Use Azure SQL migration extension to migrate to Azure SQL Database
If you can afford to take the database offline while you migrate to Azure, you have a few tools you can use.
In our bicycle manufacturing scenario, the HR database is considered business-critical but is rarely used at weekends. You've planned to execute an offline migration between Friday evening and Monday morning, but you want to assess the best migration method.
It's assumed that all pre-migration checks have been done with the Azure SQL migration extension for Azure Data Studio or Azure Migrate. This process ensures that feature and compatibility issues are addressed.
Migrate using the Azure SQL migration extension for Azure Data Studio
Azure SQL migration extension for Azure Data Studio is a tool that helps you prepare for migrating your SQL Server databases to Azure. It assesses your readiness for migration, recommends the best Azure resources for your needs, and facilitates the migration process. We suggest using the extension for databases that are small to medium in size.
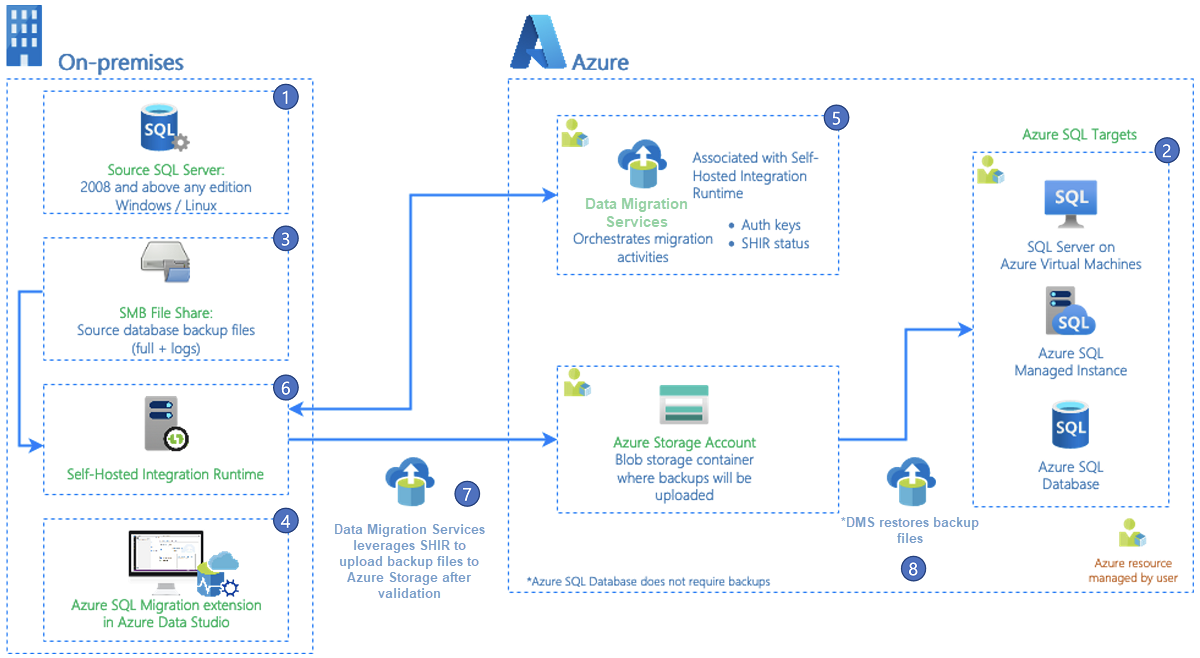
Azure SQL migration extension uses the latest version of Data Migration Services and includes an advanced assessment feature that can evaluate whether your SQL Server databases are ready to be migrated to Azure SQL.
Additionally, you can migrate multiple SQL Server databases by using Azure SQL migration extension at no charge.
The steps below highlights the process of migrating to Azure SQL Database using the Azure SQL Migration extension for Azure Data Studio.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Setup | Install Azure Data Studio and the Azure SQL Migration extension. Open Azure Data Studio and start the Migrate to Azure SQL Migration wizard. This wizard guides you through the migration process. |
| Step 1: Databases for assessment | Choose the databases you want to migrate. |
| Step 2: Assessment results and recommendations | Assess their readiness for migration. The tool identifies any potential issues that might affect the migration process. Collect performance data from your current database. This data is used to provide recommendations for your Azure SQL setup. |
| Step 3: Azure target | Select an Azure account and your target Azure SQL Database. |
| Step 4: Azure Database Migration Service | Select an existing Azure Database Migration Service, or create a new one. |
| Step 5: Data source configuration | Enter the credentials used to connect to the source from the self-hosted integration runtime. Select the tables to migrate from source to target. Before selecting the tables to migrate, ensure that you've created the database schema from the source to the target using either the dacpac extension, the SQL Database Projects extension in Azure Data Studio, or the DMA. |
| Step 6: Summary | Review the migration information and start the migration process. |
The Database Migration Service optimizes the migration process by skipping empty tables, even if you select them.
