Poznámka:
Přístup k této stránce vyžaduje autorizaci. Můžete se zkusit přihlásit nebo změnit adresáře.
Přístup k této stránce vyžaduje autorizaci. Můžete zkusit změnit adresáře.
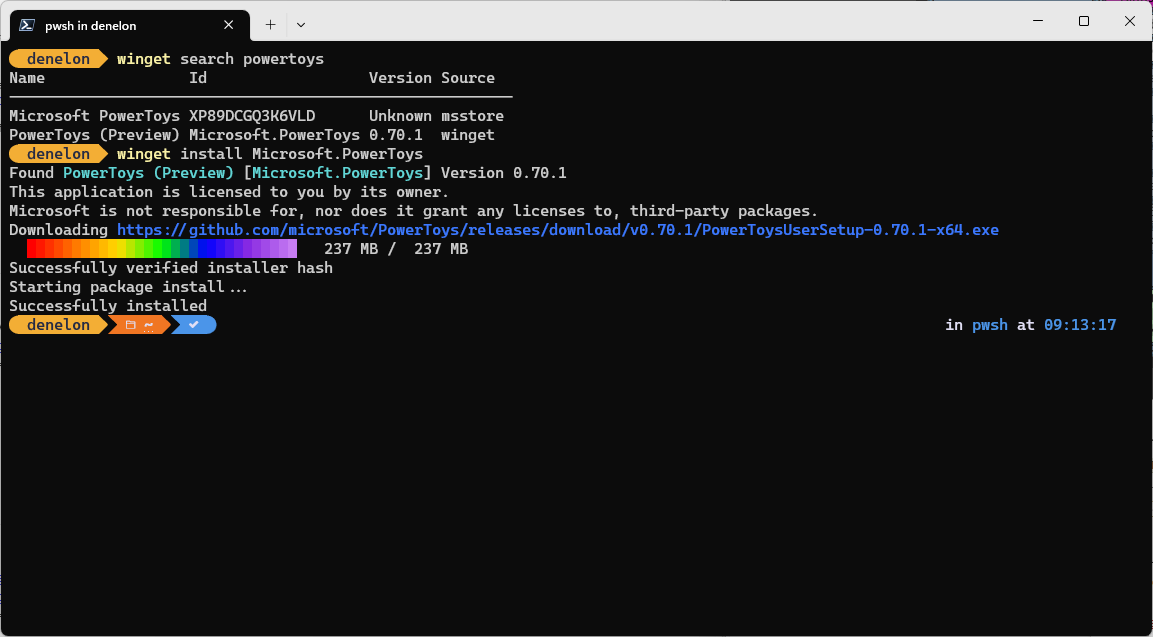
Příkaz installwinGet nainstaluje zadanou aplikaci. Pomocí vyhledávacího příkazu identifikujte aplikaci, kterou chcete nainstalovat. Pomocí příkazu show zobrazíte podrobnosti o aplikaci a instalačním programu vybraném nástrojem WinGet pro váš systém.
Příkaz install vyžaduje, abyste zadali přesný řetězec, který chcete nainstalovat. Pokud existuje nějaká nejednoznačnost, zobrazí se výzva k dalšímu filtrování příkazu install na konkrétní aplikaci.
Použití
winget install [[-q] <query> ...] [<options>]
Přezdívky
Pro tento příkaz jsou k dispozici následující aliasy:
- přidat
Argumenty
K dispozici jsou následující argumenty.
| Důvod | Popis |
|---|---|
| -q,--query | Dotaz použitý k vyhledání aplikace. |
Poznámka:
Argument dotazu je poziční. Syntaxe stylu zástupných symbolů není podporována. Nejčastěji se jedná o řetězec znaků, u kterých očekáváte jedinečnou identifikaci balíčku, který chcete nainstalovat.
Možnosti
Možnosti umožňují přizpůsobit prostředí instalace tak, aby vyhovovalo vašim potřebám.
