Quickstart: Authenticate a Durable Functions app by using Microsoft Entra ID
Microsoft Entra ID is a cloud-based identity and access management service. Identity-based connections allow Durable Functions, a feature of Azure Functions, to make authorized requests against Microsoft Entra-protected resources, such as an Azure Storage account, without using manually managed secrets. When Durable Functions uses the default Azure storage provider, it must authenticate against an Azure storage account.
In this quickstart, you complete steps to set up a Durable Functions app to use two different kinds of identity-based connections:
- Managed identity credentials (recommended)
- Client secret credentials
If you don't have an Azure account, create a free account before you begin.
Prerequisites
To complete this quickstart, you need:
- An existing Durable Functions project created in the Azure portal or a local Durable Functions project deployed to Azure.
- Familiarity running a Durable Functions app in Azure.
If you don't have an existing Durable Functions project deployed in Azure, we recommend that you start with one of the following quickstarts:
- Create a Durable Functions app - C#
- Create a Durable Functions app - JavaScript
- Create a Durable Functions app - Python
- Create a Durable Functions app - PowerShell
- Create a Durable Functions app - Java
Configure your app to use managed identity credentials
Your app can use a managed identity to easily access other Microsoft Entra-protected resources, such as an instance of Azure Key Vault. Managed identity access is supported in the Durable Functions extension version 2.7.0 and later.
Note
A managed identity is available to apps only when they execute in Azure. When an app is configured to use identity-based connections, a locally executing app instead uses your developer credentials to authenticate with Azure resources. Then, when the app is deployed in Azure, it uses your managed identity configuration.
Enable a managed identity
To begin, enable a managed identity for your application. Your function app must have either a system-assigned managed identity or a user-assigned managed identity. To enable a managed identity for your function app, and to learn more about the differences between the two types of identities, see the managed identity overview.
Assign access roles to the managed identity
Next, in the Azure portal, assign three role-based access control (RBAC) roles to your managed identity resource:
- Storage Queue Data Contributor
- Storage Blob Data Contributor
- Storage Table Data Contributor
Configure the managed identity
Before you can use your app's managed identity, make some changes to the app configuration:
In the Azure portal, on your function app resource menu under Settings, select Configuration.
In the list of settings, select AzureWebJobsStorage and select the Delete icon.
Add a setting to link your Azure storage account to the application.
Use one of the following methods depending on the cloud that your app runs in:
Azure cloud: If your app runs in public Azure, add a setting that identifies an Azure storage account name:
AzureWebJobsStorage__<accountName>Example:
AzureWebJobsStorage__mystorageaccount123
Non-Azure cloud: If your application runs in a cloud outside of Azure, you must add a specific service URI (an endpoint) for the storage account instead of an account name.
Note
If you use Azure Government or any other cloud that's separate from public Azure, you must use the option to provide a specific service URI. For more information about using Azure Storage with Azure Government, see Develop by using the Storage API in Azure Government.
AzureWebJobsStorage__<blobServiceUri>Example:
AzureWebJobsStorage__https://mystorageaccount123.blob.core.windows.net/AzureWebJobsStorage__<queueServiceUri>Example:
AzureWebJobsStorage__https://mystorageaccount123.queue.core.windows.net/AzureWebJobsStorage__<tableServiceUri>Example:
AzureWebJobsStorage__https://mystorageaccount123.table.core.windows.net/
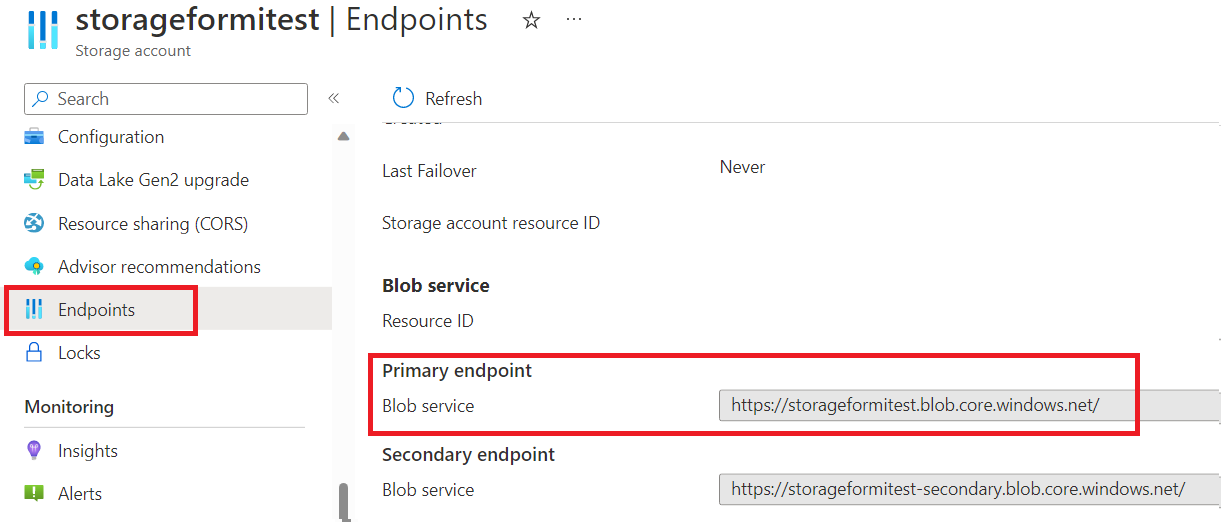
You can get the values for these URI variables in the storage account information on the Endpoints tab.