Important
Currently, Azure SQL Database does not support the migration of table names containing double-byte characters. As a workaround, you can temporarily rename these tables prior to migration and then revert them to their original names once the migration is complete.
Migration status
There are a few statuses that keep you updated on the progress of the migration.
Preparing for copy: The service is in the process of disabling autostats, triggers, and indexes in the target table.
Copying: The data copy from the source database to the target database is in progress.
Copy finished: Data copy is finished, and the service is waiting on other tables to finish copying.
Rebuilding indexes: The service is rebuilding indexes on target tables.
Succeeded: All data is copied and the indexes are rebuilt.
Performance considerations
Migration speed heavily depends on the target Azure SQL Database SKU and the self-hosted Integration Runtime host. We strongly recommend that you scale up your Azure SQL Database compute resources before initiating the migration process for an optimal migration experience.
When deciding for the server to install the self-hosted integration runtime, make sure this machine can handle the cpu and memory load of the data copy operation.
Azure SQL Database migration can be slow with a large volume of tables due to the time Azure Data Factory (ADF) takes to start activities, even for small tables.
Tables with large blob columns may fail to migrate due to timeout.
We recommend up to 10 concurrent database migrations per self-hosted integration runtime on a single computer. Scale out the self-hosted runtime or create separate instances on different computers to increase the concurrent database migrations.
Monitor migration
Once you've started the database migration, you can monitor the progress in Azure Data Studio. You can also track the progress in the Azure portal under the Azure Database Migration Service resource.
Monitor migration from Azure Data Studio
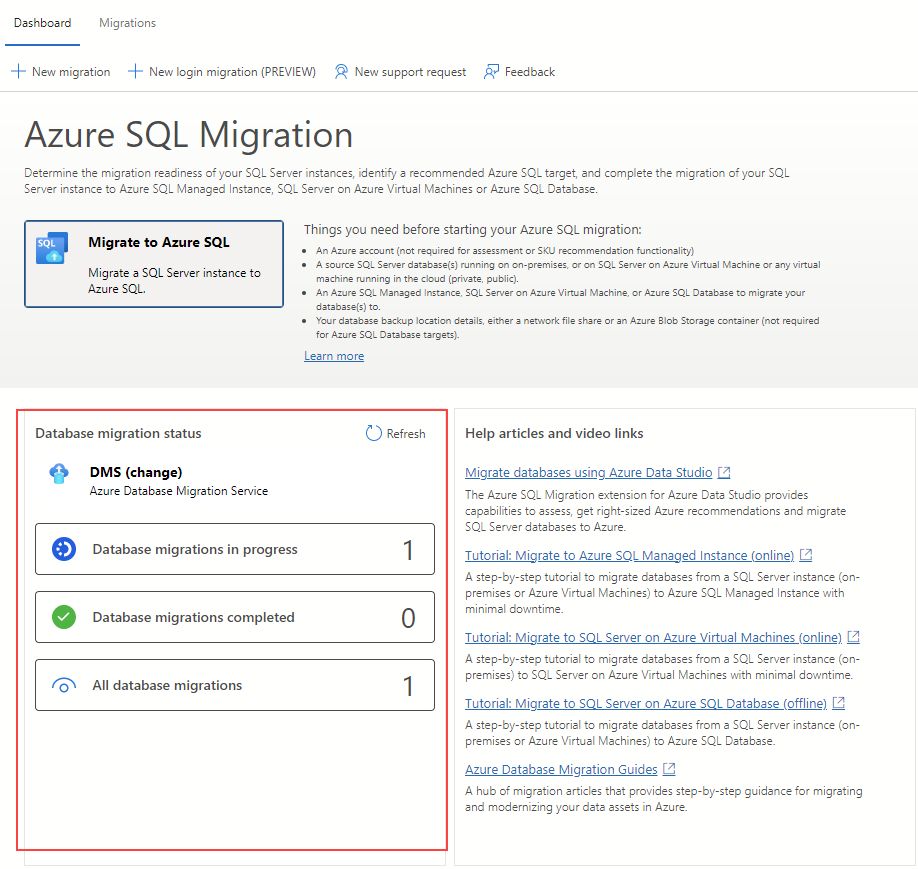
Under Database migration status, you can track migrations that are in progress, completed, and failed (if any), or you can view all database migrations.
