Azure ExpressRoute for Microsoft 365
This article applies to Microsoft 365 Enterprise.
Learn how Azure ExpressRoute is used with Microsoft 365 and how to plan the network implementation project that will be required if you meet specific requirements for deploying Azure ExpressRoute for use with Microsoft 365.
Note
We do not recommend ExpressRoute for Microsoft 365 because it does not provide the best connectivity model for the service in most circumstances. As such, Microsoft authorization is required to use this connectivity model. We review every customer request and authorize ExpressRoute for Microsoft 365 only in the rare scenarios where it is necessary. Please read the ExpressRoute for Microsoft 365 guide for more information and following a comprehensive review of the document with your productivity, network, and security teams, work with your Microsoft account team to submit an exception if needed. Unauthorized subscriptions trying to create route filters for Microsoft 365 will receive an error message.
Planning Azure ExpressRoute for Microsoft 365
In addition to internet connectivity, you may choose to route a subset of your Microsoft 365 network traffic over Azure ExpressRoute.
Regardless of whether you have an existing MPLS WAN, ExpressRoute can be added to your network architecture in one of three ways; through a supported cloud exchange colocation provider, an Ethernet point-to-point connection provider, or through an MPLS connection provider. See what providers are available in your region. The direct ExpressRoute connection enables connectivity to the applications outlined in What Microsoft 365 services are included?. Network traffic for all other applications and services will continue to traverse the internet.
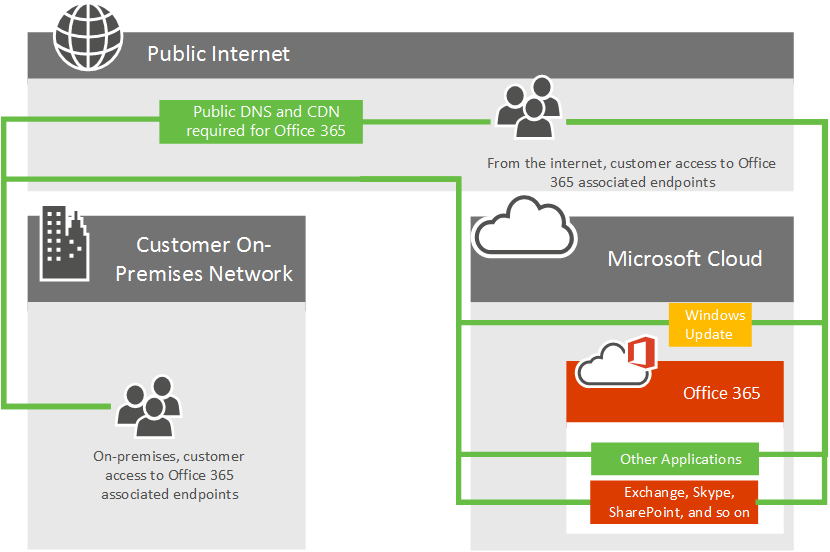
Consider the following high level network diagram, which shows a typical Microsoft 365 customer connecting to Microsoft's datacenters over the internet for access to all Microsoft applications such as Microsoft 365, Windows Update, and TechNet. Customers use a similar network path regardless of whether they're connecting from an on-premises network or from an independent internet connection.