Finish your managed identity configuration:
If you use a system-assigned identity, make no other changes.
If you use a user-assigned identity, add the following settings to your app configuration:
For AzureWebJobsStorage__credential, enter managedidentity.
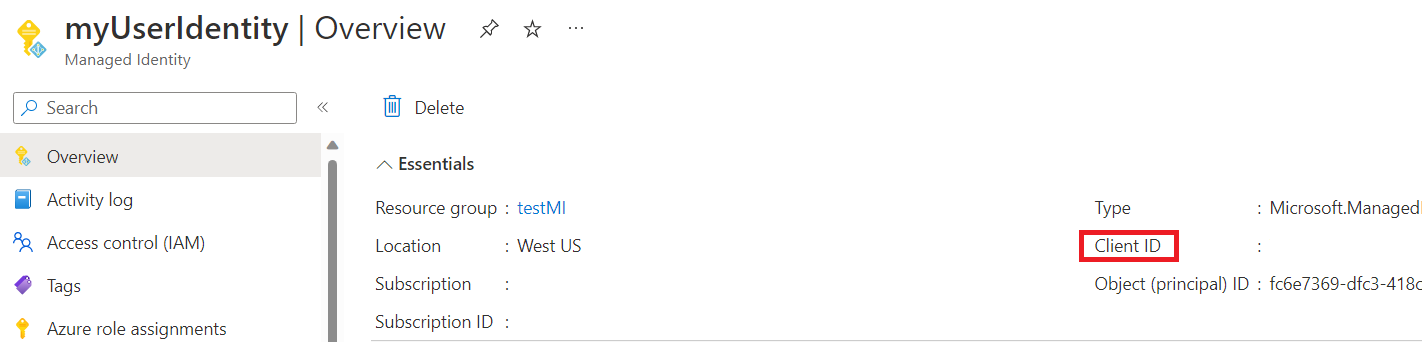
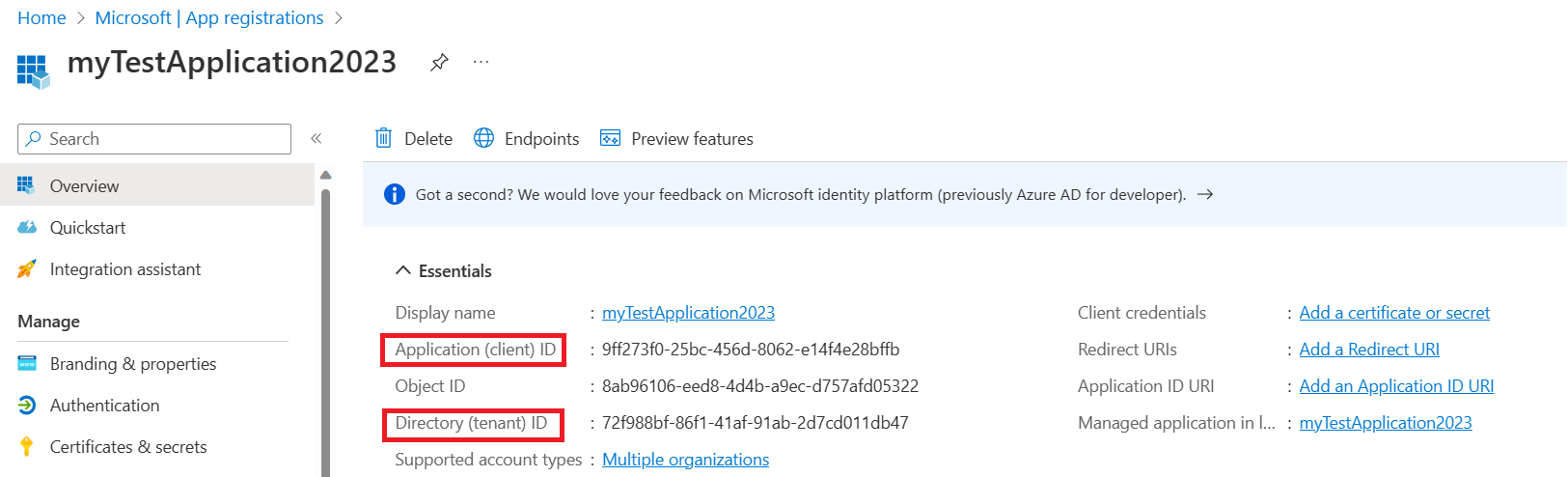
For AzureWebJobsStorage__clientId, get this GUID value from the Microsoft Entra admin center.
Configure your app to use client secret credentials
Registering a client application in Microsoft Entra ID is another way you can configure access to an Azure service for your Durable Functions app. In the following steps, you use client secret credentials