Enterprise websites Microsoft Graph connector
The Enterprise websites Microsoft Graph connector allows your organization to index articles and content from your company-owned websites. After you configure the connector and sync content from the website, end users can search for that content from any Microsoft Search client.
Note
Read the Set up Microsoft Graph connectors in the Microsoft 365 admin center article to understand the general connectors setup instructions.
This article is for anyone who configures, runs, and monitors an Enterprise websites connector. It supplements the general setup process, and shows instructions that apply only for the Enterprise websites connector. This article also includes information about Troubleshooting.
Step 1: Add a connector in the Microsoft 365 admin center
Add Enterprise website connector
(See general setup instructions for more details)
Step 2: Name the connection
Specify these attributes:
- Name (required)
- Connection ID (required)
- Description (optional)
- Select check box (required)
The connection ID creates implicit properties for your connector. It must be unique and can only contain a maximum of 32 alphanumeric characters. To change the ID, go to Advanced settings.
Step 3: Configure the connection settings
To connect to your data source, fill in the root URL of the website and select a custom vertical for the results. After you complete this information, select Test Connection to verify your settings.
Website URL
Specify the root of the website that you'd like to crawl. The enterprise websites connector will use this URL as the starting point and follow all the links from this URL for its crawl.
Note
You can index up to 50 different site URLs in a single connection. In the URLs field, enter the site URLs separated by commas (,). For example, https://www.contoso.com,https://www.contosoelectronics.com.
Use sitemap for crawling
When selected the connector will only crawl the URLs listed in the sitemap. This also allows you to configure incremental crawling during a later step. If not selected or no site map is found, the connector will do a deep crawl of all the links found on the root URL of the site.
Dynamic site configuration
If your website contains dynamic content, for example, webpages that live in content management systems like Confluence or Unily, you can enable a dynamic crawler. To turn it on, select Enable crawl for dynamic sites. The crawler will wait for dynamic content to render before it begins crawling.
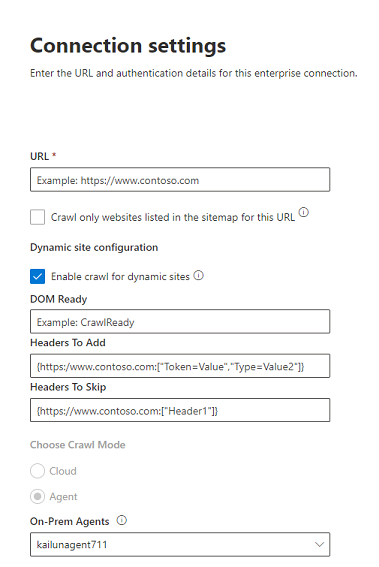
In addition to the check box, there are three optional fields available:
- DOM Ready: Enter the DOM element the crawler should use as the signal that the content is fully rendered and the crawl should begin.
- Headers to Add: Specify which HTTP headers the crawler should include when sending that specific web URL. You can set multiple headers for different websites. We suggest including auth token values.
- Headers to Skip: Specify any unnecessary headers that should be excluded from dynamic crawling requests.
Headers should be added in the following syntax: {"Root-URL":["TKey=TValue"]}
Example: {"https://www.contoso.com":["Token=Value","Type=Value2"]}
Note
Dynamic crawling is only supported for Agent crawl mode.
Crawl mode: Cloud or On-premises
The crawl mode determines the type of websites you want to index, either cloud or on-premises. For your cloud websites, select Cloud as the crawl mode.
Also, the connector now supports crawling of on-premises websites. To access your on-premises data, you must first install and configure the connector agent. To learn more, see Microsoft Graph connector agent.
For your on-premises websites, select Agent as the crawl mode and in the On-prem Agent field, choose the Graph connector agent that you installed and configured earlier.
Authentication
None requires no authentication
Basic requires a username and password.
OAuth 2.0 with Microsoft Entra ID requires a resource ID, Client ID, and a client Secret.
The resource ID, client ID and client secret values will depend on how you did the setup for Microsoft Entra ID based authentication for your website:
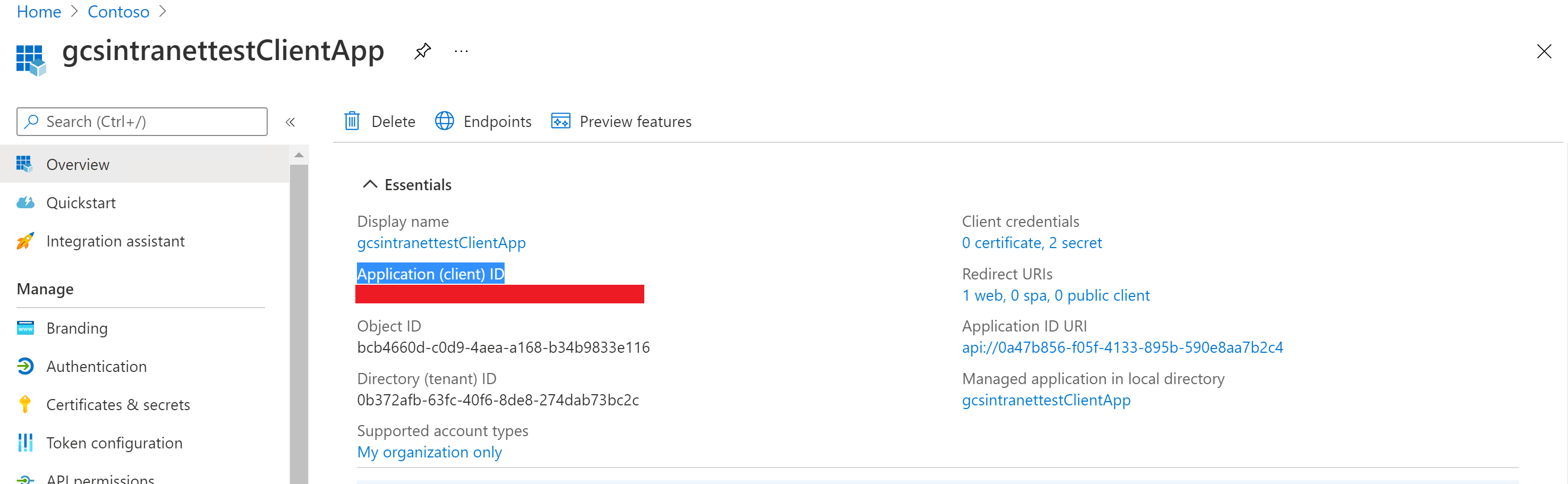
If you're using an application both as an identity provider and the client app to access the website, the client ID and the resource ID will be the application ID of the app, and the client secret will be the secret that you generated in the app.