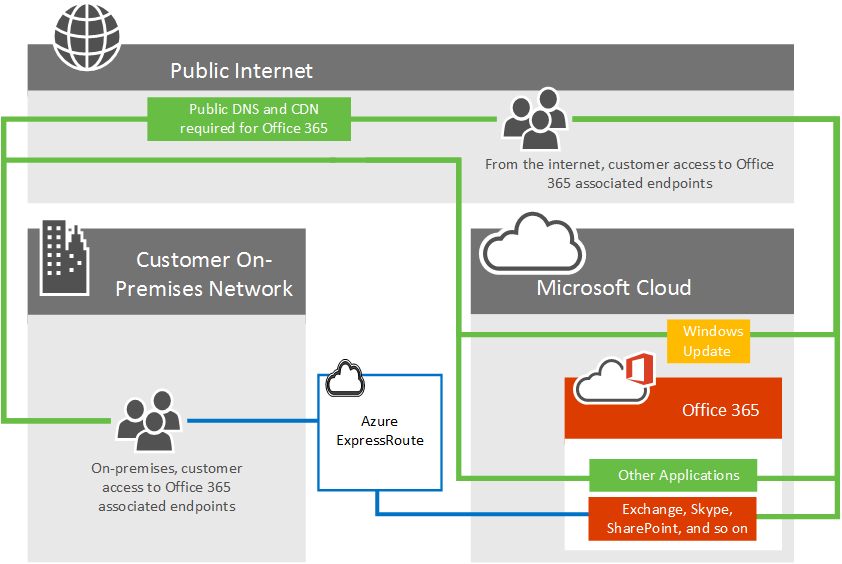
Now look at the updated diagram, which depicts a Microsoft 365 customer who uses both the internet and ExpressRoute to connect to Microsoft 365. Notice that some connections such as Public DNS and Content Delivery Network nodes still require the public internet connection. Also notice the customer's users who aren't located in their ExpressRoute connected building are connecting over the Internet.
What Microsoft 365 services are included?
The following table lists the Microsoft 365 services that are supported over ExpressRoute. Review the Microsoft 365 endpoints article to understand which network requests for these applications require internet connectivity.
| Applications included |
|---|
| Exchange Online1 Exchange Online Protection1 Delve1 |
| Skype for Business Online1 Microsoft Teams 1 |
| SharePoint1 OneDrive1 Project Online1 |
| Portal and shared1 Microsoft Entra ID 1 Microsoft Entra Connect1 Office1 |
1 Each of these applications has internet connectivity requirements not supported over ExpressRoute. See the Microsoft 365 endpoints article for more information.
The services that aren't included with ExpressRoute for Microsoft 365 are Microsoft 365 Apps for enterprise client downloads, On-premises Identity Provider Sign-In, and Microsoft 365 (operated by 21 Vianet) service in China.
Note
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint does not provide integration with Azure ExpressRoute. While this does not stop customers from defining ExpressRoute rules that enable connectivity from a private network to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint cloud services, it is up to the customer to maintain rules as the service or cloud infrastructure evolves.
Outlook for Android, iOS, and Mac do not support integration with Azure ExpressRoute and have a required IP range to function properly. As such, any rules that impact AutoDiscover services need to be maintained by the customer.
Implementing ExpressRoute for Microsoft 365
Implementing ExpressRoute requires the involvement of network and application owners and requires careful planning to determine the new network routing architecture, bandwidth requirements, where security is implemented, high availability, and so on. To implement ExpressRoute, you'll need to:
Fully understand the need ExpressRoute satisfies in your Microsoft 365 connectivity planning. Understand what applications use the internet or ExpressRoute and fully plan your network capacity, security, and high availability needs in the context of using both the internet and ExpressRoute for Microsoft 365 traffic.
Determine the egress and peering locations for both internet and ExpressRoute traffic1.
Determine the capacity required on the internet and ExpressRoute connections.
Have a plan in place for implementing security and other standard perimeter controls1.
Have a valid Microsoft Azure account to subscribe to ExpressRoute.
Select a connectivity model and an approved provider. Keep in mind, customers can select multiple connectivity models or partners and the partner doesn't need to be the same as your existing network provider.
Validate deployment prior to directing traffic to ExpressRoute.
Optionally implement QoS and evaluate regional expansion.
1 Important performance considerations. Decisions here can dramatically impact latency, which is a critical for applications such as Skype for Business.
For additional references, see What is Azure ExpressRoute?
To purchase ExpressRoute for Microsoft 365, you'll need to work with one or more approved providers to provision the desired number and size circuits with an ExpressRoute Premium subscription. There are no additional licenses to purchase from Microsoft 365.
Here's a short link you can use to come back: https://aka.ms/expressrouteoffice365
Ready to sign up for ExpressRoute for Microsoft 365?
Related articles
Assessing Microsoft 365 network connectivity
Implementing ExpressRoute for Microsoft 365
Media Quality and Network Connectivity Performance in Skype for Business Online
Microsoft 365 performance tuning using baselines and performance history
Performance troubleshooting plan for Microsoft 365
Microsoft 365 URLs and IP address ranges
Microsoft 365 network and performance tuning