for authentication to your Azure Storage account. Function apps can use this method both locally and in Azure. Using a client secret credential is less recommended than using managed identity credentials because a client secret is more complex to set up and manage. A client secret credential also requires sharing a secret credential with the Azure Functions service.
Register the client application with Microsoft Entra ID
In the Azure portal, register the client application with Microsoft Entra ID.
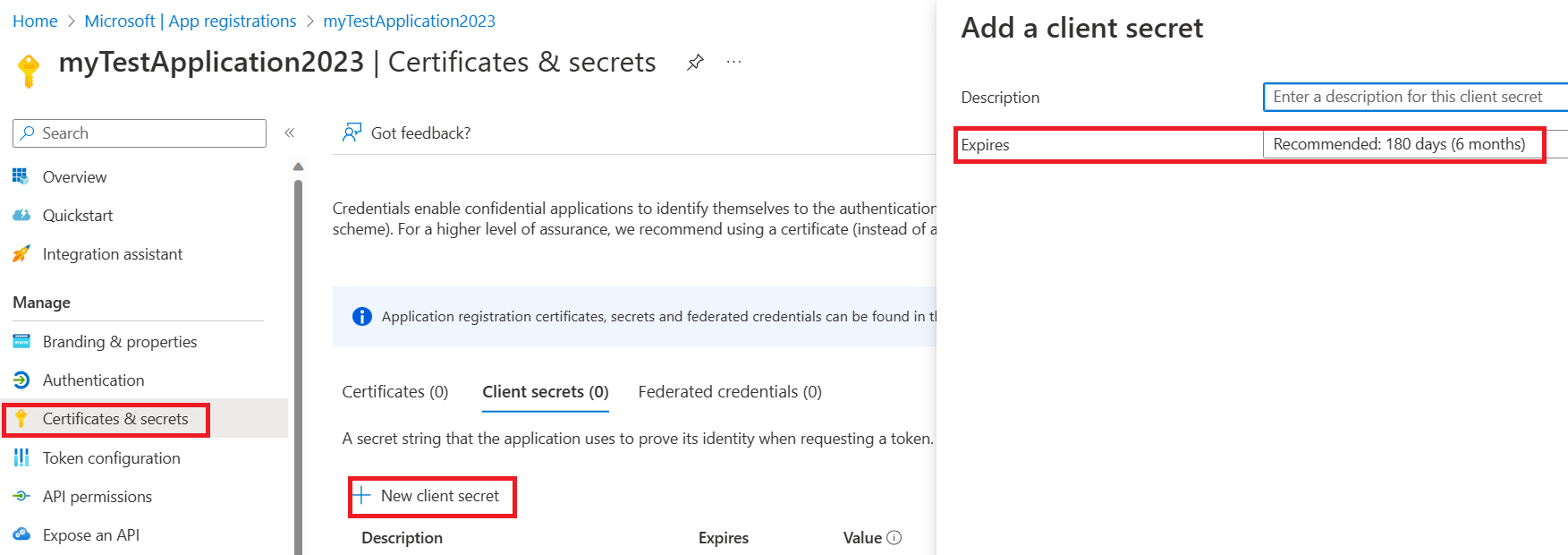
Create a client secret for your application. In your registered application, complete these steps:
Select Certificates & secrets > New client secret.
