SMART on FHIR
Substitutable Medical Applications and Reusable Technologies (SMART on FHIR) is a healthcare standard through which applications can access clinical information through a data store. It adds a security layer based on open standards including OAuth2 and OpenID Connect, to FHIR® interfaces to enable integration with EHR systems. Using SMART on FHIR provides at least three important benefits:
- Applications have a known method for obtaining authentication/authorization to a FHIR repository.
- Users accessing a FHIR repository with SMART on FHIR are restricted to resources associated with the user, rather than having access to all data in the repository.
- Users have the ability to grant applications access to a limited set of their data by using SMART clinical scopes.
The following tutorials provide steps to enable SMART on FHIR applications with FHIR Service.
Prerequisites
- An instance of the FHIR Service
- .NET SDK 6.0
- Enable cross-origin resource sharing (CORS)
- Register public client application in Microsoft Entra ID
- After registering the application, make note of the
applicationIdfor client application.
- After registering the application, make note of the
- Ensure you have access to an Azure Subscription of FHIR service, to create resources and add role assignments.
SMART on FHIR using Azure Health Data Services Samples (SMART on FHIR (Enhanced))
Step 1: Set up FHIR SMART user role
Follow the steps listed in section Manage Users: Assign Users to Role. Any user added to this role will be able to access the FHIR Service, provided their requests comply with the SMART on FHIR implementation Guide. The access granted to the users in this role will then be limited by the resources associated to their fhirUser compartment and the restrictions in the clinical scopes.
Note
SMART on FHIR Implementation Guide defines access to FHIR resource types with scopes. These scopes impact the access an application may have to FHIR resources. A user with the SMART user role has access to perform read API interactions on FHIR service. SMART user role does not grant write access to FHIR service.
Step 2: FHIR server integration with samples
Click on this link to navigate to Azure Health Data and AI Samples open source solution. The steps listed in the document enable integration of FHIR server with other Azure Services (such as APIM, Azure functions and more).
Note
Samples are open-source code, and you should review the information and licensing terms on GitHub before using it. They are not part of the Azure Health Data Service and are not supported by Microsoft Support. These samples are used to demonstrate how Azure Health Data Services (AHDS) and other open-source tools can be used together to demonstrate §170.315(g)(10) Standardized API for patient and population services criterion compliance, using Microsoft Entra ID as the identity provider workflow.
SMART on FHIR Proxy
Click to expand!
Note
This is another option to SMART on FHIR(Enhanced) using the AHDS Samples previously mentioned. We suggest you to adopt SMART on FHIR(Enhanced). SMART on FHIR Proxy option is a legacy option. SMART on FHIR(Enhanced) provides added capabilities to SMART on FHIR proxy. SMART on FHIR(Enhanced) meets requirements in SMART on FHIR Implementation Guide (v 1.0.0) and §170.315(g)(10) Standardized API for patient and population services criterion.
Step 1: Set admin consent for your client application
To use SMART on FHIR, you must first authenticate and authorize the app. The first time you use SMART on FHIR, you must also get administrative consent to let the app access your FHIR resources.
If you don't have an ownership role in the app, contact the app owner and ask them to grant admin consent for you in the app.
If you do have administrative privileges, complete the following steps to grant admin consent to yourself directly. (You can also grant admin consent to yourself later when prompted in the app.) You can use these same steps to add other users as owners, so they can view and edit the app registration.
To add yourself or another user as owner of an app:
- In the Azure portal, go to Microsoft Entra ID.
- In the left menu, select App Registration.
- Search for the app registration you created, and then select it.
- In the left menu, under Manage, select Owners.
- Select Add owners, and then add yourself or the user you want to have admin consent.
- Select Save
Step 2: Enable the SMART on FHIR proxy
SMART on FHIR requires that Audience has an identifier URI equal to the URI of the FHIR service. The standard configuration of the FHIR service uses an Audience value of https://fhir.azurehealthcareapis.com. However, you can also set a value matching the specific URL of your FHIR service (for example https://MYFHIRAPI.fhir.azurehealthcareapis.com). This is required when working with the SMART on FHIR proxy.
To enable the SMART on FHIR proxy in the Authentication settings for your FHIR instance, select the SMART on FHIR proxy check box.
The SMART on FHIR proxy acts as an intermediary between the SMART on FHIR app and Microsoft Entra ID. The authentication reply (the authentication code) must go to the SMART on FHIR proxy instead of the app itself. The proxy then forwards the reply to the app.
