RelativeLayout用來定位和調整相對於配置或同層級元素屬性的子系大小。 這可讓建立跨裝置大小按比例調整的UI。 此外,與其他版面配置類別不同的是, RelativeLayout 能夠放置子系以便重疊。
類別 RelativeLayout 會定義下列屬性:
XConstraint型Constraint別為 的 ,這是附加屬性,表示子系 X 位置的條件約束。YConstraint型Constraint別為 的 ,這是附加屬性,表示子系 Y 位置的條件約束。WidthConstraint型Constraint別為 的 ,這是附加屬性,表示子系寬度的條件約束。HeightConstraint型Constraint別為 的 ,這是附加屬性,表示子系高度的條件約束。BoundsConstraint型BoundsConstraint別為 的 ,這是附加屬性,表示子系位置和大小的條件約束。 這個屬性無法輕易從 XAML 取用。
這些屬性是由 BindableProperty 物件所支援,這表示屬性可以是數據系結和樣式的目標。 如需附加屬性的詳細資訊,請參閱 Xamarin.Forms 附加屬性。
注意
中子 RelativeLayout 系的寬度和高度也可以透過子系的 WidthRequest 和 HeightRequest 屬性來指定,而不是 WidthConstraint 和 HeightConstraint 附加屬性。
類別 RelativeLayout 衍生自 Layout<T> 類別,該類別會 Children 定義 型 IList<T>別 的屬性。 屬性 Children 是 ContentProperty 類別的 Layout<T> ,因此不需要從 XAML 明確設定。
提示
盡量避免使用 RelativeLayout。 它會導致 CPU 必須執行更多工作。
限制
RelativeLayout在 中,子系的位置和大小會使用絕對值或相對值來指定為條件約束。 未指定條件約束時,子系會位於版面配置左上角。
下表顯示如何在 XAML 和 C# 中指定條件約束:
| XAML | C# | |
|---|---|---|
| 絕對值 | 絕對條件約束是藉由將 RelativeLayout 附加屬性設定為 double 值來指定。 |
絕對條件約束是由 Constraint.Constant 方法指定,或使用 Children.Add 需要自變數的多 Func<Rectangle> 載。 |
| 相對值 | 相對條件約束是藉由將 RelativeLayout 附加屬性設定為 Constraint 標記延伸所 ConstraintExpression 傳回的物件來指定。 |
相對條件約束是由 Constraint 類別之方法所傳回的物件 Constraint 所指定。 |
如需使用絕對值指定條件約束的詳細資訊,請參閱 絕對定位和重設大小。 如需使用相對值指定條件約束的詳細資訊,請參閱 相對定位和重設大小。
在 C# 中,子系可以新增至 RelativeLayout 三 Add 個多載。 第一個多載需要 指定 Expression<Func<Rectangle>> 子系的位置和大小。 第二個多載需要、 ywidth、 和 height 自變數的x選擇性Expression<Func<double>>物件。 第三個多載需要 、y、 width和 height 自變數的x選擇性Constraint物件。
使用、 SetYConstraintSetWidthConstraint和 方法,可以變更 中RelativeLayoutSetXConstraint子系的位置和SetHeightConstraint大小。 這些方法的第一個自變數是子系,第二個 Constraint 是 物件。 此外, SetBoundsConstraint 方法也可以用來變更子系的位置和大小。 這個方法的第一個自變數是子系,第二個 BoundsConstraint 自變數是物件。
絕對定位和重設大小
RelativeLayout可以使用裝置獨立單位中指定的絕對值來定位和重設大小子系,以明確定義子系應該放在配置中的位置。 這可藉由將子系新增至 Children 的RelativeLayout集合,並將每個子系上的、 WidthConstraintYConstraint、 和 HeightConstraint 附加屬性設定XConstraint為絕對位置和/或大小值來達成。
警告
使用絕對值來定位和重設大小子系可能會有問題,因為不同的裝置有不同的螢幕大小和解析度。 因此,某個裝置上螢幕中心座標可能會在其他裝置上位移。
下列 XAML 顯示 RelativeLayout 其子系使用絕對值定位的 :
<ContentPage xmlns="http://xamarin.com/schemas/2014/forms"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
x:Class="RelativeLayoutDemos.Views.StylishHeaderDemoPage"
Title="Stylish header demo">
<RelativeLayout Margin="20">
<BoxView Color="Silver"
RelativeLayout.XConstraint="0"
RelativeLayout.YConstraint="10"
RelativeLayout.WidthConstraint="200"
RelativeLayout.HeightConstraint="5" />
<BoxView Color="Silver"
RelativeLayout.XConstraint="0"
RelativeLayout.YConstraint="20"
RelativeLayout.WidthConstraint="200"
RelativeLayout.HeightConstraint="5" />
<BoxView Color="Silver"
