Configure Dataverse search for your environment
Dataverse search delivers fast and comprehensive search results in a single list, sorted by relevance. As an administrator or customizer, you can turn on and configure Dataverse search as described in this article. Quick Find views are used for configuring Dataverse search, so you can manage global search, quick find, and lookup search behavior in one single place.
With Dataverse search enabled, a search box is always available at the top of every page in all the model-driven apps in the environment. Once Dataverse search is enabled, it applies to all apps and can't be disabled per app. Users can start a new search and quickly find the information they're looking for, from the searchable tables included in the app. Dataverse search also becomes the default and only global search experience in all model-driven apps in the environment. Users won't be able to switch to quick find search formerly known as categorized search.
Dataverse search can be extended to additional Microsoft Search canvases, including SharePoint Online, Bing, and Office. Users can search and find information from these canvases similar to searching in the app when the connector is enabled, for example quickly look up a contact’s phone number or email without opening the app.
What is Dataverse search?
Dataverse search helps you quickly find what you're looking for. It delivers fast and comprehensive results across multiple tables in a single list, sorted by relevance. In addition, Dataverse search has the following benefits:
Fast and accurate search: Provides a precise and quick search experience for model-driven apps, and performance that's superior to quick find search, formerly known as categorized search.
Suggested results as you type: Finds what you're looking for and shows you the top results, as you type.
Better matching: Finds matches to any word in the search term for columns in a table. Provides a better user experience compared to quick find search, where all words in the search term must be found in one column.
Smart: Finds matches that include inflectional words such as stream, streaming, or streamed.
Search across documents in Microsoft Dataverse: Includes search results for text in documents that are stored in Dataverse such as PDF, Microsoft Office documents, HTML, XML, ZIP, EML, plain text, and JSON file formats. It also searches text in notes and attachments.
Note
Searching across images isn't supported.
Understanding of underlying data: Understands data types like Choice and Lookup, so it can effectively interpret a search query that includes multiple search terms.
Operators for advanced search: Lets you use simple Boolean operators in your search term and craft the query to get the results you want.
Intelligence: Applies AI technology to interpret natural language such as misspellings, common abbreviations, and synonyms to deliver quality results.
For more information about Dataverse search, see Search for tables and rows by using Dataverse search.
Availability and language support
Dataverse search is available in customer engagement apps (Dynamics 365 Sales, Dynamics 365 Customer Service, Dynamics 365 Field Service, Dynamics 365 Marketing, and Dynamics 365 Project Service Automation).
Dataverse search isn't available for Customer Engagement (on-premises) organizations. Quick Find is the only search option for customer engagement apps organizations and Customer Engagement (on-premises) organizations.
Full-text Quick Find is available for Customer Engagement (on-premises) organizations, starting with Dynamics CRM 2015 Update Rollup 1.
For more detailed comparison of the searches available in Microsoft Dataverse, see Compare search options in Microsoft Dataverse.
All searchable fields in Dataverse search are processed in the language most closely matching the organization's base language, except Kazakh where all fields are processed using a basic, language-agnostic text processor.
Enable Dataverse search
Dataverse search is an opt-out feature, set to On by default with 2021 release wave 2, on all production environments, except those using their own encryption key. We recommend enabling Dataverse search so users have a superior search experience in model-driven apps with the benefits listed above. All model-driven Power Apps have the global search experience with the search bar in the header in the environment. Individual users aren't able to switch to quick find search, formerly known as categorized search. Tables must be included in the application you're using with Dataverse search. Be sure that any table you want users to search on are included in your application.
Important
If you opt in to early access of 2021 release wave 2 on a production environment, Dataverse search is enabled automatically. If you are using your own encryption key, you can disable Dataverse search after enabling early access of 2021 release wave 2 in the Power Platform admin center.


