Træning
Certificering
Microsoft Certified: Power Automate RPA Developer Associate - Certifications
Demonstrer, hvordan du kan forbedre og automatisere arbejdsprocesser med Microsoft Power Automate RPA-udvikler.
Denne browser understøttes ikke længere.
Opgrader til Microsoft Edge for at drage fordel af de nyeste funktioner, sikkerhedsopdateringer og teknisk support.
Bemærk
Adgang til denne side kræver godkendelse. Du kan prøve at logge på eller ændre mapper.
Adgang til denne side kræver godkendelse. Du kan prøve at ændre mapper.
An Azure Automation connection asset contains the information listed below. This information is required for connection to an external service or application from a runbook or DSC configuration.
The connection asset keeps together all properties for connecting to a particular application, making it unnecessary to create multiple variables. You can edit the values for a connection in one place, and you can pass the name of a connection to a runbook or DSC configuration in a single parameter. The runbook or configuration accesses the properties for a connection using the internal Get-AutomationConnection cmdlet.
When you create a connection, you must specify a connection type. The connection type is a template that defines a set of properties. You can add a connection type to Azure Automation using an integration module with a metadata file. It's also possible to create a connection type using the Azure Automation API if the integration module includes a connection type and is imported into your Automation account.
Bemærk
Secure assets in Azure Automation include credentials, certificates, connections, and encrypted variables. These assets are encrypted and stored in Azure Automation using a unique key that is generated for each Automation account. Azure Automation stores the key in the system-managed Key Vault. Before storing a secure asset, Automation loads the key from Key Vault and then uses it to encrypt the asset.
Azure Automation makes the following built-in connection types available:
Azure - Represents a connection used to manage classic resources.AzureServicePrincipal - Represents a connection used to manage resources in Azure using a service principal.AzureClassicCertificate - This connection type is used to manage resources in Azure that were created using the classic deployment model that doesn't support Service Principal authentication.The cmdlets in the following table create and manage Automation connections with PowerShell. They ship as part of the Az modules.
| Cmdlet | Description |
|---|---|
| Get-AzAutomationConnection | Retrieves information about a connection. |
| New-AzAutomationConnection | Creates a new connection. |
| Remove-AzAutomationConnection | Removes an existing connection. |
| Set-AzAutomationConnectionFieldValue | Sets the value of a particular field for an existing connection. |
The internal cmdlet in the following table is used to access connections in your runbooks and DSC configurations. This cmdlet comes with the global module Orchestrator.AssetManagement.Cmdlets. For more information, see Internal cmdlets.
| Internal Cmdlet | Description |
|---|---|
Get-AutomationConnection |
Retrieves the values of the different fields in the connection and returns them as a hashtable. You can then use this hashtable with the appropriate commands in the runbook or DSC configuration. |
Bemærk
Avoid using variables with the Name parameter of Get-AutomationConnection. Use of variables in this case can complicate discovery of dependencies between runbooks or DSC configurations and connection assets at design time.
The function in the following table is used to access connections in a Python 2 and 3 runbook. Python 3 runbooks are currently in preview.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
automationassets.get_automation_connection |
Retrieves a connection. Returns a dictionary with the properties of the connection. |
Bemærk
You must import the automationassets module at the top of your Python runbook to access the asset functions.
To create a new connection in the Azure portal:
Azure, AzureServicePrincipal, and AzureClassicCertificate.Create a new connection with Windows PowerShell using the New-AzAutomationConnection cmdlet. This cmdlet has a ConnectionFieldValues parameter that expects a hashtable defining values for each of the properties defined by the connection type.
You can use the following example commands to create a connection that can be used for authentication using Azure Service Principal.
$ConnectionAssetName = "AzureConnection"
$ConnectionFieldValues = @{"ApplicationId" = $Application.ApplicationId; "TenantId" = $TenantID.TenantId; "CertificateThumbprint" = $Cert.Thumbprint; "SubscriptionId" = $SubscriptionId}
New-AzAutomationConnection -ResourceGroupName $ResourceGroup -AutomationAccountName $AutomationAccountName -Name $ConnectionAssetName -ConnectionTypeName AzureServicePrincipal -ConnectionFieldValues $ConnectionFieldValues
If you try to create a new connection asset to connect to a service or application with a different authentication method, the operation fails because the connection type is not already defined in your Automation account. For more information on creating your own connection type for a custom module, see Add a connection type.