For Description, enter a unique description.
For Expires, enter a valid time for the secret to expire.
Copy the secret value to use later.
The secret's value doesn't appear again after you leave the pane, so be sure that you copy the secret and save it.
Assign access roles to your application
Next, assign three RBAC roles to your client application:
- Storage Queue Data Contributor
- Storage Blob Data Contributor
- Storage Table Data Contributor
To add the roles:
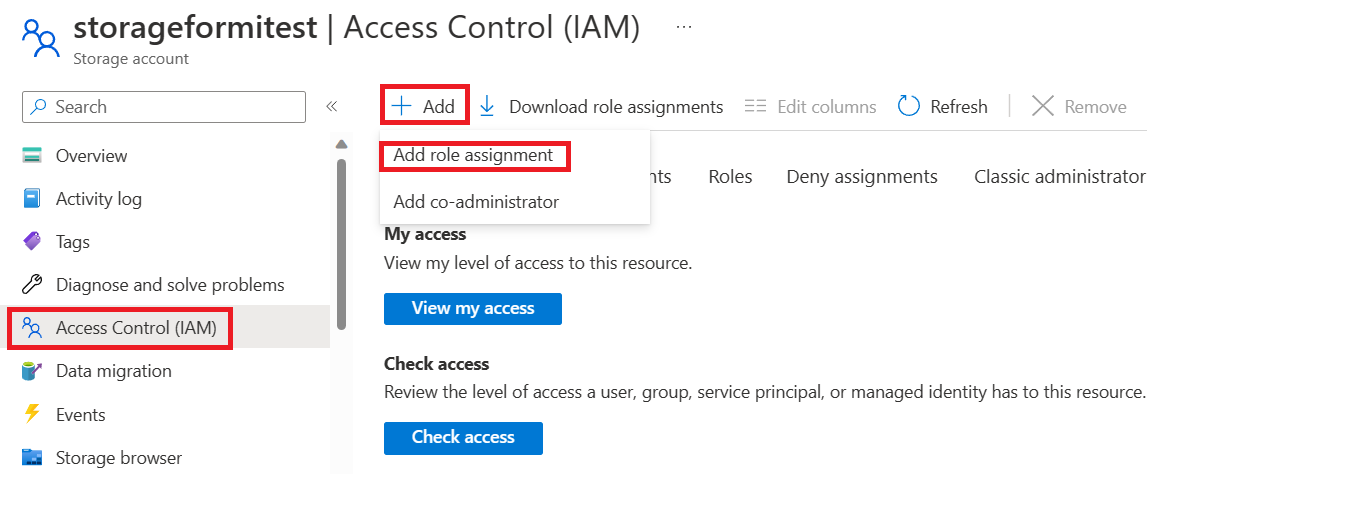
In the Azure portal, go to your function's storage account.
On the resource menu, select Access Control (IAM), and then select Add role assignment.