Note
For detailed steps to configure a client application as an Identity provider, see Quickstart: Register an application with the Microsoft identity platform and Configure your App Service or Azure Functions app to use Microsoft Entra login.
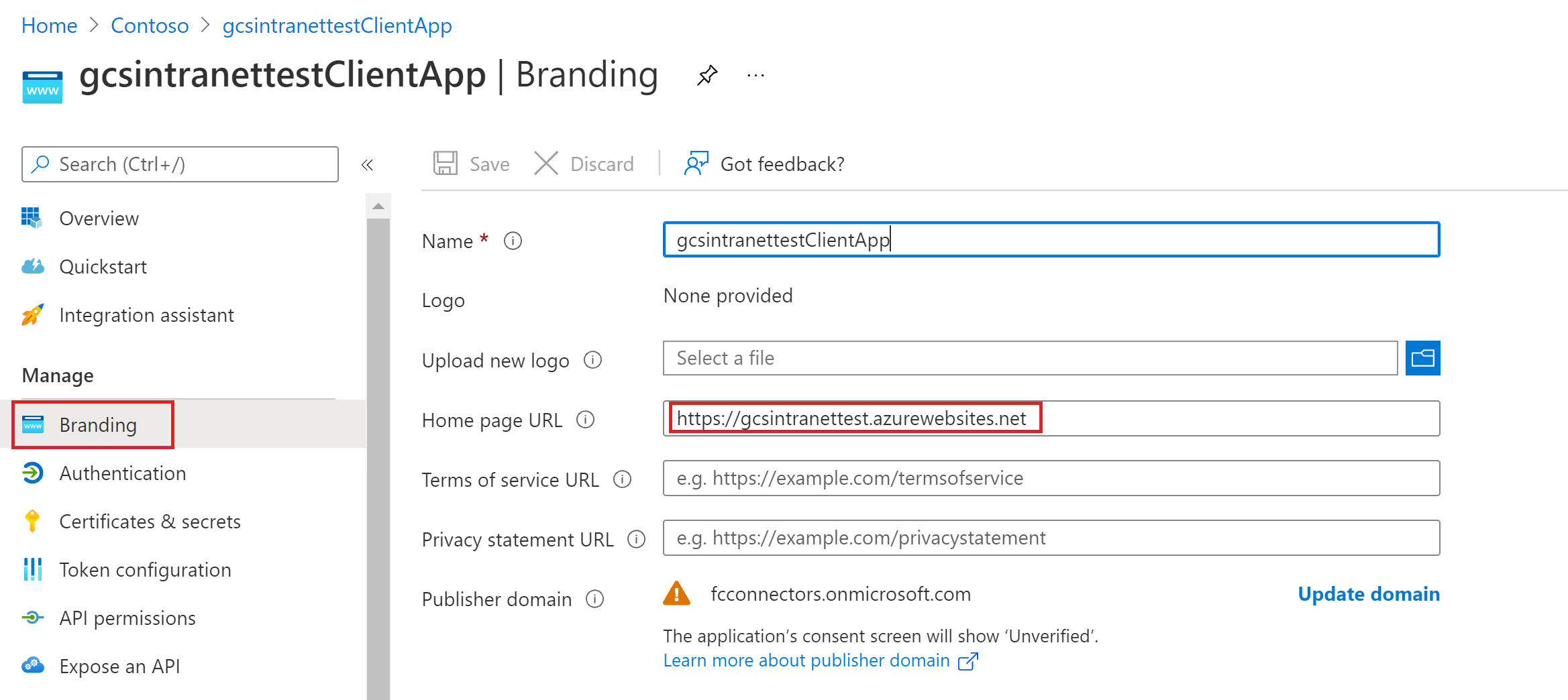
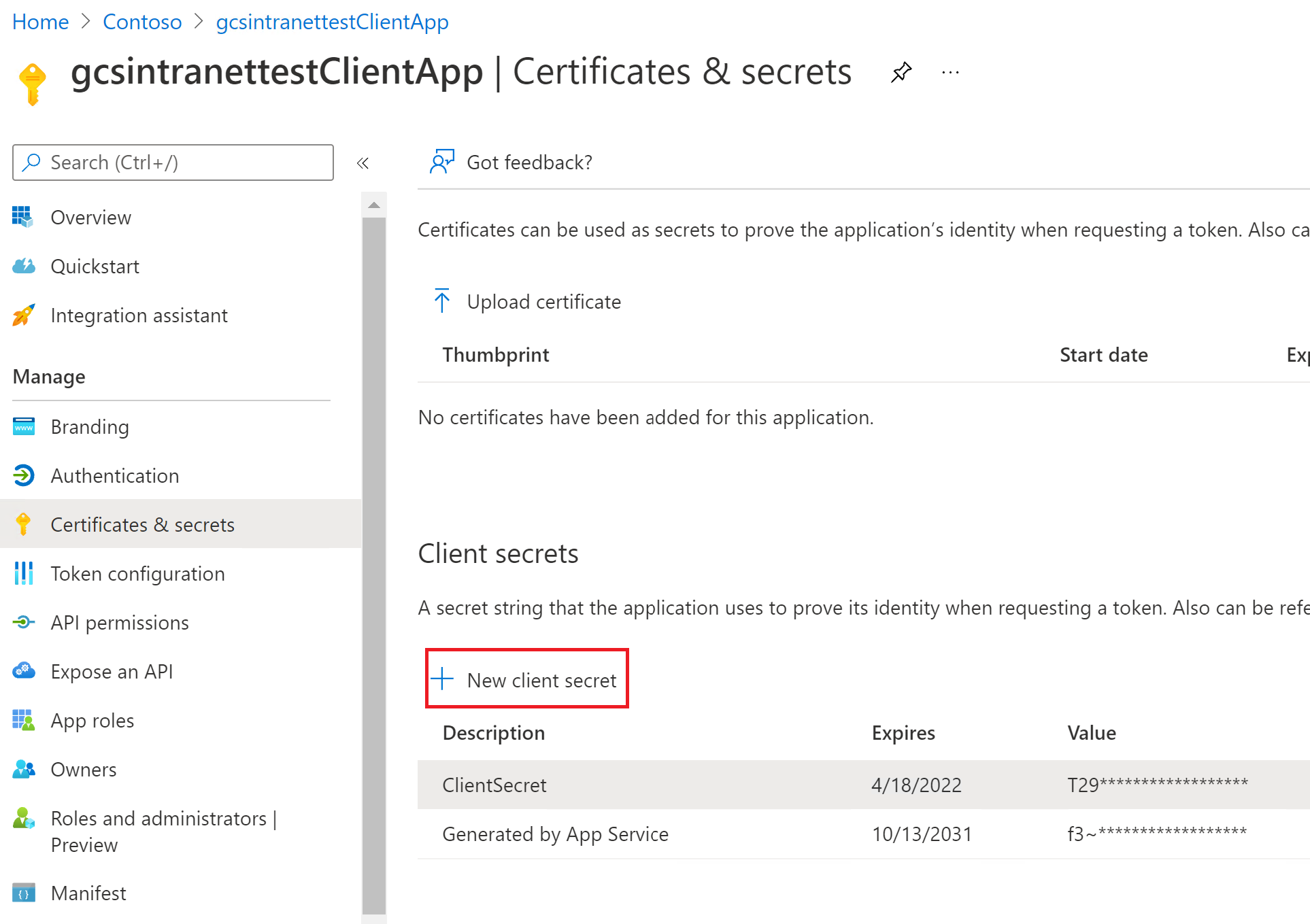
After the client app is configured, make sure you create a new client secret by going to the Certificates & Secrets section of the app. Copy the client secret value shown in the page because it won't be displayed again.
In the following screenshots you can see the steps to obtain the client ID, client secret, and set up the app if you're creating the app on your own.
