This article addresses some common questions about NVMe support on virtual machines created in Azure.
Overview
What is NVMe?
NVMe stands for nonvolatile memory express, a communication protocol that facilitates faster and more efficient data transfer between servers and storage systems. With NVMe, data can be transferred at the highest throughput and with the fastest response times. NVMe offers higher IOPS (Input/Output Operations Per Second) and throughput (MB/s), which can significantly improve the performance of both temp (local) and remote NVMe disk storage with Azure managed disks. Higher performance is especially beneficial for IO-intensive workloads that require fast data transfer to the Azure managed disks.
Which types of storage interfaces are supported in Azure’s VM families?
In Azure, there are two types of storage interfaces that we support, SCSI (Small Computer System Interface) and NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory express). The SCSI interface is a legacy standard that provides physical connectivity and data transfer between computers and peripheral devices. NVMe is similar to SCSI in that it provides connectivity and data transfer, but NVMe is a significantly faster and more efficient interface for data transfer between servers and storage systems.
How do Azure Boost and NVMe improve the performance of the VMs that Azure offers?
Azure Boost is a system designed by Microsoft that offloads server virtualization processes traditionally performed by the hypervisor and host OS onto purpose-built software and hardware, enabling faster storage and networking performance for Azure VM customers. One of the primary advantages of Azure Boost is its ability to enhance the throughput of Azure Managed Disks and local storage. This enhancement is enabled by offloading the storage processing tasks to Azure Boost’s dedicated hardware. Furthermore, Azure Boost optimizes performance by utilizing the industry standard NVMe interface, which capitalizes on the low latency and internal parallelism of solid-state storage drives. Refer to the Microsoft Azure Boost General Availability Blog for details on the performance offered.
Will Azure continue to support SCSI interface VMs?
Yes, Azure will continue to support the SCSI interface on the versions of VM offerings which offer SCSI storage, but not all new VM series will have SCSI storage as an option going forward.
NVMe Supportability
Which VM generations support NVMe Disks?
Typically, the older generations of General Purpose, Memory Optimized, and Compute Optimized VMs (i.e. D/Ev5 or Fv2 and older) support SCSI, whereas the newer generations (e.g. Da/Ea/Fav6 or after) support only the NVMe storage interface. However, Ebsv5/Ebdsv5 and Lsv2/Lsv3/Lasv3 VMs have introduced NVMe as an option for temp disk.
Always check the detailed product pages for specifics about which VM generations support which storage types.
Will Gen 1 VMs be supported with NVMe disks?
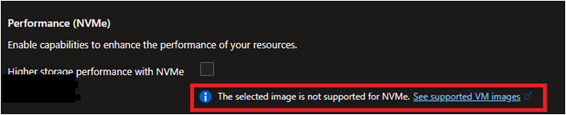
No, there are no plans to support NVMe disks on Gen 1 VMs. If you think your workload benefits from NVMe performance, you must switch to the Gen 2 VMs. Refer to the steps to create a new Gen 2 VM. If you attempt to use a Gen 1 VM image, you'll either not be able to select an NVMe capable VM or receive an error message that reads: "The selected image isn't supported for NVMe. See supported VM images".
What happens if the OS I use is not tagged as NVMe supported?
An NVMe VM can only be created using an image (Platform Image Repository (PIR) & Azure Compute Gallery) that has been tagged as NVMe. If an untagged image is used, a SCSI VM is created, and the VM may not perform as you had intended. Make sure to follow all instructions listed here. To launch VMs with an NVMe interface, it's essential to choose one of the supported OS images tagged as NVMe. If your current OS image is not supported for NVMe, you'll see an error message that reads: "The selected image isn't supported for NVMe. See supported VM images".
When will NVMe support be added to the OS image I currently use?
NVMe support is available in 50+ of the most popular OS images. We are not adding NVMe support to older OS images. However, we continuously improve the OS image coverage and recommend referring to this page for updates on the latest OS image support added for both Linux and Windows.