Note
Dataverse search doesn't support lifecycle operations (create, delete, backup, recover, copy, reset, and so on). In the event of such an operation, re-enable Dataverse search.
To enable Dataverse search, do the following:
Open the Power Platform admin center as a system administrator.
In the navigation pane, select Environment.
Select an environment.
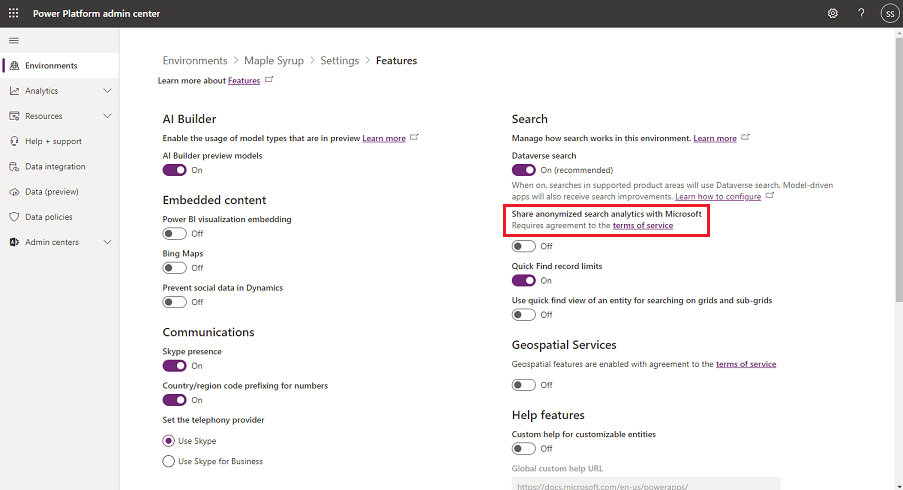
Select Settings > Product > Features.
Under Search, set Dataverse search to On.
Select Save.

When you turn on Dataverse search, it's included in all of your model-driven apps. You can't turn it off in specific apps.
If the Dataverse search index needs to be provisioned, you see an indication that provisioning is in progress. Once the index is provisioned, it may take anywhere between an hour or more to complete a full sync for average size organizations, to a couple of days for large organizations.
Important
Disabling Dataverse search will deprovision and remove the index within a period of 12 hours. If you enable Dataverse search after about 12 hours of disabling it, a fresh index is provisioned, followed by a full sync that may take up to an hour or more for average size organizations, and a couple of days for large organizations. Consider this when you're disabling Dataverse search temporarily.
Help improve Dataverse search
To help Microsoft improve Dataverse search, you can share your environment's Dataverse search queries in Dynamics 365 and Power Platform applications with Microsoft. This data helps Microsoft build, improve, and validate the Microsoft machine learning model for the Dynamics 365 Natural Language search query technology.
Your queries and results are reviewed by people using secured computers in the United States. Aggregate data about queries and results are used by Microsoft engineers and data scientists to improve future search query results for all users worldwide. Your data remains your property. Your organization's data is stored within your tenant's compliance boundary and is automatically deleted after 30 days. You can delete the data at any time by navigating to the Power Platform admin center and toggling Share anonymized search analytics with Microsoft to Off. For more information, see Terms of Service in the Power Platform admin center.
Share anonymized search analytics with Microsoft is Off by default. To enable:
In the Power Platform admin center, select an environment.
Select Settings > Product > Features.
Under Search, set Share anonymized search analytics with Microsoft to On.
Select Save
Set up Dataverse search
Setting up Dataverse search after enabling it in the Power Platform admin center involves three steps:
Select the searchable tables for Dataverse search (see below).
Review the columns that will be searched, the columns that will be displayed, and the filter conditions that will be applied in model-driven Power Apps (see below).
Ensure the tables enabled for Dataverse search are included in the model-driven app. Use the app designer to verify that the table is included in an app's components. For more information, see Add or edit model-driven app components.
Make sure your table is customizable and that the settings to Track changes and Appear in search results in the Advanced options are both set to On. For more information, see Create and edit tables using Power Apps.
Select tables for Dataverse search
Setting up search starts with reviewing the tables that are enabled for Dataverse search, in context of a solution. Using the new solution explorer, you can see a snapshot of the Dataverse search index on the Overview page.
Note
If you are selecting tables for Dataverse search on a Power Apps US Government environment, use the legacy solution explorer to choose the tables to be indexed for Dataverse search.

Sign in to Power Apps.
Select Solutions.
Select the solution you want to make the changes in, and then select Overview.

Select Manage search index.

Although there's no limit on how many tables you can index for Dataverse search, there's a limit on the total number of fields that can be enabled for Dataverse search. The maximum is 1,000 searchable fields for an organization. Out of these 1,000 fields, up to 50 fields are required by the Dataverse search system, so you can configure up to 950 searchable fields.
Important
Some columns are common to all tables, like Primary Name and ID, which are part of the 50 fields indexed by default for all tables, and are not counted for every table.
When you select a table to be indexed for Dataverse search, you can see the number of fields that will be added to the index.

