會使用 C# 表達式,而 Visual Basic 工作流程專案則使用 Visual Basic 表達式。 不論專案語言為何,使用 Visual Basic 表達式的現有 .NET Framework 4 工作流程專案都可以遷移至 .NET Framework 4.6.1,並且受到支援。 本主題提供 WF 中 C# 表達式的概觀。
在工作流程中使用 C# 運算式
在工作流程設計工具中使用 C# 運算式
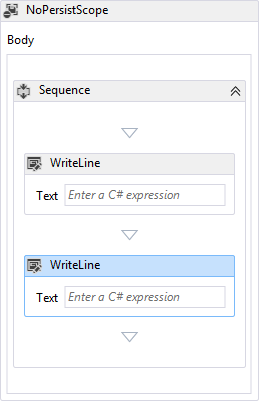
從 .NET Framework 4.5 開始,Windows Workflow Foundation (WF) 支援 C# 表達式。 以 .NET Framework 4.5 為目標的 Visual Studio 2012 中建立的 C# 工作流程專案會使用 C# 表達式,而 Visual Basic 工作流程專案則使用 Visual Basic 表達式。 若要指定所需的 C# 運算式,請在標示為 Enter a C# 運算式的方塊中輸入它。 當在設計工具中選取活動或工作流程設計工具中的活動時,此標籤會顯示在屬性視窗中。 在下列範例中,兩個WriteLine活動包含在Sequence中,且Sequence位於內。
備註
C# 運算式僅在 Visual Studio 中受到支援,而且在重新裝載的工作流程設計工具中不支援。 如需重新裝載設計工具中支援的新 WF45 功能詳細資訊,請參閱 重新裝載工作流程設計工具中的新 Workflow Foundation 4.5 功能支援。
回溯相容性
支援已移轉至 .NET Framework 4.6.1 的現有 .NET Framework 4 C# 工作流程專案中的 Visual Basic 表達式。 在工作流程設計工具中檢視 Visual Basic 運算式時,如果 Visual Basic 運算式不是有效的 C# 語法,那麼現有的 Visual Basic 運算式文字會被替換為 Value was set in XAML。 如果 Visual Basic 運算式是有效的 C# 語法,則會顯示表示式。 若要將 Visual Basic 運算式更新為 C#,您可以在工作流程設計工具中編輯它們,並指定對等的 C# 運算式。 不需要將 Visual Basic 運算式更新為 C#,但是一旦工作流程設計工具中更新運算式,它們就會轉換成 C#,而且可能不會還原為 Visual Basic。
在程序代碼工作流程中使用 C# 運算式
.NET Framework 4.6.1 的基於程式碼的工作流程支援 C# 表達式,但在呼叫工作流程之前,必須使用 TextExpressionCompiler.Compile 編譯這些 C# 表達式。 工作流程作者可以使用 CSharpValue 來表示表達式的 r 值,以及 CSharpReference 表示表達式的 l 值。 在下列範例中,會建立一個包含 Assign 活動和 WriteLine 活動於 Sequence 活動中的工作流程。 為 CSharpReference 的 To 自變數指定 Assign ,並表示表達式的 l 值。
CSharpValue為Value的Assign參數指定,並且為Text的WriteLine參數指定,均表示這兩個表達式的 r 值。
Variable<int> n = new Variable<int>
{
Name = "n"
};
Activity wf = new Sequence
{
Variables = { n },
Activities =
{
new Assign<int>
{
To = new CSharpReference<int>("n"),
Value = new CSharpValue<int>("new Random().Next(1, 101)")
},
new WriteLine
{
Text = new CSharpValue<string>("\"The number is \" + n")
}
}
};
CompileExpressions(wf);
WorkflowInvoker.Invoke(wf);
建構工作流程之後,C# 表達式會藉由呼叫 CompileExpressions 協助程式方法來編譯,然後叫用工作流程。 下列範例是 CompileExpressions 方法。
static void CompileExpressions(Activity activity)
{
// activityName is the Namespace.Type of the activity that contains the
// C# expressions.
string activityName = activity.GetType().ToString();
// Split activityName into Namespace and Type.Append _CompiledExpressionRoot to the type name
// to represent the new type that represents the compiled expressions.
// Take everything after the last . for the type name.
string activityType = activityName.Split('.').Last() + "_CompiledExpressionRoot";
// Take everything before the last . for the namespace.
string activityNamespace = string.Join(".", activityName.Split('.').Reverse().Skip(1).Reverse());
// Create a TextExpressionCompilerSettings.