View of the settings on the branding section:
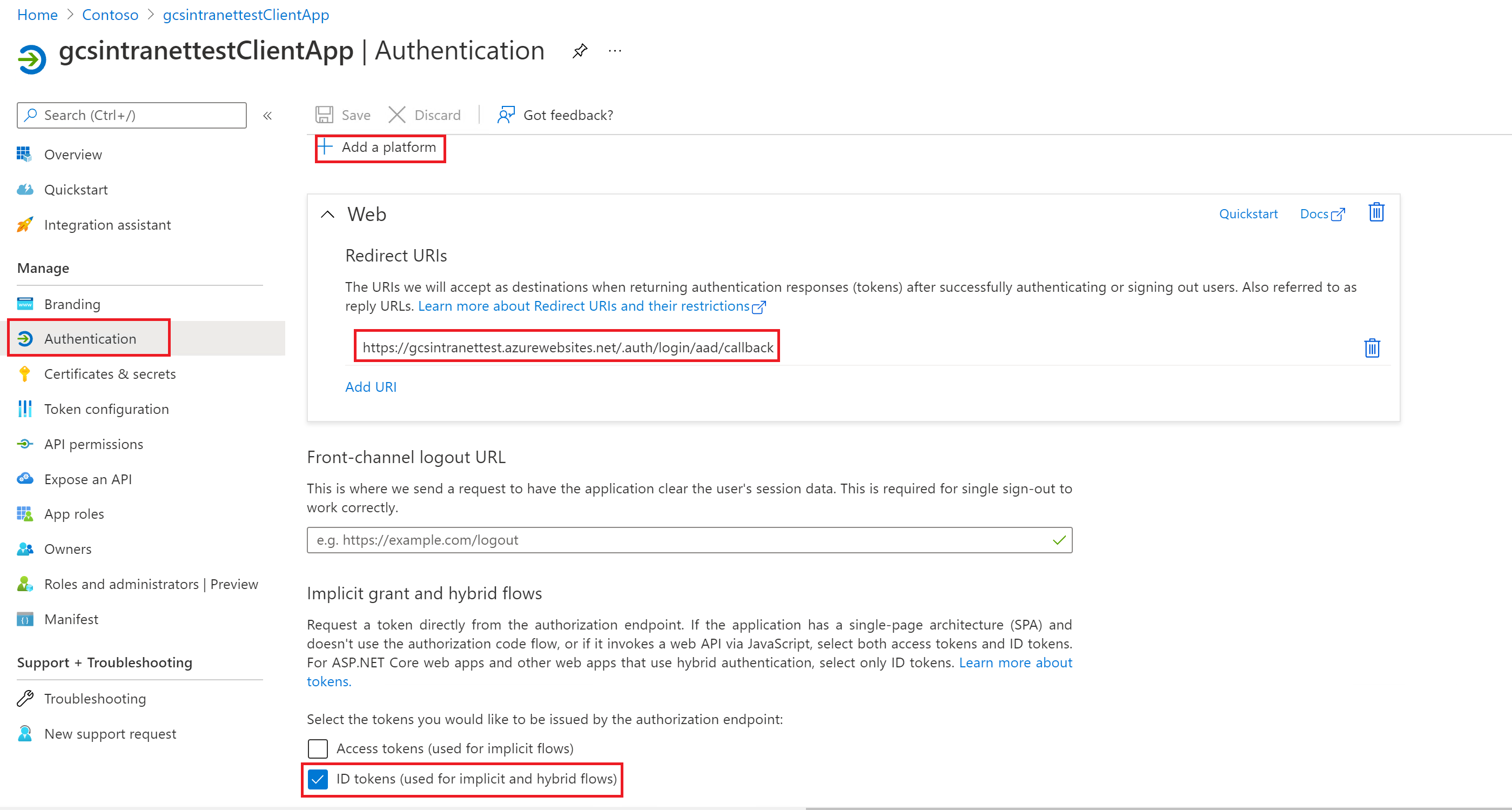
View of the settings on authentication section:
Note
It is not required to have the above specified route for Redirect URI in your website. Only if you use the user token sent by Azure in your website for authentication you will need to have the route.
View of the client ID on the Essentials section:
View of the client secret on the Certificates & secrets section:
If you're using an application as an identity provider for your website as the resource, and a different application to access the website, the client ID will be the application ID of your second app and the client