Select Database migrations in progress in the migration dashboard to view ongoing migrations.
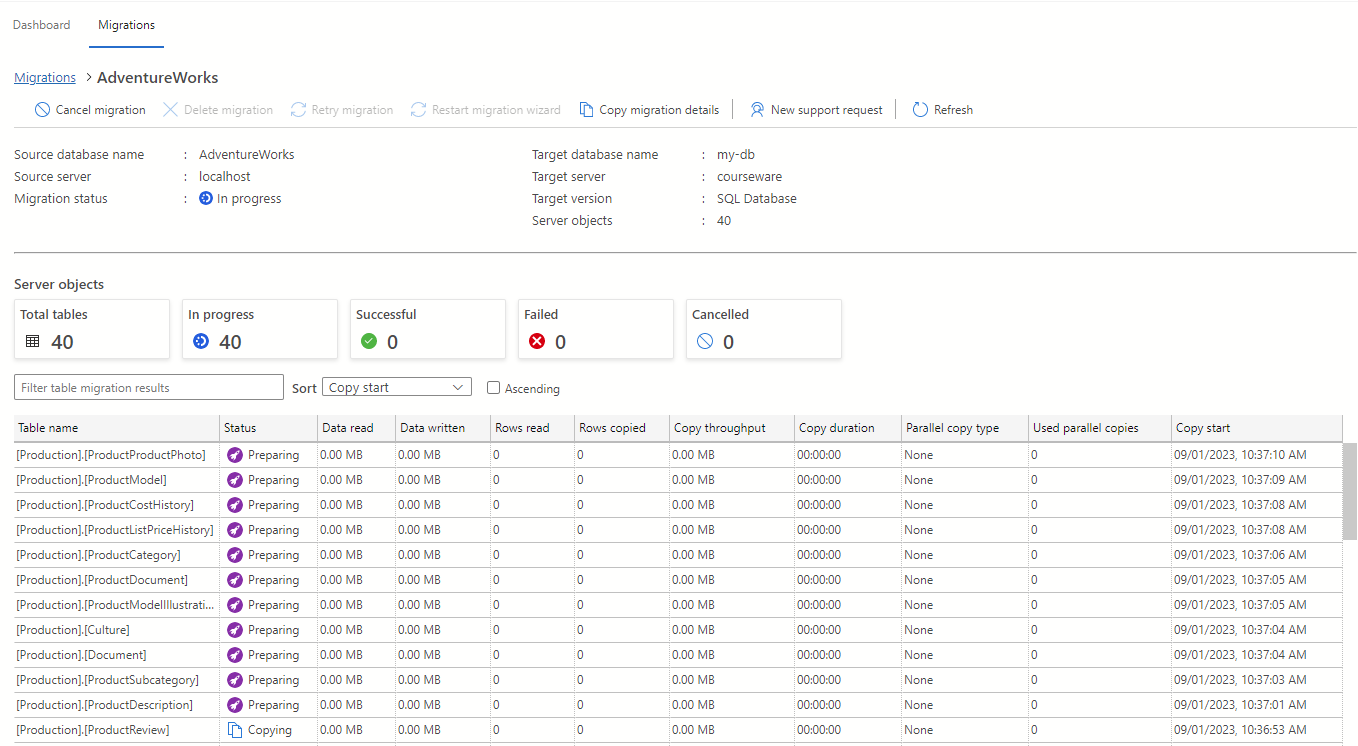
Select the database name to get further details.