RelativeLayout.XConstraint="10"
RelativeLayout.YConstraint="0"
RelativeLayout.WidthConstraint="5"
RelativeLayout.HeightConstraint="65" />
<BoxView Color="Silver"
RelativeLayout.XConstraint="20"
RelativeLayout.YConstraint="0"
RelativeLayout.WidthConstraint="5"
RelativeLayout.HeightConstraint="65" />
<Label Text="Stylish header"
FontSize="24"
RelativeLayout.XConstraint="30"
RelativeLayout.YConstraint="25" />
</RelativeLayout>
</ContentPage>
在此範例中,會使用 和 YConstraint 附加屬性中指定的XConstraint值來定義每個BoxView物件的位置。 每個 BoxView 的大小都是使用 和 HeightConstraint 附加屬性中指定的WidthConstraint值來定義。 物件的位置Label也會使用 和 YConstraint 附加屬性中指定的XConstraint值來定義。 不過,不會針對 Label指定大小值,因此它不受限制且本身會調整大小。 在所有情況下,絕對值都代表裝置無關的單位。
下列螢幕擷取畫面顯示產生的版面配置:

對等的 C# 程式代碼如下所示:
public class StylishHeaderDemoPageCS : ContentPage
{
public StylishHeaderDemoPageCS()
{
RelativeLayout relativeLayout = new RelativeLayout
{
Margin = new Thickness(20)
};
relativeLayout.Children.Add(new BoxView
{
Color = Color.Silver
}, () => new Rectangle(0, 10, 200, 5));
relativeLayout.Children.Add(new BoxView
{
Color = Color.Silver
}, () => new Rectangle(0, 20, 200, 5));
relativeLayout.Children.Add(new BoxView
{
Color = Color.Silver
}, () => new Rectangle(10, 0, 5, 65));
relativeLayout.Children.Add(new BoxView
{
Color = Color.Silver
}, () => new Rectangle(20, 0, 5, 65));
relativeLayout.Children.Add(new Label
{
Text = "Stylish Header",
FontSize = 24
}, Constraint.Constant(30), Constraint.Constant(25));
Title = "Stylish header demo";
Content = relativeLayout;
}
}
在這裡範例中,BoxView物件會使用Add需要 Expression<Func<Rectangle>> 指定每個子系位置及大小的多載,新增至 RelativeLayout 。 的位置 Label 是使用 Add 需要選擇性 Constraint 物件的多載來定義,在此案例中是由 Constraint.Constant 方法所建立。
注意
RelativeLayout使用絕對值的 可以放置和調整子系的大小,使其不符合版面配置界限。
相對定位和重設大小
RelativeLayout可以使用相對於配置屬性或同層級元素的值來定位和調整子系的大小。 這可藉由將子系新增至 Children 的集合,並使用 物件將 每個子系上的 、 WidthConstraintYConstraint、 和 HeightConstraint 附加屬性設定XConstraint為相對值Constraint。RelativeLayout
條件約束可以是常數、相對於父系或相對於同層級。 條件約束的類型是由 ConstraintType 列舉來表示,其定義下列成員:
RelativeToParent,表示相對於父系的條件約束。RelativeToView,表示相對於檢視的條件約束(或同層級)。Constant,表示常數條件約束。
條件約束標記延伸
在 XAML 中, Constraint 物件可由標記延伸建立 ConstraintExpression 。 這個標記延伸通常用來將 子系內 RelativeLayout 的位置和大小與其父系或同層級產生關聯。
類別 ConstraintExpression 會定義下列屬性:
Constant型double別為 的 ,表示條件約束常數值。ElementName型string別為 的 ,表示要計算條件約束的來源項目名稱。Factor型double別的 ,表示相對於來源項目縮放限制維度的因數。 此屬性預設為 1。Property型string別為 的 ,表示要用於條件約束計算之來源專案上的屬性名稱。Type型別為ConstraintType的 ,表示條件約束的類型。
如需標記延伸的詳細資訊 Xamarin.Forms ,請參閱 XAML 標記延伸。
下列 XAML 顯示 RelativeLayout 其子系受到 ConstraintExpression 標記延伸的限制:
<ContentPage xmlns="http://xamarin.com/schemas/2014/forms"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