secret will be the secret configured in the second app. However, the resource ID will be the ID of your first app.
Note
For steps to configure a client application as an identity provider see Quickstart: Register an application with the Microsoft identity platform and Configure your App Service or Azure Functions app to use Microsoft Entra login.
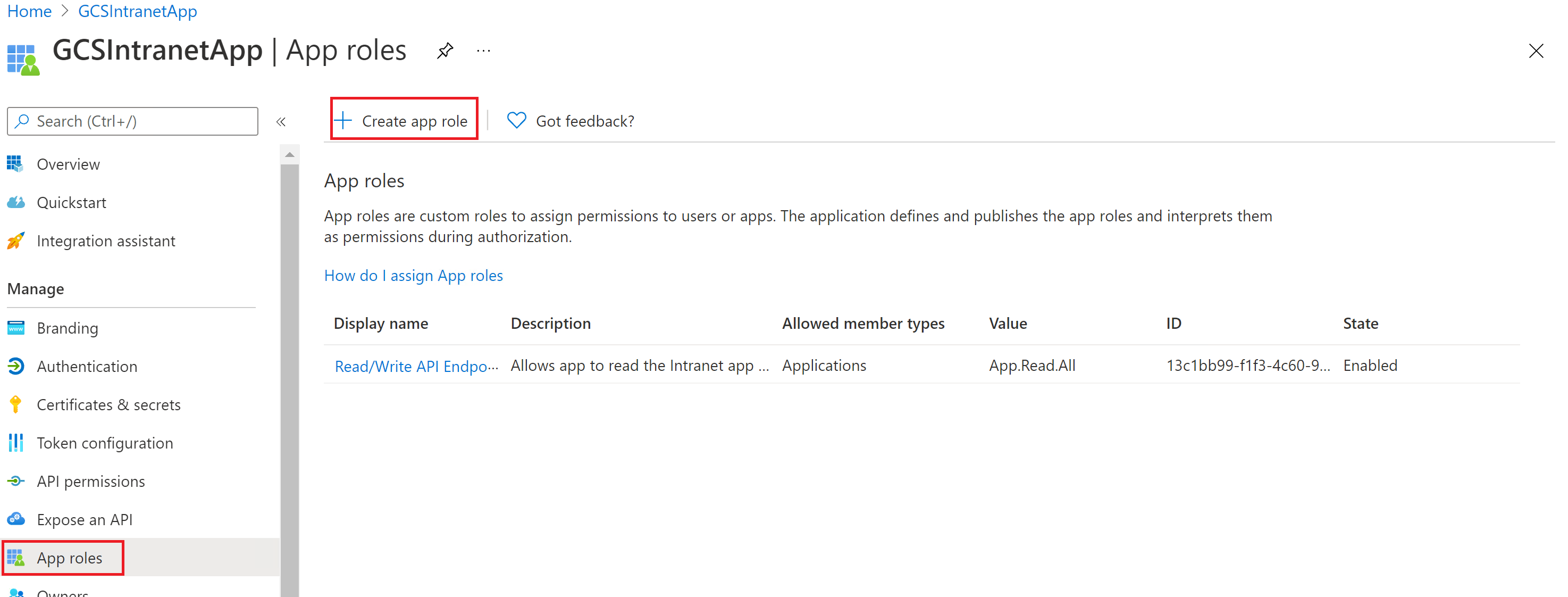
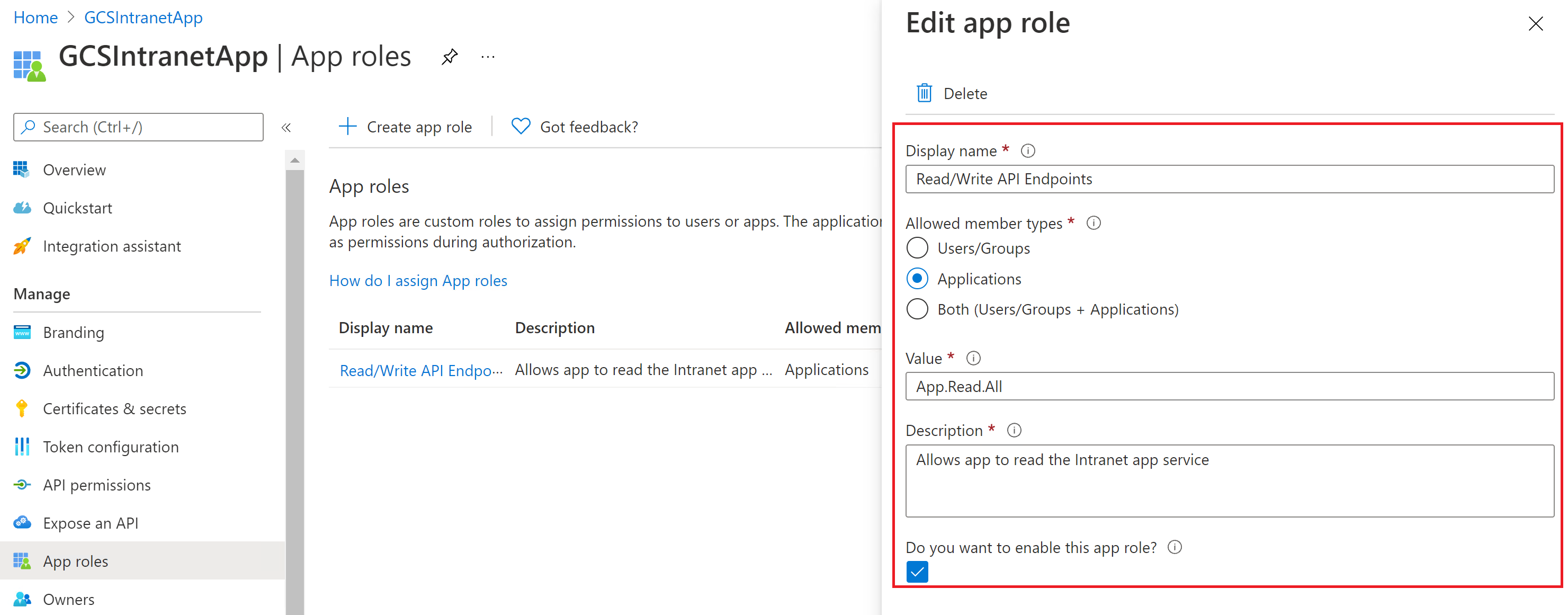
You don't need to configure a client secret in this application, but you'll need to add an app role in the App roles section, which will later be assigned to your client application. Refer to the images to see how to add an app role.