The number of fields indexed for a table is dependent on the tables quick find view. Additionally, some field types are treated as multiple fields in the Dataverse search index as indicated in this table.
| Field type | Number of fields used in the Dataverse search index |
|---|---|
| Lookup (customer, owner, or Lookup type attribute) | 3 |
| Option Set (state, or status type attribute) | 2 |
| All other types of fields | 1 |
The progress bar at the bottom shows the percentage of indexed fields as a fraction of the maximum allowed number of searchable fields.

When you've reached the indexed field limit, you'll see a warning message. If you want to add more fields to the index, you'll have to free up space, either by removing some of the fields that are already in the index or removing entire tables from Dataverse search scope.
By default, the following system tables are indexed for Dataverse search. However, custom tables aren't included. You must add them to Dataverse search for them to be searchable. The numbers in parenthesis, below, indicate the total number of columns included in the index for that table.
| Tables enabled for Dataverse search without Dynamics 365 apps enabled |
Tables enabled for Dataverse search with Dynamics 365 apps enabled |
|---|---|
| Account (8) Contact (11) Goal (19) Goal Metric (3) Knowledge Article (56) |
Campaign (2) Campaign Activity (4) Campaign Response (6) Case (5) Competitor (1) Contract (7) Invoice (4) Lead (6) Marketing List (5) Opportunity (11) Opportunity Product (8) Order (4) Product (5) Quote (4) Service (1) Service Activity (9) |
Note
Changes made to the Dataverse search configuration or to the searchable data may take up to 15 minutes to appear in the search service. It may take up to an hour or more to complete a full sync for average size organizations, and a couple of days for very large size organizations.
Select searchable fields and filters for each table
The searchable fields and filters for a table enabled for Dataverse search are driven by the table's Quick Find View. The complete set of View columns, Find columns, and Filter columns in a table's Quick Find View become part of the Dataverse search index when that table is enabled for Dataverse search. There's no limit on how many searchable fields you can add for each table. However, there's a limit on the total number of indexed fields, as explained in the previous section.
The Find Columns on a Quick Find View define the searchable fields in the Dataverse search index. Text fields such as Single Line of Text and Multiple Lines of Text, Lookups, and Option Sets are searchable. Find Columns of all other data types are ignored.
Note
Currency fields must be added to the Find Columns so the currency symbol that is visible on the record will be returned in the search results. If the currency field isn’t added to the search index, users will see the currency symbol localized according to their language settings.
The View Columns on a Quick Find View define the fields that are displayed in model-driven apps' search results page when the matched results are returned.
The filter conditions on a Quick Find View are also applied to the Dataverse search results. See the table below for the list of filter clauses not supported by Dataverse search.
| Operator |
|---|
| Like |
| NotLike |
| BeginsWith |
| DoesNotBeginWith |
| EndWith |
| DoesNotEndWith |
| ChildOf |
| Mask |
| NotMask |
| MaskSelect |
| EqualUserLanguage |
| Under |
| NotUnder |
| UnderOrEqual |
| Above |
| AboveOrEqual |
| NotNull |
| Null |
To edit the searchable fields of a table:
Sign in to Power Apps.
Select Dataverse > Tables.
Select the table you want to make the changes for and then select the Views tab.
Select the view of type Quick Find View in the list of views.
Edit View columns and Find columns by adding, removing, or reordering columns. For a more detailed description of how to add or remove columns in a view, see Choose and configure columns in model-driven app views in Power Apps.