x:Class="RelativeLayoutDemos.Views.RelativePositioningAndSizingDemoPage"
Title="RelativeLayout demo">
<RelativeLayout>
<BoxView Color="Red"
RelativeLayout.XConstraint="{ConstraintExpression Type=Constant, Constant=0}"
RelativeLayout.YConstraint="{ConstraintExpression Type=Constant, Constant=0}" />
<BoxView Color="Green"
RelativeLayout.XConstraint="{ConstraintExpression Type=RelativeToParent, Property=Width, Constant=-40}"
RelativeLayout.YConstraint="{ConstraintExpression Type=Constant, Constant=0}" />
<BoxView Color="Blue"
RelativeLayout.XConstraint="{ConstraintExpression Type=Constant, Constant=0}"
RelativeLayout.YConstraint="{ConstraintExpression Type=RelativeToParent, Property=Height, Constant=-40}" />
<BoxView Color="Yellow"
RelativeLayout.XConstraint="{ConstraintExpression Type=RelativeToParent, Property=Width, Constant=-40}"
RelativeLayout.YConstraint="{ConstraintExpression Type=RelativeToParent, Property=Height, Constant=-40}" />
<!-- Centered and 1/3 width and height of parent -->
<BoxView x:Name="oneThird"
Color="Silver"
RelativeLayout.XConstraint="{ConstraintExpression Type=RelativeToParent, Property=Width, Factor=0.33}"
RelativeLayout.YConstraint="{ConstraintExpression Type=RelativeToParent, Property=Height, Factor=0.33}"
RelativeLayout.WidthConstraint="{ConstraintExpression Type=RelativeToParent, Property=Width, Factor=0.33}"
RelativeLayout.HeightConstraint="{ConstraintExpression Type=RelativeToParent, Property=Height, Factor=0.33}" />
<!-- 1/3 width and height of previous -->
<BoxView Color="Black"
RelativeLayout.XConstraint="{ConstraintExpression Type=RelativeToView, ElementName=oneThird, Property=X}"
RelativeLayout.YConstraint="{ConstraintExpression Type=RelativeToView, ElementName=oneThird, Property=Y}"
RelativeLayout.WidthConstraint="{ConstraintExpression Type=RelativeToView, ElementName=oneThird, Property=Width, Factor=0.33}"
RelativeLayout.HeightConstraint="{ConstraintExpression Type=RelativeToView, ElementName=oneThird, Property=Height, Factor=0.33}" />
</RelativeLayout>
</ContentPage>
在此範例中,每個 BoxView 物件的位置都是藉由設定 XConstraint 和 YConstraint 附加屬性來定義。 第一個 BoxView 屬性會將其 XConstraint 和 YConstraint 附加屬性設定為常數,也就是絕對值。 其餘 BoxView 物件都會使用至少一個相對值來設定其位置。 例如,黃色 BoxView 物件會將 XConstraint 附加屬性設定為其父代 ( RelativeLayout) 減 40 的寬度。 同樣地,這 BoxView 會將 YConstraint 附加屬性設定為其父代減去 40 的高度。 這可確保黃色 BoxView 會出現在畫面右下角。
注意
BoxView未指定大小的 物件會自動調整為 40x40。Xamarin.Forms
名為 oneThird 的銀BoxView級會相對於其父系,集中定位。 它的大小也相對於其父代,是其寬度和高度的三分之一。 這可藉由將 和 WidthConstraint 附加屬性設定XConstraint為父系的寬度來RelativeLayout達成,乘以 0.33。 同樣地, YConstraint 和 HeightConstraint 附加屬性會設定為父系的高度,乘以0.33。