| Možnost | Popis |
|---|---|
| -m, --manifest | Za tím musí následovat cesta k souboru manifestu ve formátu YAML. Manifest můžete použít ke spuštění instalačního procesu z místního souboru YAML. |
| --id | Omezuje instalaci na ID aplikace. |
| --Jméno | Omezí vyhledávání na název aplikace. |
| --přezdívka | Omezí vyhledávání na moniker uvedený pro aplikaci. |
| -v, --version | Umožňuje zadat přesnou verzi, kterou chcete nainstalovat. Pokud není zadaný, nejnovější nainstaluje aplikaci s nejvyšší verzí. |
| -s, --zdroj | Omezí hledání na zadaný název zdroje. Musí následovat název zdroje. |
| --rozsah | Umožňuje určit, jestli má instalační program cílit na obor uživatele nebo počítače. Viz známé problémy související s rozsahem instalace balíčku. |
| -a, --architektura | Vyberte architekturu, která se má nainstalovat. |
| --typ-instalátoru | Vyberte typ instalačního programu, který chcete nainstalovat. Viz podporované typy instalačního programu pro klienta WinGet. |
| -e, --přesný | Používá přesný řetězec v dotazu, včetně zohlednění citlivosti na malá a velká písmena. Nebude používat výchozí chování podřetězího řetězce. |
| -i, --interactive | Spustí instalační program v interaktivním režimu. Výchozí prostředí zobrazuje průběh instalačního programu. |
| -h, --tichý | Spustí instalační program v tichém režimu. Tím se potlačí veškeré uživatelské rozhraní. Výchozí prostředí zobrazuje průběh instalačního programu. |
| --místo | Určuje, které národní prostředí se má použít (formát BCP47). |
| -o, --log | Směruje protokolování do logovacího souboru. Musíte zadat cestu k souboru, ke kterému máte práva k zápisu. |
| – vlastní | Argumenty, které se mají předat instalačnímu programu kromě výchozích hodnot. |
| — přepsání | Řetězec, který bude předán přímo instalačnímu programu. |
| -l, --umístění | Umístění, do které se má nainstalovat (pokud je podporováno). |
| --ignorovat-bezpečnostní-hash | Ignorujte selhání hash kontroly instalačního programu. Nedoporučuje se. |
| --allow-reboot | Povolí restartování, pokud je to možné. |
| --skip-dependencies | Přeskočí zpracování závislostí balíčků a funkcí systému Windows. |
| --ignore-local-archive-malware-scan | Ignorovat kontrolu malwaru provedenou v rámci instalace balíčku typu archivu z místního manifestu. |
| --dependency-source | Vyhledejte závislosti balíčků pomocí zadaného zdroje. |
| --přijmout-smlouvy-baliků | Používá se k přijetí licenční smlouvy a vyhnutí se výzvě. |
| --bez-aktualizace | Pokud už nainstalovaná verze existuje, upgrade přeskočí. |
| --záhlaví | Volitelná hlavička HTTP zdroje REST pro Windows -Package-Manager. |
| --authentication-mode | Zadejte předvolbu ověřovacího okna (tiché, silentPreferred nebo interaktivní). |
| --authentizační-účet | Zadejte účet, který se má použít k ověřování. |
| --přijmout-dohody-o-zdroji | Používá se k přijetí licenční smlouvy zdroje a vyhnutí se zobrazení výzvy. |
| -r, --přejmenovat | Hodnota pro přejmenování spustitelného souboru (přenosného). |
| --odinstalovat-předchozí | Odinstalujte předchozí verzi balíčku během upgradu. |
| --síla | Příkaz spusťte přímo a pokračujte problémy nesouvisenými se zabezpečením. |
| -?--Pomoc | Získejte další nápovědu k tomuto příkazu. |
| --Počkej | Před ukončením vyzve uživatele, aby stiskl libovolnou klávesu. |
| --logy,--otevřít-logy | Otevřete výchozí umístění protokolů. |
| --verbose, --verbose-logs | Slouží k přenastavení nastavení protokolování a vytvoření podrobného protokolu. |
| --nowarn,--ignore-warnings (bez varování, ignorovat varování) | Potlačí varovné výstupy. |
| --zakázat-interaktivitu | Zakažte interaktivní výzvy. |
| --plná moc | Nastavte proxy server, který se má použít pro toto spuštění. |
| --no-proxy | Zakažte použití proxy serveru pro toto spuštění. |
Příkladové dotazy
Následující příklad nainstaluje konkrétní verzi aplikace.
winget install powertoys --version 0.91.1
Následující příklad nainstaluje aplikaci podle jejího ID.
winget install --id Microsoft.PowerToys
Následující příklad nainstaluje aplikaci podle verze a ID.
winget install --id Microsoft.PowerToys --version 0.91.1
Více výběrů
Pokud dotaz poskytnutý pro WinGet nemá za následek jednu aplikaci, nástroj WinGet zobrazí výsledky hledání. Tím získáte další data potřebná k upřesnění hledání správné instalace.