What happens if the OS I want to use does not support NVMe?
Many of the latest Azure VM generations are NVMe-only and require an OS image that supports NVMe which can be found here. If you require an OS that does not support NVMe, you should utilize a VM series that still has SCSI support.
How can I launch a VM with the NVMe interface?
NVMe can be enabled during VM creation using various methods such as: Azure portal, CLI, PowerShell, and ARM templates. To create an NVMe VM, you must first enable the NVMe option on a VM and select the NVMe controller disk type for the VM. Note that the NVMe diskcontrollertype can be enabled during creation or updated to NVMe when the VM is stopped and deallocated, provided that the VM size supports NVMe.
Azure portal view
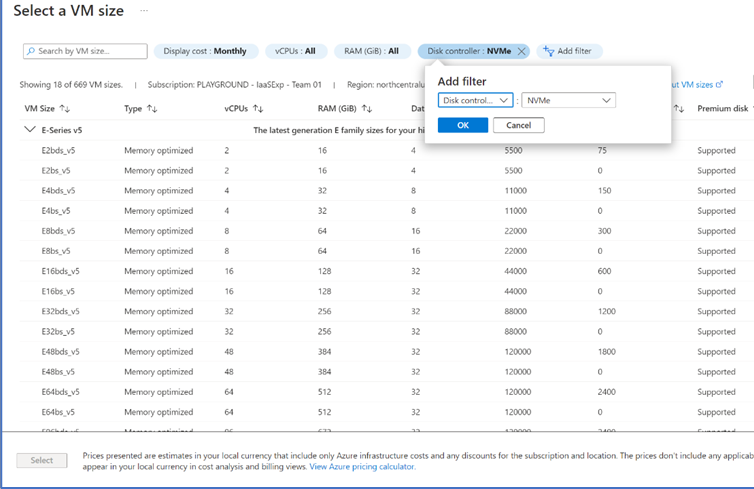
Add Disk Controller Filter. To find the NVMe eligible sizes, select See All Sizes, select the Disk Controller filter, and then select NVMe:
Enable NVMe feature by visiting the Advanced tab.
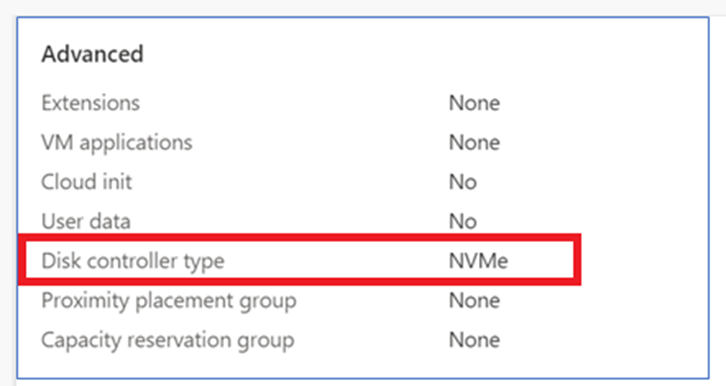
Verify Feature is enabled by going to Review and Create.
Azure storage performance with NVMe disks
What types of workloads benefit from NVMe disks?
The VM families utilizing NVMe disk will demonstrate performance benefits compared to SCSI across various workloads that require higher I/O and improved storage performance. These benefits will be achieved across VMs that utilize temp and/or remote NVMe disks. Using VMs with NVMe disks will enable performance benefits across many workloads ranging from application servers, web servers, databases, data warehousing, analytics, and more.
What performance gains can I expect from NVMe disks?
The performance gains that your applications can achieve depend on several factors, including VM type, VM size, and I/O block size. To identify the ideal block size and to achieve peak transfer rates, please test on the individual VM sizes. It is important to optimize the I/O size based on the specific requirements of your application. More details on the performance capabilities of individual VM types can be found on their detailed product pages.