黑色BoxView是相對於 的位置和大小oneThirdBoxView。 這可藉由將和 XConstraint 附加屬性分別設定為X同層級元素的和 YConstraint Y 值來達成。 同樣地,其大小會設定為其同層級元素的三分之一寬度和高度。 若要達成此目的,請將它 WidthConstraint 和 HeightConstraint 附加屬性分別設定為 Width 同層級專案的 和 Height 值,然後乘以 0.33。
下列螢幕擷取畫面顯示產生的版面配置:
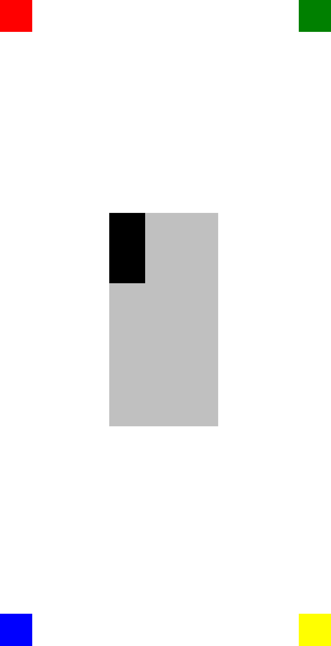
條件約束物件
類別 Constraint 會定義下列公用靜態方法,以傳回 Constraint 物件:
Constant,其會將子系限制為以double指定的大小。FromExpression,它會使用 Lambda 運算式來限制子系。RelativeToParent,其會限制子系相對於其父系的大小。RelativeToView,其會限制子系相對於檢視的大小。
此外,類別 BoundsConstraint 會定義單一方法, FromExpression它會傳回 BoundsConstraint ,其會使用 Expression<Func<Rectangle>>來限制子系的位置和大小。 這個方法可以用來設定 BoundsConstraint 附加屬性。
下列 C# 程式代碼顯示 RelativeLayout 其子系受 Constraint 物件限制的 :
public class RelativePositioningAndSizingDemoPageCS : ContentPage
{
public RelativePositioningAndSizingDemoPageCS()
{
RelativeLayout relativeLayout = new RelativeLayout();
// Four BoxView's
relativeLayout.Children.Add(
new BoxView { Color = Color.Red },
Constraint.Constant(0),
Constraint.Constant(0));
relativeLayout.Children.Add(
new BoxView { Color = Color.Green },
Constraint.RelativeToParent((parent) =>
{
return parent.Width - 40;
}), Constraint.Constant(0));
relativeLayout.Children.Add(
new BoxView { Color = Color.Blue },
Constraint.Constant(0),
Constraint.RelativeToParent((parent) =>
{
return parent.Height - 40;
}));
relativeLayout.Children.Add(
new BoxView { Color = Color.Yellow },
Constraint.RelativeToParent((parent) =>
{
return parent.Width - 40;
}),
Constraint.RelativeToParent((parent) =>
{
return parent.Height - 40;
}));
// Centered and 1/3 width and height of parent
BoxView silverBoxView = new BoxView { Color = Color.Silver };
relativeLayout.Children.Add(
silverBoxView,
Constraint.RelativeToParent((parent) =>
{
return parent.Width * 0.33;
}),
Constraint.RelativeToParent((parent) =>
{
return parent.Height * 0.33;
}),
Constraint.RelativeToParent((parent) =>
{
return parent.Width * 0.33;
}),
Constraint.RelativeToParent((parent) =>
{
return parent.Height * 0.33;
}));
// 1/3 width and height of previous
relativeLayout.Children.Add(
new BoxView { Color = Color.Black },
Constraint.RelativeToView(silverBoxView, (parent, sibling) =>
{
return sibling.X;
}),
Constraint.RelativeToView(silverBoxView, (parent, sibling) =>
{
return sibling.Y;
}),
Constraint.RelativeToView(silverBoxView, (parent, sibling) =>
{
return sibling.Width * 0.33;
}),
Constraint.RelativeToView(silverBoxView, (parent, sibling) =>
{
return sibling.Height * 0.33;
}));
Title = "RelativeLayout demo";
Content = relativeLayout;
}
}
在這裡範例中,子系會使用Add需要、 widthy、 和 height 自變數選擇性Constraint物件的 x多載加入至 RelativeLayout 。
注意
RelativeLayout使用相對值的 可以放置和調整子系的大小,使其不符合版面配置界限。