Nejlepším způsobem, jak omezit výběr na jeden soubor, je použít ID aplikace v kombinaci s přesnou volbou dotazu . Například:
winget install --id Git.Git -e
Pokud je nakonfigurovaných více zdrojů, je možné mít duplicitní položky. Zadání zdroje je nutné k dalšímu objasnění.
winget install --id Git.Git -e --source winget
Zdroj msstore používá jedinečné identifikátory jako ID pro balíčky. Nevyžadují přesnou možnost dotazu. Například:
winget install XP9KHM4BK9FZ7Q -s msstore
Můžete také použít příkaz install k instalaci více balíčků. Například:
winget install Microsoft.Edit Microsoft.NuGet
Místní instalace
Možnost manifestu umožňuje nainstalovat aplikaci předáním souboru YAML přímo klientovi. Pokud je manifest manifestem s více soubory, musí být použit adresář obsahující soubory. Možnost manifestu má následující využití.
Použití: winget install --manifest \<path>
| Možnost | Popis |
|---|---|
| -m, --manifest | Cesta k manifestům aplikace, které se mají nainstalovat. |
Instalace balíčků z místních souborů manifestu může mít rizika. Jako další opatření pro zajištění bezpečnostních opatření musí tuto funkci povolit správce. Chcete-li tuto funkci povolit, spusťte winget settings --enable LocalManifestFiles. Chcete-li tuto funkci zakázat, spusťte winget settings --disable LocalManifestFiles.
Soubory protokolu
Soubory protokolů pro WinGet, pokud nejsou přesměrovány, budou umístěny v následující složce: \%LOCALAPPDATA%\\Packages\\Microsoft.DesktopAppInstaller_8wekyb3d8bbwe\\LocalState\\DiagOutputDir\\*.log
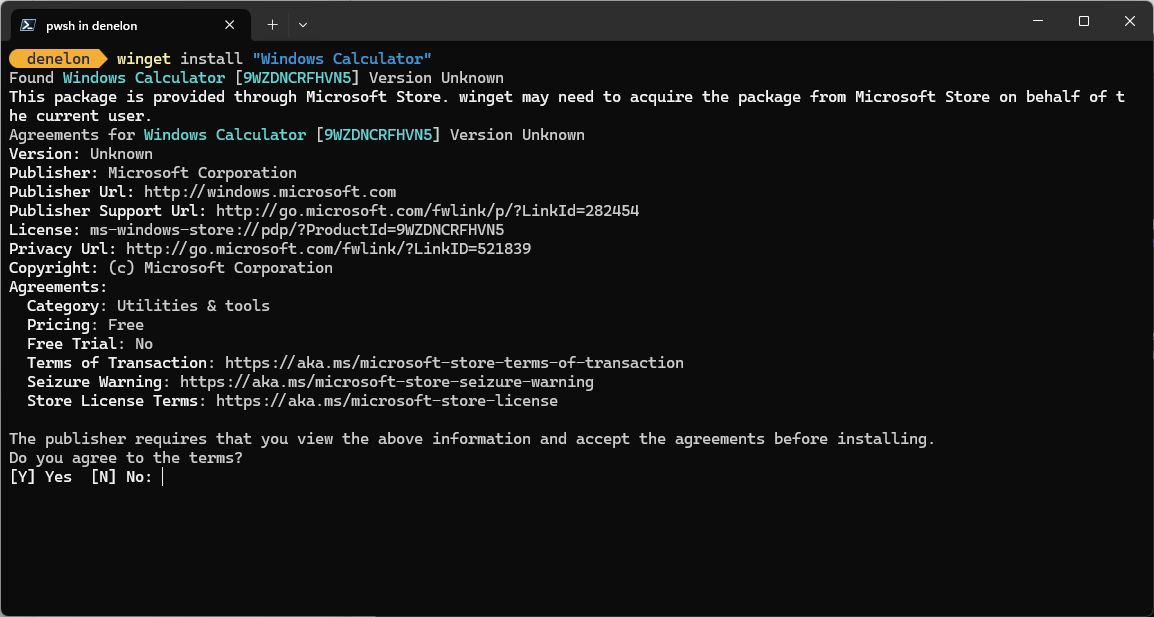
Licenční smlouvy
Některé aplikace při instalaci budou před instalací vyžadovat souhlas uživatele s licencí nebo jinými smlouvami. Pokud k tomu dojde, Správce balíčků systému Windows vyzve uživatele, aby souhlasil se smlouvami. Pokud uživatel nesouhlasí, aplikace se nenainstaluje.
Z příkazového řádku můžete smlouvy automaticky přijmout předáním následující možnosti --accept-package-agreements na příkazovém řádku. To může být užitečné při skriptování Správce balíčků systému Windows.
Související témata
Windows developer