Select Publish to publish the changes to the view.
Important
Changes to Quick Find View also apply to single-table and multi-table Quick Find configurations. Therefore, we don't prevent you from including fields that aren't supported for Dataverse search when you configure Quick Find View. However, unsupported fields aren't synced to the Dataverse search index and don't appear in the Dataverse search results.
Tip
You can use the Quick Find View to define which fields appear as facets in model-driven apps with Dataverse search enabled. All View columns with data types other than Single Line of Text and Multiple Lines of Text are marked as facetable and filterable in the index. By default, the first four facetable fields in the Quick Find View for the selected table are displayed as facets when users search by using Dataverse search. At any time, you can only have four fields selected as facets.
Note
Changes made to the Dataverse search configuration or to the searchable data may take up to 15 minutes to appear in the search service. It may take up to an hour or more to complete a full sync for average size organizations, and a couple of days for very large size organizations.
The maximum search term size is 1024 characters.
Although you can have related table fields as a View column or a Find column or a Filter column in a table's Quick Find View, related table fields are not supported by Dataverse search and hence ignored.
If the length of text in a table column is changed and the column is set to Simple Search View, the import may not be successful and the following error may occur.
Length is not valid because this is an indexed attribute and hence cannot have size greater than 1700.
The indexed attribute can't extend beyond 1700 bytes. If the corresponding column is registered in the Quick Find View, remove the corresponding column from the Quick Find View and try to re-export after a time interval. If you change or delete a Quick Find View setting, it may take up to 24 hours to be reflected in the index, as it is a once-a-day maintenance job for the on-premises product. For more information, see Maximum capacity specifications for SQL Server.
Updates to calculated fields and lookups are not automatically synced in Dataverse search. Data is refreshed whenever a field that is configured for Dataverse search is updated in a record.
There are some common fields, that are part of every table in Dataverse, which are part of the Dataverse search index by default. Some examples of common fields are:
- ownerid (Name of lookup)
- owningbusinessunit (Name of lookup)
- statecode (Label of optionset)
- statuscode (Label of optionset)
- name (Primary name field of any table. This may or may not be the same as the logical name (fullname, subject, and so on) of the table.)
If a common field is added to any table for Dataverse search, search will be performed for that common field across all entities. However, once you choose a specific table through the Record Type facet, Dataverse search will follow the settings you have defined for that specific table through Quick Find View.
Configure quick actions that appear with Dataverse search in model-driven apps
Dataverse search experience brings some of the most frequently used actions closer to search results, to help users complete their tasks without having to navigate to the record page in model-driven apps. Quick actions are a small set of commands specific to a table. Users can see quick actions when they're interacting with search in model-driven apps running on a web browser. Some of the commonly used tables are configured to show a set of commands to help them complete their task without losing context.
| Table | Quick actions |
|---|---|
| Account | Assign, Share, Email a link |
| Contact | Assign, Share, Email a link |
| Appointment | Mark complete, Cancel, Set Regarding, Assign, Email a link |
| Task | Mark complete, Cancel, Set Regarding, Assign, Email a link |
| Phone call | Mark complete, Cancel, Set Regarding, Assign, Email a link |
| Cancel, Set Regarding, Email a link |
Quick actions are a subset of the table's homepage grid commands. For example, when you select an account in its homepage grid, the Account table's quick actions are derived from the set of commands at the top of the page. This is important to understand the customization options available to configure quick actions. You can use the ribbon's EnableRule to hide or show quick actions for a table. To learn more about defining ribbon enable rules in Power Apps, see Define ribbon enable rules.
The following three new enable rules give you the flexibility to optimize quick actions:
ShowOnQuickAction rule: Use this rule to make a command appear only as a quick action.
<CommandDefinition Id="new.contact.Command.Call"> <EnableRules> <EnableRule Id="Mscrm.SelectionCountExactlyOne" /> <EnableRule Id="Mscrm.ShowOnQuickAction" /> </EnableRules> <DisplayRules /> <Actions> <JavaScriptFunction FunctionName="simplealert" /> </Actions> </CommandDefinition>ShowOnGridAndQuickAction rule: Use this rule to make a command appear on the homepage grid as well as a quick action.
ShowOnGrid rule: Use this rule to make a command appear on the homepage grid only. You can use this command to hide an existing quick action.
Note
Each table can have up to six quick actions. Quick actions currently show up only in the context of search—alongside suggestions and in the results page on the primary column. The same set of quick actions appears alongside suggestions and in the results page.
Set managed properties for Dataverse search
If you want to include a table for Dataverse search, the Can enable sync to external search index managed property must be set to True for the table. By default, the property is set to True for some of the out-of-the-box tables and all custom tables. Some of the system tables can't be enabled for Dataverse search.
To set the managed property, do the following:
Go to Advanced Settings > Customizations.
Select Customize the System.
Under Components, expand Entities, and then select the table you want.
On the menu bar, select Managed Properties. For Can enable sync to external search index, select True or False to set the property to the desired state. Select Set to exit, as shown here.

Select Publish for your changes to take effect.
If you want to change the Can enable sync to external search index property to False, you must first deselect the table from Dataverse search. If the table is included in Dataverse search, you'll see the following message: "This entity is currently syncing to an external search index. You must remove the entity from the external search index before you can set the Can enable sync to external search index property to False."
If Can enable sync to external search index is set to False, you'll see the following message when you try to include a table in Dataverse search: "Entity can't be enabled for Dataverse search because of the configuration of its managed properties." For custom tables with sensitive data, you may consider setting the Can enable sync to external search index property to False.
Important
Keep in mind that after you install the managed solution on the target system, you won't be able to change the value of the property because it's a managed property.
See also
Search for tables and rows by using Dataverse search
Dynamics 365 results in Microsoft Search