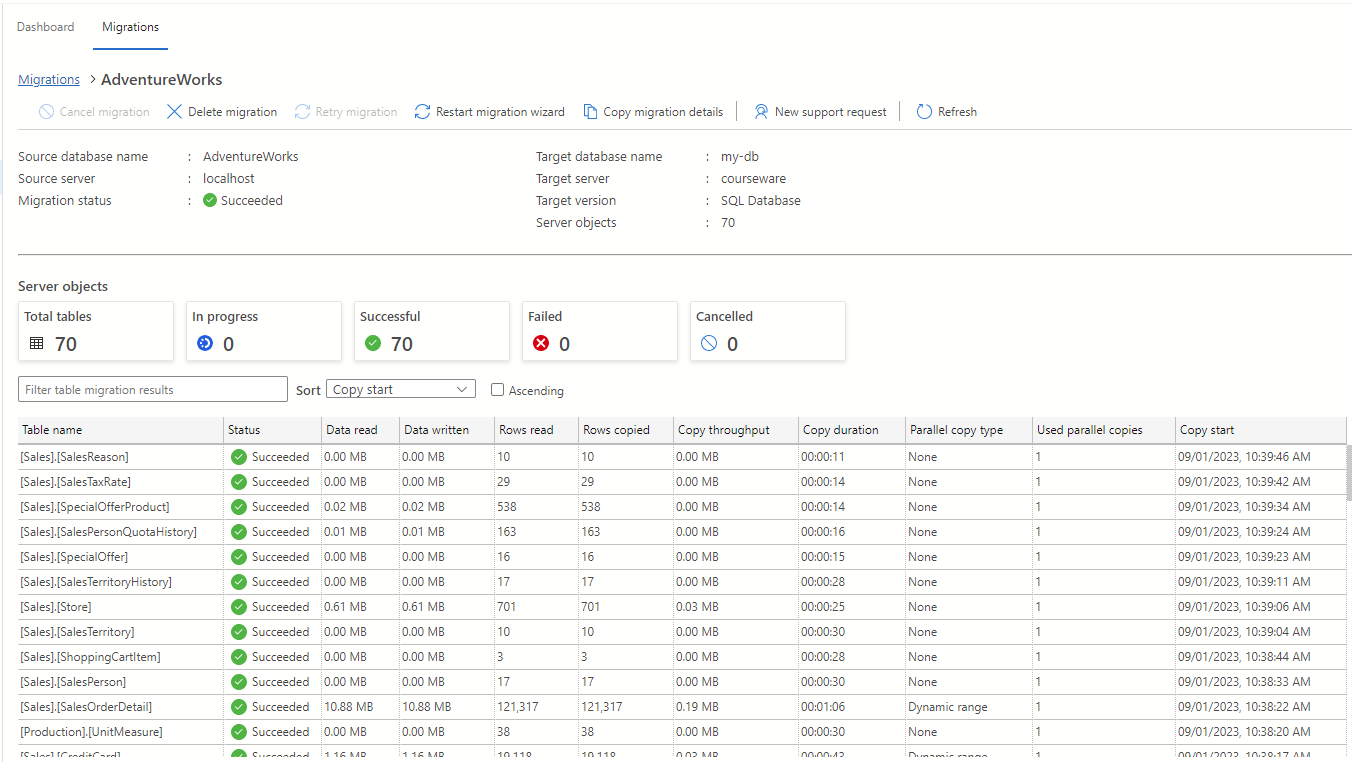
The Migration status property will change to Completing, then to Succeeded after the migration is completed.
Monitor migration from the Azure portal
Alternatively, you can also monitor the migration activity using Azure Database Migration Service.
To monitor your database migration, you would typically go to the Azure portal and find your instance of the Database Migration Service. Once you've located the service, you can view its instance overview. Select Monitor migrations to access detailed information about your ongoing database migration.
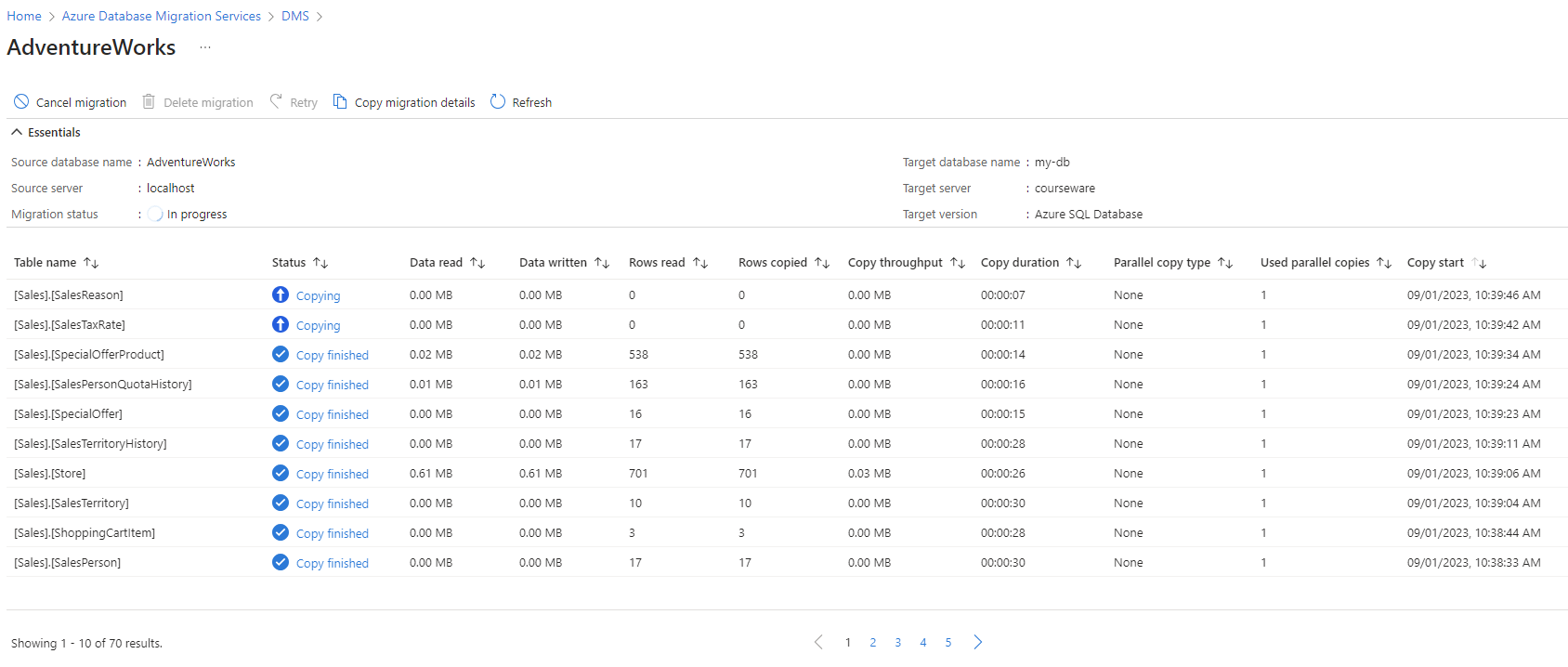
After the migration status is Succeeded, navigate to the target server, and validate the target database. Check the database schema and data.
Migrate at scale
You can also perform an offline migration of the database from SQL Server on-premises to an Azure SQL Database by using either PowerShell or Azure CLI.
The following example migrates the AdventureWorks database to Azure SQL Database.
$sourcePass = ConvertTo-SecureString "password" -AsPlainText -Force
$targetPass = ConvertTo-SecureString "password" -AsPlainText -Force
New-AzDataMigrationToSqlDb `
-ResourceGroupName MyGroup `
-SqlDbInstanceName myserver `
-Kind "SqlDb" `
-TargetDbName AdventureWorks `
-SourceDatabaseName AdventureWorks `
-SourceSqlConnectionAuthentication SQLAuthentication `
-SourceSqlConnectionDataSource myserver.microsoft.com `
-SourceSqlConnectionUserName user `
-SourceSqlConnectionPassword $sourcePass `