TextExpressionCompilerSettings settings = new TextExpressionCompilerSettings
{
Activity = activity,
Language = "C#",
ActivityName = activityType,
ActivityNamespace = activityNamespace,
RootNamespace = null,
GenerateAsPartialClass = false,
AlwaysGenerateSource = true,
ForImplementation = false
};
// Compile the C# expression.
TextExpressionCompilerResults results =
new TextExpressionCompiler(settings).Compile();
// Any compilation errors are contained in the CompilerMessages.
if (results.HasErrors)
{
throw new Exception("Compilation failed.");
}
// Create an instance of the new compiled expression type.
ICompiledExpressionRoot compiledExpressionRoot =
Activator.CreateInstance(results.ResultType,
new object[] { activity }) as ICompiledExpressionRoot;
// Attach it to the activity.
CompiledExpressionInvoker.SetCompiledExpressionRoot(
activity, compiledExpressionRoot);
}
備註
如果未編譯 C# 運算式, NotSupportedException 當工作流程叫用類似如下的訊息時,會擲回 : Expression Activity type 'CSharpValue1' 需要編譯才能執行。 請確保工作流程已完成編譯。
如果您的自定義程式碼工作流程使用 DynamicActivity,則需要對 方法進行一些變更 CompileExpressions ,如下列程式代碼範例所示。
static void CompileExpressions(DynamicActivity dynamicActivity)
{
// activityName is the Namespace.Type of the activity that contains the
// C# expressions. For Dynamic Activities this can be retrieved using the
// name property , which must be in the form Namespace.Type.
string activityName = dynamicActivity.Name;
// Split activityName into Namespace and Type.Append _CompiledExpressionRoot to the type name
// to represent the new type that represents the compiled expressions.
// Take everything after the last . for the type name.
string activityType = activityName.Split('.').Last() + "_CompiledExpressionRoot";
// Take everything before the last . for the namespace.
string activityNamespace = string.Join(".", activityName.Split('.').Reverse().Skip(1).Reverse());
// Create a TextExpressionCompilerSettings.
TextExpressionCompilerSettings settings = new TextExpressionCompilerSettings
{
Activity = dynamicActivity,
Language = "C#",
ActivityName = activityType,
ActivityNamespace = activityNamespace,
RootNamespace = null,
GenerateAsPartialClass = false,
AlwaysGenerateSource = true,
ForImplementation = true
};
// Compile the C# expression.
TextExpressionCompilerResults results =
new TextExpressionCompiler(settings).Compile();
// Any compilation errors are contained in the CompilerMessages.
if (results.HasErrors)
{
throw new Exception("Compilation failed.");
}
// Create an instance of the new compiled expression type.
ICompiledExpressionRoot compiledExpressionRoot =
Activator.CreateInstance(results.ResultType,
new object[] { dynamicActivity }) as ICompiledExpressionRoot;
// Attach it to the activity.
CompiledExpressionInvoker.SetCompiledExpressionRootForImplementation(
dynamicActivity, compiledExpressionRoot);
}
在 CompileExpressions 動態活動中編譯 C# 表達式的多載具有幾個不同之處。
CompileExpressions參數是DynamicActivity。類型名稱和命名空間是使用
DynamicActivity.Name屬性來擷取。TextExpressionCompilerSettings.ForImplementation設定為true。CompiledExpressionInvoker.SetCompiledExpressionRootForImplementation被呼叫 而不是CompiledExpressionInvoker.SetCompiledExpressionRoot。
如需在程式代碼中使用表達式的詳細資訊,請參閱 使用命令式程式碼撰寫工作流程、活動和表示式。
在 XAML 工作流程中使用 C# 運算式
XAML 工作流程支援 C# 運算式。 編譯的 XAML 工作流程會被編譯成一種類型,而在執行階段,鬆散的 XAML 工作流程會先被載入,然後在執行工作流程時編譯成活動樹狀結構。
已編譯的 Xaml
編譯的 XAML 工作流程支援 C# 運算式,這些工作流程會編譯為以 .NET Framework 4.6.1 為目標的 C# 工作流程專案的一部分。 編譯的 XAML 是 Visual Studio 中工作流程撰寫的預設類型,而以 .NET Framework 4.6.1 為目標的 Visual Studio 中建立的 C# 工作流程專案會使用 C# 表達式。