If your runbook or DSC configuration connects to an external service, you must define a connection type in a custom module called an integration module. This module includes a metadata file that specifies connection type properties and is named <ModuleName>-Automation.json, located in the module folder of your compressed .zip file. This file contains the fields of a connection that are required to connect to the system or service that the module represents. Using this file, you can set the field names, data types, encryption status, and optional status for the connection type. Multiple connection types are not supported in this file.
The following example is a template in the .json file format that defines user name and password properties for a custom connection type called MyModuleConnection:
{
"ConnectionFields": [
{
"IsEncrypted": false,
"IsOptional": true,
"Name": "Username",
"TypeName": "System.String"
},
{
"IsEncrypted": true,
"IsOptional": false,
"Name": "Password",
"TypeName": "System.String"
}
],
"ConnectionTypeName": "MyModuleConnection",
"IntegrationModuleName": "MyModule"
}
Retrieve a connection in a runbook or DSC configuration with the internal Get-AutomationConnection cmdlet. This cmdlet is preferred over the Get-AzAutomationConnection cmdlet, as it retrieves the connection values instead of information about the connection.
The following example shows how to use a connection to authenticate with Azure Resource Manager resources in your runbook. It uses a connection asset, which references the certificate-based service principal.
$Conn = Get-AutomationConnection -Name AzureConnection
Connect-AzAccount -ServicePrincipal -Tenant $Conn.TenantID -ApplicationId $Conn.ApplicationID -CertificateThumbprint $Conn.CertificateThumbprint
You can add an activity for the internal Get-AutomationConnection cmdlet to a graphical runbook. Right-click the connection in the Library pane of the graphical editor and select Add to canvas.
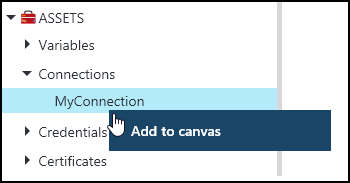
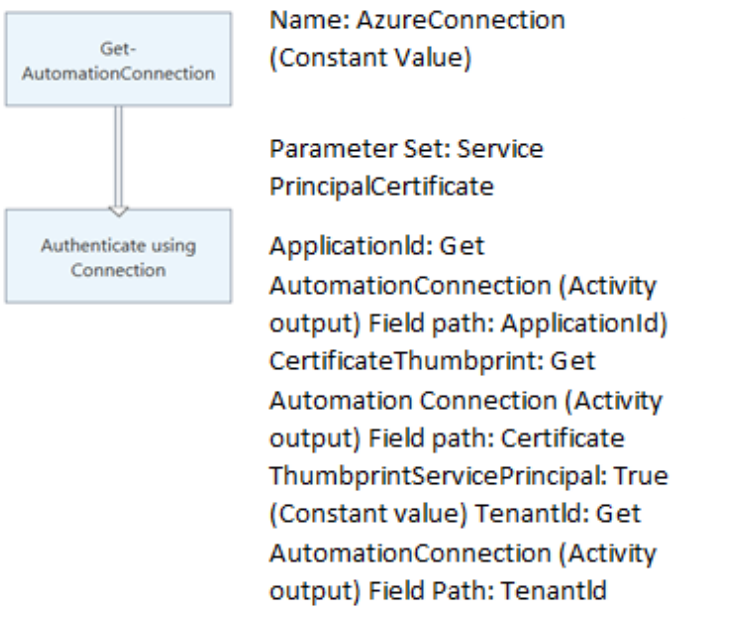
The following image shows an example of using a connection object in a graphical runbook.
Træning
Certificering
Microsoft Certified: Power Automate RPA Developer Associate - Certifications
Demonstrer, hvordan du kan forbedre og automatisere arbejdsprocesser med Microsoft Power Automate RPA-udvikler.