Creating a new app role:
Editing the new app role:
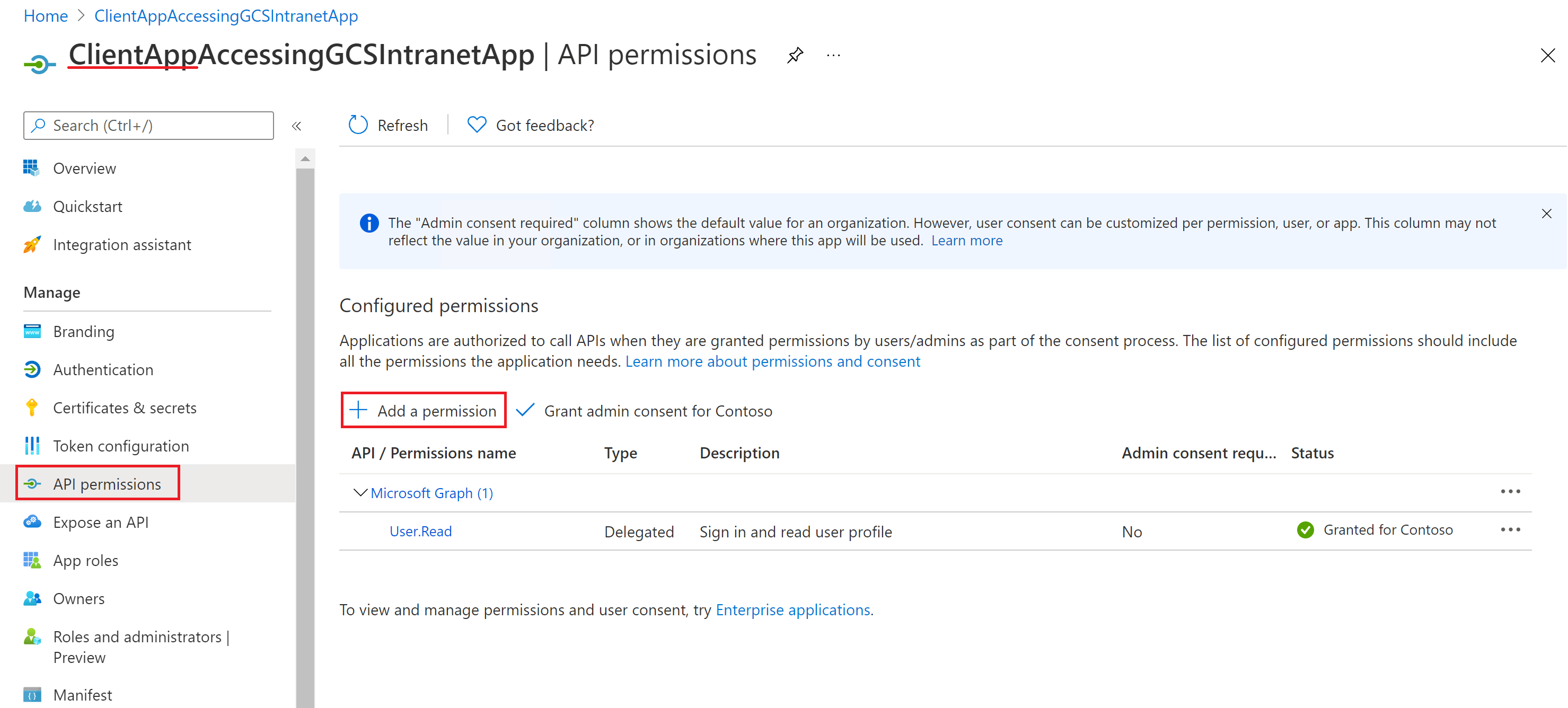
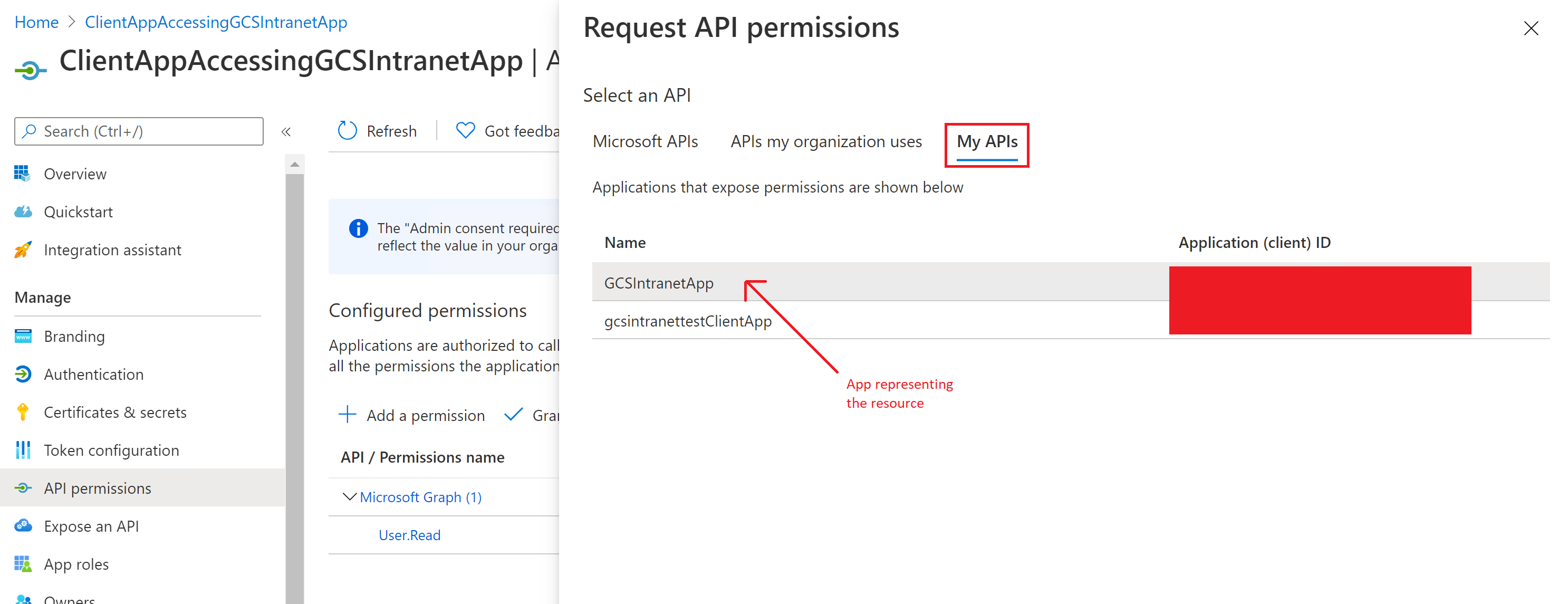
After configuring the resource app, create the client app and give it permissions to access the resource app by adding the app role configured above in the API permissions of the client app.