Because of this two-step relay of the authentication code, you need to set the reply URL (callback) for your Microsoft Entra client application to a URL that is a combination of the reply URL for the SMART on FHIR proxy, and the reply URL for the SMART on FHIR app. The combined reply URL takes the following form.
https://MYFHIRAPI.azurehealthcareapis.com/AadSmartOnFhirProxy/callback/aHR0cHM6Ly9sb2NhbGhvc3Q6NTAwMS9zYW1wbGVhcHAvaW5kZXguaHRtbA
In the reply, aHR0cHM6Ly9sb2NhbGhvc3Q6NTAwMS9zYW1wbGVhcHAvaW5kZXguaHRtbA is a URL-safe, base64-encoded version of the reply URL for the SMART on FHIR app. For the SMART on FHIR app launcher, when the app is running locally, the reply URL is https://localhost:5001/sampleapp/index.html.
You can generate the combined reply URL by using a script like the following.
$replyUrl = "https://localhost:5001/sampleapp/index.html"
$fhirServerUrl = "https://MYFHIRAPI.fhir.azurewebsites.net"
$bytes = [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetBytes($ReplyUrl)
$encodedText = [Convert]::ToBase64String($bytes)
$encodedText = $encodedText.TrimEnd('=');
$encodedText = $encodedText.Replace('/','_');
$encodedText = $encodedText.Replace('+','-');
$newReplyUrl = $FhirServerUrl.TrimEnd('/') + "/AadSmartOnFhirProxy/callback/" + $encodedText
Add the reply URL to the public client application that you created previously for Microsoft Entra ID.
Step 3: Get a test patient
To test the FHIR service and the SMART on FHIR proxy, you need to have at least one patient in the database. If you've not used the API yet, and you don't have data in the database, see Access the FHIR service using Postman to load a patient. Make a note of the ID of a specific patient.
Step 4: Download the SMART on FHIR app launcher
The open-source FHIR Server for Azure repository includes a simple SMART on FHIR app launcher and a sample SMART on FHIR app. In this tutorial, use this SMART on FHIR app launcher locally to test the setup.
You can clone the GitHub repository and go to the application by using the following commands.
git clone https://github.com/Microsoft/fhir-server
cd fhir-server/samples/apps/SmartLauncher
The application needs a few configuration settings, which you can set in appsettings.json:
{
"FhirServerUrl": "https://MYFHIRAPI.fhir.azurehealthcareapis.com",
"ClientId": "APP-ID",
"DefaultSmartAppUrl": "/sampleapp/launch.html"
}
We recommend you use the dotnet user-secrets feature:
dotnet user-secrets set FhirServerUrl https://MYFHIRAPI.fhir.azurehealthcareapis.com
dotnet user-secrets set ClientId <APP-ID>
Use the following command to run the application:
dotnet run
Step 5: Test the SMART on FHIR proxy
After you start the SMART on FHIR app launcher, you can point your browser to https://localhost:5001, where you should see the following:

When you enter Patient, Encounter, or Practitioner information, you notice that the Launch context is updated. When you're using the FHIR service, the launch context is simply a JSON document that contains information about patient, practitioner, and more. This launch context is base64 encoded and passed to the SMART on FHIR app as the launch query parameter. According to the SMART on FHIR specification, this variable is opaque to the SMART on FHIR app and passed on to the identity provider.
The SMART on FHIR proxy uses this information to populate fields in the token response. The SMART on FHIR app can use these fields to control which patient it requests data for, and how it renders the application on the screen. The SMART on FHIR proxy supports the following fields.
patientencounterpractitionerneed_patient_bannersmart_style_url
These fields are meant to provide guidance to the app, but they don't convey any security information. A SMART on FHIR application can ignore them.
Notice that the SMART on FHIR app launcher updates the Launch URL information at the bottom of the page. Select Launch to start the sample app, and you should see something like the following.