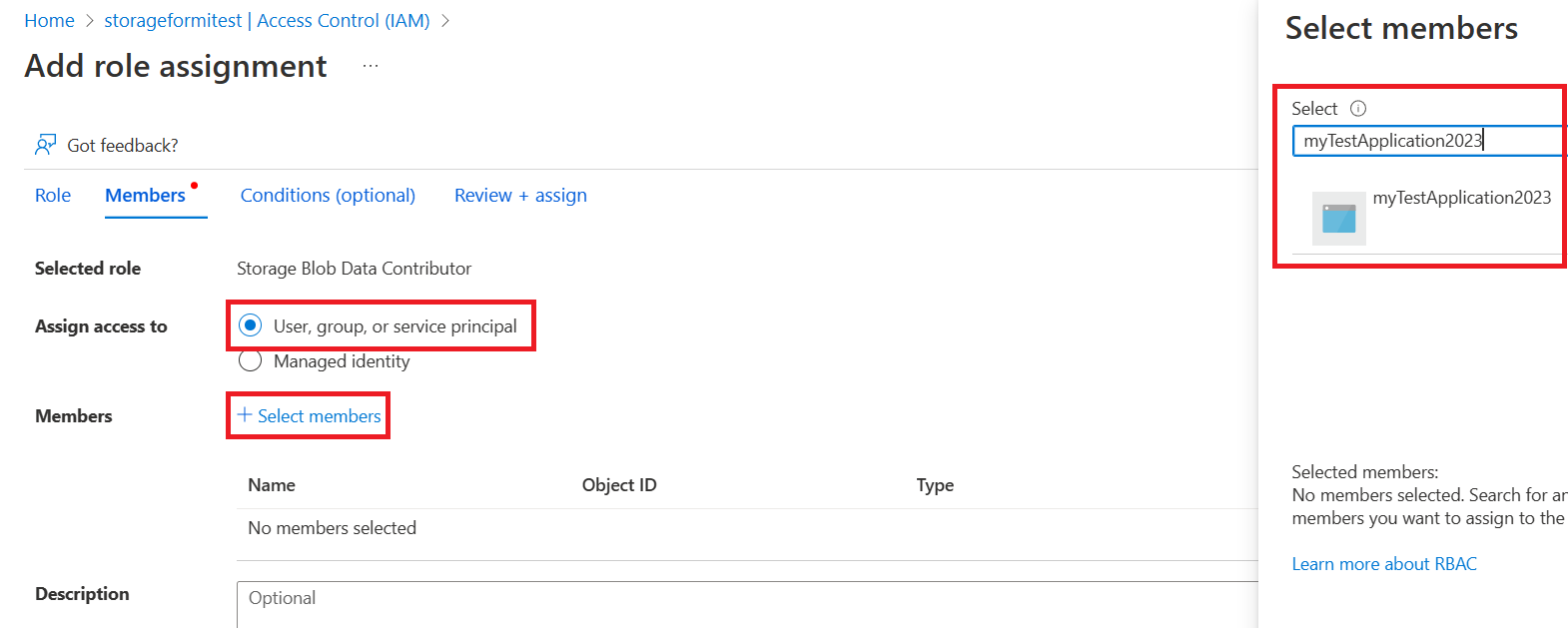
Select a role to add, select Next, and then search for your application. Review the role assignment, and then add the role.
Configure the client secret
In the Azure portal, run and test the application. To run and test the app locally, specify the following settings in the function’s local.settings.json file.
In the Azure portal, on your function app resource menu under Settings, select Configuration.
In the list of settings, select AzureWebJobsStorage and select the Delete icon.
Add a setting to link your Azure storage account to the application.
Use one of the following methods depending on the cloud that your app runs in:
Azure cloud: If your app runs in public Azure, add a setting that identifies an Azure storage account name:
AzureWebJobsStorage__<accountName>Example:
AzureWebJobsStorage__mystorageaccount123
Non-Azure cloud: If your application runs in a cloud outside of Azure, you must add a specific service URI (an endpoint) for the storage account instead of an account name.
Note
If you use Azure Government or any other cloud that's separate from public Azure, you must use the option to provide a specific service URI. For more information about using Azure Storage with Azure Government, see Develop by using the Storage API in Azure Government.
AzureWebJobsStorage__<blobServiceUri>Example:
AzureWebJobsStorage__https://mystorageaccount123.blob.core.windows.net/AzureWebJobsStorage__<queueServiceUri>Example:
AzureWebJobsStorage__https://mystorageaccount123.queue.core.windows.net/AzureWebJobsStorage__<tableServiceUri>Example:
AzureWebJobsStorage__https://mystorageaccount123.table.core.windows.net/
You can get the values for these URI variables in the storage account information on the Endpoints tab.
To add client secret credentials, set the following values:
AzureWebJobsStorage__clientId: Get this GUID value on the Microsoft Entra application pane.
AzureWebJobsStorage__ClientSecret: The secret value that you generated in the Microsoft Entra admin center in an earlier step.
AzureWebJobsStorage__tenantId: The tenant ID that the Microsoft Entra application is registered in. Get this GUID value on the Microsoft Entra application pane.
The values to use for the client ID and the tenant ID appear on your client application Overview pane. The client secret value is the one that you saved in an earlier step. The client secret's value isn't available after the pane is refreshed.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for