Note
To see how to grant permissions to the client app see Quickstart: Configure a client application to access a web API.
The following screenshots show the section to grant permissions to the client app.
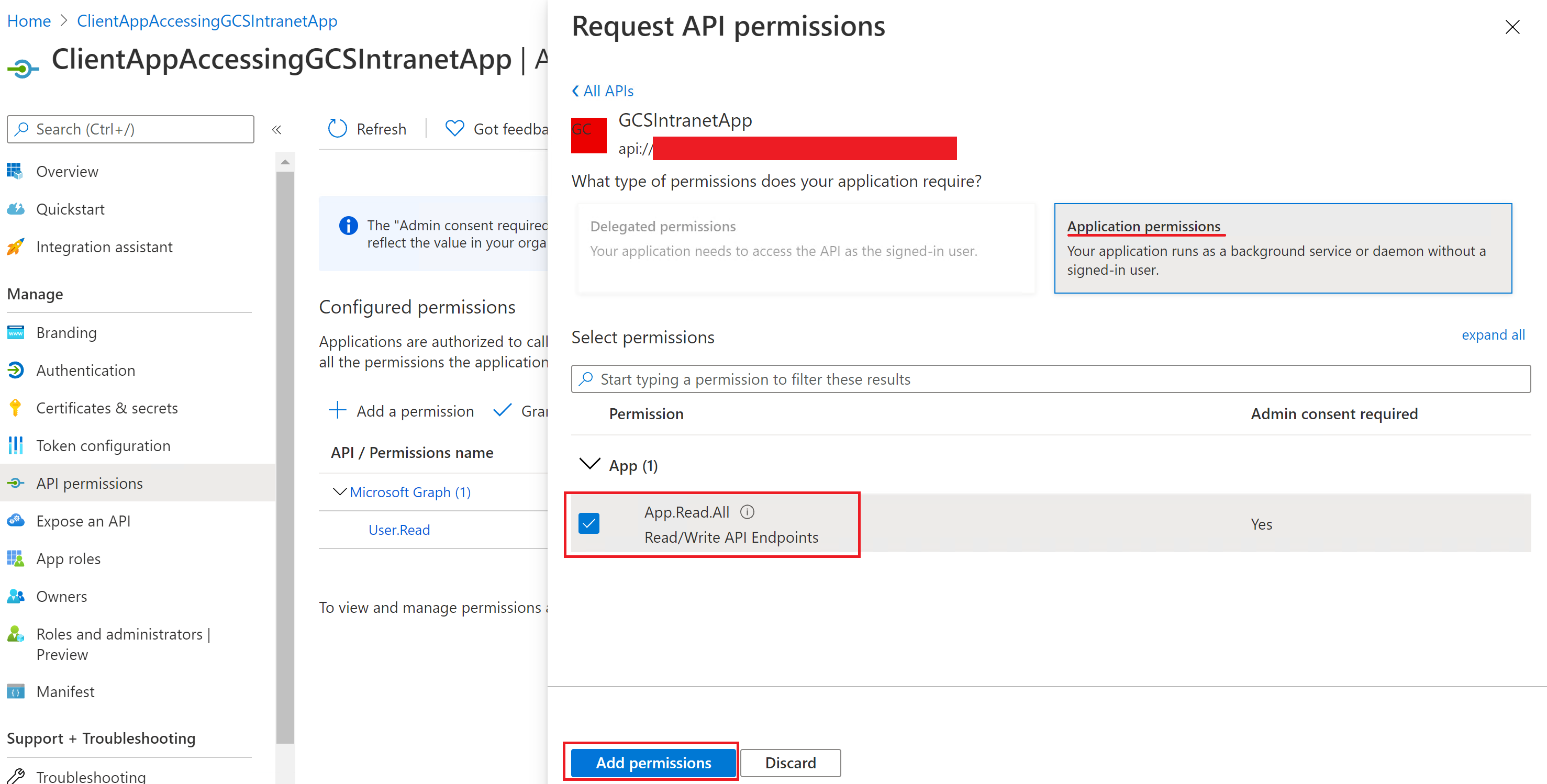
Adding a permission:
Selecting the permissions:
Adding the permissions:
Once the permissions are assigned, you'll need to create a new client secret for this application by going to the Certificates & secrets section. Copy the client secret value shown in the page as it won't be displayed again. Use the application ID from this app as the client ID, the secret from this app as the client secret, and the application ID of the first app as the resource ID.
SiteMinder requires a properly formatted URL, https://custom_siteminder_hostname/smapi/rest/createsmsession, a username, and a password.
Windows authentication is only available in agent mode. It requires username, domain and password. You need to provide the username and domain in the Username field, in any of the following formats: domain\username, or username@domain. A password must be entered in the Password field. For Windows authentication, the username provided must also be an administrator in the server where the agent is installed.
Step 4: Meta tag settings
The connector fetches any meta tags your root URLs may have and shows them. You can select which tags to include for crawling.