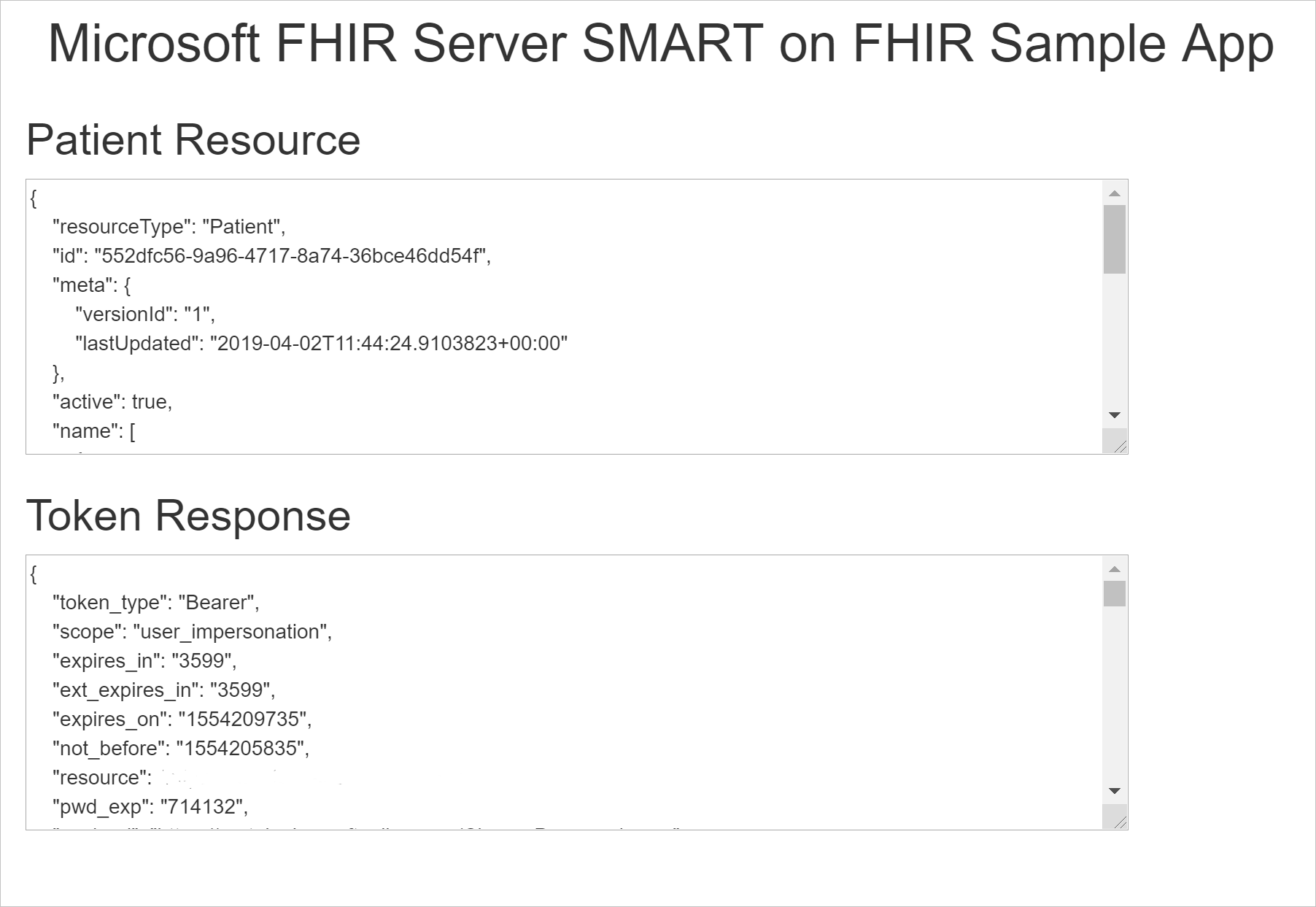
Inspect the token response to see how the launch context fields are passed on to the app.
Migrate from SMART on FHIR Proxy to SMART on FHIR (Enhanced)
Important
SMART on FHIR proxy is retiring in September 2026, transition to the SMART on FHIR (Enhanced) by that date. Beginning September 2026, applications relying on SMART on FHIR proxy will report errors in accessing the FHIR service.
SMART on FHIR (Enhanced) provides more capabilities compared to SMART on FHIR proxy. SMART on FHIR(Enhanced) can be considered to meet requirements with SMART on FHIR Implementation Guide (v 1.0.0) and §170.315(g)(10) Standardized API for patient and population services criterion. The following table lists the difference between SMART on FHIR proxy and SMART on FHIR (Enhanced).
| Capability | SMART on FHIR (Enhanced) | SMART on FHIR proxy |
|---|---|---|
| Supports Standalone Launch | Yes | No |
| Supports EHR Launch | Yes | Yes |
| Supports scope restrictions | Yes | No |
| Relies on first party Azure products | Yes, Azure products such as Azure API Management (APIM) need to be integrated | No |
| Microsoft Support | Supported for FHIR service.Open-source sample support needs to be reported and monitored via GitHub | Supported for FHIR service |
Migration Steps
- Step 1: Set up FHIR SMART user role Follow the steps listed under section Manage Users: Assign Users to Role. Any user added to SMART user role is able to access the FHIR Service, if their requests comply with the SMART on FHIR implementation Guide.
- Step 2: Deploy SMART on FHIR sample under Azure Health Data and AI OSS samples
- Step 3: Update endpoint of the FHIR service url to '{{BASEURL_FROM_APIM}}/smart.'
- Step 4: Uncheck the SMART on FHIR proxy setting under Authentication blade for the FHIR service.
If you have questions, you can get answers from community experts in Microsoft Q&A. For technical support, you can also create a support request.
Next steps
Now that you've learned about enabling SMART on FHIR functionality, see the search samples page for details about how to search using search parameters, modifiers, and other FHIR search methods.
Note
FHIR® is a registered trademark of HL7 and is used with the permission of HL7.