非編譯 XAML
鬆散的 XAML 工作流程支援 C# 運算式。 載入和叫用鬆散 XAML 工作流程的工作流程主機程式必須以 .NET Framework 4.6.1 為目標,而且 CompileExpressions 必須設定為 true (預設值為 false)。 若要設定 CompileExpressions 為 true,請建立一個 ActivityXamlServicesSettings 實體,將其 CompileExpressions 屬性設定為 true,然後將它當做參數傳遞至 ActivityXamlServices.Load。 如果 CompileExpressions 未設定為 true,將引發 NotSupportedException 並顯示類似以下的訊息: 'Expression Activity type 'CSharpValue1' 需要編譯才能執行。 請確保工作流程已完成編譯。
ActivityXamlServicesSettings settings = new ActivityXamlServicesSettings
{
CompileExpressions = true
};
DynamicActivity<int> wf = ActivityXamlServices.Load(new StringReader(serializedAB), settings) as DynamicActivity<int>;
如需使用 XAML 工作流程的詳細資訊,請參閱 序列化 XAML 的工作流程和活動。
在 XAMLX 工作流程服務中使用 C# 運算式
XAMLX 工作流程服務支援 C# 運算式。 當工作流程服務裝載於 IIS 或 WAS 時,不需要其他步驟,但如果 XAML 工作流程服務是自我裝載的,則必須編譯 C# 運算式。 若要在自我裝載的 XAMLX 工作流程服務中編譯 C# 運算式,請先將 XAMLX 檔案載入WorkflowService,然後將BodyWorkflowService 傳遞至先前在CompileExpressions一節中所述的方法。 在下列範例中,會載入 XAMLX 工作流程服務、編譯 C# 表達式,然後開啟工作流程服務並等候要求。
// Load the XAMLX workflow service.
WorkflowService workflow1 =
(WorkflowService)XamlServices.Load(xamlxPath);
// Compile the C# expressions in the workflow by passing the Body to CompileExpressions.
CompileExpressions(workflow1.Body);
// Initialize the WorkflowServiceHost.
var host = new WorkflowServiceHost(workflow1, new Uri("http://localhost:8293/Service1.xamlx"));
// Enable Metadata publishing/
ServiceMetadataBehavior smb = new ServiceMetadataBehavior();
smb.HttpGetEnabled = true;
smb.MetadataExporter.PolicyVersion = PolicyVersion.Policy15;
host.Description.Behaviors.Add(smb);
// Open the WorkflowServiceHost and wait for requests.
host.Open();
Console.WriteLine("Press enter to quit");
Console.ReadLine();
如果未編譯 C# 運算式,作業 Open 會成功,但叫用工作流程時將會失敗。 下列 CompileExpressions 方法與先前 在程序代碼工作流程中使用 C# 運算式 一節中的 方法相同。
static void CompileExpressions(Activity activity)
{
// activityName is the Namespace.Type of the activity that contains the
// C# expressions.
string activityName = activity.GetType().ToString();
// Split activityName into Namespace and Type.Append _CompiledExpressionRoot to the type name
// to represent the new type that represents the compiled expressions.
// Take everything after the last . for the type name.
string activityType = activityName.Split('.').Last() + "_CompiledExpressionRoot";
// Take everything before the last . for the namespace.
string activityNamespace = string.Join(".", activityName.Split('.').Reverse().Skip(1).Reverse());
// Create a TextExpressionCompilerSettings.
TextExpressionCompilerSettings settings = new TextExpressionCompilerSettings
{
Activity = activity,
Language = "C#",
ActivityName = activityType,
ActivityNamespace = activityNamespace,
RootNamespace = null,
GenerateAsPartialClass = false,
AlwaysGenerateSource = true,
ForImplementation = false
};
// Compile the C# expression.
TextExpressionCompilerResults results =
new TextExpressionCompiler(settings).Compile();
// Any compilation errors are contained in the CompilerMessages.
if (results.HasErrors)
{
throw new Exception("Compilation failed.");
}
// Create an instance of the new compiled expression type.
ICompiledExpressionRoot compiledExpressionRoot =
Activator.CreateInstance(results.ResultType,
new object[] { activity }) as ICompiledExpressionRoot;
// Attach it to the activity.
CompiledExpressionInvoker.SetCompiledExpressionRoot(
activity, compiledExpressionRoot);
}