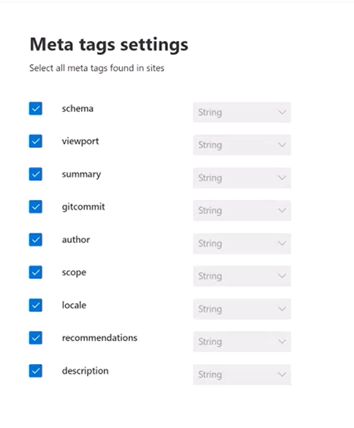
Selected meta tags can be used to create custom properties. Also, on the Schema page you can manage them further (Queryable, Searchable, Retrievable, Refinable).
Step 5: Custom property settings
You can enrich your indexed data by creating custom properties for your selected meta tags or the connector's default properties.
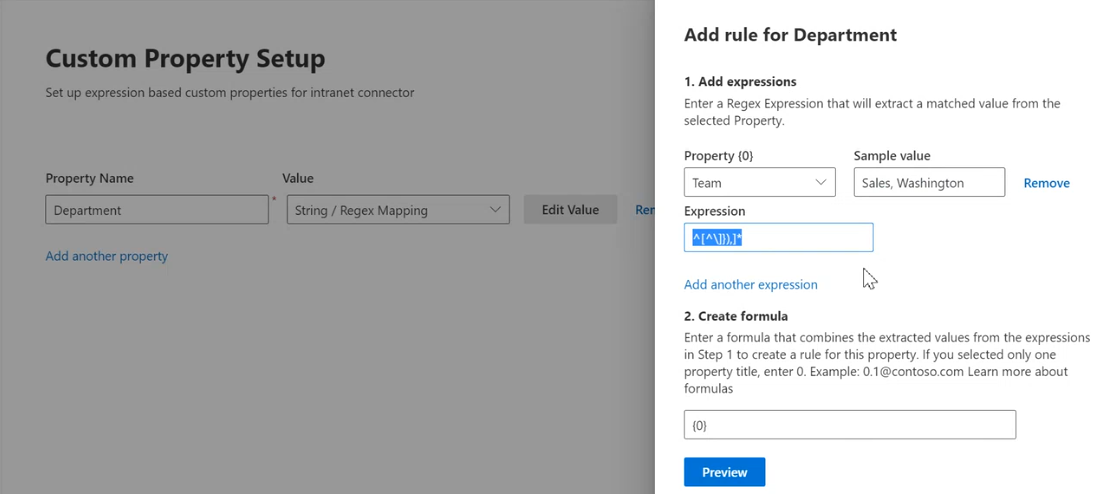
To add a custom property:
- Enter a property name. This name will appear in search results from this connector.
- For the value, select Static or String/Regex Mapping. A static value will be included in all search results from this connector. A string/regex value will vary based on the rules you add.
- Select Edit Value.
- If you selected a static value, enter the string you want to appear.
- If you selected a string/regex value:
- In the Add expressions section, in the Property list, select a default property or meta tag from the list.
- For Sample value, enter a string to represent the type of values that could appear. This sample is used when you preview your rule.
- For Expression, enter a regex expression to define the portion of the property value that should appear in search results. You can add up to three expressions. To learn more about regex expressions, see .NET regular expressions or search the web for a regex expression reference guide.
- In the Create formula section, enter a formula to combine the values extracted from the expressions.
Step 6: Add URLs to exclude (Optional crawl restrictions)
There are two ways to prevent pages from being crawled: disallow them in your robots.txt file or add them to the Exclusion list.
Support for robots.txt
The connector checks to see if there's a robots.txt file for your root site. If one exists, it will follow and respect the directions found within that file. If you don't want the connector to crawl certain pages or directories on your site, include the pages or directories in the "Disallow" declarations in your robots.txt file.
Add URLs to exclude
You can optionally create an Exclusion list to exclude some URLs from getting crawled if that content is sensitive or not worth crawling. To create an exclusion list, browse through the root URL. You can add the excluded URLs to the list during the configuration process.
Step 7: Assign property labels
You can assign a source property to each label by choosing from a menu of options. While this step isn't mandatory, having some property labels will improve the search relevance and ensure more accurate search results for end users.
Step 8: Manage schema
On the Manage Schema screen, you can change the schema attributes (the options are Query, Search, Retrieve, and Refine) associated with the default or custom properties, add optional aliases, and choose the Content property.
Step 9: Manage search permissions
The Enterprise websites connector only supports search permissions visible to Everyone. Indexed data appears in the search results and is visible to all users in the organization.
Step 10: Set the refresh schedule
The Enterprise websites connector supports full and incremental crawling. Incremental crawling is only supported for connections set up with sitemap crawling enabled. Sitemap for crawling can be selected in step 3.
During an incremental refresh interval, only URLs that have been modified since the last incremental refresh are crawled. In a full refresh interval, the connector will recrawl all the website's content. For a full refresh, we recommend you set a large refresh schedule interval, between one and two weeks, to ensure the connector have enough time to complete the crawl. We recommend a scheduled refresh.
Step 11: Review connection
Follow the general setup instructions.
Troubleshooting
After publishing your connection, you can review the status under the Data Sources tab in the admin center. To learn how to make updates and deletions, see Manage your connector. You can find troubleshooting steps for commonly seen issues here.
If you have any other issues or want to provide feedback, write to us aka.ms/TalkToGraphConnectors.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for