-Scope "/subscriptions/MySubscriptionID/resourceGroups/MyGroup/providers/Microsoft.Sql/servers/myserver" `
-TargetSqlConnectionAuthentication SQLAuthentication `
-TargetSqlConnectionDataSource myserver.database.windows.net `
-TargetSqlConnectionUserName user `
-TargetSqlConnectionPassword $targetPass `
-MigrationService "/subscriptions/MySubscriptionID/resourceGroups/MyGroup/providers/Microsoft.DataMigration/SqlMigrationServices/MyService"
The following example migrates a subset of tables from the AdventureWorks database.
New-AzDataMigrationToSqlDb `
-ResourceGroupName MyGroup `
-SqlDbInstanceName myserver `
-Kind "SqlDb" `
-TargetDbName AdventureWorks `
-SourceDatabaseName AdventureWorks `
-SourceSqlConnectionAuthentication SQLAuthentication `
-SourceSqlConnectionDataSource myserver.microsoft.com `
-SourceSqlConnectionUserName user `
-SourceSqlConnectionPassword $sourcePass `
-Scope "/subscriptions/MySubscriptionID/resourceGroups/MyGroup/providers/Microsoft.Sql/servers/myserver" `
-TargetSqlConnectionAuthentication SQLAuthentication `
-TargetSqlConnectionDataSource myserver.database.windows.net `
-TargetSqlConnectionUserName user `
-TargetSqlConnectionPassword $targetPass `
-TableList "[Person].[Person]", "[Person].[EmailAddress]" `
-MigrationService "/subscriptions/MySubscriptionID/resourceGroups/MyGroup/providers/Microsoft.DataMigration/SqlMigrationServices/MyService"
To learn more about the Azure migration extension PowerShell and Azure CLI commands available, refer to the following links: PowerShell module for data migration extension and Azure CLI for data migration extension.